Miércoles 2 de junio de 2021
Hace poco, anunciamos un filtrado de datos mejorado para los informes de rendimiento de Search Console y nos complace ver la reacción de la comunidad ante el anuncio.
También nos interesaron los comentarios que recibimos, como siempre, y en muchos casos nos solicitaron que completáramos el panorama incluyendo una opción de concordancia negativa al filtro de expresiones regulares (regex).
La buena noticia es que, a partir de hoy, el filtro de informes de rendimiento admite filtros de regex de concordancia positiva y negativa. Esta opción está disponible en un menú desplegable secundario que aparece después de elegir la opción "Personalizada (regex)" en el selector de filtros, como se muestra en la siguiente captura de pantalla. Obtén más información para filtrar los datos de rendimiento de búsqueda.
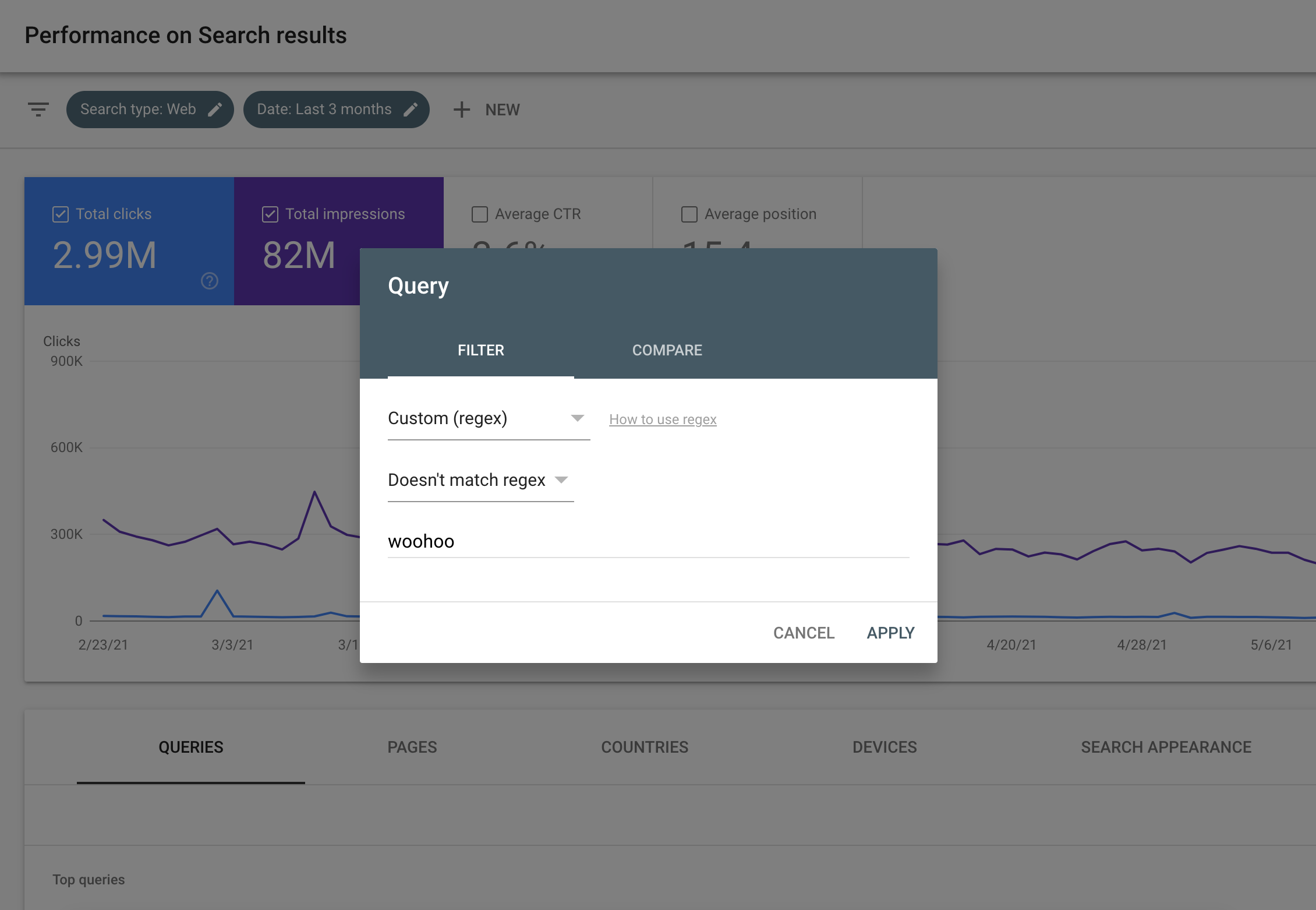
Sugerencias rápidas sobre el uso de regex en Search Console
Pensamos que sería útil proporcionar algunas sugerencias rápidas para quienes recién están comenzando con regex.
En primer lugar, ¿qué es una expresión regular? En pocas palabras, es una secuencia de caracteres que especifica un patrón de búsqueda. Puedes usarla para crear filtros avanzados a fin de incluir o excluir más de una palabra o una frase. Cuando usas regex, puedes usar una cantidad de metacaracteres, que son caracteres que tienen un significado especial, por ejemplo, para definir un criterio de búsqueda. Consulta la referencia de sintaxis de regex de RE2 para conocer todos los metacaracteres compatibles con Search Console.
En caso de que te preguntes cuándo deberías usar regex en lugar de otros tipos de filtros, a continuación te mostramos algunos ejemplos:
- Para segmentar a usuarios que ya conocen tu marca: Usa regex que especifiquen múltiples variantes del nombre de tu empresa, incluso con errores ortográficos. Así podrás ver qué tipo de búsqueda está usando cada grupo y qué sección de tu sitio web atrae a cada público.
Por ejemplo, si el nombre de tu empresa es
Willow Tree, puedes crear un filtro para todas las variantes de la siguiente manera:willow tree|wilow tree|willowtree|willowtee(el metacarácter|representa una declaración OR). - Para analizar el tráfico de una sección de un sitio web: Usa regex que se centren en directorios específicos de tu sitio web, lo que puede ayudarte a comprender cuáles son las consultas comunes de cada una de tus áreas de contenido. Por ejemplo, si la estructura de la URL es
example.com/[product]/[brand]/[size]/[color]y quieres ver el tráfico que lleva a los zapatos verdes, pero no te interesa la marca ni el tamaño, puedes utilizarshoes/.*/green(.*coincide con cualquier carácter y cualquier cantidad de veces). - Para comprender la intención de los usuarios: Utiliza regex con el objetivo de analizar qué tipos de búsquedas llevan a los usuarios a diferentes secciones de tu sitio web.
Por ejemplo, puede que te interesen las consultas con palabras que introducen preguntas. Un filtro de búsqueda
what|how|when|whypodría mostrar resultados que indiquen que tu contenido debería responder las preguntas con facilidad, tal vez mediante una sección de Preguntas frecuentes. Otro ejemplo pueden ser las consultas que contienen (o no) palabras relativas a transacciones, comobuy|purchase|order. Esto también podría mostrar qué nombres de productos se usan con más o menos frecuencia con estas expresiones.
Si quieres conocer las expresiones regulares comunes, consulta el Centro de ayuda de Search Console. Si tienes algunos ejemplos interesantes sobre los usos de regex, compártelos en Twitter con el hashtag #performanceregex.
Si tienes preguntas o inquietudes, consulta a la Comunidad de la Central de la Búsqueda de Google o búscanos en Twitter.
