Thursday, February 13, 2014
Your site's news feed or pinboard might use infinite scroll—much to your users' delight! When it comes to delighting Googlebot, however, that can be another story. With infinite scroll, crawlers cannot always emulate manual user behavior—like scrolling or clicking a button to load more items—so they don't always access all individual items in the feed or gallery. If crawlers can't access your content, it's unlikely to surface in search results.
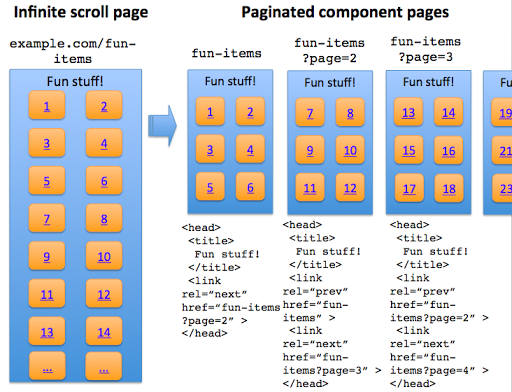
To make sure that search engines can crawl individual items linked from an infinite scroll page, make sure that you or your content management system produces a paginated series (component pages) to go along with your infinite scroll.
<title> tag declared in the
<head> tag on the page.
You can see this type of behavior in action in the infinite scroll with pagination demo created by Webmaster Trends Analyst, John Mueller. The demo illustrates some key search-engine friendly points:
- Coverage: All individual items are accessible. With traditional infinite scroll, individual items displayed after the initial page load aren't discoverable to crawlers.
- No overlap: Each item is listed only once in the paginated series (for example, no duplication of items).
Search-friendly recommendations for infinite scroll
1. Before you start
- Chunk your infinite-scroll page content into component pages that can be accessed when JavaScript is disabled.
-
Determine how much content to include on each page.
- Be sure that if a searcher came directly to this page, they could easily find the exact item they wanted (for example, without lots of scrolling before locating the desired content).
- Maintain reasonable page load time.
-
Divide content so that there's no overlap between component pages in the series (with the exception of buffering).
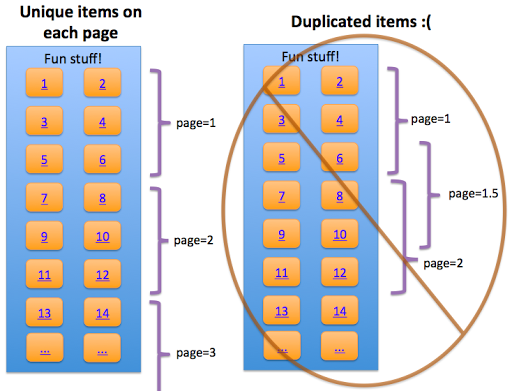
The example on the left is search-friendly, the right example isn't—the right example would cause crawling and indexing of duplicative content.
2. Structure URLs for infinite scroll search engine processing
-
Each component page contains a full URL. We recommend full URLs in this situation to minimize potential for configuration error.
-
Good:
example.com/category?name=fun-items&page=1 -
Good:
example.com/fun-items?lastid=567 -
Less optimal:
example.com/fun-items#1
-
Good:
- Test that each component page (the URL) works to take anyone directly to the content and is accessible and referenceable in a browser without the same cookie or user history.
-
Any key and value URL parameters should follow these recommendations:
-
Be sure the URL shows conceptually the same content two weeks from now. Avoid relative-time
based URL parameters:
example.com/category/page.php?name=fun-items&days-ago=3 -
Create parameters that can surface valuable content to searchers. Avoid non-searcher
valuable parameters as the primary method to access content:
example.com/fun-places?radius=5&lat=40.71&long=-73.40
-
Be sure the URL shows conceptually the same content two weeks from now. Avoid relative-time
based URL parameters:
3. Implement replaceState and pushState
Implement
replaceState and pushState
on the infinite scroll page. The decision to use one or both is
up to you and your site's user behavior. That said, we recommend including pushState
(by itself, or in conjunction with replaceState) for the following cases:
- Any user action that resembles a click or actively turning a page.
- To provide users with the ability to serially backup through the most recently paginated content.
4. Test
- Check that page values adjust as the user scrolls up or down.
-
Verify that pages that are out-of-bounds in the series return a
404response (for example,example.com/category?name=fun-items&page=999should return a404response if there are only 998 pages of content). - Investigate potential usability implications introduced by your infinite scroll implementation.
