Thứ Sáu, ngày 6 tháng 8 năm 2010
Luôn có thể xảy ra thay đổi – đôi khi, như chúng ta nhận thấy trong bài đăng trước về việc xoá URL, bạn có thể chặn hoặc xoá hoàn toàn một trang khỏi trang web của mình. Cũng có lúc có thể bạn chỉ thay đổi các phần của một trang hoặc xoá một số đoạn văn bản. Tuỳ thuộc vào tần suất thu thập dữ liệu trên một trang, có thể mất chút thời gian trước khi các thay đổi này được phản ánh trong kết quả tìm kiếm của chúng tôi. Trong bài đăng này trên blog, chúng ta sẽ tìm hiểu các bước bạn có thể thực hiện nếu nội dung cũ và đã bị xoá vẫn xuất hiện trong kết quả tìm kiếm dưới dạng "đoạn trích" hoặc trên trang lưu trong bộ nhớ đệm được liên kết đến từ kết quả tìm kiếm. Việc này là hợp lý khi nội dung cũ chứa thông tin nhạy cảm cần được xoá nhanh chóng. Nhưng bạn không cần làm vậy nếu chỉ cập nhật trang web như bình thường.
Để lấy ví dụ, hãy xem kết quả tìm kiếm giả tưởng sau đây:
| Walter E. Coyote | < Tiêu đề |
|
Chief Development Officer at Acme Corp 1948-2003: worked on the top |
< Đoạn trích |
| www.example.com/about/waltercoyote – Được lưu trong bộ nhớ đệm | < URL + đường liên kết đến trang lưu trong bộ nhớ đệm |
Để thay đổi nội dung xuất hiện trong đoạn trích (hoặc trên trang được liên kết đã lưu trong bộ nhớ đệm), trước tiên, bạn cần thay đổi nội dung trên trang thực tế (trực tiếp). Các quy trình tự động của Google sẽ tiếp tục cho thấy các phần của nội dung gốc trong kết quả tìm kiếm nếu bạn không thay đổi nội dung xuất hiện công khai trên trang.
Sau khi thay đổi nội dung của trang, bạn có một số cách để những thay đổi đó xuất hiện trong kết quả tìm kiếm:
-
Chờ Googlebot thu thập lại dữ liệu và lập chỉ mục lại trang: Đây là phương pháp tự nhiên để cập nhật hầu hết nội dung tại Google. Đôi khi, có thể mất khá nhiều thời gian, tuỳ thuộc vào tần suất Googlebot thu thập dữ liệu trên trang đó. Khi chúng tôi đã thu thập lại dữ liệu và lập chỉ mục lại trang, nội dung cũ thường sẽ không xuất hiện do được thay thế bằng nội dung hiện tại. Miễn là Googlebot không bị chặn thu thập dữ liệu trên trang được đề cập (bằng tệp robots.txt hoặc không thể truy cập vào máy chủ theo đúng cách), thì bạn không cần phải làm gì đặc biệt. Thường thì bạn không thể đẩy nhanh quá trình thu thập dữ liệu và lập chỉ mục vì các quá trình này diễn ra hoàn toàn tự động và phụ thuộc vào nhiều yếu tố bên ngoài.
-
Sử dụng Công cụ xoá URL công khai của Google để yêu cầu xoá nội dung đã bị xoá khỏi trang web của người khác. Khi sử dụng công cụ này, bạn cần nhập URL chính xác của trang đã được sửa đổi, chọn tuỳ chọn "Nội dung đã bị xoá khỏi trang" rồi chỉ định một hoặc nhiều từ đã bị xoá hoàn toàn khỏi trang đó.
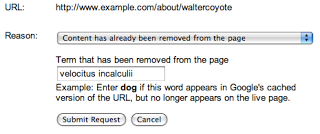
Xin lưu ý rằng không từ nào trong số các từ bạn nhập có thể xuất hiện trên trang; ngay cả khi một từ đã bị xoá khỏi một phần của trang, yêu cầu của bạn sẽ bị từ chối nếu từ đó vẫn xuất hiện trên một phần khác của trang. Hãy nhớ chọn một từ (hoặc các từ) không còn xuất hiện ở bất cứ đâu trên trang. Trong ví dụ trên, nếu đã xoá "top secret velocitus incalculii capturing device", bạn nên gửi những từ đó thay vì gửi "tên dự án của tôi". Tuy nhiên, nếu từ "top" hoặc "device" vẫn tồn tại ở bất kỳ vị trí nào trên trang, thì yêu cầu sẽ bị từ chối. Để tăng tối đa cơ hội thành công, bạn thường chỉ cần nhập một từ mà bạn chắc chắn rằng không còn xuất hiện ở bất cứ đâu trên trang.
Sau khi xử lý xong yêu cầu của bạn và nhận thấy (các) từ đã gửi không còn xuất hiện trên trang, kết quả tìm kiếm sẽ không còn cho thấy đoạn trích và trang đã lưu trong bộ nhớ đệm nữa. Tiêu đề và URL của trang sẽ vẫn hiển thị và có thể mục đó vẫn xuất hiện trong kết quả tìm kiếm cho những nội dung tìm kiếm liên quan đến nội dung đã bị xoá (chẳng hạn như nội dung tìm kiếm velocitus incalculii), ngay cả khi những từ đó không còn xuất hiện trong đoạn trích. Tuy nhiên, sau khi trang được thu thập lại dữ liệu và lập chỉ mục lại, đoạn trích mới và trang lưu trong bộ nhớ đệm có thể xuất hiện trong kết quả tìm kiếm của chúng tôi.
Xin lưu ý rằng chúng tôi cần xác minh việc xoá (các) từ này bằng cách xem trang đó. Nếu trang không còn tồn tại và máy chủ đang trả về một mã kết quả HTTP
404hoặc410thích hợp khiến chúng tôi không thể xem trang đó, có lẽ bạn nên yêu cầu xoá trang hoàn toàn. - Hãy sử dụng Công cụ xoá URL của Công cụ quản trị trang web của Google để yêu cầu xoá thông tin trên một trang khỏi trang web của bạn. Nếu có quyền truy cập vào trang web có liên quan và đã xác minh quyền sở hữu đối với trang web đó trong Công cụ quản trị trang web của Google, bạn có thể sử dụng công cụ xoá URL tại đó (trong phần Cấu hình trang web > Truy cập của trình thu thập dữ liệu) để yêu cầu xoá đoạn trích và trang lưu trong bộ nhớ đệm cho đến khi thu thập lại dữ liệu trên trang. Để sử dụng công cụ này, bạn chỉ cần gửi URL chính xác của trang (bạn không cần chỉ định bất kỳ từ nào đã bị xoá). Sau khi xử lý xong yêu cầu của bạn, chúng tôi sẽ xoá đoạn trích và trang đã lưu trong bộ nhớ đệm khỏi kết quả tìm kiếm. Tiêu đề và URL của trang sẽ vẫn xuất hiện và có thể trang đó vẫn được xếp hạng trong kết quả tìm kiếm cho những cụm từ tìm kiếm liên quan đến nội dung đã bị xoá. Sau khi Google thu thập lại dữ liệu và lập chỉ mục lại trang, kết quả tìm kiếm có chứa một đoạn trích đã cập nhật và trang đã lưu trong bộ nhớ đệm (dựa trên nội dung mới) có thể xuất hiện.
Google lập chỉ mục và xếp hạng các mục không chỉ dựa trên nội dung của trang mà còn dựa trên các yếu tố bên ngoài khác, chẳng hạn như các đường liên kết đến URL đó. Do đó, URL có thể tiếp tục xuất hiện trong kết quả tìm kiếm cho nội dung không còn tồn tại trên trang, ngay cả sau khi trang đó đã được thu thập lại dữ liệu và lập chỉ mục lại. Tuy công cụ xoá URL có thể xoá đoạn trích và trang đã lưu trong bộ nhớ đệm khỏi kết quả tìm kiếm, nhưng công cụ này sẽ không thay đổi hay xoá tiêu đề của kết quả tìm kiếm, thay đổi URL xuất hiện hoặc ngăn trang đó xuất hiện cho cụm từ tìm kiếm dựa trên nội dung bất kỳ hiện tại hoặc trước đây. Nếu điều này quan trọng đối với bạn thì bạn nên đảm bảo rằng URL đáp ứng các yêu cầu để xoá hoàn toàn kết quả tìm kiếm của chúng tôi.
Xoá nội dung không phải HTML
Nếu nội dung đã thay đổi không có trong (X)HTML (ví dụ: nếu hình ảnh, tệp Flash hoặc tệp PDF đã bị thay đổi), thì bạn sẽ không thể dùng công cụ xoá nội dung trong bộ nhớ đệm. Vì vậy, nếu nội dung cũ không còn xuất hiện trong kết quả tìm kiếm, thì giải pháp nhanh nhất là thay đổi URL của tệp để URL cũ trả về mã kết quả HTTP 404 và sử dụng công cụ xoá URL để xoá URL cũ. Còn nếu bạn chọn cho phép Google tự động làm mới thông tin của mình, hãy lưu ý rằng bản xem trước của nội dung không phải HTML (chẳng hạn như đường liên kết Quick View cho tệp PDF) có thể mất nhiều thời gian để cập nhật sau khi thu thập lại dữ liệu so với các trang HTML thông thường.
Chủ động ngăn sự xuất hiện của đoạn trích hoặc phiên bản lưu trong bộ nhớ đệm
Là quản trị viên trang web, bạn có thể sử dụng
thẻ meta robots
để ngăn chặn việc hiện đoạn trích hoặc phiên bản trong bộ nhớ đệm mà không cần dùng
công cụ xoá. Tuy bạn không nên coi cách này là phương pháp mặc định (đoạn trích có thể giúp người dùng nhận ra kết quả tìm kiếm liên quan nhanh hơn) và trang lưu trong bộ nhớ đệm cho phép họ xem nội dung của bạn ngay cả trong trường hợp không truy cập được máy chủ có thể bất ngờ xảy ra), bạn có thể dùng thẻ meta robots "nosnippet" để ngăn hiện đoạn trích hoặc dùng thẻ meta robots "noarchive" để tắt tính năng lưu vào bộ nhớ đệm cho một trang. Hãy lưu ý rằng nếu thay đổi này diễn ra trên các trang hiện có và đã biết, Googlebot sẽ cần thu thập lại dữ liệu và lập chỉ mục lại các trang đó trước khi thay đổi này thể hiện trong kết quả tìm kiếm.
Chúng tôi hy vọng bài đăng này trên blog giúp bạn nắm rõ hơn một số quy trình phía sau công cụ xoá URL cho các trang được cập nhật. Trong bài đăng tiếp theo trên blog của chúng tôi, chúng ta sẽ xem xét các cách yêu cầu xoá nội dung mà bạn không sở hữu; hãy chú ý theo dõi!
Như thường lệ, chúng tôi hoan nghênh các ý kiến phản hồi và thắc mắc của bạn trong Diễn đàn trợ giúp dành cho quản trị viên trang web.
Các bài đăng khác trong loạt bài này
- Phần I: Xoá URL và thư mục
- Phần II: Xoá và cập nhật nội dung lưu trong bộ nhớ đệm
- Phần III: Xoá nội dung mà bạn không sở hữu
- Phần IV: Theo dõi yêu cầu và những nội dung không nên xoá
Cuối cùng, bạn cũng có thể tìm hiểu về cách quản lý những thông tin hiện có về bạn trên mạng.
