Afin d'utiliser le style basé sur les données pour les limites, vous devez créer un ID de carte qui utilise la carte vectorielle JavaScript. Ensuite, créez un style de carte, sélectionnez les calques d'éléments de votre choix pour les limites et associez le style à l'ID de votre carte.
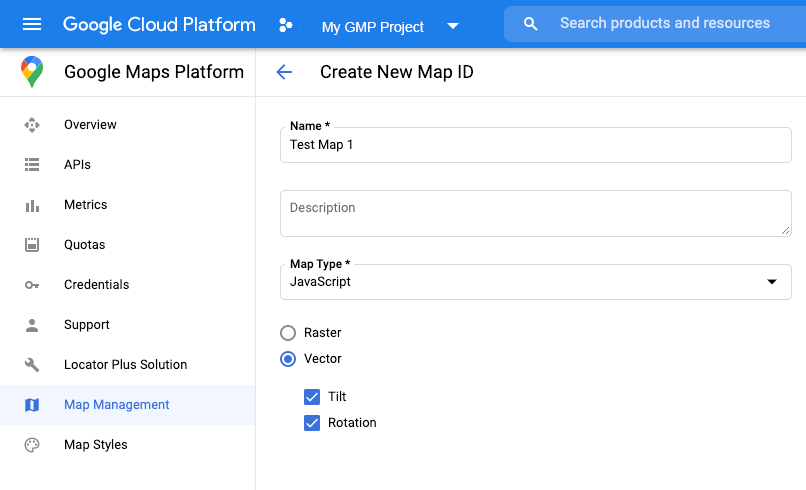
Créer un ID de carte
Pour créer un ID de carte, suivez les étapes décrites dans Personnalisation dans Cloud. Définissez le type de carte sur JavaScript, puis sélectionnez l'option Vecteur. Cochez Inclinaison et Rotation pour activer l'inclinaison et la rotation sur la carte. Si incliner ou faire tourner la carte affecte négativement votre application, décochez Inclinaison et Rotation pour que les utilisateurs ne puissent pas ajuster ces éléments.
Créer un style de carte
Pour créer un style de carte, suivez la procédure décrite dans Gérer les styles de carte, puis associez le style à l'ID de carte que vous venez de créer.
Sélectionner des calques d'éléments
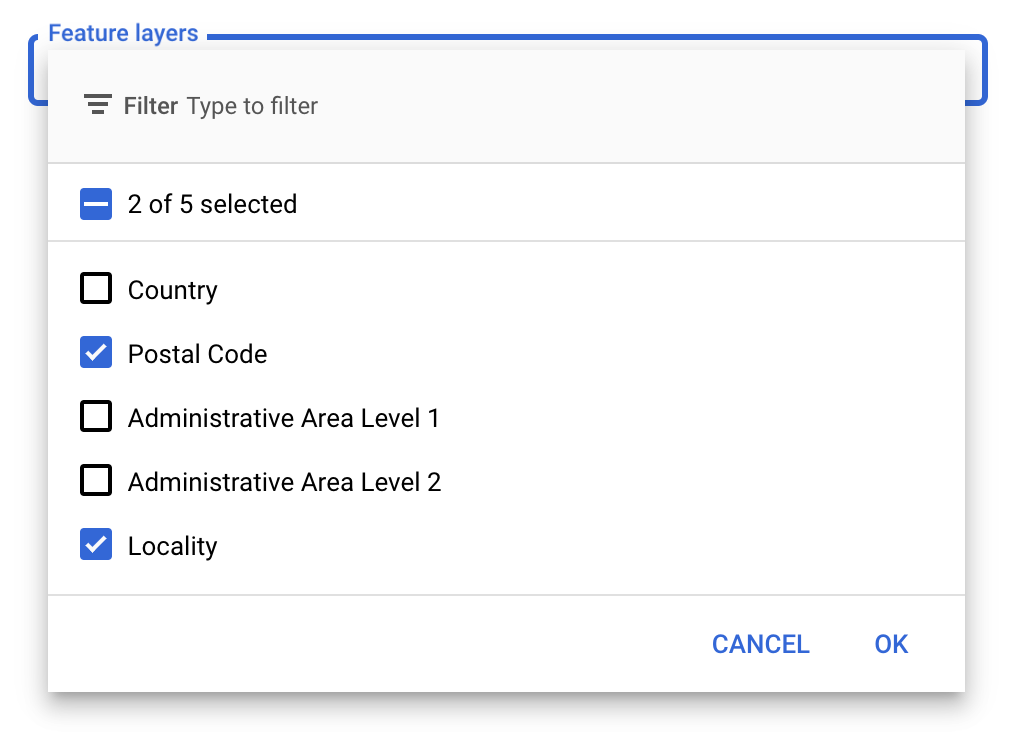
Dans la console Google APIs, vous pouvez sélectionner les calques d'éléments à afficher. Cela permet de déterminer les types de limites qui s'afficheront sur la carte (par exemple, les localités, les États, etc.).
Pour gérer les calques d'éléments
- Dans la console Google APIs, accédez à la page Styles de carte.
- Sélectionnez un projet si vous y êtes invité.
- Sélectionnez un style de carte.
- Cliquez sur le menu déroulant Calques d'éléments pour ajouter ou supprimer des calques.
- Cliquez sur Enregistrer pour enregistrer vos modifications et les appliquer à vos cartes.
Modifier le code d'initialisation de la carte
Vous aurez besoin de l'ID de carte que vous venez de créer. Il se trouve sur votre page Gestion des cartes.
- Chargez l'API Maps JavaScript en ajoutant le chargeur d'amorçage intégré au code de votre application, comme indiqué dans l'extrait suivant :
<script> (g=>{var h,a,k,p="The Google Maps JavaScript API",c="google",l="importLibrary",q="__ib__",m=document,b=window;b=b[c]||(b[c]={});var d=b.maps||(b.maps={}),r=new Set,e=new URLSearchParams,u=()=>h||(h=new Promise(async(f,n)=>{await (a=m.createElement("script"));e.set("libraries",[...r]+"");for(k in g)e.set(k.replace(/[A-Z]/g,t=>"_"+t[0].toLowerCase()),g[k]);e.set("callback",c+".maps."+q);a.src=`https://maps.${c}apis.com/maps/api/js?`+e;d[q]=f;a.onerror=()=>h=n(Error(p+" could not load."));a.nonce=m.querySelector("script[nonce]")?.nonce||"";m.head.append(a)}));d[l]?console.warn(p+" only loads once. Ignoring:",g):d[l]=(f,...n)=>r.add(f)&&u().then(()=>d[l](f,...n))})({ key: "YOUR_API_KEY", v: "weekly", // Use the 'v' parameter to indicate the version to use (weekly, beta, alpha, etc.). // Add other bootstrap parameters as needed, using camel case. }); </script>
Indiquez un ID lorsque vous instanciez la carte à l'aide de la propriété
mapId. Il doit s'agir de l'ID de carte que vous avez configuré à l'aide d'un style de carte dans lequel les calques d'éléments sont activés.map = new google.maps.Map(document.getElementById('map'), { center: {lat: -34.397, lng: 150.644}, zoom: 8, mapId: 'MAP_ID' // A map ID using a style with one or more feature layers enabled. });
Découvrez comment charger l'API Maps JavaScript.
Ajouter des calques d'éléments à une carte
Pour obtenir une référence à un calque d'éléments sur votre carte, appelez map.getFeatureLayer() lorsque la carte s'initialise :
function initMap() { map = new google.maps.Map(document.getElementById("map"), { center: { lat: 20.773, lng: -156.01 }, zoom: 12, mapId: 'MAP_ID', }); // Add a feature layer for localities. localityLayer = map.getFeatureLayer('LOCALITY'); ... }
Vérifier les fonctionnalités de la carte
Le style basé sur les données pour les limites nécessite des fonctionnalités activées dans la console Google APIs et associées à un ID de carte. Les ID de carte étant éphémères et susceptibles d'être modifiés, vous pouvez appeler map.getMapCapabilities() pour vérifier si une fonctionnalité donnée (par exemple, les styles basés sur les données) est disponible avant de l'appeler. Cette vérification est facultative.
L'exemple suivant montre comment ajouter un écouteur pour s'abonner aux modifications des fonctionnalités de la carte :
// subscribe to changes map.addListener('mapcapabilities_changed', () => { const mapCapabilities = map.getMapCapabilities(); if (!mapCapabilities.isDataDrivenStylingAvailable) { // Data-driven styling is *not* available, add a fallback. // Existing feature layers are also unavailable. } });
Étapes suivantes
- Styliser un polygone de limite
- Créer une carte choroplèthe
- Gérer les événements de souris
- Obtenir un ID de lieu pour une région
- Utiliser les API Geocoding et Places avec un style basé sur les données pour les limites
