บทนำ
เครื่องหมายระบุตำแหน่งบนแผนที่ โดยค่าเริ่มต้น เครื่องหมายจะใช้รูปภาพมาตรฐาน เครื่องหมายสามารถแสดงรูปภาพที่กําหนดเองได้ ซึ่งในกรณีนี้มักจะเรียกว่า "ไอคอน" เครื่องหมายและไอคอนเป็นออบเจ็กต์ประเภท Marker คุณสามารถตั้งค่าไอคอนที่กำหนดเองภายในคอนสตรัคเตอร์ของเครื่องหมาย หรือเรียกใช้ setIcon() บนเครื่องหมาย ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการปรับแต่งรูปภาพเครื่องหมาย
กล่าวโดยคร่าวๆ มาร์กเกอร์คือการวางซ้อนประเภทหนึ่ง ดูข้อมูลเกี่ยวกับการวางซ้อนประเภทอื่นๆ ได้ที่การวาดในแผนที่
เครื่องหมายออกแบบมาให้โต้ตอบได้ ตัวอย่างเช่น โดยค่าเริ่มต้น เหตุการณ์เหล่านี้จะรับเหตุการณ์ 'click' คุณจึงเพิ่มตัวรับเหตุการณ์เพื่อแสดงหน้าต่างข้อมูลที่แสดงข้อมูลที่กําหนดเองได้ คุณสามารถอนุญาตให้ผู้ใช้ย้ายเครื่องหมายบนแผนที่ได้โดยการตั้งค่าพร็อพเพอร์ตี้ draggable ของเครื่องหมายเป็น true ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับเครื่องหมายที่ลากได้ด้านล่าง
เพิ่มเครื่องหมาย
ตัวสร้างgoogle.maps.Markerใช้ลิเทอรัลออบเจ็กต์ Marker options รายการเดียว ซึ่งระบุพร็อพเพอร์ตี้เริ่มต้นของเครื่องหมาย
ฟิลด์ต่อไปนี้มีความสำคัญอย่างยิ่งและมักตั้งค่าเมื่อสร้างเครื่องหมาย
-
position(ต้องระบุ) ระบุLatLngที่ระบุตําแหน่งเริ่มต้นของเครื่องหมาย วิธีหนึ่งในการดึงข้อมูลLatLngคือการใช้บริการการแปลงที่อยู่เป็นพิกัดภูมิศาสตร์ -
map(ไม่บังคับ) ระบุMapที่จะวางเครื่องหมาย หากคุณไม่ได้ระบุแผนที่ในการสร้างเครื่องหมาย ระบบจะสร้างเครื่องหมายแต่ไม่แนบ (หรือแสดง) กับแผนที่ คุณสามารถเพิ่มเครื่องหมายในภายหลังได้โดยเรียกใช้เมธอดsetMap()ของเครื่องหมาย
ตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้จะเพิ่มเครื่องหมายธรรมดาลงในแผนที่ที่อุลูรู ใจกลางออสเตรเลีย
TypeScript
function initMap(): void { const myLatLng = { lat: -25.363, lng: 131.044 }; const map = new google.maps.Map( document.getElementById("map") as HTMLElement, { zoom: 4, center: myLatLng, } ); new google.maps.Marker({ position: myLatLng, map, title: "Hello World!", }); } declare global { interface Window { initMap: () => void; } } window.initMap = initMap;
JavaScript
function initMap() { const myLatLng = { lat: -25.363, lng: 131.044 }; const map = new google.maps.Map(document.getElementById("map"), { zoom: 4, center: myLatLng, }); new google.maps.Marker({ position: myLatLng, map, title: "Hello World!", }); } window.initMap = initMap;
ลองใช้ตัวอย่าง
ในตัวอย่างข้างต้น เครื่องหมายจะวางบนแผนที่เมื่อสร้างเครื่องหมายโดยใช้พร็อพเพอร์ตี้ map ในตัวเลือกเครื่องหมาย
หรือจะเพิ่มเครื่องหมายลงในแผนที่โดยตรงโดยใช้เมธอด setMap() ของเครื่องหมายก็ได้ ดังที่แสดงในตัวอย่างด้านล่าง
var myLatlng = new google.maps.LatLng(-25.363882,131.044922); var mapOptions = { zoom: 4, center: myLatlng } var map = new google.maps.Map(document.getElementById("map"), mapOptions); var marker = new google.maps.Marker({ position: myLatlng, title:"Hello World!" }); // To add the marker to the map, call setMap(); marker.setMap(map);
title ของเครื่องหมายจะปรากฏเป็นเคล็ดลับเครื่องมือ
หากไม่ต้องการส่ง Marker options ในคอนสตรคเตอร์ของมาร์กเกอร์ ให้ส่งออบเจ็กต์ว่าง {} ในอาร์กิวเมนต์สุดท้ายของคอนสตรคเตอร์แทน
นำเครื่องหมายออก
หากต้องการนำเครื่องหมายออกจากแผนที่ ให้เรียกใช้เมธอด setMap() โดยส่ง null เป็นอาร์กิวเมนต์
marker.setMap(null);
โปรดทราบว่าวิธีการข้างต้นจะไม่ลบเครื่องหมาย ซึ่งจะนำเครื่องหมายออกจากแผนที่ หากต้องการลบเครื่องหมายแทน คุณควรนำเครื่องหมายออกจากแผนที่ แล้วตั้งค่าเครื่องหมายเป็น null
หากต้องการจัดการชุดเครื่องหมาย คุณควรสร้างอาร์เรย์เพื่อเก็บเครื่องหมาย เมื่อใช้อาร์เรย์นี้ คุณจะเรียก setMap() บนเครื่องหมายแต่ละรายการในอาร์เรย์ทีละรายการได้เมื่อต้องการนำเครื่องหมายออก คุณลบเครื่องหมายได้โดยนำออกจากแผนที่ แล้วตั้งค่า length ของอาร์เรย์เป็น 0 ซึ่งจะนำการอ้างอิงทั้งหมดของเครื่องหมายออก
ปรับแต่งรูปภาพเครื่องหมาย
คุณปรับแต่งลักษณะที่ปรากฏของหมุดได้โดยระบุไฟล์รูปภาพหรือไอคอนแบบเวกเตอร์ให้แสดงแทนไอคอนหมุดของ Google Maps เริ่มต้น คุณสามารถเพิ่มข้อความด้วยป้ายกำกับเครื่องหมาย และใช้ไอคอนที่ซับซ้อนเพื่อกำหนดภูมิภาคที่คลิกได้ รวมถึงกำหนดลําดับกองของหมุด
เครื่องหมายที่มีไอคอนรูปภาพ
ในกรณีพื้นฐานที่สุด ไอคอนจะระบุรูปภาพที่จะใช้แทนไอคอนหมุดของ Google Maps เริ่มต้นได้ หากต้องการระบุไอคอนดังกล่าว ให้ตั้งค่าพร็อพเพอร์ตี้ icon ของเครื่องหมายเป็น URL ของรูปภาพ Maps JavaScript API จะปรับขนาดไอคอนโดยอัตโนมัติ
TypeScript
// This example adds a marker to indicate the position of Bondi Beach in Sydney, // Australia. function initMap(): void { const map = new google.maps.Map( document.getElementById("map") as HTMLElement, { zoom: 4, center: { lat: -33, lng: 151 }, } ); const image = "https://developers.google.com/maps/documentation/javascript/examples/full/images/beachflag.png"; const beachMarker = new google.maps.Marker({ position: { lat: -33.89, lng: 151.274 }, map, icon: image, }); } declare global { interface Window { initMap: () => void; } } window.initMap = initMap;
JavaScript
// This example adds a marker to indicate the position of Bondi Beach in Sydney, // Australia. function initMap() { const map = new google.maps.Map(document.getElementById("map"), { zoom: 4, center: { lat: -33, lng: 151 }, }); const image = "https://developers.google.com/maps/documentation/javascript/examples/full/images/beachflag.png"; const beachMarker = new google.maps.Marker({ position: { lat: -33.89, lng: 151.274 }, map, icon: image, }); } window.initMap = initMap;
ลองใช้ตัวอย่าง
เครื่องหมายที่มีไอคอนแบบเวกเตอร์
คุณสามารถใช้เส้นทางเวกเตอร์ SVG ที่กําหนดเองเพื่อกําหนดลักษณะที่ปรากฏของหมุดได้ โดยส่งลิเทอรัลออบเจ็กต์ Symbol ที่มีเส้นทางที่ต้องการไปยังพร็อพเพอร์ตี้ icon ของเครื่องหมาย คุณสามารถกำหนดเส้นทางที่กำหนดเองโดยใช้การเขียนเส้นทาง SVG หรือใช้เส้นทางที่กําหนดไว้ล่วงหน้ารายการใดรายการหนึ่งใน google.maps.SymbolPath ต้องมีพร็อพเพอร์ตี้ anchor เพื่อให้เครื่องหมายแสดงผลอย่างถูกต้องเมื่อระดับการซูมเปลี่ยนแปลง ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้สัญลักษณ์เพื่อสร้างไอคอนแบบเวกเตอร์สำหรับเครื่องหมาย (และเส้นประกอบ)
TypeScript
// This example uses SVG path notation to add a vector-based symbol // as the icon for a marker. The resulting icon is a marker-shaped // symbol with a blue fill and no border. function initMap(): void { const center = new google.maps.LatLng(-33.712451, 150.311823); const map = new google.maps.Map( document.getElementById("map") as HTMLElement, { zoom: 9, center: center, } ); const svgMarker = { path: "M-1.547 12l6.563-6.609-1.406-1.406-5.156 5.203-2.063-2.109-1.406 1.406zM0 0q2.906 0 4.945 2.039t2.039 4.945q0 1.453-0.727 3.328t-1.758 3.516-2.039 3.070-1.711 2.273l-0.75 0.797q-0.281-0.328-0.75-0.867t-1.688-2.156-2.133-3.141-1.664-3.445-0.75-3.375q0-2.906 2.039-4.945t4.945-2.039z", fillColor: "blue", fillOpacity: 0.6, strokeWeight: 0, rotation: 0, scale: 2, anchor: new google.maps.Point(0, 20), }; new google.maps.Marker({ position: map.getCenter(), icon: svgMarker, map: map, }); } declare global { interface Window { initMap: () => void; } } window.initMap = initMap;
JavaScript
// This example uses SVG path notation to add a vector-based symbol // as the icon for a marker. The resulting icon is a marker-shaped // symbol with a blue fill and no border. function initMap() { const center = new google.maps.LatLng(-33.712451, 150.311823); const map = new google.maps.Map(document.getElementById("map"), { zoom: 9, center: center, }); const svgMarker = { path: "M-1.547 12l6.563-6.609-1.406-1.406-5.156 5.203-2.063-2.109-1.406 1.406zM0 0q2.906 0 4.945 2.039t2.039 4.945q0 1.453-0.727 3.328t-1.758 3.516-2.039 3.070-1.711 2.273l-0.75 0.797q-0.281-0.328-0.75-0.867t-1.688-2.156-2.133-3.141-1.664-3.445-0.75-3.375q0-2.906 2.039-4.945t4.945-2.039z", fillColor: "blue", fillOpacity: 0.6, strokeWeight: 0, rotation: 0, scale: 2, anchor: new google.maps.Point(0, 20), }; new google.maps.Marker({ position: map.getCenter(), icon: svgMarker, map: map, }); } window.initMap = initMap;
ลองใช้ตัวอย่าง
ป้ายกำกับเครื่องหมาย
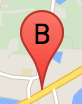
ป้ายกำกับเครื่องหมายคือตัวอักษรหรือตัวเลขที่ปรากฏภายในเครื่องหมาย รูปภาพเครื่องหมายในส่วนนี้จะแสดงป้ายกำกับเครื่องหมายที่มีตัวอักษร "B" คุณสามารถระบุป้ายกำกับเครื่องหมายเป็นสตริงหรือออบเจ็กต์ MarkerLabel ที่มีสตริงและพร็อพเพอร์ตี้ป้ายกำกับอื่นๆ
เมื่อสร้างเครื่องหมาย คุณสามารถระบุพร็อพเพอร์ตี้ label ในออบเจ็กต์ MarkerOptions หรือจะเรียก setLabel() ในออบเจ็กต์ Marker เพื่อตั้งค่าป้ายกำกับบนเครื่องหมายที่มีอยู่ก็ได้
ตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้แสดงเครื่องหมายที่ติดป้ายกำกับเมื่อผู้ใช้คลิกแผนที่
TypeScript
// In the following example, markers appear when the user clicks on the map. // Each marker is labeled with a single alphabetical character. const labels = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"; let labelIndex = 0; function initMap(): void { const bangalore = { lat: 12.97, lng: 77.59 }; const map = new google.maps.Map( document.getElementById("map") as HTMLElement, { zoom: 12, center: bangalore, } ); // This event listener calls addMarker() when the map is clicked. google.maps.event.addListener(map, "click", (event) => { addMarker(event.latLng, map); }); // Add a marker at the center of the map. addMarker(bangalore, map); } // Adds a marker to the map. function addMarker(location: google.maps.LatLngLiteral, map: google.maps.Map) { // Add the marker at the clicked location, and add the next-available label // from the array of alphabetical characters. new google.maps.Marker({ position: location, label: labels[labelIndex++ % labels.length], map: map, }); } declare global { interface Window { initMap: () => void; } } window.initMap = initMap;
JavaScript
// In the following example, markers appear when the user clicks on the map. // Each marker is labeled with a single alphabetical character. const labels = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"; let labelIndex = 0; function initMap() { const bangalore = { lat: 12.97, lng: 77.59 }; const map = new google.maps.Map(document.getElementById("map"), { zoom: 12, center: bangalore, }); // This event listener calls addMarker() when the map is clicked. google.maps.event.addListener(map, "click", (event) => { addMarker(event.latLng, map); }); // Add a marker at the center of the map. addMarker(bangalore, map); } // Adds a marker to the map. function addMarker(location, map) { // Add the marker at the clicked location, and add the next-available label // from the array of alphabetical characters. new google.maps.Marker({ position: location, label: labels[labelIndex++ % labels.length], map: map, }); } window.initMap = initMap;
ลองใช้ตัวอย่าง
ไอคอนที่ซับซ้อน
คุณสามารถระบุรูปร่างที่ซับซ้อนเพื่อระบุภูมิภาคที่คลิกได้ และระบุลักษณะที่ไอคอนควรปรากฏเมื่อเทียบกับการวางซ้อนอื่นๆ ("ลําดับกองซ้อน") ไอคอนที่ระบุด้วยวิธีนี้ควรตั้งค่าพร็อพเพอร์ตี้ icon ให้ออบเจ็กต์ประเภท Icon
Icon
ออบเจ็กต์กำหนดรูปภาพ นอกจากนี้ ยังกำหนด size ของไอคอน, origin ของไอคอน (เช่น หากรูปภาพที่ต้องการเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของรูปภาพขนาดใหญ่ในสไปรต์) และ anchor ที่ควรเป็นตําแหน่งฮอตสปอตของไอคอน (ซึ่งอิงตามต้นทาง)
หากใช้ป้ายกำกับที่มีเครื่องหมายที่กำหนดเอง คุณสามารถกำหนดตำแหน่งป้ายกำกับด้วยพร็อพเพอร์ตี้ labelOrigin ในแออบเจ็กต์ Icon
TypeScript
// The following example creates complex markers to indicate beaches near // Sydney, NSW, Australia. Note that the anchor is set to (0,32) to correspond // to the base of the flagpole. function initMap(): void { const map = new google.maps.Map( document.getElementById("map") as HTMLElement, { zoom: 10, center: { lat: -33.9, lng: 151.2 }, } ); setMarkers(map); } // Data for the markers consisting of a name, a LatLng and a zIndex for the // order in which these markers should display on top of each other. const beaches: [string, number, number, number][] = [ ["Bondi Beach", -33.890542, 151.274856, 4], ["Coogee Beach", -33.923036, 151.259052, 5], ["Cronulla Beach", -34.028249, 151.157507, 3], ["Manly Beach", -33.80010128657071, 151.28747820854187, 2], ["Maroubra Beach", -33.950198, 151.259302, 1], ]; function setMarkers(map: google.maps.Map) { // Adds markers to the map. // Marker sizes are expressed as a Size of X,Y where the origin of the image // (0,0) is located in the top left of the image. // Origins, anchor positions and coordinates of the marker increase in the X // direction to the right and in the Y direction down. const image = { url: "https://developers.google.com/maps/documentation/javascript/examples/full/images/beachflag.png", // This marker is 20 pixels wide by 32 pixels high. size: new google.maps.Size(20, 32), // The origin for this image is (0, 0). origin: new google.maps.Point(0, 0), // The anchor for this image is the base of the flagpole at (0, 32). anchor: new google.maps.Point(0, 32), }; // Shapes define the clickable region of the icon. The type defines an HTML // <area> element 'poly' which traces out a polygon as a series of X,Y points. // The final coordinate closes the poly by connecting to the first coordinate. const shape = { coords: [1, 1, 1, 20, 18, 20, 18, 1], type: "poly", }; for (let i = 0; i < beaches.length; i++) { const beach = beaches[i]; new google.maps.Marker({ position: { lat: beach[1], lng: beach[2] }, map, icon: image, shape: shape, title: beach[0], zIndex: beach[3], }); } } declare global { interface Window { initMap: () => void; } } window.initMap = initMap;
JavaScript
// The following example creates complex markers to indicate beaches near // Sydney, NSW, Australia. Note that the anchor is set to (0,32) to correspond // to the base of the flagpole. function initMap() { const map = new google.maps.Map(document.getElementById("map"), { zoom: 10, center: { lat: -33.9, lng: 151.2 }, }); setMarkers(map); } // Data for the markers consisting of a name, a LatLng and a zIndex for the // order in which these markers should display on top of each other. const beaches = [ ["Bondi Beach", -33.890542, 151.274856, 4], ["Coogee Beach", -33.923036, 151.259052, 5], ["Cronulla Beach", -34.028249, 151.157507, 3], ["Manly Beach", -33.80010128657071, 151.28747820854187, 2], ["Maroubra Beach", -33.950198, 151.259302, 1], ]; function setMarkers(map) { // Adds markers to the map. // Marker sizes are expressed as a Size of X,Y where the origin of the image // (0,0) is located in the top left of the image. // Origins, anchor positions and coordinates of the marker increase in the X // direction to the right and in the Y direction down. const image = { url: "https://developers.google.com/maps/documentation/javascript/examples/full/images/beachflag.png", // This marker is 20 pixels wide by 32 pixels high. size: new google.maps.Size(20, 32), // The origin for this image is (0, 0). origin: new google.maps.Point(0, 0), // The anchor for this image is the base of the flagpole at (0, 32). anchor: new google.maps.Point(0, 32), }; // Shapes define the clickable region of the icon. The type defines an HTML // <area> element 'poly' which traces out a polygon as a series of X,Y points. // The final coordinate closes the poly by connecting to the first coordinate. const shape = { coords: [1, 1, 1, 20, 18, 20, 18, 1], type: "poly", }; for (let i = 0; i < beaches.length; i++) { const beach = beaches[i]; new google.maps.Marker({ position: { lat: beach[1], lng: beach[2] }, map, icon: image, shape: shape, title: beach[0], zIndex: beach[3], }); } } window.initMap = initMap;
ลองใช้ตัวอย่าง
แปลงออบเจ็กต์ MarkerImage เป็นประเภท Icon
จนถึง Maps JavaScript API เวอร์ชัน 3.10 ไอคอนที่ซับซ้อนจะกำหนดให้เป็นออบเจ็กต์ MarkerImage เราได้เพิ่มลิเทอรัลออบเจ็กต์ Icon ในเวอร์ชัน 3.10 และแทนที่ MarkerImage ตั้งแต่เวอร์ชัน 3.11 เป็นต้นไป
นิพจน์ลิเทอรัลออบเจ็กต์ Icon รองรับพารามิเตอร์เดียวกับ MarkerImage ซึ่งช่วยให้คุณแปลง MarkerImage เป็น Icon ได้โดยง่ายด้วยการนําตัวสร้างออก ใส่พารามิเตอร์ก่อนหน้าใน {} และเพิ่มชื่อของพารามิเตอร์แต่ละรายการ เช่น
var image = new google.maps.MarkerImage( place.icon, new google.maps.Size(71, 71), new google.maps.Point(0, 0), new google.maps.Point(17, 34), new google.maps.Size(25, 25));
กลายเป็น
var image = { url: place.icon, size: new google.maps.Size(71, 71), origin: new google.maps.Point(0, 0), anchor: new google.maps.Point(17, 34), scaledSize: new google.maps.Size(25, 25) };
เพิ่มประสิทธิภาพเครื่องหมาย
การเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพจะช่วยปรับปรุงประสิทธิภาพด้วยการแสดงผลเครื่องหมายหลายรายการเป็นองค์ประกอบแบบคงที่รายการเดียว ซึ่งมีประโยชน์ในกรณีที่ต้องใช้เครื่องหมายจํานวนมาก โดยค่าเริ่มต้น Maps JavaScript API จะเป็นผู้ตัดสินใจว่าจะเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพเครื่องหมายหรือไม่ เมื่อเครื่องหมายมีจํานวนมาก Maps JavaScript API จะพยายามแสดงผลเครื่องหมายด้วยการเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพ มาร์กเกอร์บางรายการไม่สามารถเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพได้ ในบางสถานการณ์ Maps JavaScript API อาจต้องแสดงผลมาร์กเกอร์โดยไม่มีการเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพ ปิดใช้การแสดงผลแบบเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพสำหรับ GIF หรือ PNG แบบเคลื่อนไหว หรือเมื่อต้องแสดงผลเครื่องหมายแต่ละรายการเป็นองค์ประกอบ DOM แยกกัน ตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้แสดงการสร้างเครื่องหมายที่เพิ่มประสิทธิภาพ
var marker = new google.maps.Marker({ position: myLatlng, title:"Hello World!", optimized: true });
ทำให้เข้าถึงเครื่องหมายได้
คุณทําให้เครื่องหมายเข้าถึงได้โดยการเพิ่มเหตุการณ์ Listener การคลิก และตั้งค่า optimized เป็น false โปรแกรมรับฟังการคลิกทำให้เครื่องหมายมีความหมายของปุ่ม ซึ่งเข้าถึงได้โดยใช้การไปยังส่วนต่างๆ ด้วยแป้นพิมพ์ โปรแกรมอ่านหน้าจอ และอื่นๆ ใช้ตัวเลือก title เพื่อแสดงข้อความที่เข้าถึงได้สำหรับเครื่องหมาย
ในตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้ เครื่องหมายแรกจะได้รับโฟกัสเมื่อกด Tab จากนั้นคุณจะใช้ปุ่มลูกศรเพื่อย้ายไปมาระหว่างเครื่องหมายได้ กด Tab อีกครั้งเพื่อไปยังส่วนควบคุมแผนที่อื่นๆ หากเครื่องหมายมีหน้าต่างข้อมูล คุณสามารถเปิดหน้าต่างได้โดยคลิกเครื่องหมาย หรือกดแป้น Enter หรือ Space เมื่อเลือกเครื่องหมาย เมื่อหน้าต่างข้อมูลปิดลง โฟกัสจะกลับไปที่เครื่องหมายที่เกี่ยวข้อง
TypeScript
// The following example creates five accessible and // focusable markers. function initMap(): void { const map = new google.maps.Map( document.getElementById("map") as HTMLElement, { zoom: 12, center: { lat: 34.84555, lng: -111.8035 }, } ); // Set LatLng and title text for the markers. The first marker (Boynton Pass) // receives the initial focus when tab is pressed. Use arrow keys to // move between markers; press tab again to cycle through the map controls. const tourStops: [google.maps.LatLngLiteral, string][] = [ [{ lat: 34.8791806, lng: -111.8265049 }, "Boynton Pass"], [{ lat: 34.8559195, lng: -111.7988186 }, "Airport Mesa"], [{ lat: 34.832149, lng: -111.7695277 }, "Chapel of the Holy Cross"], [{ lat: 34.823736, lng: -111.8001857 }, "Red Rock Crossing"], [{ lat: 34.800326, lng: -111.7665047 }, "Bell Rock"], ]; // Create an info window to share between markers. const infoWindow = new google.maps.InfoWindow(); // Create the markers. tourStops.forEach(([position, title], i) => { const marker = new google.maps.Marker({ position, map, title: `${i + 1}. ${title}`, label: `${i + 1}`, optimized: false, }); // Add a click listener for each marker, and set up the info window. marker.addListener("click", () => { infoWindow.close(); infoWindow.setContent(marker.getTitle()); infoWindow.open(marker.getMap(), marker); }); }); } declare global { interface Window { initMap: () => void; } } window.initMap = initMap;
JavaScript
// The following example creates five accessible and // focusable markers. function initMap() { const map = new google.maps.Map(document.getElementById("map"), { zoom: 12, center: { lat: 34.84555, lng: -111.8035 }, }); // Set LatLng and title text for the markers. The first marker (Boynton Pass) // receives the initial focus when tab is pressed. Use arrow keys to // move between markers; press tab again to cycle through the map controls. const tourStops = [ [{ lat: 34.8791806, lng: -111.8265049 }, "Boynton Pass"], [{ lat: 34.8559195, lng: -111.7988186 }, "Airport Mesa"], [{ lat: 34.832149, lng: -111.7695277 }, "Chapel of the Holy Cross"], [{ lat: 34.823736, lng: -111.8001857 }, "Red Rock Crossing"], [{ lat: 34.800326, lng: -111.7665047 }, "Bell Rock"], ]; // Create an info window to share between markers. const infoWindow = new google.maps.InfoWindow(); // Create the markers. tourStops.forEach(([position, title], i) => { const marker = new google.maps.Marker({ position, map, title: `${i + 1}. ${title}`, label: `${i + 1}`, optimized: false, }); // Add a click listener for each marker, and set up the info window. marker.addListener("click", () => { infoWindow.close(); infoWindow.setContent(marker.getTitle()); infoWindow.open(marker.getMap(), marker); }); }); } window.initMap = initMap;
ลองใช้ตัวอย่าง
สร้างภาพเคลื่อนไหวของเครื่องหมาย
คุณทำให้เครื่องหมายเคลื่อนไหวได้เพื่อให้แสดงการเคลื่อนไหวแบบไดนามิกในสถานการณ์ต่างๆ หากต้องการระบุลักษณะการแสดงผลภาพเคลื่อนไหวของหมุด ให้ใช้พร็อพเพอร์ตี้ animation ของหมุดซึ่งมีประเภทเป็น google.maps.Animation ระบบรองรับค่า Animation ต่อไปนี้
-
DROPบ่งบอกว่าเครื่องหมายควรวางจากด้านบนของแผนที่ไปยังตำแหน่งสุดท้ายเมื่อวางบนแผนที่เป็นครั้งแรก ภาพเคลื่อนไหวจะหยุดลงเมื่อเครื่องหมายหยุดลงและanimationจะเปลี่ยนกลับไปเป็นnullโดยปกติแล้วภาพเคลื่อนไหวประเภทนี้จะระบุในระหว่างการสร้างMarker -
BOUNCEบ่งชี้ว่าเครื่องหมายควรเด้งอยู่ในตำแหน่ง เครื่องหมายการตีกลับจะตีกลับต่อไปจนกว่าจะมีการตั้งค่าพร็อพเพอร์ตี้animationเป็นnullอย่างชัดเจน
คุณเริ่มภาพเคลื่อนไหวบนเครื่องหมายที่มีอยู่ได้โดยเรียกใช้ setAnimation() บนออบเจ็กต์ Marker
TypeScript
// The following example creates a marker in Stockholm, Sweden using a DROP // animation. Clicking on the marker will toggle the animation between a BOUNCE // animation and no animation. let marker: google.maps.Marker; function initMap(): void { const map = new google.maps.Map( document.getElementById("map") as HTMLElement, { zoom: 13, center: { lat: 59.325, lng: 18.07 }, } ); marker = new google.maps.Marker({ map, draggable: true, animation: google.maps.Animation.DROP, position: { lat: 59.327, lng: 18.067 }, }); marker.addListener("click", toggleBounce); } function toggleBounce() { if (marker.getAnimation() !== null) { marker.setAnimation(null); } else { marker.setAnimation(google.maps.Animation.BOUNCE); } } declare global { interface Window { initMap: () => void; } } window.initMap = initMap;
JavaScript
// The following example creates a marker in Stockholm, Sweden using a DROP // animation. Clicking on the marker will toggle the animation between a BOUNCE // animation and no animation. let marker; function initMap() { const map = new google.maps.Map(document.getElementById("map"), { zoom: 13, center: { lat: 59.325, lng: 18.07 }, }); marker = new google.maps.Marker({ map, draggable: true, animation: google.maps.Animation.DROP, position: { lat: 59.327, lng: 18.067 }, }); marker.addListener("click", toggleBounce); } function toggleBounce() { if (marker.getAnimation() !== null) { marker.setAnimation(null); } else { marker.setAnimation(google.maps.Animation.BOUNCE); } } window.initMap = initMap;
ลองใช้ตัวอย่าง
หากมีเครื่องหมายจำนวนมาก คุณอาจไม่ต้องการวางเครื่องหมายทั้งหมดในแผนที่พร้อมกัน คุณสามารถใช้ setTimeout() เพื่อเว้นระยะห่างระหว่างภาพเคลื่อนไหวของเครื่องหมายโดยใช้รูปแบบดังที่แสดงด้านล่าง
function drop() { for (var i =0; i < markerArray.length; i++) { setTimeout(function() { addMarkerMethod(); }, i * 200); } }
ทําให้เครื่องหมายลากได้
หากต้องการอนุญาตให้ผู้ใช้ลากเครื่องหมายไปยังตำแหน่งอื่นบนแผนที่ ให้ตั้งค่า draggable เป็น true ในตัวเลือกเครื่องหมาย
var myLatlng = new google.maps.LatLng(-25.363882,131.044922); var mapOptions = { zoom: 4, center: myLatlng } var map = new google.maps.Map(document.getElementById("map"), mapOptions); // Place a draggable marker on the map var marker = new google.maps.Marker({ position: myLatlng, map: map, draggable:true, title:"Drag me!" });
การปรับแต่งเครื่องหมายเพิ่มเติม
ดูตัวอย่างเครื่องหมายที่กำหนดเองทั้งหมดได้ที่ตัวอย่างป๊อปอัปที่กำหนดเอง
ดูส่วนขยายเพิ่มเติมของคลาสเครื่องหมาย การรวมกลุ่มและการจัดการเครื่องหมาย รวมถึงการปรับแต่งการวางซ้อนได้ที่ไลบรารีโอเพนซอร์ส
