Na tej stronie znajdziesz opis narzędzia do tworzenia mapy cieplnej, które jest dostępne w bibliotece narzędziowej pakietu Maps SDK na iOS. Mapy termiczne przydają się do przedstawiania rozkładu i gęstości punktów danych na mapie.
Ten film omawia użycie map cieplnych jako alternatywy dla znaczników, gdy dane wymagają dużej liczby punktów danych na mapie.
Mapy termiczne ułatwiają widzom zrozumienie rozkładu i względnej intensywności punktów danych na mapie. Zamiast umieszczać znacznik w każdej lokalizacji, mapy cieplne wykorzystują kolor do przedstawiania rozkładu danych.
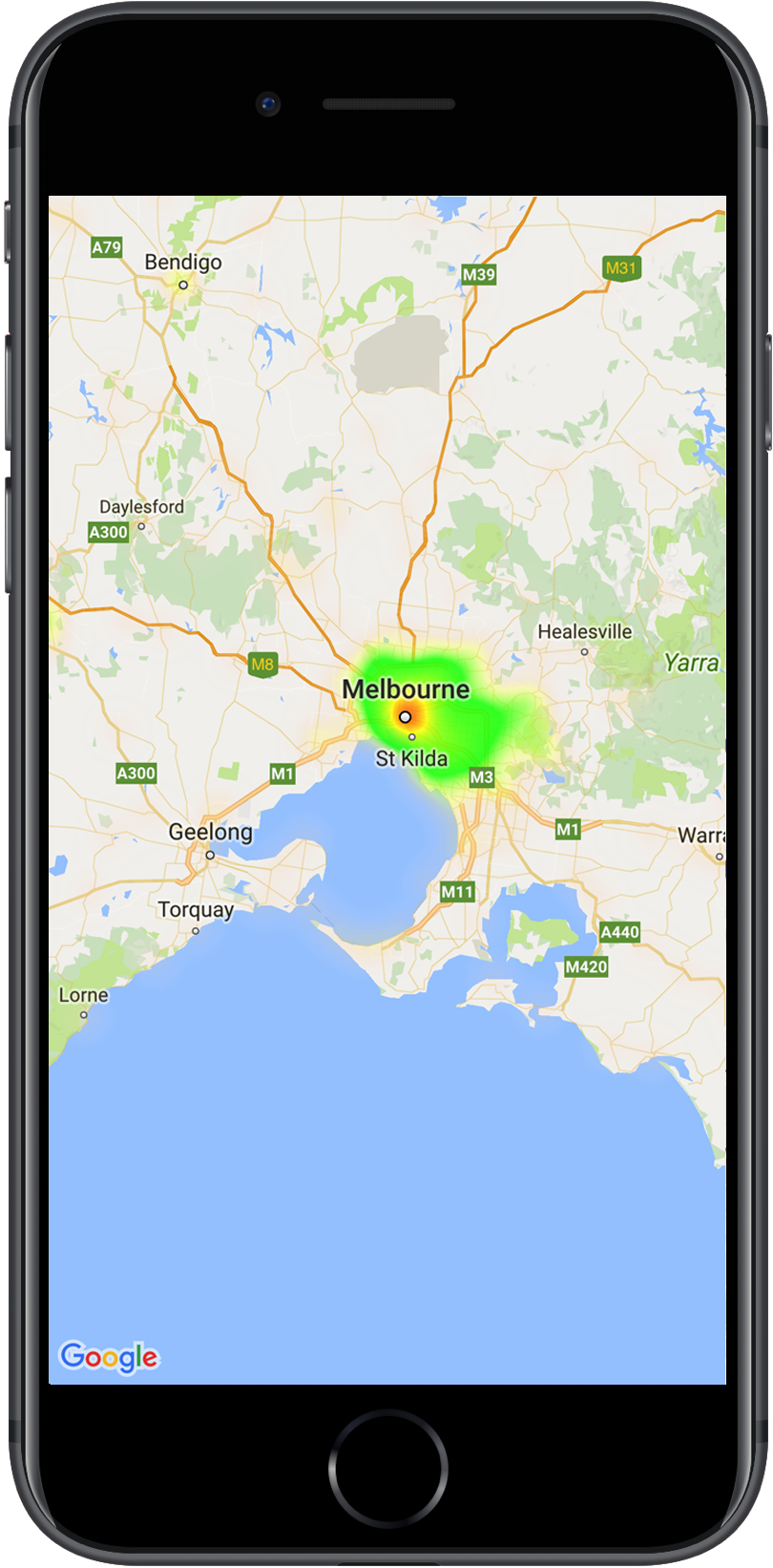
W przykładzie poniżej czerwony kolor oznacza obszary o wysokim zagęszczeniu komisariatów policji w stanie Wiktoria w Australii.
Jeśli nie masz jeszcze skonfigurowanej biblioteki, przed przeczytaniem reszty tej strony zapoznaj się z przewodnikiem po konfiguracji.
Dodawanie prostej mapy termicznej
Aby dodać do mapy mapę cieplną, potrzebujesz zbioru danych zawierającego współrzędne każdej interesującej Cię lokalizacji. Najpierw utwórz instancję GMUHeatmapTileLayer, ustawiając właściwość map na GMSMapView.
Zrób to w funkcji viewDidLoad() aplikacji, aby mieć pewność, że mapa bazowa zostanie wczytana przed rozpoczęciem pracy z mapą cieplną. Następnie przekaż kolekcję obiektów GMUWeightedLatLng do instancji GMUHeatmapTileLayer.
Narzędzie udostępnia klasę GMUHeatmapTileLayer, która akceptuje kolekcję obiektów GMUWeightedLatLng. Tworzy obrazy kafelków dla różnych poziomów powiększenia na podstawie podanych opcji promienia, gradientu i krycia.
Przyjrzyjmy się szczegółowo poszczególnym etapom:
- Utwórz instancję
GMUHeatmapTileLayer, ustawiając właściwośćmapnaGMSMapView(zrób to w funkcjiviewDidLoad()aplikacji). - Przekaż kolekcję obiektów
GMUWeightedLatLngdo instancjiGMUHeatmapTileLayer. - Wywołaj funkcję
GMUHeatmapTileLayer.map, przekazując widok mapy.Swift
class Heatmap: UIViewController { private var mapView: GMSMapView! private var heatmapLayer: GMUHeatmapTileLayer! override func viewDidLoad() { super.viewDidLoad() heatmapLayer = GMUHeatmapTileLayer() heatmapLayer.map = mapView } // ... func addHeatmap() { // Get the data: latitude/longitude positions of police stations. guard let path = Bundle.main.url(forResource: "police_stations", withExtension: "json") else { return } guard let data = try? Data(contentsOf: path) else { return } guard let json = try? JSONSerialization.jsonObject(with: data, options: []) else { return } guard let object = json as? [[String: Any]] else { print("Could not read the JSON.") return } var list = [GMUWeightedLatLng]() for item in object { let lat = item["lat"] as! CLLocationDegrees let lng = item["lng"] as! CLLocationDegrees let coords = GMUWeightedLatLng( coordinate: CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(lat, lng), intensity: 1.0 ) list.append(coords) } // Add the latlngs to the heatmap layer. heatmapLayer.weightedData = list } }
Objective-C
@implementation Heatmap { GMSMapView *_mapView; GMUHeatmapTileLayer *_heatmapLayer; } - (void)viewDidLoad { [super viewDidLoad]; _heatmapLayer = [[GMUHeatmapTileLayer alloc] init]; _heatmapLayer.map = _mapView; } // ... - (void) addHeatmap { // Get the data: latitude/longitude positions of police stations. NSURL *path = [NSBundle.mainBundle URLForResource:@"police_stations" withExtension:@"json"]; NSData *data = [NSData dataWithContentsOfURL:path]; NSArray *json = [NSJSONSerialization JSONObjectWithData:data options:0 error:nil]; NSMutableArray<GMUWeightedLatLng *> *list = [[NSMutableArray alloc] init]; [json enumerateObjectsUsingBlock:^(id _Nonnull obj, NSUInteger idx, BOOL * _Nonnull stop) { NSDictionary *item = (NSDictionary *)obj; CLLocationDegrees lat = [(NSNumber *) [item valueForKey:@"lat"] doubleValue]; CLLocationDegrees lng = [(NSNumber *) [item valueForKey:@"lng"] doubleValue]; GMUWeightedLatLng *coords = [[GMUWeightedLatLng alloc] initWithCoordinate:CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(lat, lng) intensity:1.0]; [list addObject:coords]; }]; // Add the latlngs to the heatmap layer. _heatmapLayer.weightedData = list; } @end
W tym przykładzie dane są przechowywane w pliku JSON police_stations.json.
Oto fragment pliku:
[
{"lat" : -37.1886, "lng" : 145.708 } ,
{"lat" : -37.8361, "lng" : 144.845 } ,
{"lat" : -38.4034, "lng" : 144.192 } ,
{"lat" : -38.7597, "lng" : 143.67 } ,
{"lat" : -36.9672, "lng" : 141.083 }
]
Dostosowywanie mapy termicznej
Mapa cieplna ma kilka właściwości, które można dostosować. Opcje możesz ustawić podczas początkowego tworzenia instancji GMUHeatmapTileLayer lub w dowolnym momencie, ustawiając nową wartość opcji.
Dostępne są te ustawienia:
Promień: rozmiar rozmycia Gaussa zastosowanego do mapy aktywności wyrażony w pikselach. Wartość domyślna to 20. Musi mieścić się w zakresie od 10 do 50. Użyj
GMUHeatmapTileLayer.radius, aby ustawić promień.Gradient: zakres kolorów, których mapa cieplna używa do generowania mapy kolorów, od najniższej do najwyższej intensywności.
GMUGradientjest tworzony za pomocą tablicy liczb całkowitych zawierającej kolory i tablicy liczb zmiennoprzecinkowych wskazującej punkt początkowy każdego koloru, podany jako procent maksymalnej intensywności i wyrażony jako ułamek od 0 do 1. W przypadku gradientu jednokolorowego musisz podać tylko jeden kolor, a w przypadku gradientu wielokolorowego – co najmniej dwa kolory. Mapa kolorów jest generowana przy użyciu interpolacji między tymi kolorami. Domyślny gradient ma 2 kolory. ParametrcolorMapSizeokreśla liczbę kroków w gradiencie. Większe liczby spowodują płynniejsze przejścia, a mniejsze – ostrzejsze, podobne do wykresu konturowego. Aby ustawić gradient, użyjGMUHeatmapTileLayer.gradient.Przezroczystość: przezroczystość całej warstwy mapy termicznej, która mieści się w zakresie od 0 do 1. Wartość domyślna to 0,7. Użyj
GMUHeatmapTileLayer.opacity, aby ustawić wartość przezroczystości.
Na przykład utwórz Gradient:
Swift
let gradientColors: [UIColor] = [.green, .red] let gradientStartPoints: [NSNumber] = [0.2, 1.0] heatmapLayer.gradient = GMUGradient( colors: gradientColors, startPoints: gradientStartPoints, colorMapSize: 256 )
Objective-C
NSArray<UIColor *> *gradientColors = @[UIColor.greenColor, UIColor.redColor]; NSArray<NSNumber *> *gradientStartPoints = @[@0.2, @1.0]; _heatmapLayer.gradient = [[GMUGradient alloc] initWithColors:gradientColors startPoints:gradientStartPoints colorMapSize:256];
Aby zmienić krycie istniejącej mapy cieplnej:
Swift
heatmapLayer.opacity = 0.7
Objective-C
_heatmapLayer.opacity = 0.7;
Aktualizowanie istniejącej opcji
Aby zaktualizować opcję, która została już ustawiona, wykonaj te czynności:
- Zmień opcję na wybraną wartość.
- Zadzwoń do firmy
GMUHeatmapTileLayer.clearTileCache().
Zmiana zbioru danych
Aby zmienić zbiór danych, na podstawie którego jest tworzona mapa cieplna:
- Zaktualizuj zbieranie danych. Użyj konta
GMUHeatmapTileLayer.weightedData, przekazując tablicęGMUWeightedLatLng. - Zadzwoń do firmy
GMUHeatmapTileLayer.clearTileCache().
Usuwanie mapy termicznej
Aby usunąć mapę cieplną, wywołaj funkcję GMUHeatmapTileLayer.map, przekazując wartość nil.
Swift
heatmapLayer.map = nil
Objective-C
_heatmapLayer.map = nil;
Wyświetlanie aplikacji demonstracyjnej
Inny przykład implementacji mapy cieplnej znajdziesz w HeatmapViewController w aplikacji demonstracyjnej dostarczanej z biblioteką narzędzi.
Przewodnik po konfiguracji zawiera instrukcje uruchamiania aplikacji demonstracyjnej.
