Halaman ini menjelaskan utilitas peta panas yang tersedia di library utilitas untuk Maps SDK for iOS. Peta panas berguna untuk menampilkan distribusi dan kepadatan titik data pada peta.
Video ini membahas penggunaan peta panas sebagai alternatif pananda jika data Anda memerlukan banyak titik data pada peta.
Peta panas memudahkan penonton memahami distribusi dan intensitas relatif titik data pada peta. Peta panas tidak menempatkan penanda di setiap lokasi, tetapi menggunakan warna untuk menampilkan distribusi data.
Dalam contoh di bawah ini, merah mewakili area kantor polisi dengan konsentrasi tinggi di Victoria, Australia.
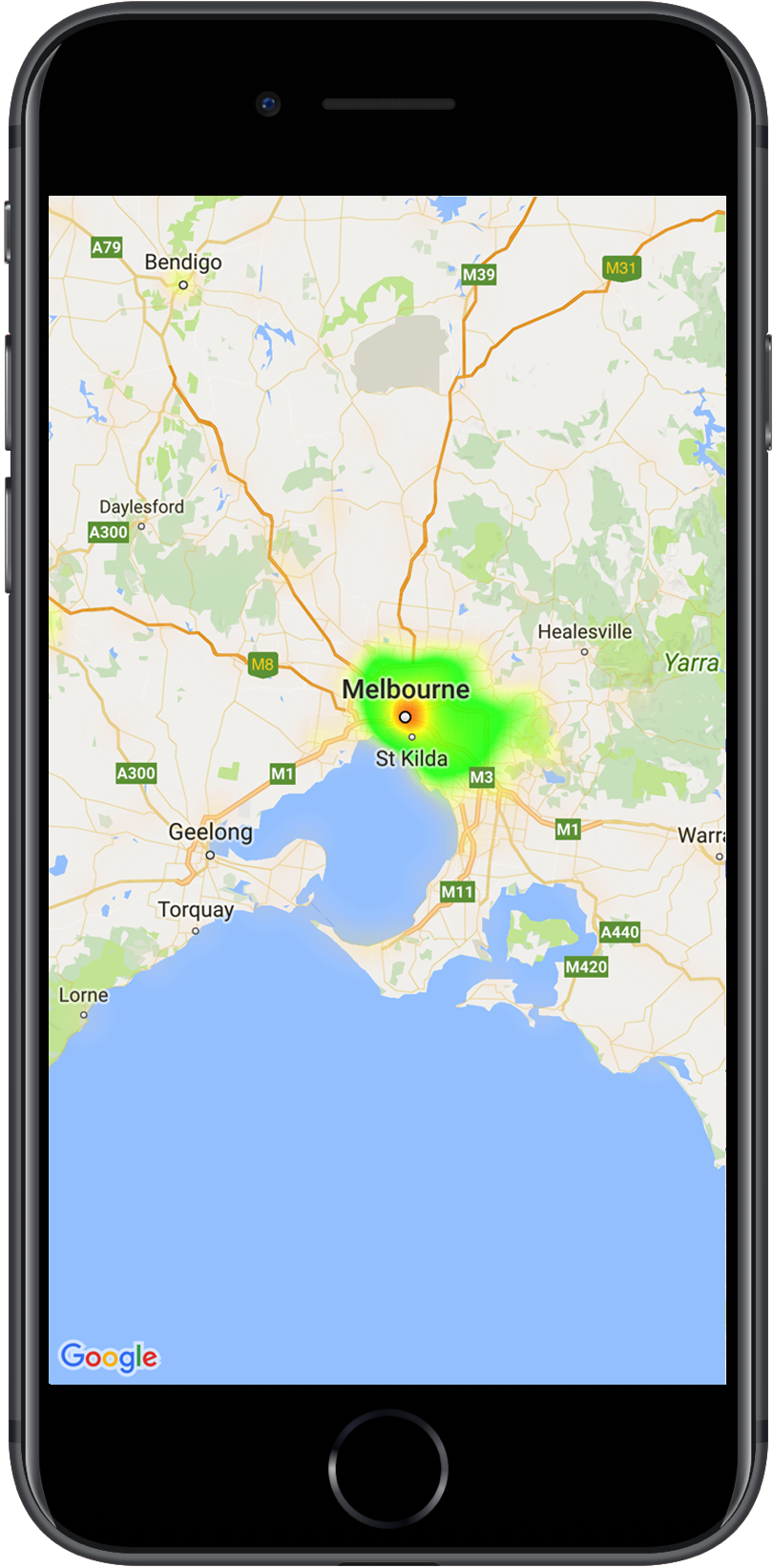
Jika Anda belum menyiapkan library, ikuti panduan penyiapan sebelum membaca bagian lainnya dari halaman ini.
Menambahkan peta panas sederhana
Untuk menambahkan peta panas ke peta, Anda membutuhkan set data yang terdiri dari
koordinat untuk setiap lokasi yang diinginkan. Pertama, buat instance
GMUHeatmapTileLayer, tetapkan properti map ke GMSMapView.
Lakukan hal ini di fungsi viewDidLoad() aplikasi Anda, untuk memastikan peta dasar dimuat sebelum menggunakan peta panas. Kemudian, teruskan kumpulan objek GMUWeightedLatLng ke instance GMUHeatmapTileLayer.
Utilitas ini menyediakan class GMUHeatmapTileLayer, yang menerima kumpulan objek GMUWeightedLatLng. Class ini akan membuat gambar ubin untuk berbagai tingkat zoom, berdasarkan opsi radius, gradien, dan opasitas yang disediakan.
Lihat detail selengkapnya untuk langkah-langkah ini:
- Buat instance
GMUHeatmapTileLayer, tetapkan propertimapkeGMSMapView(lakukan ini dalam fungsiviewDidLoad()aplikasi Anda). - Teruskan kumpulan objek
GMUWeightedLatLngke instanceGMUHeatmapTileLayer. - Panggil
GMUHeatmapTileLayer.map, dengan meneruskan tampilan peta.Swift
class Heatmap: UIViewController { private var mapView: GMSMapView! private var heatmapLayer: GMUHeatmapTileLayer! override func viewDidLoad() { super.viewDidLoad() heatmapLayer = GMUHeatmapTileLayer() heatmapLayer.map = mapView } // ... func addHeatmap() { // Get the data: latitude/longitude positions of police stations. guard let path = Bundle.main.url(forResource: "police_stations", withExtension: "json") else { return } guard let data = try? Data(contentsOf: path) else { return } guard let json = try? JSONSerialization.jsonObject(with: data, options: []) else { return } guard let object = json as? [[String: Any]] else { print("Could not read the JSON.") return } var list = [GMUWeightedLatLng]() for item in object { let lat = item["lat"] as! CLLocationDegrees let lng = item["lng"] as! CLLocationDegrees let coords = GMUWeightedLatLng( coordinate: CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(lat, lng), intensity: 1.0 ) list.append(coords) } // Add the latlngs to the heatmap layer. heatmapLayer.weightedData = list } }
Objective-C
@implementation Heatmap { GMSMapView *_mapView; GMUHeatmapTileLayer *_heatmapLayer; } - (void)viewDidLoad { [super viewDidLoad]; _heatmapLayer = [[GMUHeatmapTileLayer alloc] init]; _heatmapLayer.map = _mapView; } // ... - (void) addHeatmap { // Get the data: latitude/longitude positions of police stations. NSURL *path = [NSBundle.mainBundle URLForResource:@"police_stations" withExtension:@"json"]; NSData *data = [NSData dataWithContentsOfURL:path]; NSArray *json = [NSJSONSerialization JSONObjectWithData:data options:0 error:nil]; NSMutableArray<GMUWeightedLatLng *> *list = [[NSMutableArray alloc] init]; [json enumerateObjectsUsingBlock:^(id _Nonnull obj, NSUInteger idx, BOOL * _Nonnull stop) { NSDictionary *item = (NSDictionary *)obj; CLLocationDegrees lat = [(NSNumber *) [item valueForKey:@"lat"] doubleValue]; CLLocationDegrees lng = [(NSNumber *) [item valueForKey:@"lng"] doubleValue]; GMUWeightedLatLng *coords = [[GMUWeightedLatLng alloc] initWithCoordinate:CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(lat, lng) intensity:1.0]; [list addObject:coords]; }]; // Add the latlngs to the heatmap layer. _heatmapLayer.weightedData = list; } @end
Untuk contoh ini, data disimpan dalam file JSON, police_stations.json.
Berikut adalah ekstrak dari file tersebut:
[
{"lat" : -37.1886, "lng" : 145.708 } ,
{"lat" : -37.8361, "lng" : 144.845 } ,
{"lat" : -38.4034, "lng" : 144.192 } ,
{"lat" : -38.7597, "lng" : 143.67 } ,
{"lat" : -36.9672, "lng" : 141.083 }
]
Menyesuaikan peta panas
Peta panas memiliki beberapa properti yang dapat disesuaikan. Anda dapat menetapkan opsi saat
membuat instance GMUHeatmapTileLayer pada awalnya, atau kapan saja dengan
menetapkan nilai baru untuk opsi tersebut.
Tersedia opsi-opsi berikut:
Radius: Ukuran blur Gaussian yang diterapkan pada peta panas, dinyatakan dalam piksel. Nilai default-nya adalah 20. Harus antara 10 dan 50. Gunakan
GMUHeatmapTileLayer.radiusuntuk menetapkan radius.Gradien: Serangkaian warna yang digunakan peta panas untuk menghasilkan peta warna, berkisar dari intensitas terendah hingga tertinggi.
GMUGradientdibuat menggunakan array integer yang berisi warna, dan array float yang menunjukkan titik awal untuk setiap warna, diberikan sebagai persentase intensitas maksimum, dan dinyatakan dalam pecahan antara 0 hingga 1. Anda hanya perlu menentukan satu warna untuk gradien satu warna, atau minimal dua warna untuk gradien multi-warna. Peta warna dibuat menggunakan interpolasi antar warna tersebut. Gradien default memiliki dua warna. ParametercolorMapSizemenentukan jumlah langkah dalam gradien. Angka yang lebih besar akan menghasilkan gradasi yang lebih halus, sedangkan angka yang lebih kecil akan memberikan transisi yang lebih tajam, mirip dengan grafik kontur. GunakanGMUHeatmapTileLayer.gradientuntuk menyetel gradien.Opasitas: Ini adalah opasitas seluruh lapisan peta panas, dengan rentang antara 0 sampai 1. Nilai defaultnya adalah 0,7. Gunakan
GMUHeatmapTileLayer.opacityuntuk menetapkan nilai keburaman.
Misalnya, buat Gradient:
Swift
let gradientColors: [UIColor] = [.green, .red] let gradientStartPoints: [NSNumber] = [0.2, 1.0] heatmapLayer.gradient = GMUGradient( colors: gradientColors, startPoints: gradientStartPoints, colorMapSize: 256 )
Objective-C
NSArray<UIColor *> *gradientColors = @[UIColor.greenColor, UIColor.redColor]; NSArray<NSNumber *> *gradientStartPoints = @[@0.2, @1.0]; _heatmapLayer.gradient = [[GMUGradient alloc] initWithColors:gradientColors startPoints:gradientStartPoints colorMapSize:256];
Untuk mengubah opasitas peta panas yang sudah ada:
Swift
heatmapLayer.opacity = 0.7
Objective-C
_heatmapLayer.opacity = 0.7;
Memperbarui opsi yang ada
Untuk memperbarui opsi yang telah ditetapkan, lakukan langkah-langkah berikut:
- Perbarui opsi ke nilai yang diinginkan.
- Hubungi
GMUHeatmapTileLayer.clearTileCache().
Mengubah set data
Untuk mengubah set data yang digunakan untuk membuat peta panas:
- Perbarui pengumpulan data Anda. Gunakan
GMUHeatmapTileLayer.weightedData, dengan meneruskan arrayGMUWeightedLatLng. - Hubungi
GMUHeatmapTileLayer.clearTileCache().
Menghapus peta panas
Untuk menghapus peta panas, panggil GMUHeatmapTileLayer.map, dengan meneruskan nil.
Swift
heatmapLayer.map = nil
Objective-C
_heatmapLayer.map = nil;
Melihat aplikasi demo
Untuk contoh penerapan peta panas lainnya, lihat
HeatmapViewController di aplikasi demo yang disertakan dengan library utilitas.
Panduan penyiapan menunjukkan cara menjalankan aplikasi demo.
