Nakładki na mapie są powiązane ze współrzędnymi geograficznymi, więc przesuwają się, gdy przeciągasz lub powiększasz mapę.
Wprowadzenie
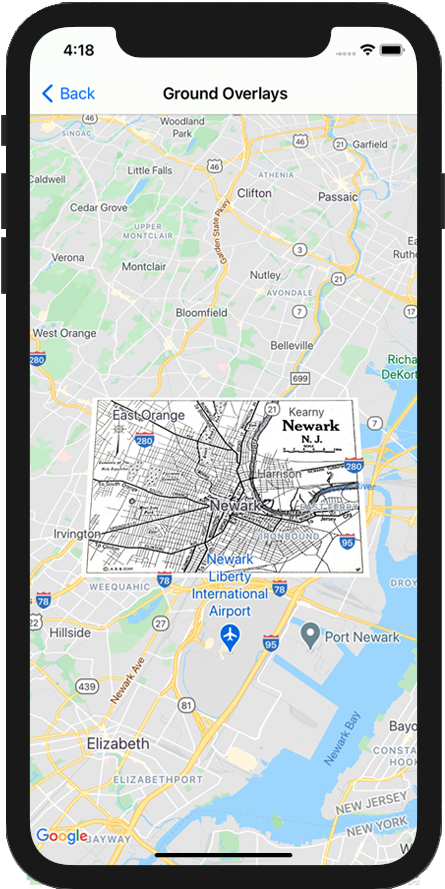
Nakładka na teren to obraz przymocowany do mapy. W przeciwieństwie do markerów nakładki na ziemię są zorientowane względem powierzchni Ziemi, a nie ekranu, więc obracanie, przechylanie lub powiększanie mapy spowoduje zmianę orientacji obrazu.
Aby dodać nakładkę na ziemię, utwórz obiekt GMSGroundOverlay, który definiuje zarówno ikonę, jak i granice. Jeśli nie określisz żadnego z tych parametrów, nakładka na ziemię nie będzie widoczna na mapie. Możesz opcjonalnie określić dodatkowe ustawienia, które wpłyną na pozycjonowanie obrazu na mapie.
Po zdefiniowaniu niezbędnych opcji ustaw właściwość map tego obiektu, aby dodać nakładkę.
Dodawanie nakładki
- Utwórz nowy obiekt
GMSGroundOverlay. - Ustaw właściwość
iconna instancjęUIImage. - Ustaw właściwość
boundsna instancjęGMSCoordinateBounds. Granice reprezentują południowo-zachodni i północno-wschodni róg obrazu. - W razie potrzeby ustaw opcjonalne właściwości, takie jak
bearingizoomLevel. - Ustaw właściwość
map– obraz pojawi się na mapie.
Poniższy przykład pokazuje, jak dodać nakładkę na ziemię do istniejącego obiektu GMSMapView.
Swift
let southWest = CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 40.712216, longitude: -74.22655) let northEast = CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 40.773941, longitude: -74.12544) let overlayBounds = GMSCoordinateBounds(coordinate: southWest, coordinate: northEast) // Image from http://www.lib.utexas.edu/maps/historical/newark_nj_1922.jpg let icon = UIImage(named: "newark_nj_1922") let overlay = GMSGroundOverlay(bounds: overlayBounds, icon: icon) overlay.bearing = 0 overlay.map = mapView
Objective-C
CLLocationCoordinate2D southWest = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(40.712216,-74.22655); CLLocationCoordinate2D northEast = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(40.773941,-74.12544); GMSCoordinateBounds *overlayBounds = [[GMSCoordinateBounds alloc] initWithCoordinate:southWest coordinate:northEast]; // Image from http://www.lib.utexas.edu/maps/historical/newark_nj_1922.jpg UIImage *icon = [UIImage imageNamed:@"newark_nj_1922"]; GMSGroundOverlay *overlay = [GMSGroundOverlay groundOverlayWithBounds:overlayBounds icon:icon]; overlay.bearing = 0; overlay.map = mapView;
Usuwanie nakładki
Możesz usunąć nakładkę na ziemię z mapy, ustawiając właściwość GMSGroundOverlay obiektu map na nil. Możesz też usunąć wszystkie nakładki (w tym nakładki na ziemię, które są obecnie na mapie), wywołując metodę GMSMapView clear.
Swift
mapView.clear()
Objective-C
[mapView clear];
Jeśli po dodaniu nakładki na mapę chcesz ją zmodyfikować, zachowaj obiekt GMSGroundOverlay. Możesz później zmodyfikować nakładkę na podłoże, wprowadzając zmiany w tym obiekcie.
Swift
let overlay = GMSGroundOverlay(bounds: overlayBounds, icon: icon) overlay.bearing = 0 overlay.map = mapView // ... overlay.isTappable = true
Objective-C
GMSGroundOverlay *overlay = [GMSGroundOverlay groundOverlayWithBounds:overlayBounds icon:icon]; overlay.bearing = 0; overlay.map = mapView; // ... overlay.tappable = YES;
Wydarzenia
Możesz nasłuchiwać zdarzeń, które występują na mapie, np. gdy użytkownik kliknie nakładkę. Aby nasłuchiwać zdarzeń, musisz zaimplementować protokół GMSMapViewDelegate. Zapoznaj się z przewodnikiem po zdarzeniach i listą metod na stronie GMSMapViewDelegate.
