Page Summary
-
Streetscape Geometry APIs provide the geometry of terrain, buildings, or other structures for use in AR content placement or occlusion.
-
Streetscape Geometry data is obtained through Google Street View imagery and requires the Geospatial API and Streetscape Geometry mode to be enabled.
-
You can obtain Streetscape Geometry data in an ARCore session using
Session.getAllTrackables()and filtering byStreetscapeGeometry.class. -
StreetscapeGeometrycontains information about the structure including its type, mesh data, pose, and quality level (LOD 1 or LOD 2). -
AR content can be attached to Streetscape Geometry by enabling Geospatial Depth and using a Depth hit-test or by using
Trackable.createAnchor()after a hit-test against the geometry.
The Streetscape Geometry APIs provide the geometry of terrain, buildings, or other structures in a scene. The geometry can be used for occlusion, rendering, or placing AR content via hit-test APIs. Streetscape Geometry data is obtained through Google Street View imagery.
Try the sample
The geospatial_java sample app demonstrates how to obtain and render Streetscape Geometries.
Set up the Geospatial API
To use Streetscape Geometry, you'll need to set up the Geospatial API in your project. Follow instructions on Enabling the Geospatial API to set up the Geospatial API.
Enable Streetscape Geometry
The Geospatial API obtains Streetscape Geometry data when the GeospatialMode is set to GeospatialMode.ENABLED and StreetscapeGeometryMode is set to StreetscapeGeometryMode.ENABLED.
Java
Config config = session.getConfig(); // Streetscape Geometry requires the Geospatial API to be enabled. config.setGeospatialMode(Config.GeospatialMode.ENABLED); // Enable Streetscape Geometry. config.setStreetscapeGeometryMode(Config.StreetscapeGeometryMode.ENABLED); session.configure(config);
Kotlin
session.configure( session.config.apply { // Streetscape Geometry requires the Geospatial API to be enabled. geospatialMode = Config.GeospatialMode.ENABLED // Enable Streetscape Geometry. streetscapeGeometryMode = Config.StreetscapeGeometryMode.ENABLED } )
Obtain Streetscape Geometry in an ARCore session
UseSession.getAllTrackables() and use StreetscapeGeometry.class to filter results.
Java
session.getAllTrackables(StreetscapeGeometry.class);
Kotlin
session.getAllTrackables(StreetscapeGeometry::class.java)
Understand StreetscapeGeometry
StreetscapeGeometry contains information about a building:
-
StreetscapeGeometry.getType()
Identifies the StreetscapeGeometry as either terrain or a building. -
StreetscapeGeometry.getMesh()
Obtain a polygonMeshthat corresponds to this terrain or building. -
StreetscapeGeometry.getMeshPose()
Describes the origin of the geometry. All points in theMeshshould be transformed byStreetscapeGeometry.getMeshPose(). -
StreetscapeGeometry.getQuality()
Provides the quality of the mesh data. Levels of detail are described in the CityGML 2.0 standard.
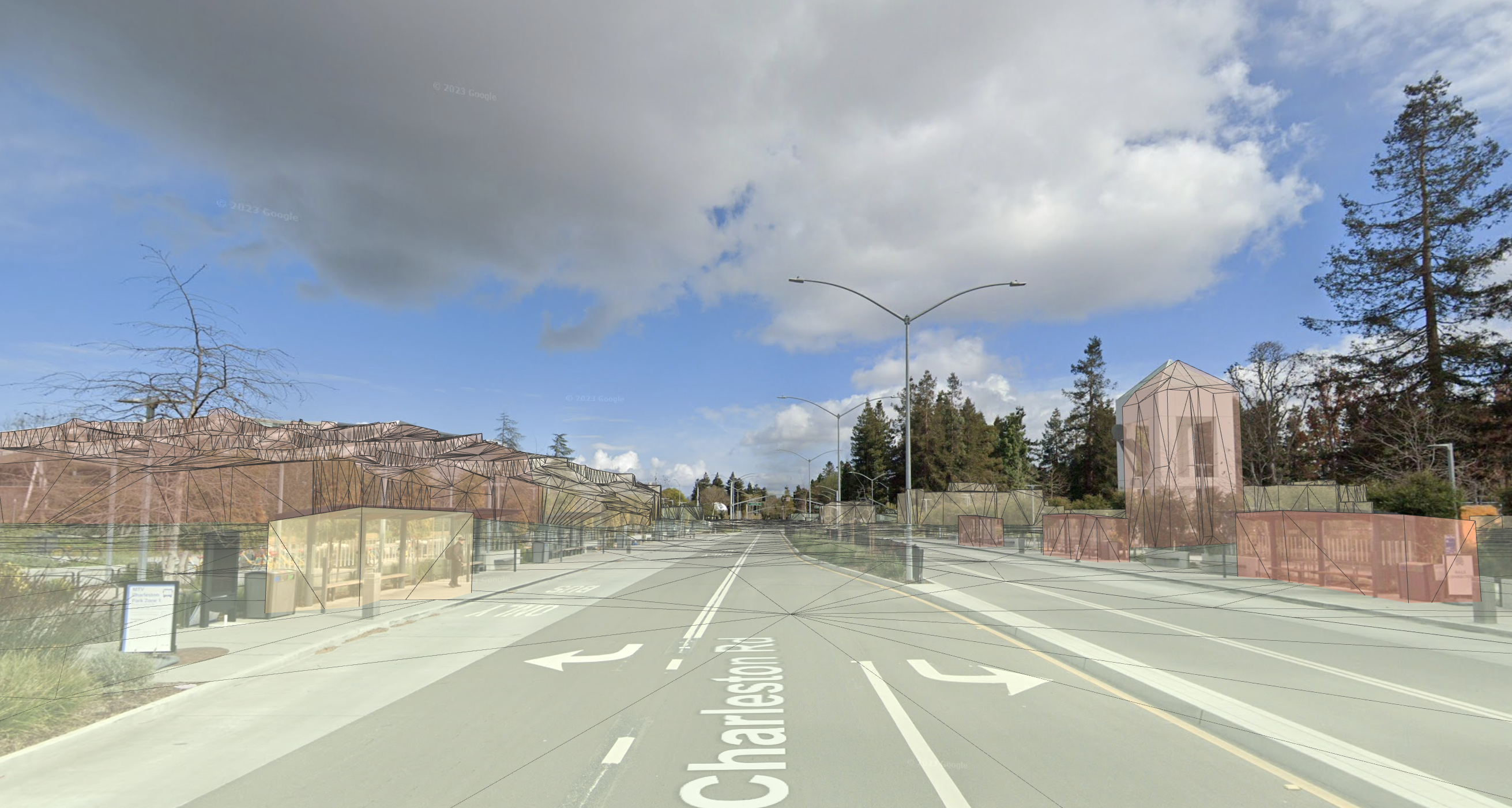
Building LOD 1
StreetscapeGeometry.Quality.BUILDING_LOD_1 consists of building footprints extruded upwards to a flat top. Building heights may be inaccurate.

Building LOD 2
StreetscapeGeometry.Quality.BUILDING_LOD_2 will have higher fidelity geometry. Mesh walls and roofs will more closely match the building's shape. Smaller features like chimneys or roof vents may still poke outside of the mesh.

Understand Mesh
Mesh is a polygon mesh representing a surface reconstruction of the Streetscape Geometry.
Each Mesh includes a vertex buffer and index buffer:
Mesh.getVertexListSize()
Retrieves the number of vertices in this mesh.Mesh.getVertexList()
Obtain the concatenated positions of mesh vertices, in coordinates relative toStreetscapeGeometry.getMeshPose().Mesh.getIndexListSize()
Retrieves the number of indices in this mesh.Mesh.getIndexList()
Obtain the indexes of vertices that make up a face.
Attach AR content to a StreetscapeGeometry
There are two ways to attach AR content to Streetscape Geometry:
- Enable Geospatial Depth and use a Depth hit-test. This is the recommended and easier method.
- Use
Trackable.createAnchor()to create an anchor at a given pose attached to aStreetscapeGeometry. This anchor will inherit its tracking state from the parentStreetscapeGeometry.
Perform a hit-test against StreetscapeGeometry
Frame.hitTest() can be used to hit-test against Streetscape Geometry. If intersections are found, HitResult contains pose information about the hit location as well as a reference to the StreetscapeGeometry which was hit. This Streetscape Geometry can be passed to Trackable.createAnchor() to create an anchor attached to it.
Java
for (HitResult hit : frame.hitTest(singleTapEvent)) { if (hit.getTrackable() instanceof StreetscapeGeometry) { Pose hitPose = hit.getHitPose(); hit.getTrackable().createAnchor(hitPose); } }
Kotlin
for (hit in frame.hitTest(singleTapEvent)) { if (hit.trackable is StreetscapeGeometry) { val hitPose = hit.hitPose hit.trackable.createAnchor(hitPose) } }
Enable Geospatial Depth
Geospatial Depth combines Streetscape Geometry with local sensor input to enhance depth data. When Geospatial Depth is enabled, the output depth and raw depth images are modified to include rasterized Streetscape Geometry in addition to locally observed depth. This may improve the accuracy of poses using Depth.
