W tym dokumencie opisano format webhooka służący do komunikacji między Actions on Google a usługą realizacji, która określa niestandardowy interfejs konwersacyjny.
Warto wiedzieć, w jaki sposób działania Actions on Google i realizacja zamówień komunikują się za pomocą formatów webhooka Actions on Google:
- Aby uczestniczyć w rozmowach w Actions on Google, realizacja wymaga webhooka, który może odpowiadać na żądania HTTP wysyłane przez Actions on Google.
- Gdy użytkownicy wywołają akcję, otrzyma ona
HTTP POSTz ładunkiem JSON opisującym żądanie użytkownika. - Z kolei Twoja realizacja odpowiada za odczytanie parametrów z ładunku żądania, wygenerowanie odpowiedniej odpowiedzi w formacie JSON i wysłanie tej odpowiedzi do Asystenta.
Typy żądań
Ta tabela zawiera podsumowanie typów żądań, które webhook może otrzymywać od Asystenta:
| Typ | Opis | Przykłady kodu JSON |
|---|---|---|
| Żądania wywołania | Wypowiedzi użytkownika, które inicjują rozmowę z Twoją realizacją lub wywołują działania z precyzyjnymi linkami (np. „Porozmawiaj z osobistym szefem kuchni, aby znaleźć przepisy na obiad”).
|
|
| Prośby o rozmowę | Wypowiedzi użytkowników w tej samej sesji po rozpoczęciu rozmowy z Twoją realizacją. W formacie webhooka rozmowy są to nieprzetworzone odpowiedzi tekstowe od użytkownika odpowiadające intencjom actions.intent.TEXT, których realizacja zażądała w poprzedniej turze. |
|
| Wyniki pomocnicze | Żądania wysłane przez Asystenta do Twojej realizacji, gdy webhook wysłał w poprzednim kroku rozmowy prośbę o intencję pomocniczą na potrzeby obsługi części rozmowy (na przykład actions.intent.OPTION i actions.intent.PERMISSION). |
Prośby o rozmowę i odpowiedzi
W typowym scenariuszu interakcji w Actions on Google użytkownicy wypowiadają wyrażenie wywołujące akcję. Aby dostarczyć odpowiedź, Actions on Google znajduje realizację odpowiadającą temu działaniu wywołanemu przez użytkownika i wysyła do niej żądanie.
Gdy usługa Actions on Google ustali, że realizacja odpowiada wywołaniu użytkownika, rozpocznie sesję rozmowy, wysyłając żądanie HTTP zawierające ładunek JSON z informacjami o żądaniu użytkownika do punktu końcowego realizacji realizacji. Realizacja analizuje żądanie i zwraca odpowiedź zawierającą ładunek JSON. Actions on Google konwertuje następnie ładunek na renderowane mowę i multimedialne dane wyjściowe dla użytkowników.
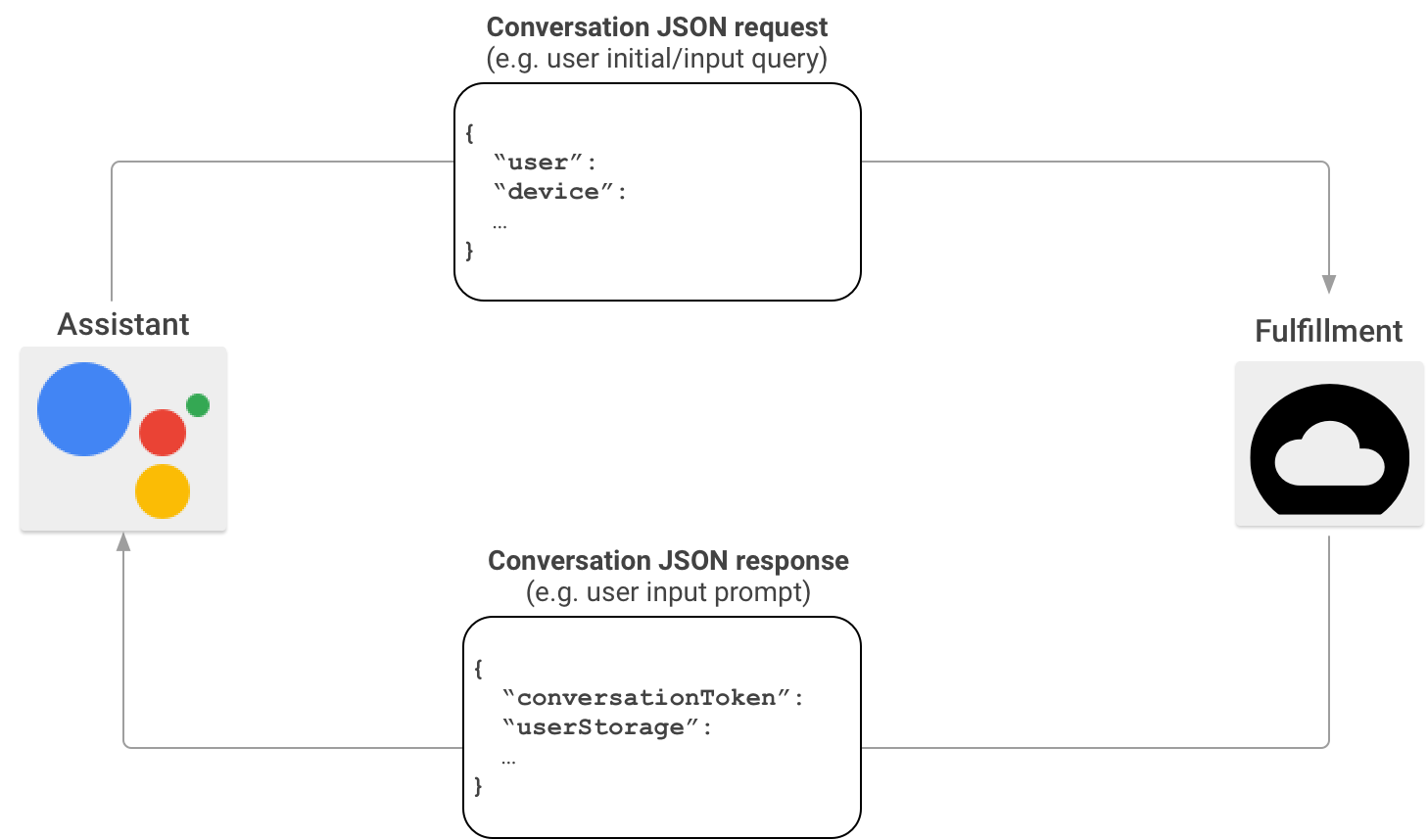
Więcej informacji o formacie ładunku JSON, gdy Actions on Google wywołuje Twoją realizację za pomocą pakietu SDK Actions, znajdziesz w sekcji Format webhooka rozmowy.
Żądania i odpowiedzi Dialogflow
Podczas tworzenia akcji możesz opcjonalnie użyć Dialogflow, aby uprościć zadanie tworzenia interfejsów rozmów. W tym scenariuszu Dialogflow działa jako serwer proxy między Actions on Google a Twoją realizacją. Zamiast wysyłać żądanie HTTP/JSON bezpośrednio do punktu końcowego realizacji, Actions on Google wysyła je do Dialogflow.
Dialogflow pakuje ładunek JSON zawarte w pierwotnym żądaniu do formatu webhooka Dialogflow i przekazuje wynikowe żądanie do realizacji Dialogflow.
I na odwrót – gdy realizacja wysyła odpowiedź do Dialogflow, ładunek JSON odpowiedzi musi być zgodny z formatem webhooka Dialogflow. Realizacja analizuje parametry z żądania JSON Dialogflow i generuje odpowiedź w formacie webhooka Dialogflow. Dialogflow konwertuje następnie odpowiedź z realizacji na wiadomość zrozumiałą dla Asystenta.
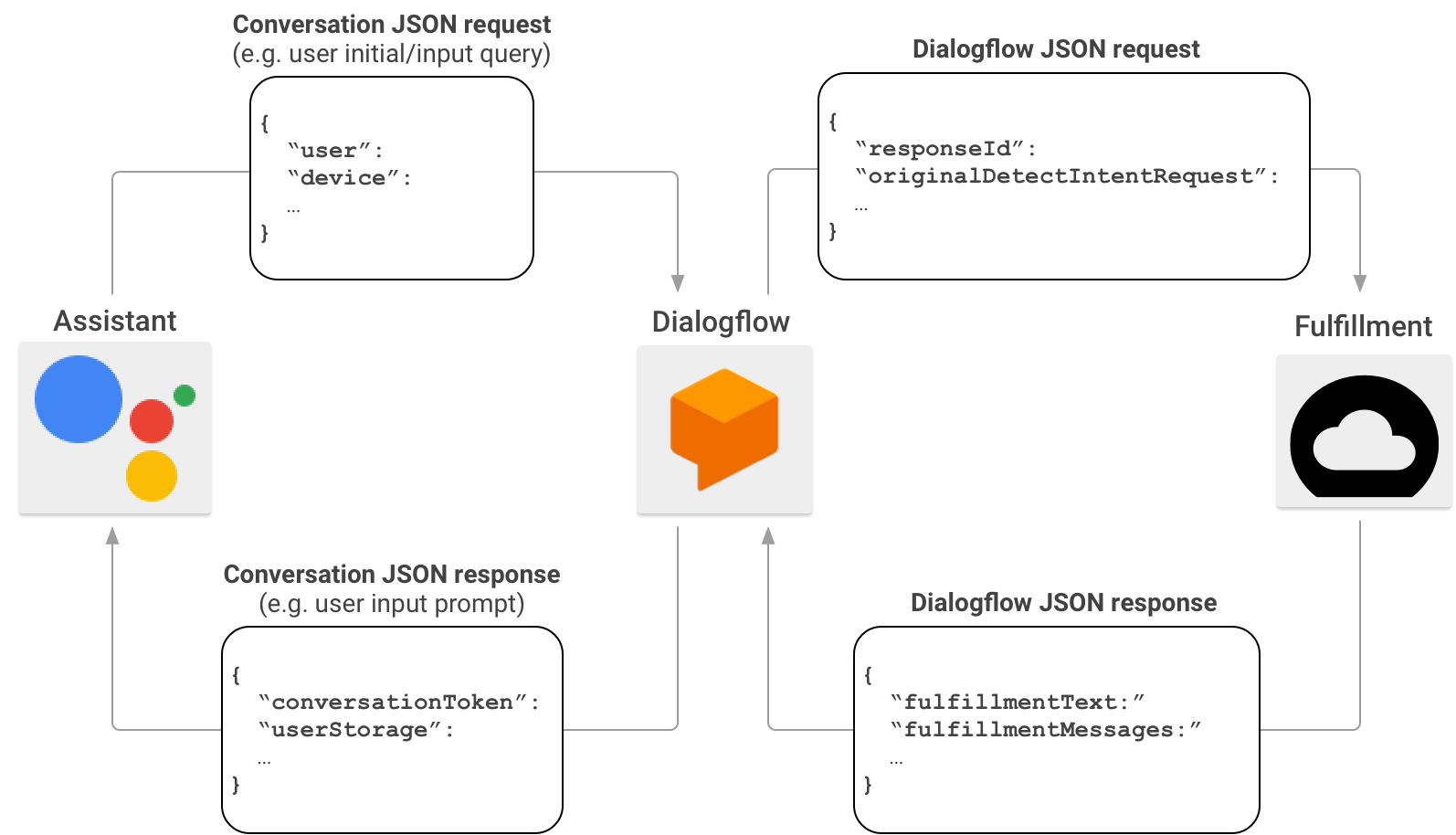
Więcej informacji o formacie ładunku JSON, gdy Actions on Google wywołuje Twoją realizację za pomocą Dialogflow, znajdziesz w artykule Format webhooka Dialogflow.