En este documento, se describe el formato de webhook para la comunicación entre Actions on Google y un servicio de entrega que define una interfaz de usuario conversacional personalizada.
Es importante comprender cómo Actions on Google y tu entrega se comunican a través de los formatos de webhook de Actions on Google:
- Para participar en conversaciones con Actions on Google, tu entrega implementa un webhook que puede responder a solicitudes HTTP de Actions on Google.
- Cuando los usuarios invocan tu acción, la entrega recibe una
HTTP POSTcon una carga útil de JSON que describe la solicitud del usuario. - A su vez, tu entrega es responsable de leer los parámetros de la carga útil de la solicitud, generar una respuesta adecuada con formato JSON y enviar una respuesta al Asistente con esta respuesta.
Tipos de solicitud
En esta tabla, se resumen los tipos de solicitudes que tu webhook puede recibir del Asistente:
| Tipo | Descripción | Ejemplos de JSON |
|---|---|---|
| Solicitudes de invocación | Declaraciones de usuario que inician la conversación con tu entrega o activan acciones de vínculos directos (por ejemplo, "Hablar con Personal Chef para buscar recetas para la cena").
|
|
| Solicitudes de conversación | Declaraciones de usuarios en la misma sesión una vez que haya comenzado la conversación con tu entrega. En el formato de webhook de conversación, estas son las respuestas de texto sin procesar del usuario que corresponden a los intents actions.intent.TEXT que tu entrega solicitó en el turno anterior. |
|
| Resultados de ayuda | Solicitudes enviadas por Asistente a tu entrega cuando el webhook solicitó un intent auxiliar en el turno anterior de la conversación para controlar partes de ella (por ejemplo, actions.intent.OPTION y actions.intent.PERMISSION). |
Solicitudes y respuestas de conversación
En una situación típica de interacción de Actions on Google, los usuarios pronuncian una frase para invocar una acción. Para proporcionar una respuesta, Actions on Google encuentra la entrega que coincide con la acción que invocó el usuario y envía la solicitud allí.
Una vez que Actions on Google establece que tu entrega es una coincidencia adecuada para la invocación del usuario, inicia una sesión de conversación con el envío de una solicitud HTTP que contiene una carga útil de JSON con la información de la solicitud del usuario a tu extremo de entrega. Tu entrega analiza la solicitud y muestra una respuesta que contiene una carga útil de JSON. Luego, Actions on Google convierte la carga útil en salidas multimedia y de voz renderizadas para los usuarios.
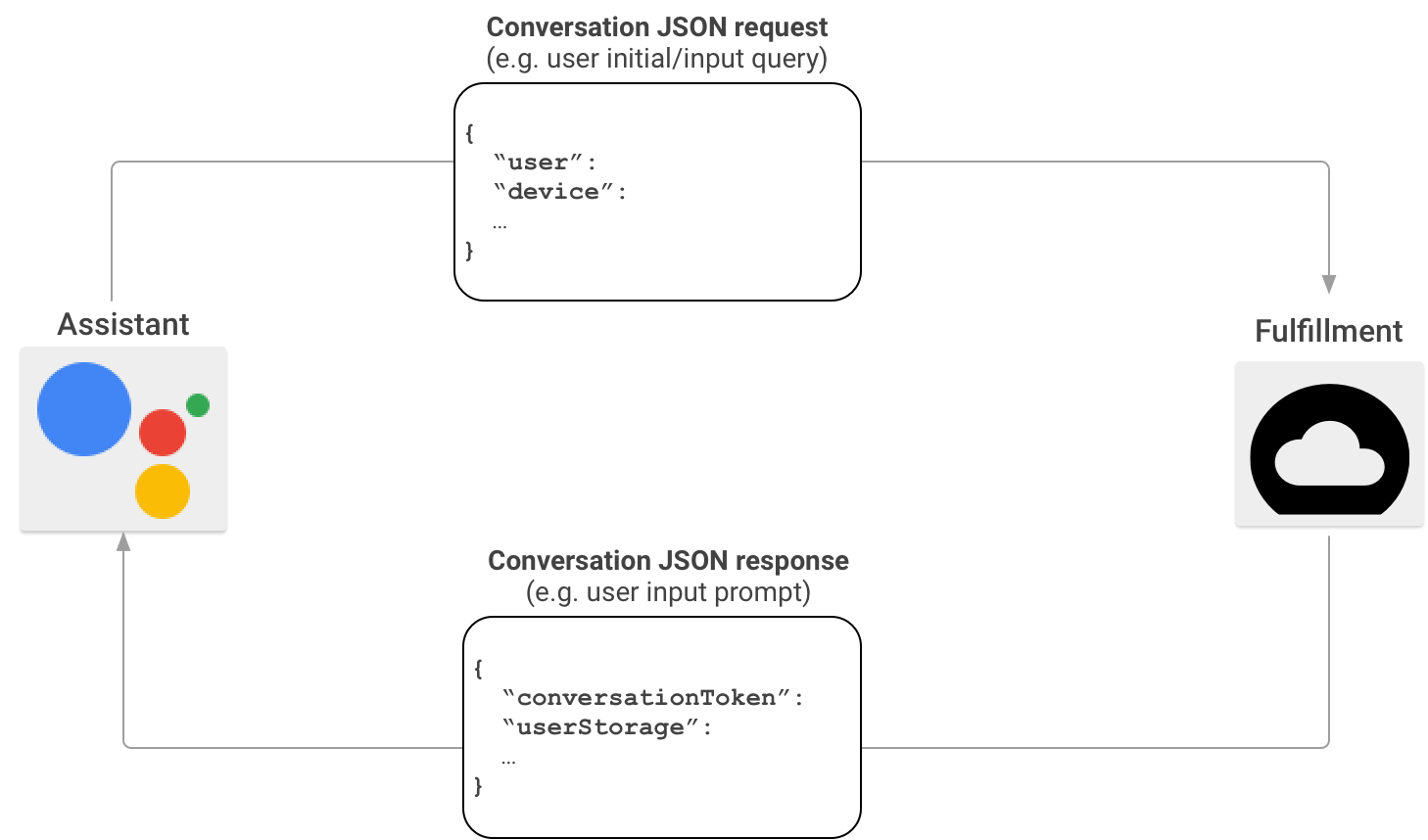
Para obtener más información sobre el formato de la carga útil de JSON cuando Actions on Google invoca tu entrega a través del SDK de Actions, consulta Formato de webhook de conversación.
Solicitudes y respuestas de Dialogflow
Cuando creas acciones, tienes la opción de usar Dialogflow para simplificar la tarea de compilar interfaces conversacionales. En esta situación, Dialogflow actúa como un proxy entre Actions on Google y tu entrega. En lugar de enviar la solicitud HTTP/JSON directamente a tu extremo de entrega, Actions on Google la envía a Dialogflow.
Dialogflow une la carga útil JSON contenida en la solicitud original al formato de webhook de Dialogflow y reenvía la solicitud resultante a tu entrega de Dialogflow.
Por el contrario, cuando tu entrega envía una respuesta a Dialogflow, la carga útil JSON de la respuesta debe cumplir con el formato del webhook de Dialogflow. Tu entrega analiza los parámetros de la solicitud JSON de Dialogflow y genera una respuesta en el formato de webhook de Dialogflow. Luego, Dialogflow convierte la respuesta de tu entrega en un mensaje de respuesta que el Asistente comprende.
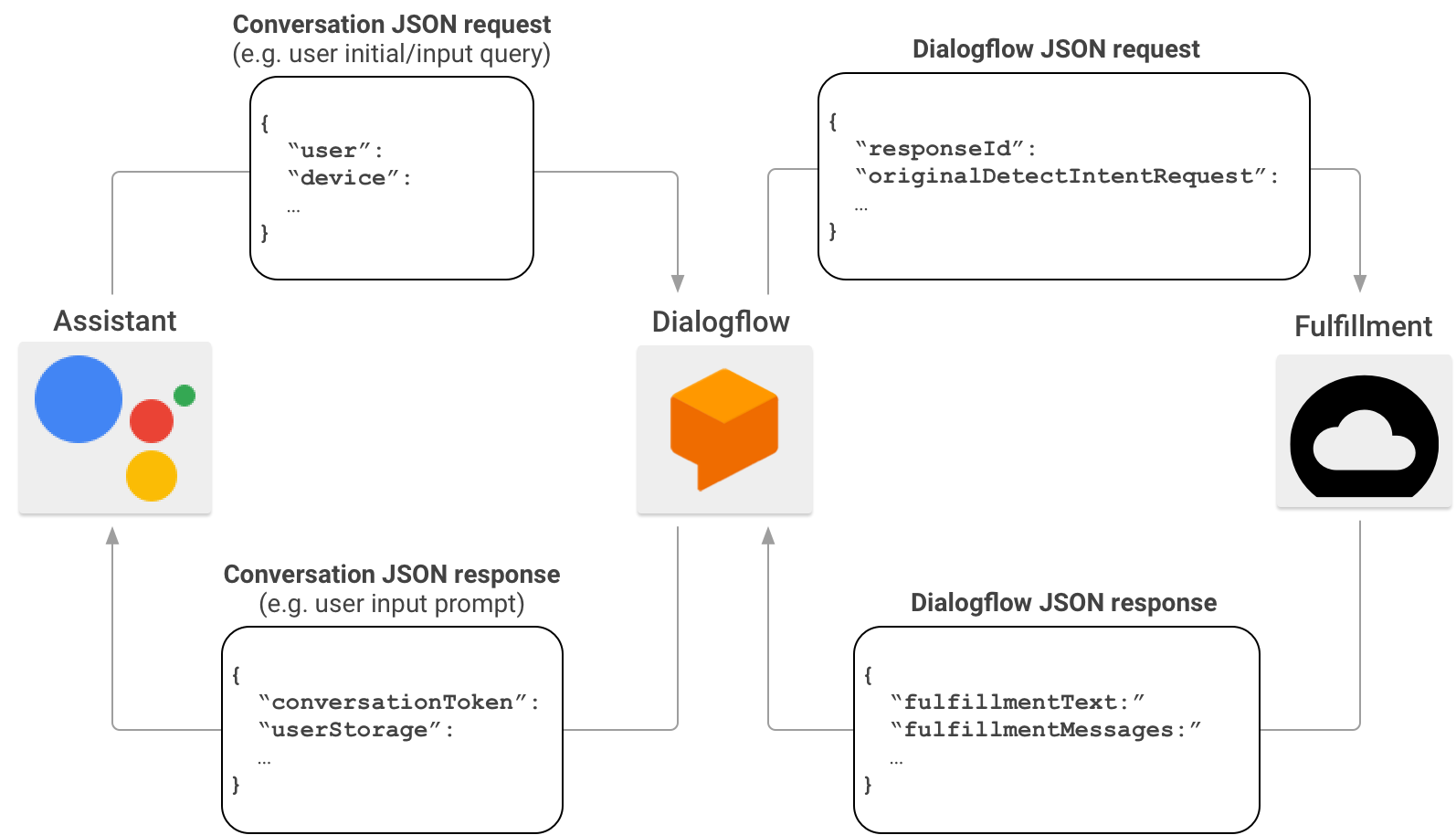
Para obtener más información sobre el formato de la carga útil de JSON cuando Actions on Google invoca tu entrega a través de Dialogflow, consulta Formato de webhook de Dialogflow.