Tài liệu này mô tả định dạng webhook để giao tiếp giữa Actions on Google và dịch vụ thực hiện đơn hàng giúp xác định giao diện người dùng trò chuyện tuỳ chỉnh.
Bạn cần phải hiểu cách Actions on Google và phương thức thực hiện của bạn giao tiếp thông qua các định dạng webhook của Actions on Google:
- Để tham gia vào các cuộc trò chuyện bằng Actions on Google, phương thức thực hiện của bạn sẽ triển khai một webhook có thể phản hồi các yêu cầu HTTP từ Actions on Google.
- Khi người dùng gọi Hành động của bạn, phương thức thực hiện của bạn sẽ nhận được một
HTTP POSTcó tải trọng JSON mô tả yêu cầu của người dùng. - Đổi lại, phương thức thực hiện của bạn chịu trách nhiệm đọc các tham số từ tải trọng yêu cầu, tạo phản hồi thích hợp ở định dạng JSON và gửi phản hồi này cho Trợ lý.
Loại yêu cầu
Bảng này tóm tắt các loại yêu cầu mà webhook của bạn có thể nhận được từ Trợ lý:
| Loại | Nội dung mô tả | Ví dụ về JSON |
|---|---|---|
| Yêu cầu gọi | Câu nói của người dùng bắt đầu cuộc trò chuyện với phương thức thực hiện của bạn hoặc kích hoạt Hành động liên kết sâu (ví dụ: "Trò chuyện với Đầu bếp cá nhân để tìm công thức nấu bữa tối").
|
|
| Yêu cầu trò chuyện | Các lệnh của người dùng trong cùng một phiên hoạt động sau khi cuộc trò chuyện với phương thức thực hiện của bạn bắt đầu. Ở định dạng webhook đối với cuộc trò chuyện, đây là các phản hồi dạng văn bản thô của người dùng tương ứng với ý định actions.intent.TEXT mà phương thức thực hiện của bạn đã yêu cầu ở lượt trước. |
|
| Kết quả của trình trợ giúp | Các yêu cầu do Trợ lý gửi tới phương thức thực hiện của bạn khi webhook của bạn đã
yêu cầu một ý định trợ giúp
trong lượt trước đó của cuộc trò chuyện để xử lý các phần của
cuộc trò chuyện (ví dụ: actions.intent.OPTION và
actions.intent.PERMISSION). |
Yêu cầu và phản hồi về cuộc trò chuyện
Trong một tình huống tương tác thông thường trên Actions on Google, người dùng sẽ nói một cụm từ để gọi ra một Hành động. Để cung cấp phản hồi, Actions on Google sẽ tìm phương thức thực hiện khớp với Hành động do người dùng gọi và gửi yêu cầu tới đó.
Sau khi Actions on Google xác minh rằng phương thức thực hiện của bạn phù hợp với lệnh gọi của người dùng, hành động đó sẽ bắt đầu phiên trò chuyện bằng cách gửi một yêu cầu HTTP chứa trọng tải JSON chứa thông tin yêu cầu của người dùng đến điểm cuối của phương thức thực hiện. Phương thức thực hiện của bạn sẽ phân tích cú pháp yêu cầu và trả về một phản hồi chứa tải trọng JSON. Sau đó, Actions on Google sẽ chuyển đổi tải trọng thành giọng nói và đầu ra đa phương tiện được kết xuất cho người dùng.
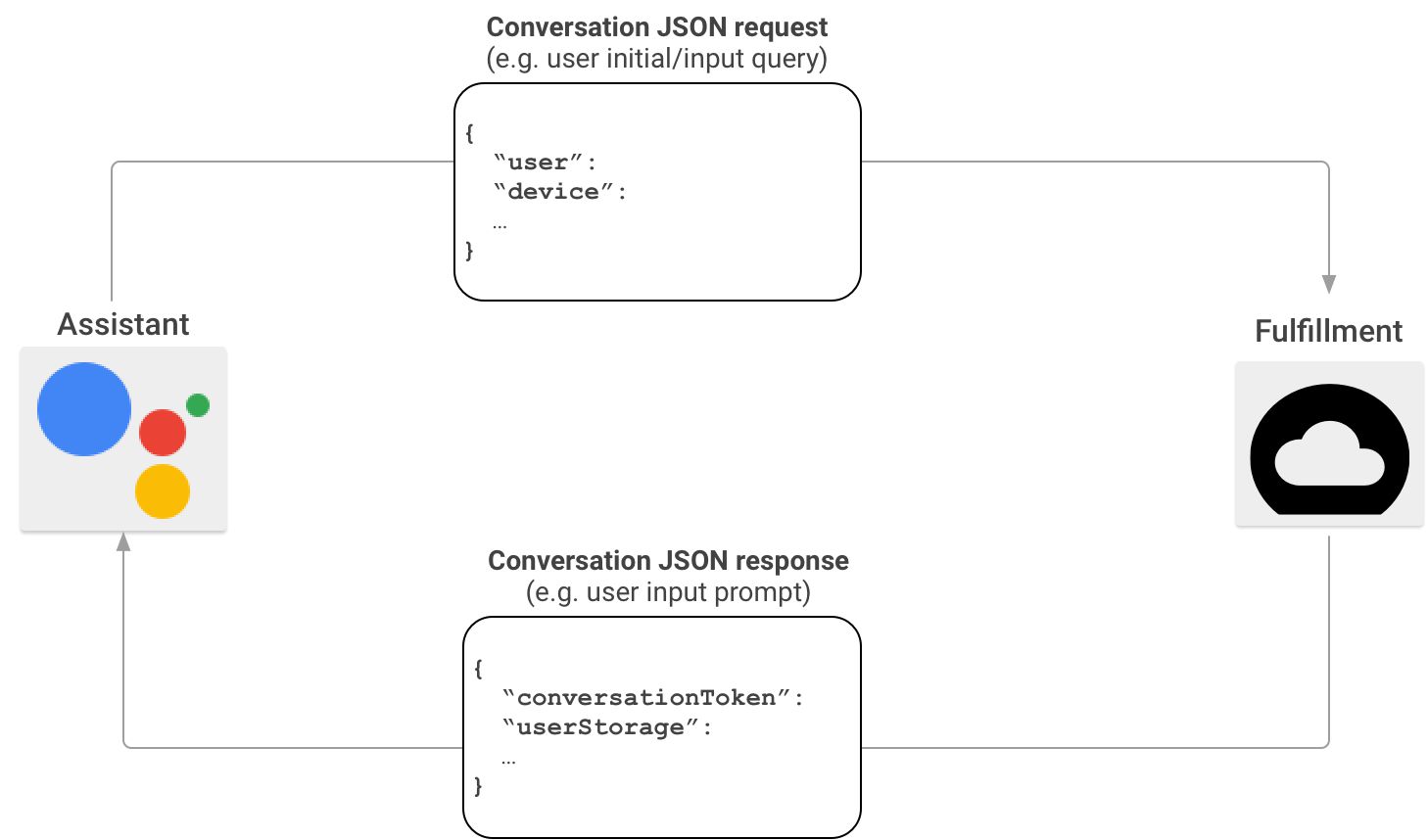
Để tìm hiểu thêm về định dạng của tải trọng JSON khi Actions on Google gọi phương thức thực hiện của bạn thông qua SDK Actions, hãy xem phần Định dạng webhook trò chuyện.
Yêu cầu và phản hồi Dialogflow
Khi tạo Hành động, bạn có thể tuỳ ý sử dụng Dialogflow để đơn giản hoá nhiệm vụ tạo giao diện trò chuyện. Trong trường hợp này, Dialogflow hoạt động như một proxy giữa Actions on Google và phương thức thực hiện của bạn. Thay vì trực tiếp gửi yêu cầu HTTP/JSON đến điểm cuối của phương thức thực hiện, Actions on Google sẽ gửi yêu cầu đó đếnDialogflow.
Dialogflow gói tải trọng JSON có trong yêu cầu ban đầu thành định dạng webhookDialogflow và chuyển tiếp yêu cầu nhận được đến phương thức thực hiện Dialogflow của bạn.
Ngược lại, khi phương thức thực hiện của bạn gửi phản hồi cho Dialogflow, tải trọng JSON của phản hồi phải tuân thủ định dạng webhook của Dialogflow. Phương thức thực hiện của bạn sẽ phân tích cú pháp các tham số trong yêu cầu JSON cho Dialogflow và tạo một phản hồi ở định dạng webhook của Dialogflow. Sau đó, Dialogflow chuyển đổi phản hồi từ phương thức thực hiện của bạn thành tin nhắn phản hồi mà Trợ lý hiểu được.
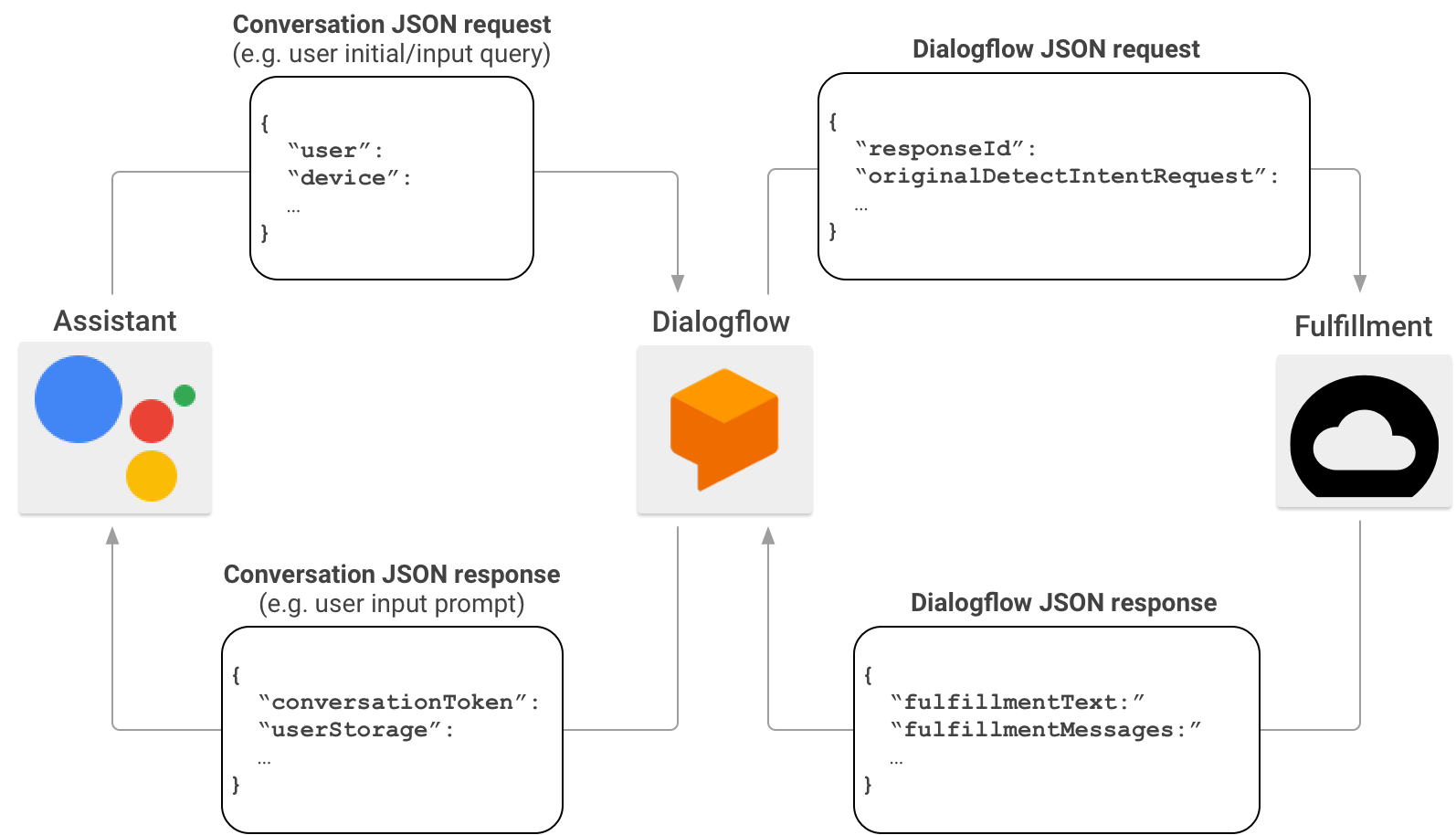
Để tìm hiểu thêm về định dạng của tải trọng JSON khi Actions on Google gọi phương thức thực hiện của bạn thông qua Dialogflow, hãy xem định dạng webhook củaDialogflow.