Neste documento, descrevemos o formato do webhook para a comunicação entre o Actions on Google e um serviço de fulfillment que define uma interface do usuário conversacional personalizada.
É importante entender como o Actions on Google e o fulfillment se comunicam pelos formatos de webhook da Actions on Google:
- Para participar de conversas com o Actions on Google, o fulfillment implementa um webhook que pode responder a solicitações HTTP do Actions on Google.
- Quando os usuários invocam sua ação, seu fulfillment recebe um
HTTP POSTcom um payload JSON que descreve a solicitação do usuário. - O fulfillment, por sua vez, é responsável por ler os parâmetros do payload da solicitação, gerar uma resposta JSON apropriada e enviar uma resposta ao Google Assistente com essa resposta.
Tipos de solicitação
Esta tabela resume os tipos de solicitações que o webhook pode receber do Assistente:
| Tipo | Descrição | Exemplos de JSON |
|---|---|---|
| Solicitações de invocação | Enunciados do usuário que iniciam a conversa com o fulfillment ou
acionam ações de link direto (por exemplo, "Talk to Personal Chef to find
personal Chef to find
jantar receitas").
|
|
| Solicitações de conversa | Enunciados por usuários na mesma sessão assim que a conversa com o
fulfillment começou. No formato de webhook de conversa, essas são as
respostas de texto bruta do usuário correspondentes às intents actions.intent.TEXT
solicitadas pelo fulfillment na conversão anterior. |
|
| Resultados de ajuda | Solicitações enviadas pelo Assistente ao fulfillment quando o webhook solicita uma intent de auxiliar na conversão anterior para processar partes da conversa (por exemplo, actions.intent.OPTION e actions.intent.PERMISSION). |
Solicitações e respostas de conversa
Em um cenário típico de interação no Actions on Google, os usuários enunciam uma frase para invocar uma ação. Para fornecer uma resposta, o Actions on Google encontra o fulfillment que corresponde à ação invocada pelo usuário, depois envia a solicitação para ele.
Depois que o Actions on Google estabelece que seu fulfillment é uma correspondência adequada para a invocação do usuário, ele inicia uma sessão de conversa enviando uma solicitação HTTP que contém um payload JSON com as informações da solicitação do usuário para o endpoint de fulfillment. O fulfillment analisa a solicitação e retorna uma resposta que contém um payload JSON. O Actions on Google converte o payload em voz renderizada e saída multimídia para os usuários.
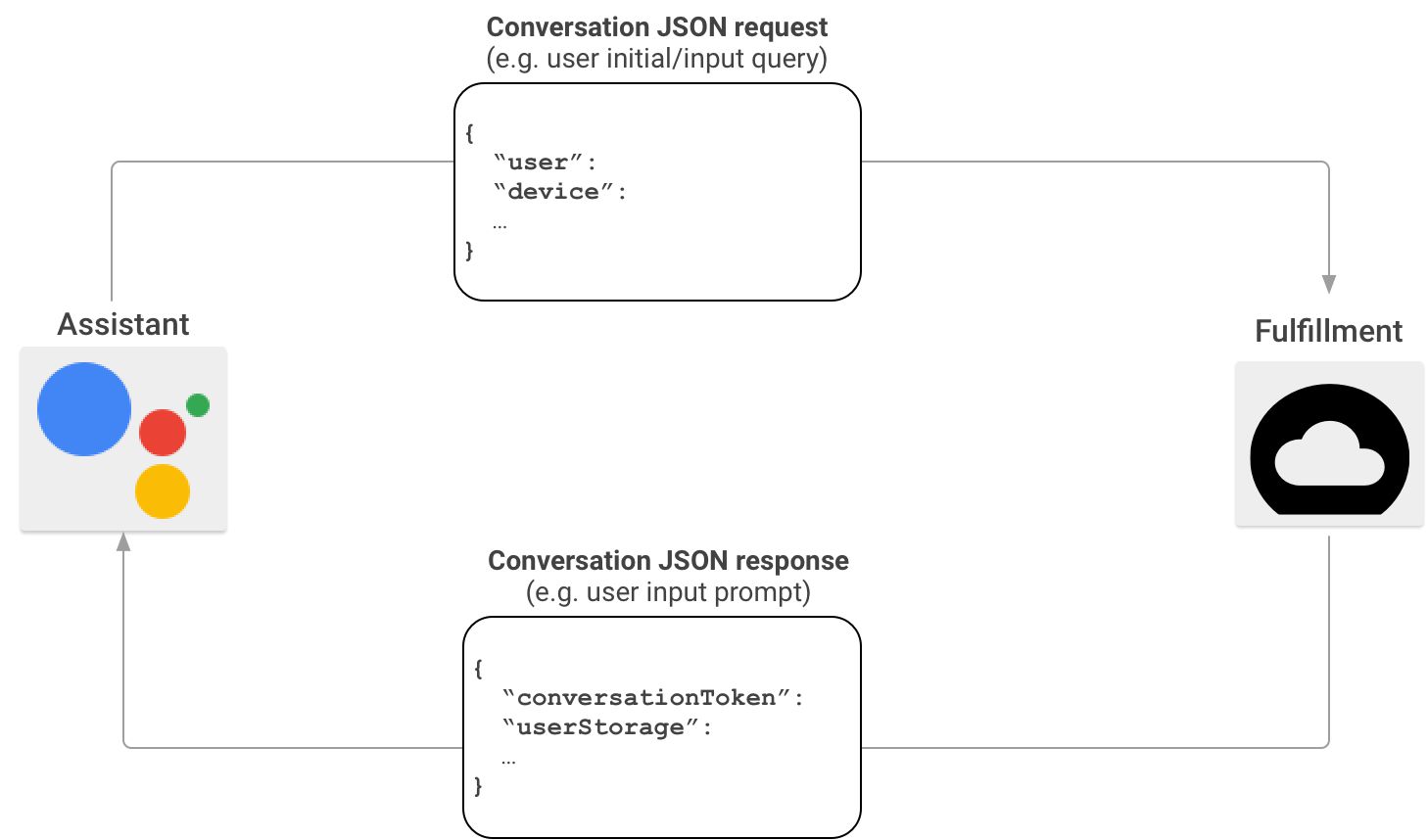
Para saber mais sobre o formato do payload JSON quando o Actions on Google invocar o fulfillment usando o SDK do Actions, consulte Formato do webhook da conversa.
Solicitações e respostas do Dialogflow
Ao criar ações, é possível usar o Dialogflow para simplificar a tarefa de criar interfaces de conversa. Nesse cenário, o Dialogflow atua como um proxy entre o Actions on Google e o fulfillment. Em vez de enviar a solicitação HTTP/JSON diretamente para o endpoint de fulfillment, o Actions on Google a envia para o Dialogflow.
O Dialogflow encapsula o payload JSON da solicitação original no formato de webhook do Dialogflow e encaminha a solicitação resultante para o fulfillment do Dialogflow.
Por outro lado, quando o fulfillment envia uma resposta ao Dialogflow, o payload JSON da resposta precisa estar em conformidade com o formato do webhook do Dialogflow. O fulfillment analisa os parâmetros da solicitação JSON do Dialogflow e gera uma resposta no formato do webhook do Dialogflow. O Dialogflow converte a resposta do fulfillment em uma mensagem de resposta que o Google Assistente entende.
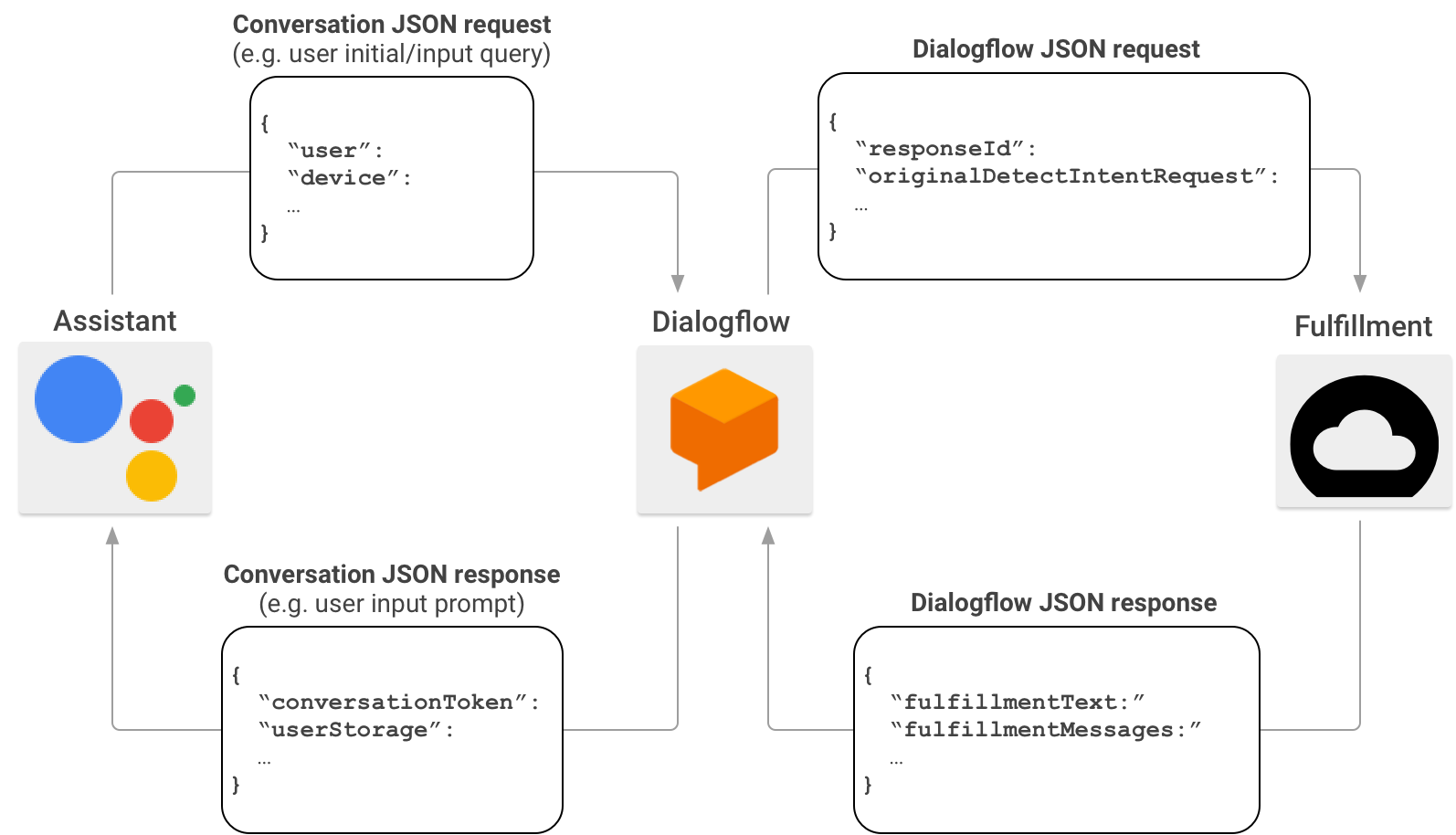
Para saber mais sobre o formato do payload JSON quando o Actions on Google invoca seu fulfillment por meio do Dialogflow, consulte Formato do webhook do Dialogflow.