Questo documento descrive il formato webhook per la comunicazione tra Actions on Google e un servizio di fulfillment che definisce un'interfaccia utente conversazionale personalizzata.
È importante capire in che modo Actions on Google e il tuo fulfillment comunicano tramite i formati webhook Actions on Google:
- Per partecipare alle conversazioni con Actions on Google, il tuo fulfillment implementa un webhook in grado di rispondere alle richieste HTTP da Actions on Google.
- Quando gli utenti richiamano l'Azione, il fulfillment riceve un elemento
HTTP POSTcon un payload JSON che descrive la richiesta dell'utente. - A sua volta, il tuo fulfillment è responsabile della lettura dei parametri dal payload della richiesta, della generazione di una risposta in formato JSON appropriata e dell'invio di una risposta all'assistente con questa risposta.
Tipi di richiesta
Questa tabella riassume i tipi di richieste che il webhook potrebbe ricevere dall'assistente:
| Tipo | Descrizione | Esempi JSON |
|---|---|---|
| Richieste di chiamata | Espressioni dell'utente che avviano la conversazione con il fulfillment o attivano azioni sul link diretto (ad esempio "Parla con Personal Chef per trovare ricette per la cena").
|
|
| Richieste di conversazione | Espressioni degli utenti nella stessa sessione dopo l'inizio della conversazione con il fulfillment. Nel formato webhook di conversazione, queste sono le
risposte di testo non elaborate dell'utente corrispondenti agli intent actions.intent.TEXT
richiesti dal fulfillment nel turno precedente. |
|
| Risultati Helper | Richieste inviate dall'assistente al fulfillment quando il webhook ha richiesto un intent help nel passaggio precedente della conversazione per gestire parti della conversazione (ad esempio, actions.intent.OPTION e actions.intent.PERMISSION). |
Richieste di conversazione e risposte
In uno scenario di interazione tipico di Actions on Google, gli utenti pronunciano una frase per richiamare un'azione. Per fornire una risposta, Actions on Google trova il fulfillment che corrisponde all'azione richiamata dall'utente e invia la richiesta lì.
Dopo che Actions on Google ha stabilito che il tuo fulfillment è una corrispondenza adatta per la chiamata dell'utente, avvia una sessione di conversazione inviando una richiesta HTTP che contiene un payload JSON con le informazioni della richiesta dell'utente all'endpoint di fulfillment. Il fulfillment analizza la richiesta e restituisce una risposta contenente un payload JSON. Actions on Google converte il payload in output vocale e multimediale sottoposto a rendering per gli utenti.
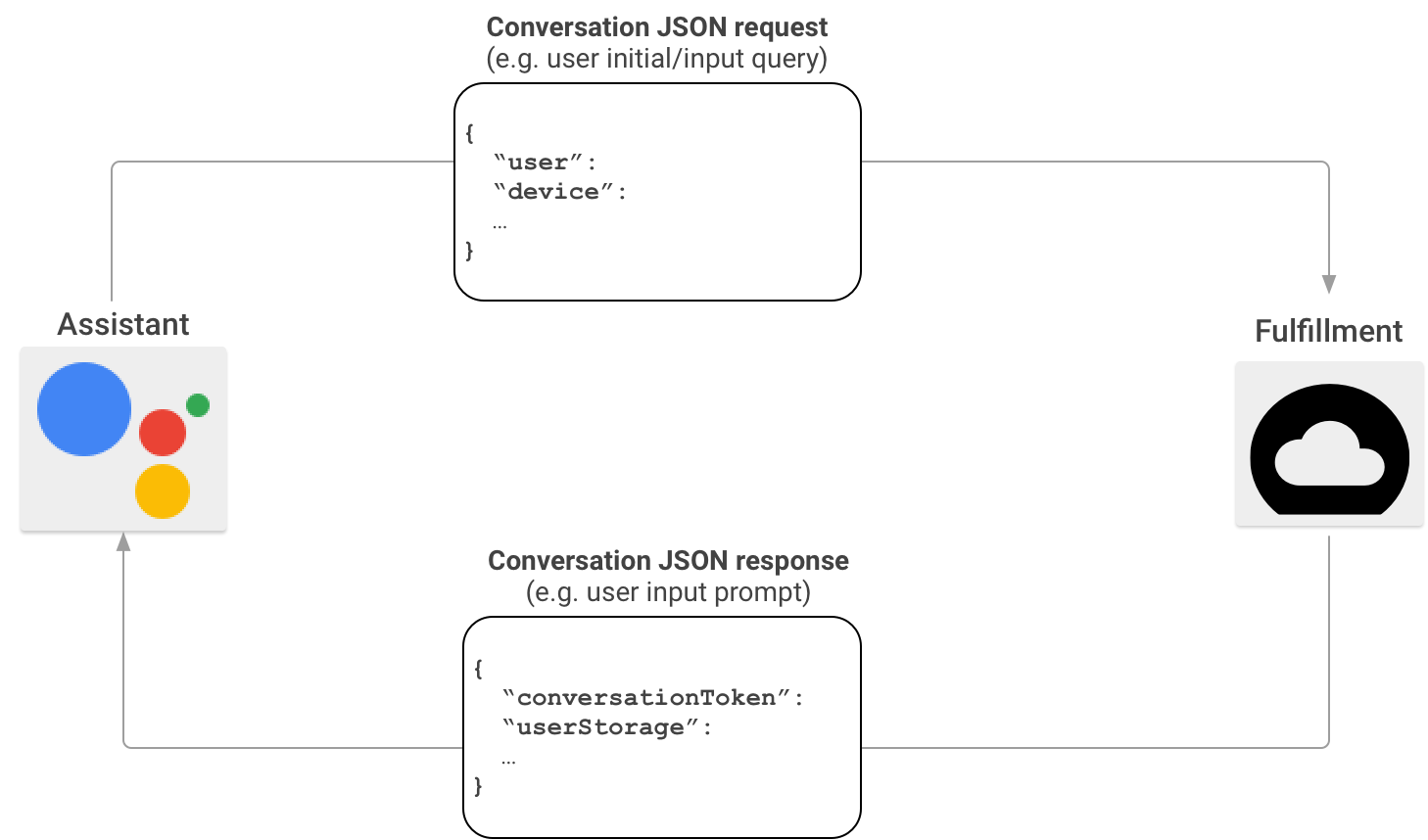
Per scoprire di più sul formato del payload JSON quando Actions on Google richiama il tuo fulfillment tramite l'SDK Actions, consulta Formato webhook di conversazione.
Richieste e risposte Dialogflow
Quando crei azioni, puoi facoltativamente utilizzare Dialogflow per semplificare l'attività di creazione delle interfacce di conversazione. In questo scenario, Dialogflow funge da proxy tra Actions on Google e il tuo fulfillment. Anziché inviare la richiesta HTTP/JSON direttamente al tuo endpoint di fulfillment, Actions on Google la invia a Dialogflow.
Dialogflow aggrega il payload JSON contenuto nella richiesta originale nel formato webhook di Dialogflow e inoltra la richiesta risultante al fulfillment Dialogflow.
Al contrario, quando il fulfillment invia una risposta a Dialogflow, il payload JSON della risposta deve essere conforme al formato webhook di Dialogflow. Il fulfillment analizza i parametri della richiesta JSON Dialogflow e genera una risposta nel formato webhook Dialogflow. Dialogflow converte quindi la risposta dal fulfillment in un messaggio di risposta comprensibile dall'assistente.
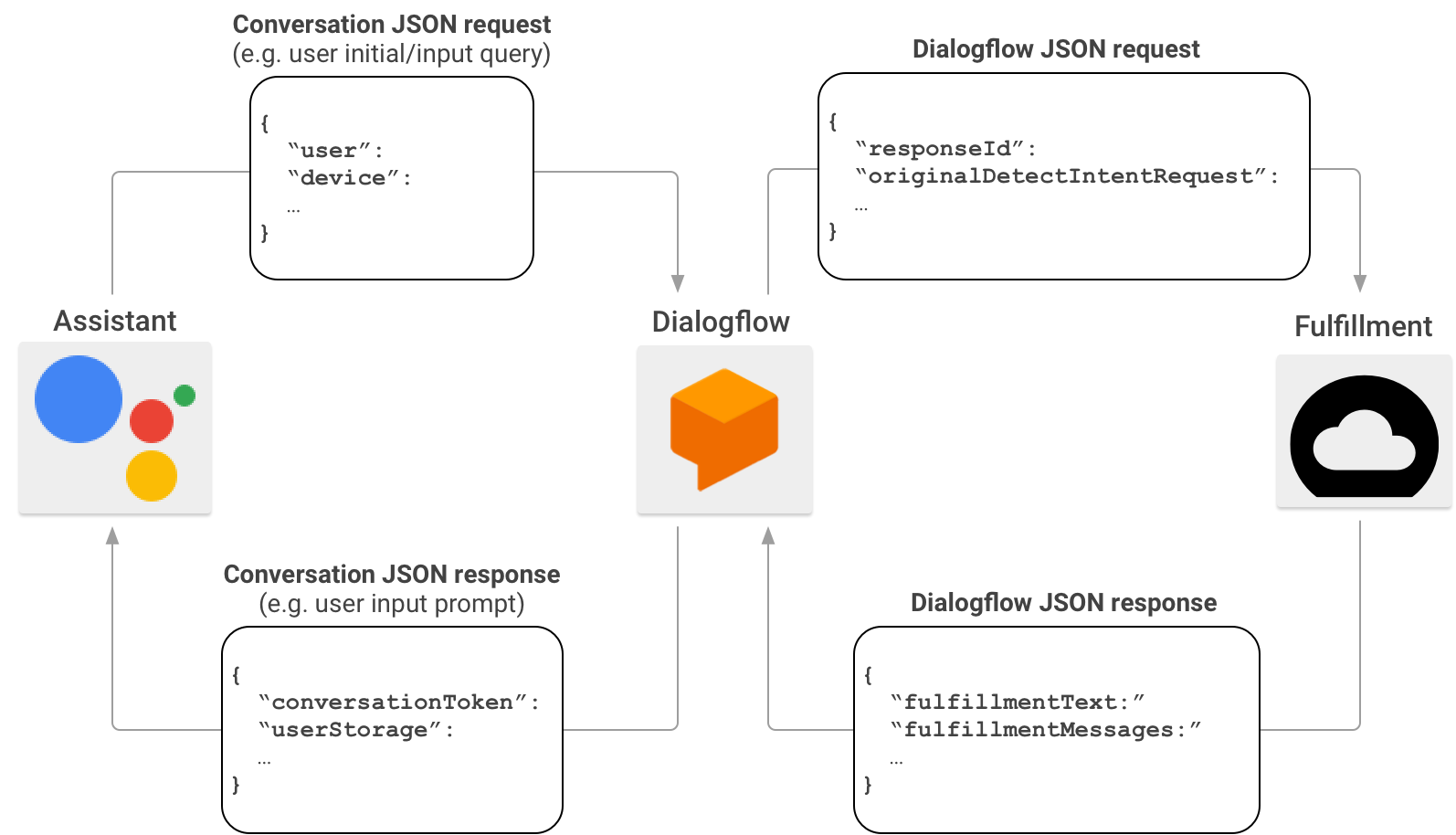
Per scoprire di più sul formato del payload JSON quando Actions on Google richiama il tuo fulfillment tramite Dialogflow, consulta Formato webhook di Dialogflow.