این آموزش به شما نشان میدهد که چگونه یک نقشه گوگل را به برنامه اندروید خود اضافه کنید و از چندخطیها و چندضلعیها برای نمایش مسیرها و مناطق روی نقشه استفاده کنید.
برای ساخت یک برنامه اندروید با استفاده از Maps SDK برای اندروید، آموزش را دنبال کنید. محیط توسعه پیشنهادی ، اندروید استودیو است.
کد را دریافت کنید
مخزن نمونههای Google Maps Android API v2 را از GitHub کپی یا دانلود کنید .
نسخه جاوای اکتیویتی را مشاهده کنید:
// Copyright 2020 Google LLC // // Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); // you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. // You may obtain a copy of the License at // // http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 // // Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software // distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, // WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. // See the License for the specific language governing permissions and // limitations under the License. package com.example.polygons; import android.os.Bundle; import android.widget.Toast; import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import com.google.android.gms.maps.CameraUpdateFactory; import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap; import com.google.android.gms.maps.OnMapReadyCallback; import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.BitmapDescriptorFactory; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.CustomCap; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Dash; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Dot; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Gap; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.JointType; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.LatLng; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.PatternItem; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Polygon; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.PolygonOptions; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Polyline; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.PolylineOptions; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.RoundCap; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; /** * An activity that displays a Google map with polylines to represent paths or routes, * and polygons to represent areas. */ public class PolyActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements OnMapReadyCallback, GoogleMap.OnPolylineClickListener, GoogleMap.OnPolygonClickListener { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps); // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. SupportMapFragment mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager() .findFragmentById(R.id.map); mapFragment.getMapAsync(this); } /** * Manipulates the map when it's available. * The API invokes this callback when the map is ready to be used. * This is where we can add markers or lines, add listeners or move the camera. * In this tutorial, we add polylines and polygons to represent routes and areas on the map. */ @Override public void onMapReady(GoogleMap googleMap) { // Add polylines to the map. // Polylines are useful to show a route or some other connection between points. Polyline polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(new PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), new LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), new LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), new LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), new LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), new LatLng(-32.491, 147.309))); // Store a data object with the polyline, used here to indicate an arbitrary type. polyline1.setTag("A"); // Style the polyline. stylePolyline(polyline1); Polyline polyline2 = googleMap.addPolyline(new PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-29.501, 119.700), new LatLng(-27.456, 119.672), new LatLng(-25.971, 124.187), new LatLng(-28.081, 126.555), new LatLng(-28.848, 124.229), new LatLng(-28.215, 123.938))); polyline2.setTag("B"); stylePolyline(polyline2); // Add polygons to indicate areas on the map. Polygon polygon1 = googleMap.addPolygon(new PolygonOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-27.457, 153.040), new LatLng(-33.852, 151.211), new LatLng(-37.813, 144.962), new LatLng(-34.928, 138.599))); // Store a data object with the polygon, used here to indicate an arbitrary type. polygon1.setTag("alpha"); // Style the polygon. stylePolygon(polygon1); Polygon polygon2 = googleMap.addPolygon(new PolygonOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-31.673, 128.892), new LatLng(-31.952, 115.857), new LatLng(-17.785, 122.258), new LatLng(-12.4258, 130.7932))); polygon2.setTag("beta"); stylePolygon(polygon2); // Position the map's camera near Alice Springs in the center of Australia, // and set the zoom factor so most of Australia shows on the screen. googleMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(new LatLng(-23.684, 133.903), 4)); // Set listeners for click events. googleMap.setOnPolylineClickListener(this); googleMap.setOnPolygonClickListener(this); } private static final int COLOR_BLACK_ARGB = 0xff000000; private static final int POLYLINE_STROKE_WIDTH_PX = 12; /** * Styles the polyline, based on type. * @param polyline The polyline object that needs styling. */ private void stylePolyline(Polyline polyline) { String type = ""; // Get the data object stored with the polyline. if (polyline.getTag() != null) { type = polyline.getTag().toString(); } switch (type) { // If no type is given, allow the API to use the default. case "A": // Use a custom bitmap as the cap at the start of the line. polyline.setStartCap( new CustomCap( BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromResource(R.drawable.ic_arrow), 10)); break; case "B": // Use a round cap at the start of the line. polyline.setStartCap(new RoundCap()); break; } polyline.setEndCap(new RoundCap()); polyline.setWidth(POLYLINE_STROKE_WIDTH_PX); polyline.setColor(COLOR_BLACK_ARGB); polyline.setJointType(JointType.ROUND); } private static final int PATTERN_GAP_LENGTH_PX = 20; private static final PatternItem DOT = new Dot(); private static final PatternItem GAP = new Gap(PATTERN_GAP_LENGTH_PX); // Create a stroke pattern of a gap followed by a dot. private static final List<PatternItem> PATTERN_POLYLINE_DOTTED = Arrays.asList(GAP, DOT); /** * Listens for clicks on a polyline. * @param polyline The polyline object that the user has clicked. */ @Override public void onPolylineClick(Polyline polyline) { // Flip from solid stroke to dotted stroke pattern. if ((polyline.getPattern() == null) || (!polyline.getPattern().contains(DOT))) { polyline.setPattern(PATTERN_POLYLINE_DOTTED); } else { // The default pattern is a solid stroke. polyline.setPattern(null); } Toast.makeText(this, "Route type " + polyline.getTag().toString(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } /** * Listens for clicks on a polygon. * @param polygon The polygon object that the user has clicked. */ @Override public void onPolygonClick(Polygon polygon) { // Flip the values of the red, green, and blue components of the polygon's color. int color = polygon.getStrokeColor() ^ 0x00ffffff; polygon.setStrokeColor(color); color = polygon.getFillColor() ^ 0x00ffffff; polygon.setFillColor(color); Toast.makeText(this, "Area type " + polygon.getTag().toString(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } private static final int COLOR_WHITE_ARGB = 0xffffffff; private static final int COLOR_DARK_GREEN_ARGB = 0xff388E3C; private static final int COLOR_LIGHT_GREEN_ARGB = 0xff81C784; private static final int COLOR_DARK_ORANGE_ARGB = 0xffF57F17; private static final int COLOR_LIGHT_ORANGE_ARGB = 0xffF9A825; private static final int POLYGON_STROKE_WIDTH_PX = 8; private static final int PATTERN_DASH_LENGTH_PX = 20; private static final PatternItem DASH = new Dash(PATTERN_DASH_LENGTH_PX); // Create a stroke pattern of a gap followed by a dash. private static final List<PatternItem> PATTERN_POLYGON_ALPHA = Arrays.asList(GAP, DASH); // Create a stroke pattern of a dot followed by a gap, a dash, and another gap. private static final List<PatternItem> PATTERN_POLYGON_BETA = Arrays.asList(DOT, GAP, DASH, GAP); /** * Styles the polygon, based on type. * @param polygon The polygon object that needs styling. */ private void stylePolygon(Polygon polygon) { String type = ""; // Get the data object stored with the polygon. if (polygon.getTag() != null) { type = polygon.getTag().toString(); } List<PatternItem> pattern = null; int strokeColor = COLOR_BLACK_ARGB; int fillColor = COLOR_WHITE_ARGB; switch (type) { // If no type is given, allow the API to use the default. case "alpha": // Apply a stroke pattern to render a dashed line, and define colors. pattern = PATTERN_POLYGON_ALPHA; strokeColor = COLOR_DARK_GREEN_ARGB; fillColor = COLOR_LIGHT_GREEN_ARGB; break; case "beta": // Apply a stroke pattern to render a line of dots and dashes, and define colors. pattern = PATTERN_POLYGON_BETA; strokeColor = COLOR_DARK_ORANGE_ARGB; fillColor = COLOR_LIGHT_ORANGE_ARGB; break; } polygon.setStrokePattern(pattern); polygon.setStrokeWidth(POLYGON_STROKE_WIDTH_PX); polygon.setStrokeColor(strokeColor); polygon.setFillColor(fillColor); } }
نسخه کاتلین فعالیت را مشاهده کنید:
// Copyright 2020 Google LLC // // Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); // you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. // You may obtain a copy of the License at // // http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 // // Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software // distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, // WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. // See the License for the specific language governing permissions and // limitations under the License. package com.example.polygons import android.os.Bundle import android.widget.Toast import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity import com.google.android.gms.maps.CameraUpdateFactory import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap.OnPolygonClickListener import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap.OnPolylineClickListener import com.google.android.gms.maps.OnMapReadyCallback import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.BitmapDescriptorFactory import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.CustomCap import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Dash import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Dot import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Gap import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.JointType import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.LatLng import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.PatternItem import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Polygon import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.PolygonOptions import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Polyline import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.PolylineOptions import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.RoundCap /** * An activity that displays a Google map with polylines to represent paths or routes, * and polygons to represent areas. */ class PolyActivity : AppCompatActivity(), OnMapReadyCallback, OnPolylineClickListener, OnPolygonClickListener { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps) // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager .findFragmentById(R.id.map) as SupportMapFragment? mapFragment?.getMapAsync(this) } /** * Manipulates the map when it's available. * The API invokes this callback when the map is ready to be used. * This is where we can add markers or lines, add listeners or move the camera. * In this tutorial, we add polylines and polygons to represent routes and areas on the map. */ override fun onMapReady(googleMap: GoogleMap) { // Add polylines to the map. // Polylines are useful to show a route or some other connection between points. val polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), LatLng(-32.491, 147.309))) // Store a data object with the polyline, used here to indicate an arbitrary type. polyline1.tag = "A" // Style the polyline. stylePolyline(polyline1) val polyline2 = googleMap.addPolyline(PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-29.501, 119.700), LatLng(-27.456, 119.672), LatLng(-25.971, 124.187), LatLng(-28.081, 126.555), LatLng(-28.848, 124.229), LatLng(-28.215, 123.938))) polyline2.tag = "B" stylePolyline(polyline2) // Add polygons to indicate areas on the map. val polygon1 = googleMap.addPolygon(PolygonOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-27.457, 153.040), LatLng(-33.852, 151.211), LatLng(-37.813, 144.962), LatLng(-34.928, 138.599))) // Store a data object with the polygon, used here to indicate an arbitrary type. polygon1.tag = "alpha" // Style the polygon. stylePolygon(polygon1) val polygon2 = googleMap.addPolygon(PolygonOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-31.673, 128.892), LatLng(-31.952, 115.857), LatLng(-17.785, 122.258), LatLng(-12.4258, 130.7932))) polygon2.tag = "beta" stylePolygon(polygon2) // Position the map's camera near Alice Springs in the center of Australia, // and set the zoom factor so most of Australia shows on the screen. googleMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(LatLng(-23.684, 133.903), 4f)) // Set listeners for click events. googleMap.setOnPolylineClickListener(this) googleMap.setOnPolygonClickListener(this) } private val COLOR_BLACK_ARGB = -0x1000000 private val POLYLINE_STROKE_WIDTH_PX = 12 /** * Styles the polyline, based on type. * @param polyline The polyline object that needs styling. */ private fun stylePolyline(polyline: Polyline) { // Get the data object stored with the polyline. val type = polyline.tag?.toString() ?: "" when (type) { "A" -> { // Use a custom bitmap as the cap at the start of the line. polyline.startCap = CustomCap( BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromResource(R.drawable.ic_arrow), 10f) } "B" -> { // Use a round cap at the start of the line. polyline.startCap = RoundCap() } } polyline.endCap = RoundCap() polyline.width = POLYLINE_STROKE_WIDTH_PX.toFloat() polyline.color = COLOR_BLACK_ARGB polyline.jointType = JointType.ROUND } private val PATTERN_GAP_LENGTH_PX = 20 private val DOT: PatternItem = Dot() private val GAP: PatternItem = Gap(PATTERN_GAP_LENGTH_PX.toFloat()) // Create a stroke pattern of a gap followed by a dot. private val PATTERN_POLYLINE_DOTTED = listOf(GAP, DOT) /** * Listens for clicks on a polyline. * @param polyline The polyline object that the user has clicked. */ override fun onPolylineClick(polyline: Polyline) { // Flip from solid stroke to dotted stroke pattern. if (polyline.pattern == null || !polyline.pattern!!.contains(DOT)) { polyline.pattern = PATTERN_POLYLINE_DOTTED } else { // The default pattern is a solid stroke. polyline.pattern = null } Toast.makeText(this, "Route type " + polyline.tag.toString(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show() } /** * Listens for clicks on a polygon. * @param polygon The polygon object that the user has clicked. */ override fun onPolygonClick(polygon: Polygon) { // Flip the values of the red, green, and blue components of the polygon's color. var color = polygon.strokeColor xor 0x00ffffff polygon.strokeColor = color color = polygon.fillColor xor 0x00ffffff polygon.fillColor = color Toast.makeText(this, "Area type ${polygon.tag?.toString()}", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show() } private val COLOR_WHITE_ARGB = -0x1 private val COLOR_DARK_GREEN_ARGB = -0xc771c4 private val COLOR_LIGHT_GREEN_ARGB = -0x7e387c private val COLOR_DARK_ORANGE_ARGB = -0xa80e9 private val COLOR_LIGHT_ORANGE_ARGB = -0x657db private val POLYGON_STROKE_WIDTH_PX = 8 private val PATTERN_DASH_LENGTH_PX = 20 private val DASH: PatternItem = Dash(PATTERN_DASH_LENGTH_PX.toFloat()) // Create a stroke pattern of a gap followed by a dash. private val PATTERN_POLYGON_ALPHA = listOf(GAP, DASH) // Create a stroke pattern of a dot followed by a gap, a dash, and another gap. private val PATTERN_POLYGON_BETA = listOf(DOT, GAP, DASH, GAP) /** * Styles the polygon, based on type. * @param polygon The polygon object that needs styling. */ private fun stylePolygon(polygon: Polygon) { // Get the data object stored with the polygon. val type = polygon.tag?.toString() ?: "" var pattern: List<PatternItem>? = null var strokeColor = COLOR_BLACK_ARGB var fillColor = COLOR_WHITE_ARGB when (type) { "alpha" -> { // Apply a stroke pattern to render a dashed line, and define colors. pattern = PATTERN_POLYGON_ALPHA strokeColor = COLOR_DARK_GREEN_ARGB fillColor = COLOR_LIGHT_GREEN_ARGB } "beta" -> { // Apply a stroke pattern to render a line of dots and dashes, and define colors. pattern = PATTERN_POLYGON_BETA strokeColor = COLOR_DARK_ORANGE_ARGB fillColor = COLOR_LIGHT_ORANGE_ARGB } } polygon.strokePattern = pattern polygon.strokeWidth = POLYGON_STROKE_WIDTH_PX.toFloat() polygon.strokeColor = strokeColor polygon.fillColor = fillColor } }
پروژه توسعه خود را تنظیم کنید
برای ایجاد پروژه آموزشی در اندروید استودیو، این مراحل را دنبال کنید.
- اندروید استودیو را دانلود و نصب کنید .
- بسته خدمات گوگل پلی را به اندروید استودیو اضافه کنید .
- اگر هنگام شروع خواندن این آموزش، مخزن نمونههای Google Maps Android API v2 را دانلود یا کپی نکردهاید، آن را دانلود کنید .
پروژه آموزشی را وارد کنید:
- در اندروید استودیو، مسیر File > New > Import Project را انتخاب کنید.
- پس از دانلود مخزن نمونههای Google Maps Android API v2، به محلی که آن را ذخیره کردهاید، بروید.
- پروژه Polygons را در این مکان پیدا کنید:
PATH-TO-SAVED-REPO /android-samples/tutorials/java/Polygons(جاوا) یا
PATH-TO-SAVED-REPO /android-samples/tutorials/kotlin/Polygons(کاتلین) - پوشهی پروژه را انتخاب کنید، سپس روی Open کلیک کنید. اکنون اندروید استودیو با استفاده از ابزار Gradle build، پروژهی شما را میسازد.
API های لازم را فعال کنید و یک کلید API دریافت کنید
برای تکمیل این آموزش، به یک پروژه Google Cloud با API های لازم فعال و یک کلید API که مجاز به استفاده از Maps SDK برای اندروید باشد، نیاز دارید. برای جزئیات بیشتر، به موارد زیر مراجعه کنید:
کلید API را به برنامه خود اضافه کنید
- فایل
local.propertiesپروژه خود را باز کنید. رشته زیر را اضافه کنید و سپس
YOUR_API_KEYرا با مقدار کلید API خود جایگزین کنید:MAPS_API_KEY=YOUR_API_KEYوقتی برنامه خود را میسازید، افزونه Secrets Gradle برای اندروید، کلید API را کپی کرده و آن را به عنوان یک متغیر ساخت در مانیفست اندروید، همانطور که در زیر توضیح داده شده است، در دسترس قرار میدهد.
برنامه خود را بسازید و اجرا کنید
برای ساخت و اجرای برنامه:
یک دستگاه اندروید را به رایانه خود وصل کنید. دستورالعملها را دنبال کنید تا گزینههای توسعهدهنده را در دستگاه اندروید خود فعال کنید و سیستم خود را برای شناسایی دستگاه پیکربندی کنید.
به عنوان یک روش جایگزین، میتوانید از Android Virtual Device Manager (AVD) برای پیکربندی یک دستگاه مجازی استفاده کنید. هنگام انتخاب یک شبیهساز، مطمئن شوید که تصویری را انتخاب میکنید که شامل APIهای گوگل باشد. برای جزئیات بیشتر، به بخش «راهاندازی یک پروژه اندروید استودیو» مراجعه کنید.
در اندروید استودیو، روی گزینهی منوی Run (یا آیکون دکمهی پخش) کلیک کنید. دستگاهی را که از شما خواسته میشود انتخاب کنید.
اندروید استودیو، Gradle را برای ساخت برنامه فراخوانی میکند و سپس برنامه را روی دستگاه یا روی شبیهساز اجرا میکند.
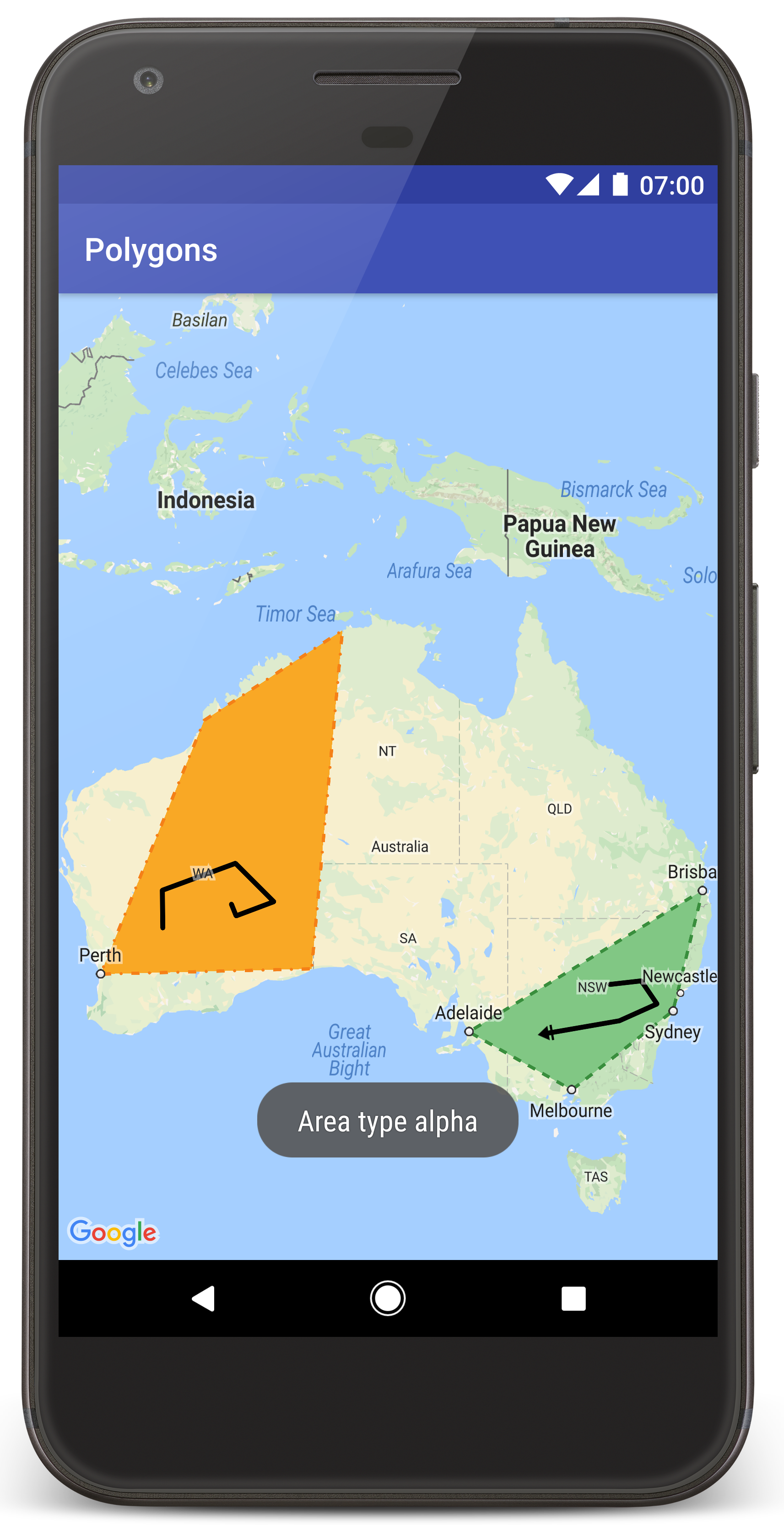
شما باید نقشهای با دو چندضلعی که روی استرالیا قرار گرفتهاند، مشابه تصویر این صفحه، ببینید.
عیبیابی:
- اگر نقشهای نمیبینید، بررسی کنید که آیا کلید API را دریافت کرده و آن را همانطور که در بالا توضیح داده شد به برنامه اضافه کردهاید یا خیر. برای مشاهده پیامهای خطا در مورد کلید API، به بخش Android Monitor در اندروید استودیو مراجعه کنید.
- از ابزارهای اشکالزدایی اندروید استودیو برای مشاهده گزارشها و اشکالزدایی برنامه استفاده کنید.
کد را بفهمید
این بخش از آموزش، مهمترین بخشهای برنامه Polygons را توضیح میدهد تا به شما در درک نحوه ساخت یک برنامه مشابه کمک کند.
مانیفست اندروید خود را بررسی کنید
به عناصر زیر در فایل AndroidManifest.xml برنامه خود توجه کنید:
یک عنصر
meta-dataاضافه کنید تا نسخه سرویسهای گوگل پلی که برنامه با آن کامپایل شده است، در آن جاسازی شود.<meta-data android:name="com.google.android.gms.version" android:value="@integer/google_play_services_version" />یک عنصر
meta-dataکه کلید API شما را مشخص میکند، اضافه کنید. نمونهای که همراه این آموزش ارائه شده است، مقدار کلید API را به یک متغیر ساخت که با نام کلیدی که قبلاً تعریف کردهاید، یعنیMAPS_API_KEYمطابقت دارد، نگاشت میکند. هنگامی که برنامه خود را میسازید، افزونه Secrets Gradle برای اندروید، کلیدهای موجود در فایلlocal.propertiesشما را به عنوان متغیرهای ساخت manifest در دسترس قرار میدهد.<meta-data android:name="com.google.android.geo.API_KEY" android:value="${MAPS_API_KEY}" />در فایل
build.gradleشما، خط زیر کلید API شما را به مانیفست اندروید شما منتقل میکند.id 'com.google.android.libraries.mapsplatform.secrets-gradle-plugin'
در زیر نمونه کاملی از مانیفست را مشاهده میکنید:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!-- Copyright 2020 Google LLC Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. --> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:supportsRtl="true" android:theme="@style/AppTheme"> <meta-data android:name="com.google.android.gms.version" android:value="@integer/google_play_services_version" /> <!-- The API key for Google Maps-based APIs. --> <meta-data android:name="com.google.android.geo.API_KEY" android:value="${MAPS_API_KEY}" /> <activity android:name="com.example.polygons.PolyActivity" android:exported="true" android:label="@string/title_activity_maps"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> </application> </manifest>
اضافه کردن نقشه
نمایش نقشه، با استفاده از Maps SDK برای اندروید.
یک عنصر
<fragment>به فایل طرحبندی فعالیت خود،activity_maps.xml، اضافه کنید. این عنصر یکSupportMapFragmentتعریف میکند که به عنوان ظرفی برای نقشه عمل میکند و دسترسی به شیءGoogleMapرا فراهم میکند. این آموزش از نسخه کتابخانه پشتیبانی اندروید از قطعه نقشه استفاده میکند تا سازگاری با نسخههای قبلی چارچوب اندروید را تضمین کند.<!-- Copyright 2020 Google LLC Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. --> <fragment xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/map" android:name="com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context="com.example.polygons.PolyActivity" />
در متد
onCreate()مربوط به activity خود، فایل layout را به عنوان content view تنظیم کنید. با فراخوانیFragmentManager.findFragmentById()یک هندل به قطعه map دریافت کنید. سپسgetMapAsync()برای ثبت نام در فراخوانی map استفاده کنید:جاوا
@Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps); // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. SupportMapFragment mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager() .findFragmentById(R.id.map); mapFragment.getMapAsync(this); }
کاتلین
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps) // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager .findFragmentById(R.id.map) as SupportMapFragment? mapFragment?.getMapAsync(this) }
رابط کاربری
OnMapReadyCallbackپیادهسازی کنید و متدonMapReady()را بازنویسی کنید. API این فراخوانی را زمانی که شیءGoogleMapدر دسترس باشد، فراخوانی میکند، بنابراین میتوانید اشیاء را به نقشه اضافه کنید و آن را برای برنامه خود سفارشیسازی کنید:جاوا
public class PolyActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements OnMapReadyCallback, GoogleMap.OnPolylineClickListener, GoogleMap.OnPolygonClickListener { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps); // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. SupportMapFragment mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager() .findFragmentById(R.id.map); mapFragment.getMapAsync(this); } /** * Manipulates the map when it's available. * The API invokes this callback when the map is ready to be used. * This is where we can add markers or lines, add listeners or move the camera. * In this tutorial, we add polylines and polygons to represent routes and areas on the map. */ @Override public void onMapReady(GoogleMap googleMap) { // Add polylines to the map. // Polylines are useful to show a route or some other connection between points. Polyline polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(new PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), new LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), new LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), new LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), new LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), new LatLng(-32.491, 147.309))); // Position the map's camera near Alice Springs in the center of Australia, // and set the zoom factor so most of Australia shows on the screen. googleMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(new LatLng(-23.684, 133.903), 4)); // Set listeners for click events. googleMap.setOnPolylineClickListener(this); googleMap.setOnPolygonClickListener(this); }
کاتلین
class PolyActivity : AppCompatActivity(), OnMapReadyCallback, OnPolylineClickListener, OnPolygonClickListener { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps) // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager .findFragmentById(R.id.map) as SupportMapFragment? mapFragment?.getMapAsync(this) } /** * Manipulates the map when it's available. * The API invokes this callback when the map is ready to be used. * This is where we can add markers or lines, add listeners or move the camera. * In this tutorial, we add polylines and polygons to represent routes and areas on the map. */ override fun onMapReady(googleMap: GoogleMap) { // Add polylines to the map. // Polylines are useful to show a route or some other connection between points. val polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), LatLng(-32.491, 147.309))) // Position the map's camera near Alice Springs in the center of Australia, // and set the zoom factor so most of Australia shows on the screen. googleMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(LatLng(-23.684, 133.903), 4f)) // Set listeners for click events. googleMap.setOnPolylineClickListener(this) googleMap.setOnPolygonClickListener(this) }
برای رسم خط روی نقشه، یک چندخطی اضافه کنید
Polyline مجموعهای از پارهخطهای متصل به هم است. چندخطیها برای نمایش مسیرها، راهها یا سایر ارتباطات بین مکانها روی نقشه مفید هستند.
یک شیء
PolylineOptionsایجاد کنید و نقاطی را به آن اضافه کنید. هر نقطه نشان دهنده یک مکان روی نقشه است که شما آن را با یک شیءLatLngحاوی مقادیر طول و عرض جغرافیایی تعریف میکنید. نمونه کد زیر یک چندخطی با ۶ نقطه ایجاد میکند.برای اضافه کردن چندخطی به نقشه، تابع
GoogleMap.addPolyline()را فراخوانی کنید.جاوا
Polyline polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(new PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), new LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), new LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), new LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), new LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), new LatLng(-32.491, 147.309)));
کاتلین
val polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), LatLng(-32.491, 147.309)))
اگر میخواهید رویدادهای کلیک روی چندخطی را مدیریت کنید، گزینهی clickable مربوط به چندخطی را روی true تنظیم کنید. در ادامهی این آموزش، اطلاعات بیشتری در مورد مدیریت رویدادها ارائه خواهد شد.
ذخیره دادههای دلخواه با یک چندخطی
شما میتوانید اشیاء داده دلخواه را با چندخطیها و سایر اشیاء هندسی ذخیره کنید.
برای ذخیره یک شیء داده به همراه چندخطی، تابع
Polyline.setTag()را فراخوانی کنید. کد زیر یک برچسب دلخواه (A) را تعریف میکند که نشاندهنده نوع چندخطی است.جاوا
Polyline polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(new PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), new LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), new LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), new LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), new LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), new LatLng(-32.491, 147.309))); // Store a data object with the polyline, used here to indicate an arbitrary type. polyline1.setTag("A");
کاتلین
val polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), LatLng(-32.491, 147.309))) // Store a data object with the polyline, used here to indicate an arbitrary type. polyline1.tag = "A
دادهها را با استفاده از
Polyline.getTag()بازیابی کنید، همانطور که در بخش بعدی نشان داده شده است.
اضافه کردن استایل سفارشی به چندخطی شما
شما میتوانید ویژگیهای مختلف استایلبندی را در شیء PolylineOptions مشخص کنید. گزینههای استایلبندی شامل رنگ خط دور، عرض خط دور، الگوی خط دور، انواع اتصالات و اندازه شروع و پایان خطوط است. اگر ویژگی خاصی را مشخص نکنید، API از پیشفرض آن ویژگی استفاده میکند.
کد زیر یک کلاهک گرد را به انتهای خط اعمال میکند و یک کلاهک شروع متفاوت بسته به نوع چندخطی اعمال میکند، که در آن نوع یک ویژگی دلخواه است که در شیء داده برای چندخطی ذخیره میشود. این نمونه همچنین عرض خط، رنگ خط و نوع اتصال را مشخص میکند:
جاوا
private static final int COLOR_BLACK_ARGB = 0xff000000; private static final int POLYLINE_STROKE_WIDTH_PX = 12; /** * Styles the polyline, based on type. * @param polyline The polyline object that needs styling. */ private void stylePolyline(Polyline polyline) { String type = ""; // Get the data object stored with the polyline. if (polyline.getTag() != null) { type = polyline.getTag().toString(); } switch (type) { // If no type is given, allow the API to use the default. case "A": // Use a custom bitmap as the cap at the start of the line. polyline.setStartCap( new CustomCap( BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromResource(R.drawable.ic_arrow), 10)); break; case "B": // Use a round cap at the start of the line. polyline.setStartCap(new RoundCap()); break; } polyline.setEndCap(new RoundCap()); polyline.setWidth(POLYLINE_STROKE_WIDTH_PX); polyline.setColor(COLOR_BLACK_ARGB); polyline.setJointType(JointType.ROUND); }
کاتلین
private val COLOR_BLACK_ARGB = -0x1000000 private val POLYLINE_STROKE_WIDTH_PX = 12 /** * Styles the polyline, based on type. * @param polyline The polyline object that needs styling. */ private fun stylePolyline(polyline: Polyline) { // Get the data object stored with the polyline. val type = polyline.tag?.toString() ?: "" when (type) { "A" -> { // Use a custom bitmap as the cap at the start of the line. polyline.startCap = CustomCap( BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromResource(R.drawable.ic_arrow), 10f) } "B" -> { // Use a round cap at the start of the line. polyline.startCap = RoundCap() } } polyline.endCap = RoundCap() polyline.width = POLYLINE_STROKE_WIDTH_PX.toFloat() polyline.color = COLOR_BLACK_ARGB polyline.jointType = JointType.ROUND }
کد بالا یک بیتمپ سفارشی برای شروع چندخطی نوع A مشخص میکند و عرض خط مرجع را 10 پیکسل تعیین میکند. API، بیتمپ را بر اساس عرض خط مرجع مقیاسبندی میکند. هنگام تعیین عرض خط مرجع، عرضی را که هنگام طراحی تصویر بیتمپ استفاده کردهاید، در ابعاد اصلی تصویر وارد کنید. نکته: تصویر بیتمپ خود را با بزرگنمایی 100٪ در یک ویرایشگر تصویر باز کنید و عرض مورد نظر خط خط را نسبت به تصویر رسم کنید.
درباره خطوط بزرگ و سایر گزینههای سفارشیسازی شکلها بیشتر بخوانید.
مدیریت رویدادهای کلیک روی چندخطی
با فراخوانی
Polyline.setClickable()چندخطی را قابل کلیک کنید. (به طور پیشفرض، چندخطیها قابل کلیک نیستند و برنامه شما وقتی کاربر روی یک چندخطی ضربه میزند، اعلانی دریافت نمیکند.)رابط
OnPolylineClickListenerپیادهسازی کنید وGoogleMap.setOnPolylineClickListener()را برای تنظیم شنونده روی نقشه فراخوانی کنید:جاوا
public class PolyActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements OnMapReadyCallback, GoogleMap.OnPolylineClickListener, GoogleMap.OnPolygonClickListener { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps); // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. SupportMapFragment mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager() .findFragmentById(R.id.map); mapFragment.getMapAsync(this); } /** * Manipulates the map when it's available. * The API invokes this callback when the map is ready to be used. * This is where we can add markers or lines, add listeners or move the camera. * In this tutorial, we add polylines and polygons to represent routes and areas on the map. */ @Override public void onMapReady(GoogleMap googleMap) { // Add polylines to the map. // Polylines are useful to show a route or some other connection between points. Polyline polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(new PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), new LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), new LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), new LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), new LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), new LatLng(-32.491, 147.309))); // Position the map's camera near Alice Springs in the center of Australia, // and set the zoom factor so most of Australia shows on the screen. googleMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(new LatLng(-23.684, 133.903), 4)); // Set listeners for click events. googleMap.setOnPolylineClickListener(this); googleMap.setOnPolygonClickListener(this); }
کاتلین
class PolyActivity : AppCompatActivity(), OnMapReadyCallback, OnPolylineClickListener, OnPolygonClickListener { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps) // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager .findFragmentById(R.id.map) as SupportMapFragment? mapFragment?.getMapAsync(this) } /** * Manipulates the map when it's available. * The API invokes this callback when the map is ready to be used. * This is where we can add markers or lines, add listeners or move the camera. * In this tutorial, we add polylines and polygons to represent routes and areas on the map. */ override fun onMapReady(googleMap: GoogleMap) { // Add polylines to the map. // Polylines are useful to show a route or some other connection between points. val polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), LatLng(-32.491, 147.309))) // Position the map's camera near Alice Springs in the center of Australia, // and set the zoom factor so most of Australia shows on the screen. googleMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(LatLng(-23.684, 133.903), 4f)) // Set listeners for click events. googleMap.setOnPolylineClickListener(this) googleMap.setOnPolygonClickListener(this) }
متد فراخوانی
onPolylineClick()را نادیده بگیرید. مثال زیر الگوی خط دور خط را هر بار که کاربر روی چندخطی کلیک میکند، بین حالت توپر و نقطهچین تغییر میدهد:جاوا
private static final int PATTERN_GAP_LENGTH_PX = 20; private static final PatternItem DOT = new Dot(); private static final PatternItem GAP = new Gap(PATTERN_GAP_LENGTH_PX); // Create a stroke pattern of a gap followed by a dot. private static final List<PatternItem> PATTERN_POLYLINE_DOTTED = Arrays.asList(GAP, DOT); /** * Listens for clicks on a polyline. * @param polyline The polyline object that the user has clicked. */ @Override public void onPolylineClick(Polyline polyline) { // Flip from solid stroke to dotted stroke pattern. if ((polyline.getPattern() == null) || (!polyline.getPattern().contains(DOT))) { polyline.setPattern(PATTERN_POLYLINE_DOTTED); } else { // The default pattern is a solid stroke. polyline.setPattern(null); } Toast.makeText(this, "Route type " + polyline.getTag().toString(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); }
کاتلین
private val PATTERN_GAP_LENGTH_PX = 20 private val DOT: PatternItem = Dot() private val GAP: PatternItem = Gap(PATTERN_GAP_LENGTH_PX.toFloat()) // Create a stroke pattern of a gap followed by a dot. private val PATTERN_POLYLINE_DOTTED = listOf(GAP, DOT) /** * Listens for clicks on a polyline. * @param polyline The polyline object that the user has clicked. */ override fun onPolylineClick(polyline: Polyline) { // Flip from solid stroke to dotted stroke pattern. if (polyline.pattern == null || !polyline.pattern!!.contains(DOT)) { polyline.pattern = PATTERN_POLYLINE_DOTTED } else { // The default pattern is a solid stroke. polyline.pattern = null } Toast.makeText(this, "Route type " + polyline.tag.toString(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show() }
چندضلعیها را برای نمایش مناطق روی نقشه اضافه کنید
Polygon شکلی است که از مجموعهای از مختصات در یک توالی منظم تشکیل شده است، شبیه به Polyline . تفاوت این است که چندضلعی یک ناحیه بسته با فضای داخلی قابل پر شدن را تعریف میکند، در حالی که چندخطی انتهای باز دارد.
یک شیء
PolygonOptionsایجاد کنید و نقاطی را به آن اضافه کنید. هر نقطه نشان دهنده یک مکان روی نقشه است که شما آن را با یک شیءLatLngحاوی مقادیر عرض جغرافیایی و طول جغرافیایی تعریف میکنید. نمونه کد زیر یک چندضلعی با ۴ نقطه ایجاد میکند.با فراخوانی
Polygon.setClickable()، چندضلعی را قابل کلیک کنید. (به طور پیشفرض، چندضلعیها قابل کلیک نیستند و برنامه شما وقتی کاربر روی یک چندضلعی ضربه میزند، اعلانی دریافت نمیکند.) مدیریت رویدادهای کلیک چندضلعی مشابه مدیریت رویدادهای روی چندخطیها است که قبلاً در این آموزش توضیح داده شده است.برای اضافه کردن چندضلعی به نقشه، تابع
GoogleMap.addPolygon()را فراخوانی کنید.برای ذخیره یک شیء داده به همراه چندضلعی، تابع
Polygon.setTag()را فراخوانی کنید. کد زیر یک نوع دلخواه (alpha) برای چندضلعی تعریف میکند.جاوا
// Add polygons to indicate areas on the map. Polygon polygon1 = googleMap.addPolygon(new PolygonOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-27.457, 153.040), new LatLng(-33.852, 151.211), new LatLng(-37.813, 144.962), new LatLng(-34.928, 138.599))); // Store a data object with the polygon, used here to indicate an arbitrary type. polygon1.setTag("alpha");
کاتلین
// Add polygons to indicate areas on the map. val polygon1 = googleMap.addPolygon(PolygonOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-27.457, 153.040), LatLng(-33.852, 151.211), LatLng(-37.813, 144.962), LatLng(-34.928, 138.599))) // Store a data object with the polygon, used here to indicate an arbitrary type. polygon1.tag = "alpha" // Style the polygon.
اضافه کردن استایل سفارشی به چندضلعی شما
شما میتوانید تعدادی از ویژگیهای استایلبندی را در شیء PolygonOptions مشخص کنید. گزینههای استایلبندی شامل رنگ خط دور، عرض خط دور، الگوی خط دور، انواع اتصالات خط دور و رنگ پر کردن است. اگر یک ویژگی خاص را مشخص نکنید، API از پیشفرض آن ویژگی استفاده میکند.
کد زیر بسته به نوع چندضلعی، رنگها و الگوهای خط دور خاصی را اعمال میکند، که در آن نوع، یک ویژگی دلخواه است که در شیء داده برای چندضلعی ذخیره میشود:
جاوا
private static final int COLOR_WHITE_ARGB = 0xffffffff; private static final int COLOR_DARK_GREEN_ARGB = 0xff388E3C; private static final int COLOR_LIGHT_GREEN_ARGB = 0xff81C784; private static final int COLOR_DARK_ORANGE_ARGB = 0xffF57F17; private static final int COLOR_LIGHT_ORANGE_ARGB = 0xffF9A825; private static final int POLYGON_STROKE_WIDTH_PX = 8; private static final int PATTERN_DASH_LENGTH_PX = 20; private static final PatternItem DASH = new Dash(PATTERN_DASH_LENGTH_PX); // Create a stroke pattern of a gap followed by a dash. private static final List<PatternItem> PATTERN_POLYGON_ALPHA = Arrays.asList(GAP, DASH); // Create a stroke pattern of a dot followed by a gap, a dash, and another gap. private static final List<PatternItem> PATTERN_POLYGON_BETA = Arrays.asList(DOT, GAP, DASH, GAP); /** * Styles the polygon, based on type. * @param polygon The polygon object that needs styling. */ private void stylePolygon(Polygon polygon) { String type = ""; // Get the data object stored with the polygon. if (polygon.getTag() != null) { type = polygon.getTag().toString(); } List<PatternItem> pattern = null; int strokeColor = COLOR_BLACK_ARGB; int fillColor = COLOR_WHITE_ARGB; switch (type) { // If no type is given, allow the API to use the default. case "alpha": // Apply a stroke pattern to render a dashed line, and define colors. pattern = PATTERN_POLYGON_ALPHA; strokeColor = COLOR_DARK_GREEN_ARGB; fillColor = COLOR_LIGHT_GREEN_ARGB; break; case "beta": // Apply a stroke pattern to render a line of dots and dashes, and define colors. pattern = PATTERN_POLYGON_BETA; strokeColor = COLOR_DARK_ORANGE_ARGB; fillColor = COLOR_LIGHT_ORANGE_ARGB; break; } polygon.setStrokePattern(pattern); polygon.setStrokeWidth(POLYGON_STROKE_WIDTH_PX); polygon.setStrokeColor(strokeColor); polygon.setFillColor(fillColor); }
کاتلین
private val COLOR_WHITE_ARGB = -0x1 private val COLOR_DARK_GREEN_ARGB = -0xc771c4 private val COLOR_LIGHT_GREEN_ARGB = -0x7e387c private val COLOR_DARK_ORANGE_ARGB = -0xa80e9 private val COLOR_LIGHT_ORANGE_ARGB = -0x657db private val POLYGON_STROKE_WIDTH_PX = 8 private val PATTERN_DASH_LENGTH_PX = 20 private val DASH: PatternItem = Dash(PATTERN_DASH_LENGTH_PX.toFloat()) // Create a stroke pattern of a gap followed by a dash. private val PATTERN_POLYGON_ALPHA = listOf(GAP, DASH) // Create a stroke pattern of a dot followed by a gap, a dash, and another gap. private val PATTERN_POLYGON_BETA = listOf(DOT, GAP, DASH, GAP) /** * Styles the polygon, based on type. * @param polygon The polygon object that needs styling. */ private fun stylePolygon(polygon: Polygon) { // Get the data object stored with the polygon. val type = polygon.tag?.toString() ?: "" var pattern: List<PatternItem>? = null var strokeColor = COLOR_BLACK_ARGB var fillColor = COLOR_WHITE_ARGB when (type) { "alpha" -> { // Apply a stroke pattern to render a dashed line, and define colors. pattern = PATTERN_POLYGON_ALPHA strokeColor = COLOR_DARK_GREEN_ARGB fillColor = COLOR_LIGHT_GREEN_ARGB } "beta" -> { // Apply a stroke pattern to render a line of dots and dashes, and define colors. pattern = PATTERN_POLYGON_BETA strokeColor = COLOR_DARK_ORANGE_ARGB fillColor = COLOR_LIGHT_ORANGE_ARGB } } polygon.strokePattern = pattern polygon.strokeWidth = POLYGON_STROKE_WIDTH_PX.toFloat() polygon.strokeColor = strokeColor polygon.fillColor = fillColor }
درباره الگوهای ضربه و سایر گزینههای سفارشیسازی شکلها بیشتر بخوانید.
مراحل بعدی
درباره شیء Circle اطلاعات کسب کنید. دایرهها شبیه چندضلعیها هستند اما ویژگیهایی دارند که شکل دایره را منعکس میکنند.

