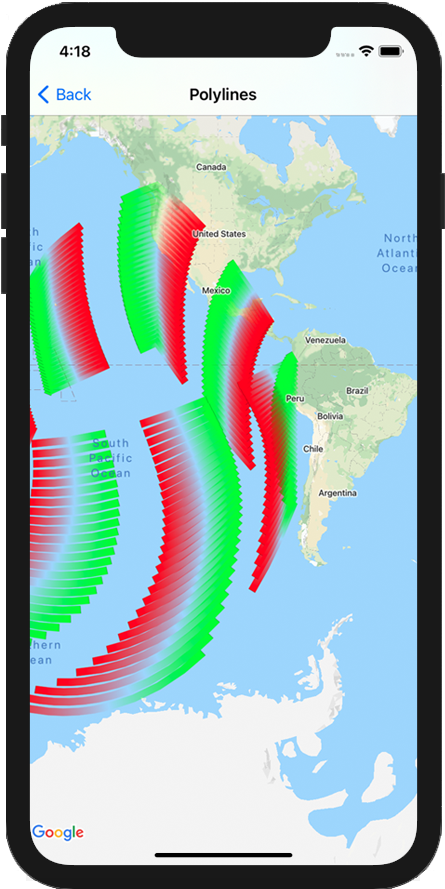
El SDK de Maps para iOS ofrece varias formas de agregar formas a tu Maps. Se admiten las siguientes formas:
- Una polilínea es una serie de segmentos conectados que pueden formar cualquier forma que desees y se pueden usar para marcar recorridos y rutas en el mapa.
- Un polígono es una forma delimitada que se puede utilizar para marcar áreas en el mapa.
- Un círculo es una proyección geográficamente precisa de un círculo en el de ataque de la nube.
Puedes modificar el aspecto de cada forma de varias maneras.
Polilíneas
Las polilíneas te permiten dibujar líneas en el mapa. Un objeto GMSPolyline
representa una secuencia ordenada de ubicaciones, que se muestra como una serie de
segmentos de línea. Puedes establecer el color de una polilínea con
GMSStrokeStyle
Para crear una polilínea, deberás especificar su trazado creando una
El objeto GMSMutablePath correspondiente con dos o más puntos.
Cada CLLocationCoordinate2D representa un lugar de la superficie de la Tierra. Línea
los segmentos se dibujan entre puntos según el orden en el que los agregas
a la ruta. Puedes agregar puntos a la ruta con el addCoordinate: o
addLatitude:longitude:.
Swift
let path = GMSMutablePath()
path.add(CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: -33.85, longitude: 151.20))
path.add(CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: -33.70, longitude: 151.40))
path.add(CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: -33.73, longitude: 151.41))
let polyline = GMSPolyline(path: path)
Objective-C
GMSMutablePath *path = [GMSMutablePath path];
[path addCoordinate:CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(-33.85, 151.20)];
[path addCoordinate:CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(-33.70, 151.40)];
[path addCoordinate:CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(-33.73, 151.41)];
GMSPolyline *polyline = [GMSPolyline polylineWithPath:path];
Cómo agregar una polilínea
- Crea un objeto
GMSMutablePath. - Establece los puntos en la ruta con el prefijo
addCoordinate:.addLatitude:longitude:. - Crea una instancia de un objeto
GMSPolylinenuevo con la ruta de acceso. argumento. - Configura otras propiedades, como
strokeWidthystrokeColor, según sea necesario. - Configura la propiedad
mapdeGMSPolyline. - La polilínea aparece en el mapa.
Con el fragmento de código siguiente se agrega un rectángulo a un mapa:
Swift
let rectanglePath = GMSMutablePath()
rectanglePath.add(CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 37.36, longitude: -122.0))
rectanglePath.add(CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 37.45, longitude: -122.0))
rectanglePath.add(CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 37.45, longitude: -122.2))
rectanglePath.add(CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 37.36, longitude: -122.2))
rectanglePath.add(CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 37.36, longitude: -122.0))
let rectangle = GMSPolyline(path: path)
rectangle.map = mapView
Objective-C
GMSMutablePath *rectanglePath = [GMSMutablePath path];
[rectanglePath addCoordinate:CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(37.36, -122.0)];
[rectanglePath addCoordinate:CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(37.45, -122.0)];
[rectanglePath addCoordinate:CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(37.45, -122.2)];
[rectanglePath addCoordinate:CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(37.36, -122.2)];
[rectanglePath addCoordinate:CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(37.36, -122.0)];
GMSPolyline *rectangle = [GMSPolyline polylineWithPath:path];
rectangle.map = mapView;
Cómo quitar una polilínea
Para quitar una polilínea del mapa, configura la map de tu GMSPolyline
propiedad a nil. De manera alternativa, puedes eliminar todas las superposiciones (incluidas las
polilíneas y otras formas) en el mapa llamando a GMSMapView.
clear.
Swift
mapView.clear()
Objective-C
[mapView clear];
Cómo personalizar una polilínea
El objeto GMSPolyline proporciona varias propiedades para controlar
la apariencia de la línea. Se admiten las siguientes opciones:
strokeWidth- Es el ancho de toda la línea, en puntos de la pantalla. El valor predeterminado es 1. El ancho no se adapta cuando se aplica zoom al mapa.
geodesic-
Cuando sea
YES, renderiza este borde de polilínea como una línea geodésica. Segmentos geodésicos seguir la ruta más corta en la superficie de la Tierra y puede aparecen como líneas curvas en un mapa con la proyección de Mercator. No geodésica los segmentos se dibujan como líneas rectas en el mapa. La configuración predeterminada esNO. spans- Se usa para especificar el color de uno o más segmentos de una polilínea. El
La propiedad spans es un array de
GMSStyleSpanobjetos. Configurar la propiedadspanses la forma preferida de cambiar el color de una polilínea strokeColor- Es un objeto
UIColorque especifica el color de la polilínea. La configuración predeterminada esblueColor. La propiedadstrokeColorse ignora si se configuraspans.
El siguiente fragmento agrega una polilínea gruesa desde Melbourne hasta Perth, con interpolación geodésica.
Swift
let path = GMSMutablePath()
path.addLatitude(-37.81319, longitude: 144.96298)
path.addLatitude(-31.95285, longitude: 115.85734)
let polyline = GMSPolyline(path: path)
polyline.strokeWidth = 10.0
polyline.geodesic = true
polyline.map = mapView
Objective-C
GMSMutablePath *path = [GMSMutablePath path];
[path addLatitude:-37.81319 longitude:144.96298];
[path addLatitude:-31.95285 longitude:115.85734];
GMSPolyline *polyline = [GMSPolyline polylineWithPath:path];
polyline.strokeWidth = 10.f;
polyline.geodesic = YES;
polyline.map = mapView;
Para modificar una polilínea después de agregarla al mapa, asegúrate de conservar
el objeto GMSPolyline
Swift
polyline.strokeColor = .blue
Objective-C
polyline.strokeColor = [UIColor blueColor];
Cómo cambiar el color de una polilínea
Las polilíneas se dibujan como una serie de segmentos en el mapa. Puedes cambiar el color
de segmentos individuales o toda la línea, con la propiedad spans Mientras que
esta propiedad te brinda un control detallado sobre el color de una polilínea,
existen varias ventajas que te permiten aplicar un único estilo a toda la
línea.
En el siguiente fragmento, se usa el método spanWithColor: para cambiar el color de la
toda la línea a rojo.
Swift
polyline.spans = [GMSStyleSpan(color: .red)]
Objective-C
polyline.spans = @[[GMSStyleSpan spanWithColor:[UIColor redColor]]];
De manera alternativa, si ya tienes acceso a un GMSStrokeStyle
puedes usar el método spanWithStyle:.
Swift
let solidRed = GMSStrokeStyle.solidColor(.red)
polyline.spans = [GMSStyleSpan(style: solidRed)]
Objective-C
GMSStrokeStyle *solidRed = [GMSStrokeStyle solidColor:[UIColor redColor]];
polyline.spans = @[[GMSStyleSpan spanWithStyle:solidRed]];
Antes de la versión 1.7 del SDK de Maps para iOS, la única propiedad
strokeColor estaba disponible para establecer todo el color de una
GMSPolyline La propiedad spans tiene prioridad sobre
strokeColor
Swift
polyline.strokeColor = .red
Objective-C
polyline.strokeColor = [UIColor redColor];
Estilos
Si tu app aplica el mismo color de trazo varias veces, puede resultarte útil.
para definir un estilo reutilizable. Los estilos de polilínea se especifican
Objeto GMSStrokeStyle. Un estilo de trazo puede ser sólido
color o un gradiente de un color a otro. Una vez que hayas creado una
puedes aplicarlo a un GMSStyleSpan con el
spanWithStyle:.
Swift
// Create two styles: one that is solid blue, and one that is a gradient from red to yellow
let solidBlue = GMSStrokeStyle.solidColor(.blue)
let solidBlueSpan = GMSStyleSpan(style: solidBlue)
let redYellow = GMSStrokeStyle.gradient(from: .red, to: .yellow)
let redYellowSpan = GMSStyleSpan(style: redYellow)
Objective-C
// Create two styles: one that is solid blue, and one that is a gradient from red to yellow
GMSStrokeStyle *solidBlue = [GMSStrokeStyle solidColor:[UIColor blueColor]];
GMSStyleSpan *solidBlueSpan = [GMSStyleSpan spanWithStyle:solidBlue];
GMSStrokeStyle *redYellow =
[GMSStrokeStyle gradientFromColor:[UIColor redColor] toColor:[UIColor yellowColor]];
GMSStyleSpan *redYellowSpan = [GMSStyleSpan spanWithStyle:redYellow];
El diseño de span continuará hasta el final de la polilínea o hasta que se
de que se haya establecido el estilo de vida. Puedes cambiar el color de toda la línea si configuras spans
propiedad de una polilínea a un solo elemento GMSStyleSpan. El ejemplo
demuestra cómo aplicar un gradiente en toda la longitud de la polilínea.
Swift
polyline.spans = [GMSStyleSpan(style: redYellow)]
Objective-C
polyline.spans = @[[GMSStyleSpan spanWithStyle:redYellow]];
Cómo cambiar el color de segmentos de líneas individuales
Si quieres aplicar diseño a cada segmento de la polilínea de forma individual, puedes hacerlo
Para ello, crea un array de objetos GMSStyleSpan y pásalo
a la propiedad spans. De forma predeterminada, cada elemento del array establece el color de
el segmento de línea correspondiente. Si hay más elementos en el array que
segmentos en la línea, los elementos adicionales se ignorarán. Si hay menos
elementos del array, la GMSStyleSpan final describe la
color para el resto de la línea.
Puedes usar bloques de color o polilíneas de gradientes para indicar cambios en tu polilínea, como la elevación o la velocidad. El siguiente fragmento establece el color de los dos primeros segmentos de una polilínea al rojo, y el resto de la línea es una gradiente de rojo a amarillo.
Swift
polyline.spans = [
GMSStyleSpan(style: solidRed),
GMSStyleSpan(style: solidRed),
GMSStyleSpan(style: redYellow)
]
Objective-C
polyline.spans = @[[GMSStyleSpan spanWithStyle:solidRed],
[GMSStyleSpan spanWithStyle:solidRed],
[GMSStyleSpan spanWithStyle:redYellow]];
Puedes usar el método spanWithStyle:segments: para configurar el estilo de varias
de una sola vez. Por ejemplo, el siguiente código es equivalente al anterior.
Siempre se ignora la longitud del segmento del objeto GMSStyleSpan final.
ya que el estilo se usa para describir el resto de la línea.
Swift
polyline.spans = [
GMSStyleSpan(style: solidRed, segments:2),
GMSStyleSpan(style: redYellow, segments:10)
]
Objective-C
polyline.spans = @[[GMSStyleSpan spanWithStyle:solidRed segments:2],
[GMSStyleSpan spanWithStyle:redYellow segments:10]];
Segmentos fraccionarios
Los segmentos también pueden especificarse como un valor fraccionario. Esto aplicará el estilo
al número fraccionario de segmentos, lo que puede provocar una división en una sola
segmento. Cada GMSStyleSpan comienza inmediatamente después de
anterior: en el siguiente ejemplo, el color gris comienza desde 1⁄2 hasta
el segundo segmento y pasar
a la mitad del tercer segmento.
Swift
polyline.spans = [
GMSStyleSpan(style: solidRed, segments: 2.5),
GMSStyleSpan(color: .gray),
GMSStyleSpan(color: .purple, segments: 0.75),
GMSStyleSpan(style: redYellow)
]
Objective-C
polyline.spans = @[[GMSStyleSpan spanWithStyle:solidRed segments:2.5],
[GMSStyleSpan spanWithColor:[UIColor grayColor]],
[GMSStyleSpan spanWithColor:[UIColor purpleColor] segments:0.75],
[GMSStyleSpan spanWithStyle:redYellow]];
Cómo agregar un patrón de color repetido a una polilínea
Si quieres agregar un patrón a una polilínea, puedes usar la
Método de utilidad GMSStyleSpans en GMSGeometryUtils. El
El método GMSStyleSpans acepta dos arrays que definen un patrón repetitivo. Uno
array establece los estilos que deben repetirse y el otro define
de repetición. Si los usas juntos, puedes crear un patrón que se puede
se aplican en cualquier polilínea, independientemente de su longitud o la cantidad de segmentos
disponibles.
Por ejemplo, el siguiente fragmento de código define una polilínea en blanco y negro
patrón alternante. Su longitud se considera como metros a lo largo de una línea de pulgar (en
Mercator, es una línea recta), ya que el tipo se especifica como
kGMSLengthRhumb
Swift
let styles = [
GMSStrokeStyle.solidColor(.white),
GMSStrokeStyle.solidColor(.black)
]
let lengths: [NSNumber] = [100000, 50000]
polyline.spans = GMSStyleSpans(
polyline.path!,
styles,
lengths,
GMSLengthKind.rhumb
)
Objective-C
NSArray *styles = @[[GMSStrokeStyle solidColor:[UIColor whiteColor]],
[GMSStrokeStyle solidColor:[UIColor blackColor]]];
NSArray *lengths = @[@100000, @50000];
polyline.spans = GMSStyleSpans(polyline.path, styles, lengths, kGMSLengthRhumb);
Polilíneas estampadas de objeto
Las polilíneas estampadas con objeto te permiten crear una polilínea a partir de un mapa de bits repetitivo imagen que elijas. Las formas se muestran con un trazo de fondo claro, pero el sello no se trunca en las esquinas. Por lo tanto, son útiles en situaciones como puntos para ilustrar las instrucciones sobre cómo llegar a pie.
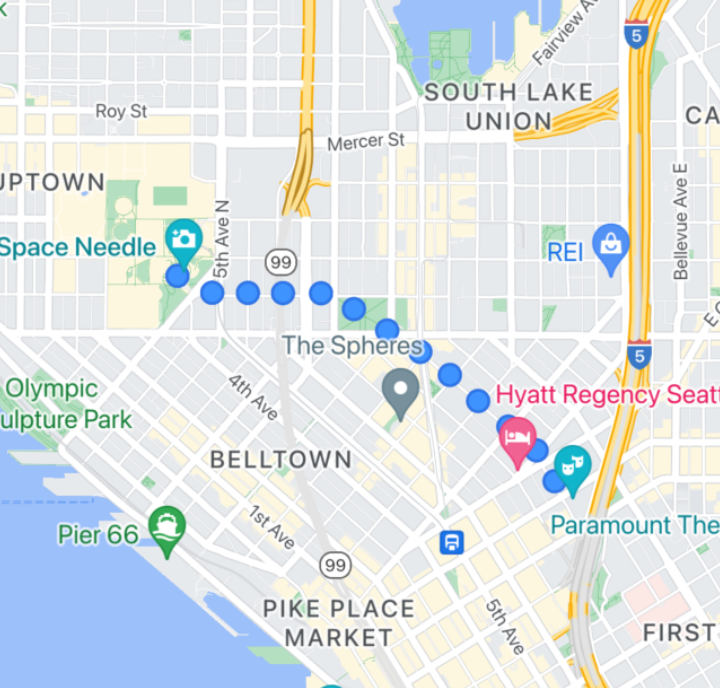
Para usar esta función, debes usar GMSSpriteStyle y configurarla
como sello con el elemento stampStyle de GMSStrokeStyle
propiedad.
Swift
let path = GMSMutablePath()
path.addLatitude(-37.81319, longitude: 144.96298)
path.addLatitude(-31.95285, longitude: 115.85734)
let polyline = GMSPolyline(path: path)
polyline.strokeWidth = 20
let image = UIImage(named: "imageFromBundleOrAsset")! // Image could be from anywhere
let stampStyle = GMSSpriteStyle(image: image)
let transparentStampStroke = GMSStrokeStyle.transparentStroke(withStamp: stampStyle)
let span = GMSStyleSpan(style: transparentStampStroke)
polyline.spans = [span]
polyline.map = mapView
Objective-C
GMSMutablePath *path = [GMSMutablePath path];
[path addLatitude:-37.81319 longitude:144.96298];
[path addLatitude:-31.95285 longitude:115.85734];
polyline.strokeWidth = 20;
GMSPolyline *polyline = [GMSPolyline polylineWithPath:path];
UIImage *image = [UIImage imageNamed:@"imageFromBundleOrAsset"];
GMSStrokeStyle *transparentStampStroke = [GMSStrokeStyle transparentStrokeWithStampStyle:[GMSSpriteStyle spriteStyleWithImage:image]];
GMSStyleSpan *span = [GMSStyleSpan spanWithStyle:transparentStampStroke];
polyline.spans = @[span];
polyline.map = _mapView;
Polilíneas con texturas estampadas
Las polilíneas selladas con textura te permiten crear una polilínea a partir de una polilínea la textura que elijas. Las formas se pueden mostrar con un color claro y sólido o con gradiente. trazo de fondo. La textura cambia de tamaño a medida que cambian los niveles de zoom. Imágenes al final del final o del comienzo de los recorridos o de los puntos de trayectos se truncan cuando se utiliza un determinado nivel de zoom. niveles.
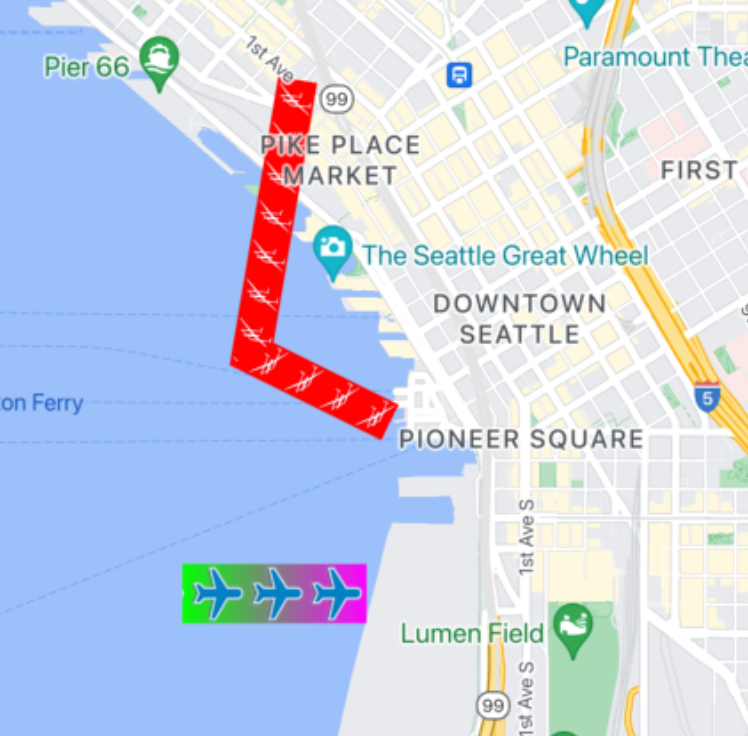
Puedes usar esta función con GMSTextureStyle y la configuración
como sello con el elemento stampStyle de GMSStrokeStyle
propiedad.
Swift
let path = GMSMutablePath()
path.addLatitude(-37.81319, longitude: 144.96298)
path.addLatitude(-31.95285, longitude: 115.85734)
let polyline = GMSPolyline(path: path)
polyline.strokeWidth = 20
let redWithStamp = GMSStrokeStyle.solidColor(.red)
let image = UIImage(named: "imageFromBundleOrAsset")! // Image could be from anywhere
redWithStamp.stampStyle = GMSTextureStyle(image: image)
let span = GMSStyleSpan(style: redWithStamp)
polyline.spans = [span]
polyline.map = mapView
Objective-C
GMSMutablePath *path = [GMSMutablePath path];
[path addLatitude:-37.81319 longitude:144.96298];
[path addLatitude:-31.95285 longitude:115.85734];
GMSPolyline *polyline = [GMSPolyline polylineWithPath:path];
polyline.strokeWidth = 20;
GMSStrokeStyle *redWithStamp = [GMSStrokeStyle solidColor:[UIColor redColor]];
UIImage *image = [UIImage imageNamed:@"imageFromBundleOrAsset"]; // Image could be from anywhere
redWithStamp.stampStyle = [GMSTextureStyle textureStyleWithImage:image];
GMSStyleSpan *span = [GMSStyleSpan spanWithStyle:redWithStamp];
polyline.spans = @[span];
polyline.map = _mapView;
Funciones del mapa
La propiedad mapCapabilities en GMSMapView agrega publicidad programática
verificar características específicas del mapa. Esto es útil cuando se desea saber si
están disponibles algunas capabilities de mapas antes de llamar a APIs específicas. Esta
determina si la vista de mapa admite polilíneas con sellos de Sprite.
Swift
let path = GMSMutablePath()
path.addLatitude(-37.81319, longitude: 144.96298)
path.addLatitude(-31.95285, longitude: 115.85734)
let polyline = GMSPolyline(path: path)
polyline.strokeWidth = 20
let image = UIImage(named: "imageFromBundleOrAsset")! // Image could be from anywhere
let spans: [GMSStyleSpan]
if (mapView.mapCapabilities.contains(.spritePolylines)) {
let spriteStyle = GMSSpriteStyle(image: image)
let stroke = GMSStrokeStyle.transparentStroke(withStamp: spriteStyle)
spans = [ GMSStyleSpan(style: stroke) ]
} else {
let stroke = GMSStrokeStyle.solidColor(.clear)
stroke.stampStyle = GMSTextureStyle(image: image)
spans = [ GMSStyleSpan(style: stroke) ]
}
polyline.spans = spans
polyline.map = mapView
Objective-C
GMSMutablePath *path = [GMSMutablePath path];
[path addLatitude:-37.81319 longitude:144.96298];
[path addLatitude:-31.95285 longitude:115.85734];
UIImage *_Nonnull image = [UIImage imageNamed:@"imageFromBundleOrAsset"]; // Image could be from anywhere
NSArray<GMSStyleSpan *> * spans;
if (_mapView.mapCapabilities & GMSMapCapabilityFlagsSpritePolylines) {
GMSSpriteStyle *spriteStyle = [GMSSpriteStyle spriteStyleWithImage:image];
GMSStrokeStyle *stroke = [GMSStrokeStyle transparentStrokeWithStampStyle:spriteStyle];
spans = @[ [GMSStyleSpan spanWithStyle:stroke] ];
} else {
GMSStrokeStyle *stroke = [GMSStrokeStyle solidColor:UIColor.clearColor];
stroke.stampStyle = [GMSTextureStyle textureStyleWithImage:image];
spans = @[ [GMSStyleSpan spanWithStyle:stroke] ];
}
GMSPolyline *polyline = [GMSPolyline polylineWithPath:path];
polyline.strokeWidth = 20;
polyline.spans = spans;
polyline.map = _mapView;
Este patrón te permite suscribirte a los cambios y reaccionar a las actualizaciones con tu mapa
el estado de vista. También puedes implementar didChangeMapCapabilities en
GMSMapViewDelegate para recibir actualizaciones sobre la función
disponibilidad.
Polígonos
Los polígonos son similares a las polilíneas, ya que constan de una serie de
coordenadas en una secuencia ordenada. Sin embargo, en lugar de ser abiertas,
están diseñados para definir regiones sólidas dentro de un bucle cerrado. Los polígonos son
definido en el SDK de Maps para iOS por el archivo GMSPolygon
.
Puedes agregar un objeto GMSPolygon al mapa de la misma manera en que agregas un elemento
GMSPolyline Primero, especifica su ruta creando un
el objeto GMSMutablePath correspondiente y agregarle puntos.
Estos puntos forman el contorno del polígono. Cada CLLocationCoordinate2D
representa un lugar de la superficie terrestre. Los segmentos de línea se dibujan entre
puntos según el orden en el que los agregues a la ruta.
Cómo agregar un polígono
- Crea un objeto
GMSMutablePath. - Establece los puntos en la ruta con el prefijo
addCoordinate:.addLatitude:longitude:. Estos puntos forman el esquema del polígono. - Crea una instancia de un objeto
GMSPolygonnuevo con la ruta de acceso. argumento. - Configura otras propiedades, como
strokeWidth,strokeColoryfillColor, como desees. - Asigna el polígono a un objeto
GMSMapViewestableciendo laGMSPolygon.map. - El polígono aparece en el mapa.
Con el fragmento de código siguiente se agrega un rectángulo a un mapa.
Swift
// Create a rectangular path
let rect = GMSMutablePath()
rect.add(CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 37.36, longitude: -122.0))
rect.add(CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 37.45, longitude: -122.0))
rect.add(CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 37.45, longitude: -122.2))
rect.add(CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 37.36, longitude: -122.2))
// Create the polygon, and assign it to the map.
let polygon = GMSPolygon(path: rect)
polygon.fillColor = UIColor(red: 0.25, green: 0, blue: 0, alpha: 0.05);
polygon.strokeColor = .black
polygon.strokeWidth = 2
polygon.map = mapView
Objective-C
// Create a rectangular path
GMSMutablePath *rect = [GMSMutablePath path];
[rect addCoordinate:CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(37.36, -122.0)];
[rect addCoordinate:CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(37.45, -122.0)];
[rect addCoordinate:CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(37.45, -122.2)];
[rect addCoordinate:CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(37.36, -122.2)];
// Create the polygon, and assign it to the map.
GMSPolygon *polygon = [GMSPolygon polygonWithPath:rect];
polygon.fillColor = [UIColor colorWithRed:0.25 green:0 blue:0 alpha:0.05];
polygon.strokeColor = [UIColor blackColor];
polygon.strokeWidth = 2;
polygon.map = mapView;
Puedes personalizar el aspecto del polígono antes de agregarlo al mapa. y después de haberlo agregado al mapa.
Cómo quitar un polígono
Para quitar un polígono, configura su propiedad GMSPolygon.map como nil y desconéctala
el layer de su elemento superior.
Swift
polygon.map = nil polygon.layer.removeFromSuperLayer()
Objective-C
polygon.map = nil; [polygon.layer removeFromSuperlayer];
Círculos
Además de la clase GMSPolygon genérica, el archivo
El SDK de Maps para iOS también incluye GMSCircle, lo que te permite
para dibujar círculos en la superficie de la Tierra.
Para construir un círculo, debes especificar las dos propiedades siguientes:
positioncomoCLLocationCoordinate2Dradiusen metros
Por lo tanto, un círculo se define como el conjunto de todos los puntos de la superficie terrestre, que se encuentran a radius metros del objeto center especificado. Debido a cómo la
La proyección de Mercator que usa la API de Google Maps renderiza una esfera en una superficie plana,
aparece como un círculo casi perfecto en el mapa cuando se ubica cerca del
del Ecuador y parece cada vez más no circular (en la pantalla) porque el círculo
se aleja del ecuador.
Cómo agregar un círculo
En el fragmento de código siguiente se agrega un círculo al mapa:
Swift
let circleCenter = CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 37.35, longitude: -122.0)
let circle = GMSCircle(position: circleCenter, radius: 1000)
circle.map = mapView
Objective-C
CLLocationCoordinate2D circleCenter = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(37.35, -122.0);
GMSCircle *circle = [GMSCircle circleWithPosition:circleCenter
radius:1000];
circle.map = mapView;
Puedes personalizar el aspecto del círculo antes de agregarlo al mapa. y después de haberlo agregado al mapa.
Cómo personalizar un círculo
Puedes especificar colores y anchos de trazo personalizados modificando las propiedades de
GMSCircle Se admiten las siguientes opciones:
fillColor- : Es un objeto
UIColorque especifica el color interior de la círculo. La configuración predeterminada es el transparente. strokeColor- Es un objeto
UIColorque especifica el color del círculo. esquema. La configuración predeterminada esblackColor. strokeWidth- Espesor del contorno del círculo, en puntos de la pantalla. El valor predeterminado es 1. El grosor no se adapta cuando se aplica zoom al mapa.
El siguiente fragmento agrega un círculo rojo grueso con un color rojo semitransparente interior.
Swift
circle.fillColor = UIColor(red: 0.35, green: 0, blue: 0, alpha: 0.05)
circle.strokeColor = .red
circle.strokeWidth = 5
Objective-C
circle.fillColor = [UIColor colorWithRed:0.25 green:0 blue:0 alpha:0.05];
circle.strokeColor = [UIColor redColor];
circle.strokeWidth = 5;
Cómo crear un polígono hueco
Puedes combinar varias rutas en un solo objeto GMSPolygon para hacer lo siguiente:
crear formas complejas, como aros rellenos, o donas (en las que las áreas poligonales
aparecerán dentro del polígono como formas separadas). Las formas complejas son las
la composición de varias rutas.
Crea un polígono con un trazado que especifique el área más grande cubierta por la
polígono. Luego, especifica la propiedad holes del polígono como un array de uno o más.
más objetos GMSPath, que definen los agujeros dentro del polígono.
Si una ruta más pequeña está delimitada por completo por la más grande, aparece como si del polígono se eliminó.
En el siguiente ejemplo de código se crea un polígono con dos orificios:
Swift
let hydeParkLocation = CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: -33.87344, longitude: 151.21135)
let camera = GMSCameraPosition.camera(withTarget: hydeParkLocation, zoom: 16)
let mapView = GMSMapView.map(withFrame: .zero, camera: camera)
mapView.animate(to: camera)
let hydePark = "tpwmEkd|y[QVe@Pk@BsHe@mGc@iNaAKMaBIYIq@qAMo@Eo@@[Fe@DoALu@HUb@c@XUZS^ELGxOhAd@@ZB`@J^BhFRlBN\\BZ@`AFrATAJAR?rAE\\C~BIpD"
let archibaldFountain = "tlvmEqq|y[NNCXSJQOB[TI"
let reflectionPool = "bewmEwk|y[Dm@zAPEj@{AO"
let hollowPolygon = GMSPolygon()
hollowPolygon.path = GMSPath(fromEncodedPath: hydePark)
hollowPolygon.holes = [GMSPath(fromEncodedPath: archibaldFountain)!, GMSPath(fromEncodedPath: reflectionPool)!]
hollowPolygon.fillColor = UIColor(red: 1.0, green: 0.0, blue: 0.0, alpha: 0.2)
hollowPolygon.strokeColor = UIColor(red: 1.0, green: 0.0, blue: 0.0, alpha: 1.0)
hollowPolygon.strokeWidth = 2
hollowPolygon.map = mapView
Objective-C
CLLocationCoordinate2D hydeParkLocation = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(-33.87344, 151.21135);
GMSCameraPosition *camera = [GMSCameraPosition cameraWithTarget:hydeParkLocation
zoom:16];
mapView = [GMSMapView mapWithFrame:CGRectZero camera:camera];
NSString *hydePark = @"tpwmEkd|y[QVe@Pk@BsHe@mGc@iNaAKMaBIYIq@qAMo@Eo@@[Fe@DoALu@HUb@c@XUZS^ELGxOhAd@@ZB`@J^BhFRlBN\\BZ@`AFrATAJAR?rAE\\C~BIpD";
NSString *archibaldFountain = @"tlvmEqq|y[NNCXSJQOB[TI";
NSString *reflectionPool = @"bewmEwk|y[Dm@zAPEj@{AO";
GMSPolygon *hollowPolygon = [[GMSPolygon alloc] init];
hollowPolygon.path = [GMSPath pathFromEncodedPath:hydePark];
hollowPolygon.holes = @[[GMSPath pathFromEncodedPath:archibaldFountain],
[GMSPath pathFromEncodedPath:reflectionPool]];
hollowPolygon.fillColor = [UIColor colorWithRed:1.0 green:0.0 blue:0.0 alpha:0.2];
hollowPolygon.strokeColor = [UIColor colorWithRed:1.0 green:0.0 blue:0.0 alpha:1.0];
hollowPolygon.strokeWidth = 2;
hollowPolygon.map = mapView;

