This page explains how to set up and respond to commands as a Google Chat app.
Commands help users discover and use key features of a Chat app. Only Chat apps can see the content of a command. For example, if a user sends a message with a slash command, the message is only visible to the user and the Chat app.
To decide whether you should build commands, and to understand how to design user interactions, see Define all user journeys.
Types of Chat app commands
You can build Chat app commands as slash commands or quick commands. To discover commands, users can type a slash/ in the reply area, or click Google Workspace tools -
Slash commands: Users can select a slash command from the menu or type a slash (
/) and then a predefined text, such as/about. Chat apps typically require argument text for the slash command.Create a slash command if your Chat app requires additional input from the user. For example, you can create a slash command called
/searchthat runs after the user enters a phrase to search for, like/search receipts. -
Quick commands: Users use commands by opening the menu from the reply area of a Chat message. To use a command, they click Add
and select a command from the menu.
Create a quick command if your Chat app can respond to the user immediately, without waiting for additional input. For example, you can create a quick command called Random image that responds immediately with an image.

Prerequisites
Node.js
A Google Chat app that receives and responds to interaction events. To create an interactive Chat app using an HTTP service, complete this quickstart.
Apps Script
A Google Chat app that receives and responds to interaction events. To create an interactive Chat app in Apps Script, complete this quickstart.
Python
A Google Chat app that receives and responds to interaction events. To create an interactive Chat app using an HTTP service, complete this quickstart.
Java
A Google Chat app that receives and responds to interaction events. To create an interactive Chat app using an HTTP service, complete this quickstart.
Set up the command
This section explains how to complete the following steps to set up the command:
- Create a name and description for the command.
- Configure the command in the Google Cloud console.
Name and describe the command
The name of a command is what users type or select to invoke the Chat app. A short description also appears below the name, to prompt users further about how to use the command:
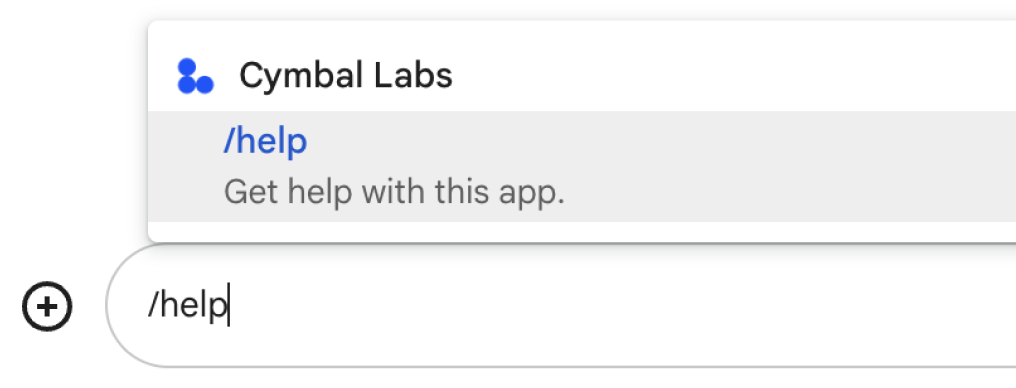
When choosing a name and description for your command, consider the following recommendations:
To name a command:
- Use short, descriptive, and actionable words or phrases to make the commands clear to the
user. For example, instead of the name
Create a reminder, useRemind me. - Consider using a unique or common name for your command. If your command describes a
typical interaction or feature, you can use a common name that users recognize and expect,
such as
SettingsorFeedback. Otherwise, try to use unique command names, because if your command name is the same for other Chat apps, the user must filter through similar commands to find and use yours.
To describe a command:
- Keep the description short and clear so that users know what to expect when they use the command.
- Let users know if there are any formatting requirements for the command. For example, if you
create a slash command that requires argument text, set the description to something like
Remind me to do [something] at [time]. - Let users know if the Chat app replies to everyone in the space, or
privately to the user who invokes the command. For example, for the quick command
About, you could describe it asLearn about this app (Only visible to you).
Configure the command in the Google Cloud console
To create a slash or quick command, you specify information about the command in your Chat app's configuration for the Google Chat API.
To configure a command in the Google Chat API, complete the following steps:
In the Google Cloud console, click Menu > APIs & Services > Enabled APIs & Services > Google Chat API
Click Configuration.
Under Commands, click Add a command.
Enter a command ID, description, command type, and name for the command:
- Command ID: a number from 1 to 1000 that your Chat app uses to recognize the command and return a response.
- Description: the text that describes what the command does. Descriptions can be up to 50 characters and can include special characters.
- Command type: select either Quick command or Slash command.
- Specify a name for the quick command or slash command:
- Quick command name: The display name that users select from the
menu to invoke the command. Can be up to 50 characters and include
special characters. For example,
Remind me. - Slash command name: The text that users type to invoke the
command in a message. Must start with a slash, contain only text, and
can be up to 50 characters. For example,
/remindMe.
- Quick command name: The display name that users select from the
menu to invoke the command. Can be up to 50 characters and include
special characters. For example,
Optional: If you want your Chat app to respond to the command with a dialog, select the Open a dialog checkbox.
Click Save.
The command is now configured for the Chat app.
Respond to a command
When users use a command, your Chat app receives an interaction event. The event payload contains metadata with details about the command that was invoked (including the command ID and the command type), so that you can return an appropriate response.
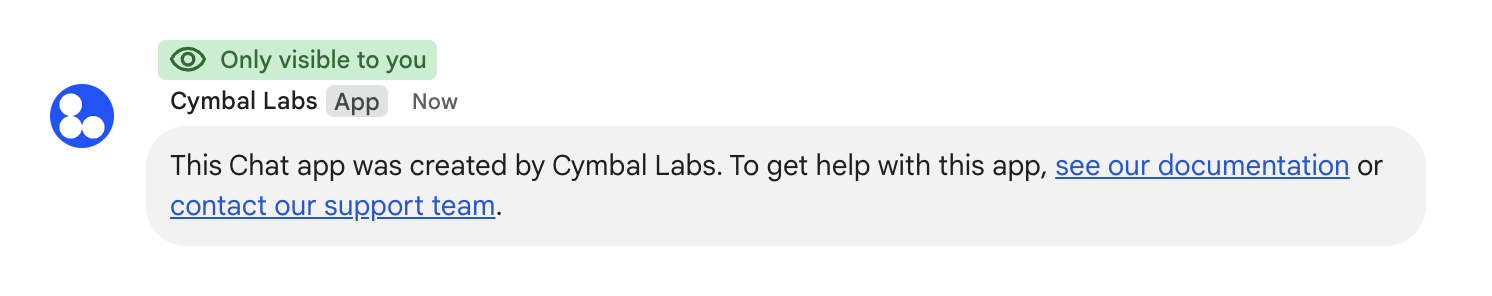
/help to explain how to get support.To respond to each type of command, you must handle different event types and metadata objects in the event payload:
| Command type | Event type | Command metadata |
|---|---|---|
| Slash command | MESSAGE |
message.slashCommand
or message.annotation.slashCommand |
| Quick command | APP_COMMAND |
appCommandMetadata
|
To learn how to respond to a command with a message, see the following sections.
Respond to a slash command
The following code shows an example of a Chat app that
replies to the slash command /about. The Chat app
handles MESSAGE interaction events, detects whether the interaction event
contains the matching command ID, and returns a private message:
Node.js
Apps Script
Python
Java
Replace ABOUT_COMMAND_ID with the command ID that you
specified when you configured the command in the Google Cloud console.
Respond to a quick command
The following code shows an example of a Chat app that
replies to the quick command Help. The Chat app
handles APP_COMMAND interaction events, detects whether the interaction event
contains the matching command ID, and returns a private message:
Node.js
Apps Script
Python
Java
Replace HELP_COMMAND_ID with the command ID that you
specified when you configured the command in the Google Cloud console.
Test the command
To test the command and code, see Test interactive features for Google Chat apps.
To learn how to test and use the command in the Chat UI, see Use apps in Google Chat in the Google Chat Help documentation.
Related topics
- View Chat app samples that use commands
- Send a message
- Open interactive dialogs