Page Summary
-
Google Chat apps can collect user information using forms embedded within cards, offering interactive elements like text inputs, selection inputs, and date-time pickers.
-
These apps can utilize data from both Google Workspace and external sources, enhancing their functionality and data integration capabilities.
-
Upon form submission, the app receives user input data, enabling it to process, transfer data to other cards, or provide direct responses within the Chat interface.
-
Multiselect menus support dynamic suggestions as users type, streamlining interactions and data entry processes, especially when utilizing external data sources.
-
Developers can leverage Node.js or Apps Script along with a Google Workspace add-on to build and deploy these interactive Google Chat apps.
This guide describes how Google Chat apps can collect and process information from users by building form inputs in card-based interfaces.

Chat apps request information from users to perform actions in or outside of Chat, including in the following ways:
- Configure settings. For example, to let users customize notification settings or configure and add the Chat app to one or more spaces.
- Create or update information in other Google Workspace applications. For example, let users create a Google Calendar event.
- Let users access and update resources in other apps or web services. For example, a Chat app can help users update the status of a support ticket directly from a Chat space.
Prerequisites
HTTP
A Google Workspace add-on that extends Google Chat. To build one, complete the HTTP quickstart.
Apps Script
A Google Workspace add-on that extends Google Chat. To build one, complete the Apps Script quickstart.
Build forms using cards
To collect information, Chat apps design forms and their inputs, and build them into cards. To display cards to users, Chat apps can use the following Chat interfaces:
- Chat messages that contain one or more cards.
- Dialogs, which are cards that open in a new window from messages and homepages.
Chat apps can build the cards using the following widgets:
Form input widgets that request information from users. Optionally, you can add validation to form input widgets, to ensure that users input and format information correctly. Chat apps can use the following form input widgets:
- Text inputs
(
textInput) for free-form or suggested text. Selection inputs (
selectionInput) are selectable UI elements such as checkboxes, radio buttons, and drop-down menus. Selection input widgets can also populate and suggest items from Google Workspace data (such as a Chat space) or a dynamic data source. For details, see the following section Add a multiselect menu.Date time pickers (
dateTimePicker) for date and time entries.
- Text inputs
(
A button widget so that users can submit values that they've input in the card. After a user clicks the button, the Chat app can then process the information that it receives.
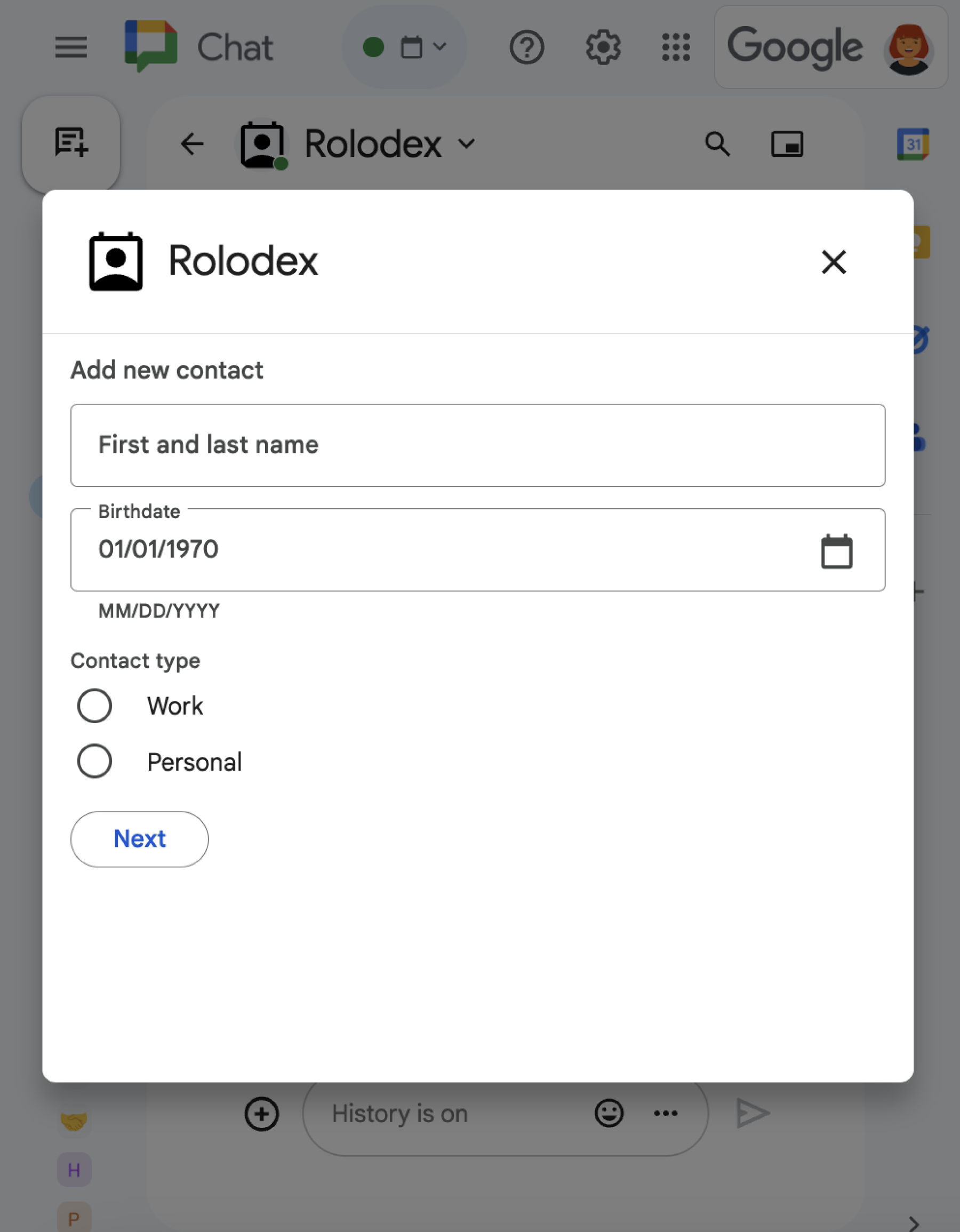
In the following example, a card collects contact information using a text input, date time picker, and selection input:
For more examples of interactive widgets that you can use to collect information, see Design an interactive card or dialog in the Google Chat API documentation.
Add a multiselect menu
To customize selection items or let users select items from a dynamic data
source, Chat apps can use multiselect menus, which are a type of
SelectionInput widget. For example, the following card displays a multiselect
menu where users can dynamically select from a list of contacts:
You can populate items for a multiselect menu from the following data sources:
- Google Workspace data, which includes users or Chat spaces of which the user is a member. The menu only populates items from the same Google Workspace organization.
- External data sources, such as a relational database. For example, you can use multiselect menus to help a user select from a list of sales leads from a customer relationship management (CRM) system.
Populate items from a Google Workspace data source
To use Google Workspace data sources, specify the
platformDataSource
field in the SelectionInput widget. Unlike other selection input types, you
omit
SelectionItem
objects, because these selection items are dynamically sourced from
Google Workspace.
The following code shows a multiselect menu of Google Workspace users.
To populate users, the selection input sets commonDataSource to USER:
JSON
{
"selectionInput": {
"name": "contacts",
"type": "MULTI_SELECT",
"label": "Selected contacts",
"multiSelectMaxSelectedItems": 5,
"multiSelectMinQueryLength": 1,
"platformDataSource": {
"commonDataSource": "USER"
}
}
}
The following code shows a multiselect menu of Chat
spaces. To populate spaces, the selection input specifies the
hostAppDataSource field. The multiselect menu also sets
defaultToCurrentSpace to true, which makes the current space the default
selection in the menu:
JSON
{
"selectionInput": {
"name": "spaces",
"type": "MULTI_SELECT",
"label": "Selected contacts",
"multiSelectMaxSelectedItems": 3,
"multiSelectMinQueryLength": 1,
"platformDataSource": {
"hostAppDataSource": {
"chatDataSource": {
"spaceDataSource": {
"defaultToCurrentSpace": true
}
}
}
}
}
}
Populate items from an external data source
Multiselect menus can also populate items from a third-party or external data
source. To use an external data source, you specify the
externalDataSource
field in the SelectionInput widget that contains the function that queries and
returns items from the data source.
To reduce the requests to an external data source, you can include
suggested items that appear in the multiselect menu before users type in
the menu. For example, you can populate recently searched contacts for the
user. To populate suggested items from an external data source, specify static
SelectionItem
objects.
The following code sample shows a multiselect menu that queries and populates items from an external data source:
Node.js
Replace FUNCTION_URL with the HTTP endpoint that queries
the external data source.
Python
Replace FUNCTION_URL with the HTTP endpoint that queries
the external data source.
Java
Replace FUNCTION_URL with the HTTP endpoint that queries
the external data source.
Apps Script
This example sends a card message by returning card JSON. You can also use the Apps Script card service.
For a complete example that shows how to return suggested items, see the section Suggest multiselect items.
Receive data from interactive widgets
Whenever users click a button, its Chat apps
action
is triggered with information about the interaction. In the
commonEventObject
of the event payload, the formInputs object contains any values that the
user inputs.
You can retrieve the values from the object
commonEventObject.formInputs.WIDGET_NAME, where
WIDGET_NAME is the name field that you specified for the widget.
The values are returned as a specific data type for the widget.
The following shows a portion of an event object where a user inputted values for each widget:
{
"commonEventObject": { "formInputs": {
"contactName": { "stringInputs": {
"value": ["Kai 0"]
}},
"contactBirthdate": { "dateInput": {
"msSinceEpoch": 1000425600000
}},
"contactType": { "stringInputs": {
"value": ["Personal"]
}}
}}
}
To receive the data, your Chat app handles the event object to get the values that users input into widgets. The following table shows how to get the value for a given form input widget. For each widget, the table shows the data type that the widget accepts, where the value is stored in the event object, and an example value.
| Form input widget | Type of input data | Input value from the event object | Example value |
|---|---|---|---|
textInput |
stringInputs |
event.commonEventObject.formInputs.contactName.stringInputs.value[0] |
Kai O |
selectionInput |
stringInputs |
To get the first or only value, event.commonEventObject.formInputs.contactType.stringInputs.value[0] |
Personal |
dateTimePicker that only accepts dates. |
dateInput |
event.commonEventObject.formInputs.contactBirthdate.dateInput.msSinceEpoch. |
1000425600000 |
After the Chat app receives data, it can do any of the following:
- For cards that contain a multiselect menu, populate or suggest items based on what the user types into the menu.
- Transfer the data to another card, so that the user can review their information or continue to the next section of the form.
- Respond to the user to confirm that the user successfully completed the form.
Suggest multiselect items
If a card contains a multiselect menu that
populates items from an external data source,
the Chat app can return suggested items based on what
users type into the menu. For example, if a user starts typing Atl for a menu
that populates cities in the United States, your
Chat app can autosuggest Atlanta before the user
finishes typing. The Chat app can suggest up to 100
items.
To suggest and dynamically populate items in a multiselect menu, the
SelectionInput widget on the card must specify a
function that queries the external data source. To
return suggested items, the function must do the following:
- Handle an event object, which the Chat app receives when users type into the menu.
- From the event object, get the value that the user types, which is
represented in the
event.commonEventObject.parameters["autocomplete_widget_query"]field. - Query the data source using the user input value to get one or more
SelectionItemsto suggest to the user. - Return suggested items by returning the action
RenderActionswith amodifyCardobject.
The following code sample shows how a Chat app
dynamically suggests items in the multiselect menu on a card. When a user types
into the menu, the function or endpoint provided in the widget's
externalDataSource field queries an external data source, and suggests items
that that the user can select.
Node.js
Replace FUNCTION_URL with the HTTP endpoint that queries
the external data source.
Python
Replace FUNCTION_URL with the HTTP endpoint that queries
the external data source.
Java
Replace FUNCTION_URL with the HTTP endpoint that queries
the external data source.
Apps Script
This example sends a card message by returning card JSON. You can also use the Apps Script card service.
Transfer data to another card
After a user submits information from a card, you might need to return additional cards to do any of the following:
- Help users to complete longer forms by creating distinct sections.
- Let users preview and confirm information from the initial card, so that they can review their answers before submitting.
- Dynamically populate the remaining parts of the form. For example, to prompt users to create an appointment, a Chat app could display an initial card that requests the reason for the appointment, and then populates another card that provides available times based on the appointment type.
To transfer the data input from the initial card, you can build the button
widget with
actionParameters
that contain the widget's name and the value the user inputs, as shown
in the following example:
Node.js
Replace FUNCTION_URL with the HTTP endpoint that handles
the button clicks.
Python
Replace FUNCTION_URL with the HTTP endpoint that handles
the button clicks.
Java
Replace FUNCTION_URL with the HTTP endpoint that handles
the button clicks.
Apps Script
This example sends a card message by returning card JSON. You can also use the Apps Script card service.
When a user clicks the button, your Chat app receives an event object from which you can receive data.
Respond to a form submission
After receiving the data from a card message or dialog, the Chat app responds by either acknowledging receipt or returning an error.
In the following example, a Chat app sends a text message to confirm that it has successfully received a form submitted from a card message.
Node.js
Python
Java
Apps Script
This example sends a card message by returning card JSON. You can also use the Apps Script card service.
To process and close a dialog, you return an
RenderActions
object that specifies whether you want to send a confirmation message, update
the original message or card, or just close the dialog. For steps, see
Close a dialog.
Troubleshoot
When a Google Chat app or card returns an error, the Chat interface surfaces a message saying "Something went wrong." or "Unable to process your request." Sometimes the Chat UI doesn't display any error message, but the Chat app or card produces an unexpected result; for example, a card message might not appear.
Although an error message might not display in the Chat UI, descriptive error messages and log data are available to help you fix errors when error logging for Chat apps is turned on. For help viewing, debugging, and fixing errors, see Troubleshoot and fix Google Chat errors.