الهدف
أرشدك البرنامج التعليمي التحقّق من صحة العناوين ذات الحجم الكبير إلى سيناريوهات مختلفة يمكن فيها استخدام ميزة التحقّق من صحة العناوين ذات الحجم الكبير. في هذا البرنامج التعليمي، سنقدّم لك أنماط تصميم مختلفة ضمن "منصة Google Cloud" لتنفيذ عملية "التحقّق من صحة العناوين" بكميات كبيرة.
سنبدأ بنظرة عامة حول تنفيذ خدمة "التحقّق من صحة العناوين" ذات الحجم الكبير في Google Cloud Platform باستخدام Cloud Run أو Compute Engine أو Google Kubernetes Engine لعمليات التنفيذ لمرة واحدة. سنرى بعد ذلك كيف يمكن تضمين هذه الإمكانية كجزء من مسار نقل البيانات.
في نهاية هذه المقالة، يجب أن يكون لديك فهم جيد للخيارات المختلفة لتنفيذ خدمة "التحقّق من صحة العناوين" بكميات كبيرة في بيئة Google Cloud.
البنية المرجعية على Google Cloud Platform
يتعمّق هذا القسم في أنماط التصميم المختلفة لخدمة High Volume Address Validation باستخدام Google Cloud Platform. من خلال التشغيل على Google Cloud Platform، يمكنك الدمج مع العمليات الحالية وقنوات نقل البيانات.
تشغيل خدمة High Volume Address Validation لمرة واحدة على Google Cloud Platform
في ما يلي بنية مرجعية توضّح كيفية إنشاء عملية دمج على Google Cloud Platform، وهي أكثر ملاءمة للعمليات أو الاختبارات لمرة واحدة.
في هذه الحالة، ننصحك بتحميل ملف CSV إلى حزمة Cloud Storage. يمكن بعد ذلك تشغيل النص البرمجي لخدمة "التحقّق من صحة العناوين" ذات الحجم الكبير من بيئة Cloud Run. ومع ذلك، يمكنك تنفيذها في أي بيئة وقت تشغيل أخرى، مثل Compute Engine أو Google Kubernetes Engine. يمكن أيضًا تحميل ملف CSV الناتج إلى حزمة Cloud Storage.
التشغيل كمسار بيانات في Google Cloud Platform
إنّ نمط النشر الموضّح في القسم السابق مناسب لاختبار خدمة High Volume Address Validation بسرعة عند استخدامها لمرة واحدة. ومع ذلك، إذا كنت بحاجة إلى استخدامها بانتظام كجزء من مسار نقل البيانات، يمكنك الاستفادة بشكل أفضل من الإمكانات الأصلية في Google Cloud Platform لجعلها أكثر فعالية. تشمل بعض التغييرات التي يمكنك إجراؤها ما يلي:
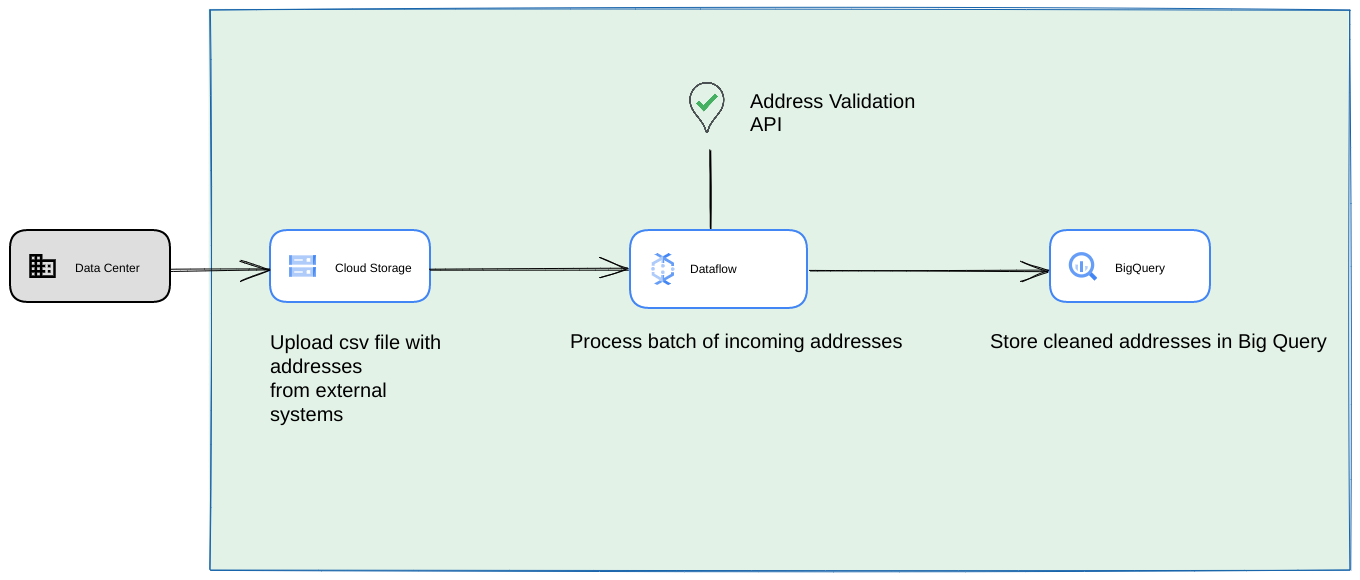
- في هذه الحالة، يمكنك إفراغ ملفات CSV في حِزم Cloud Storage.
- يمكن أن تسترد مهمة Dataflow العناوين المطلوب معالجتها ثم تخزّنها مؤقتًا في BigQuery.
- يمكن توسيع نطاق مكتبة Dataflow Python لتضمين منطق خدمة High Volume Address Validation من أجل التحقّق من صحة العناوين من مهمة Dataflow.
تشغيل النص البرمجي من مسار بيانات كعملية متكررة طويلة الأمد
هناك طريقة شائعة أخرى تتمثل في التحقّق من صحة مجموعة من العناوين كجزء من مسار البيانات المتدفقة كعملية متكررة. قد تكون العناوين أيضًا في مستودع بيانات BigQuery. في هذا النهج، سنرى كيفية إنشاء مسار بيانات متكرّر (يجب تشغيله يوميًا أو أسبوعيًا أو شهريًا).
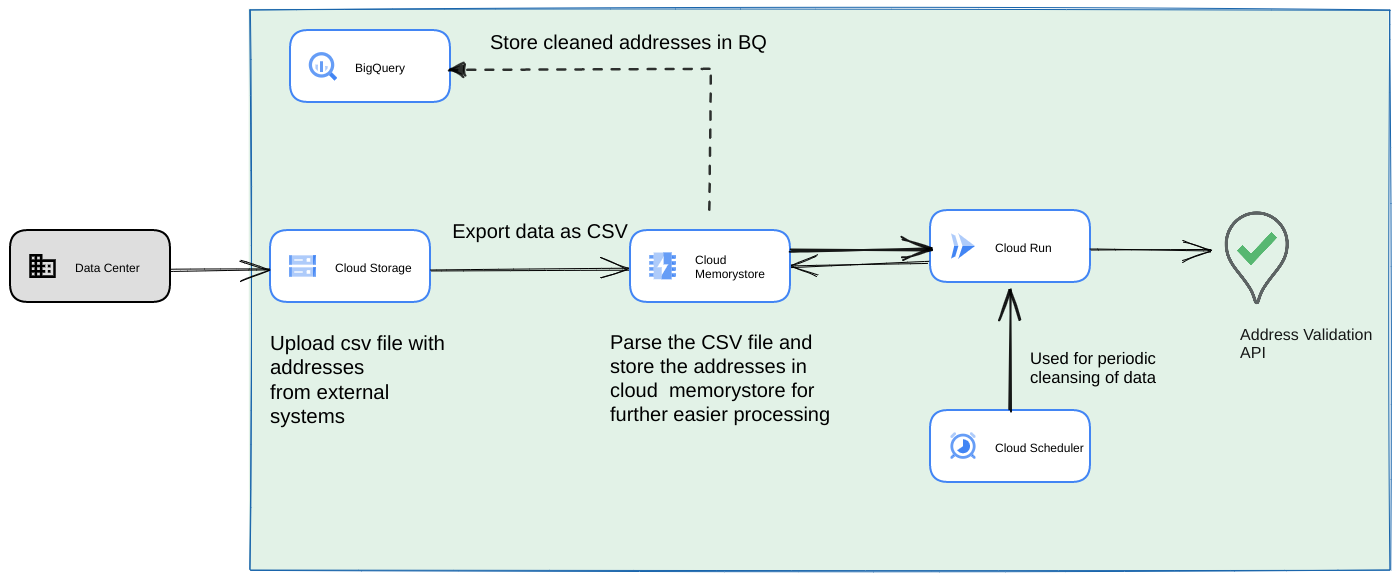
- حمِّل ملف CSV الأوّلي إلى حزمة Cloud Storage.
- استخدِم Memorystore كمخزن بيانات ثابت للحفاظ على الحالة الوسيطة للعملية الطويلة الأمد.
- تخزين العناوين النهائية مؤقتًا في مساحة تخزين بيانات BigQuery
- يمكنك إعداد Cloud Scheduler لتشغيل النص البرمجي بشكل دوري.
تتضمّن هذه البنية المزايا التالية:
- باستخدام Cloud Scheduler، يمكن التحقّق من صحة العناوين بشكل دوري. ننصحك بإعادة التحقّق من صحة العناوين شهريًا أو التحقّق من صحة أي عناوين جديدة شهريًا أو كل ثلاثة أشهر. تساعد هذه البنية في حلّ حالة الاستخدام هذه.
إذا كانت بيانات العملاء في BigQuery، يمكن تخزين العناوين التي تم التحقّق من صحتها أو علامات التحقّق من الصحة مباشرةً هناك. ملاحظة: يتم وصف المحتوى الذي يمكن تخزينه مؤقتًا وكيفية ذلك بالتفصيل في مقالة "التحقّق من صحة العناوين بكميات كبيرة".
يوفّر استخدام Memorystore مرونة أكبر وقدرة على معالجة المزيد من العناوين. تضيف هذه الخطوة حالة إلى مسار المعالجة بأكمله، وهو أمر ضروري للتعامل مع مجموعات بيانات العناوين الكبيرة جدًا. يمكن استخدام تكنولوجيات قواعد البيانات الأخرى، مثل Cloud SQL[https://cloud.google.com/sql] أو أي نوع آخر من قواعد البيانات التي توفّرها "منصة Google Cloud" هنا أيضًا. ومع ذلك، نعتقد أنّ Memorystore perfectless يحقّق التوازن بين احتياجات التوسيع والبساطة، وبالتالي يجب أن يكون الخيار الأول.
الخاتمة
من خلال تطبيق الأنماط الموضّحة هنا، يمكنك استخدام Address Validation API في حالات استخدام مختلفة ومن حالات استخدام مختلفة على Google Cloud Platform.
لقد كتبنا مكتبة Python مفتوحة المصدر لمساعدتك في البدء بحالات الاستخدام الموضّحة أعلاه. يمكن استدعاؤها من سطر أوامر على جهاز الكمبيوتر أو من Google Cloud Platform أو موفّري خدمات سحابية آخرين.
يمكنك الاطّلاع على مزيد من المعلومات حول كيفية استخدام المكتبة من خلال هذه المقالة.
الخطوات التالية
يمكنك تنزيل المستند التعريفي "تحسين عمليات الدفع والتوصيل والعمليات باستخدام عناوين موثوقة" ومشاهدة ندوة "تحسين عمليات الدفع والتوصيل والعمليات باستخدام خدمة التحقّق من صحة العناوين" على الويب.
مقالات مقترَحة للقراءة:
- مستندات Address Validation API
- الترميز الجغرافي والتحقّق من صحة العنوان
- استكشاف العرض التوضيحي لخدمة Address Validation
المساهمون
تتولّى Google صيانة هذه المقالة. كتب المساهمون التاليون هذا المحتوى في الأصل.
المؤلفون الرئيسيون:
هنريك فالف | مهندس حلول
توماس أنغلاريت | مهندس حلول
سارتاك غانغولي | مهندس حلول

