Dokumen ini menunjukkan cara membuat permintaan pertama ke Route Optimization API menggunakan skenario kasus penggunaan di dunia nyata.
Agar lebih sederhana, contoh ini menggunakan HTTP dan JSON untuk mendemonstrasikan REST API. Namun, untuk lingkungan produksi Anda, rekomendasi secara keseluruhan adalah menggunakan gRPC karena manfaat performanya. Namun, gRPC memerlukan penginstalan. Untuk mengetahui informasi selengkapnya, lihat Library klien Route Optimization API.
Skenario
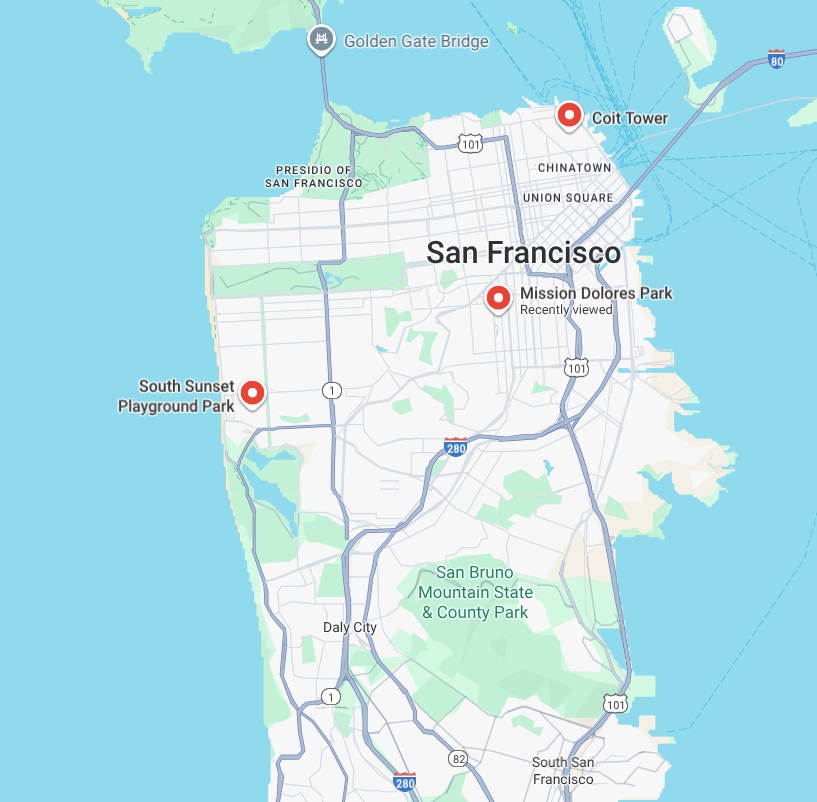
Anda menjalankan layanan penitipan dari pukul 07.00 hingga 19.00 di Jakarta. Pagi ini, Anda harus menjemput dua dari lokasi yang berbeda di kota. Kedua pemilik memberi Anda jangka waktu pengambilan antara pukul 07.30 dan 09.30.
Anda memiliki satu van untuk pekerjaan tersebut, dan Anda membayar pengemudi 27 dolar per jam. Pengemudi dan van memulai hari di pusat penitipan anak Anda pada pukul 07.00 dan harus kembali dari penjemputan pagi pada pukul 12.00 untuk istirahat makan siang.
Hari ini adalah 13 Februari 2024, dan pengemudi memiliki tugas berikut:
- Ambil gunung Bernese di dekat Coit Tower.
- Ambil Chihuahua di South Sunset Playground Park.
- Mengantar kedua ke pusat penitipan di Mission Dolores Park.
Anda memerlukan rute yang meminimalkan waktu yang dihabiskan di dalam van, sekaligus memenuhi persyaratan pengambilan dan pengantaran.
Sebelum memulai
Untuk menjalankan kode dalam contoh skenario ini, Anda harus menyelesaikan petunjuk di Menyiapkan Route Optimization API terlebih dahulu.
1. Memilih pendekatan pengoptimalan rute
Route Optimization API memiliki beberapa metode yang dapat Anda pilih, bergantung pada kompleksitas masalah pengoptimalan Anda.
Karena skenario penitipan ini adalah permintaan kecil dan sederhana, gunakan
metode pemblokiran, seperti optimizeTours, yang dengan cepat memberikan hasil
untuk permintaan kecil. Untuk mengetahui informasi selengkapnya tentang metode Route Optimization API, lihat Endpoint sinkron dan asinkron.
Gunakan URL berikut untuk membuat permintaan POST HTTP ke metode optimizeTours:
https://routeoptimization.googleapis.com/v1/projects/PROJECT_OR_ID:optimizeTours
Anda juga perlu menyetel waktu tunggu dan setelan batas waktu menjadi singkat untuk mengurangi waktu tunggu yang tidak perlu. Untuk skenario penitipan ini, pengoptimal tidak memerlukan banyak waktu untuk merespons permintaan Anda, jadi gunakan setelan berikut:
- Tetapkan parameter
timeoutke 2 detik. - Biarkan setelan batas waktu pada default, yaitu 60 detik untuk permintaan REST.
2. Membuat isi pesan permintaan
Setelah memilih metode optimizeTours pemblokiran dan menentukan setelan waktu tunggu dan batas waktu, langkah selanjutnya adalah membuat isi pesan permintaan.
Untuk skenario ini, permintaan adalah pesan OptimizeToursRequest yang dienkode sebagai JSON di REST API.
Untuk membuat pesan permintaan, ikuti langkah-langkah berikutnya:
Mulai dengan struktur permintaan dasar, yang adalah sebagai berikut:
{ "timeout": ..., "model": { "shipments": [...], "vehicles": [...], "globalStartTime": "...", "globalEndTime": "..." } }Untuk mengetahui informasi selengkapnya tentang struktur, lihat panduan konsep utama untuk Struktur dasar (ShipmentModel, Shipment, dan Vehicle).
Tentukan pengiriman. Di kolom
shipments, tambahkan pesanShipmentuntuk setiap yang perlu dijemput dan diantar pada pagi hari. Di sinilah Anda menentukan setiap lokasi dan waktu pilihan pemilik untuk mengambil anjingnya, serta lokasi dan waktu pusat penitipan untuk mengantarkan.Untuk setiap, buat
VisitRequestuntuk pengambilan dan satu lagi untuk pengiriman, yang dalam skenario ini disebut sebagai pengantaran di tempat penitipan.Dalam pengambilan, tetapkan
arrivalWaypointke lokasi pengambilan (Coit Tower untuk gunung Bernese atau South Sunset Playground Park untuk Chihuahua) dantimeWindowske waktu pengambilan yang diminta pemilik (07.30 hingga 09.30).Dalam pengiriman, tetapkan
arrivalWaypointke pusat penitipan anak dantimeWindowsuntuk waktu pengantaran yang diperlukan (09.30 hingga 11.30).
Untuk mengetahui informasi selengkapnya tentang periode waktu, lihat Periode waktu.
Anda dapat menggunakan kolom
labeluntuk menambahkan ID untuk setiap pengiriman, seperti " gunung Bernese" dan "Chihuahua". Hal ini dapat membantu Anda mengidentifikasi pengiriman dalam respons.
Untuk mengetahui informasi selengkapnya tentang cara menentukan pengiriman, lihat Pengiriman.
Tentukan kendaraan. Di kolom
vehicles, tambahkan pesanVehicleuntuk satu van Anda dengan pusat penitipan anak sebagai titik awal dan akhir, biaya upah pengemudi, dan jam operasional van.Tetapkan
startWaypointdanendWaypointuntuk van ke lokasi awal dan akhir hari, yaitu pusat penitipan anak di dekat Mission Dolores Park.Untuk meminimalkan biaya operasi, Anda harus menentukan batasan biaya bisnis Anda. Tetapkan parameter biaya
costPerHourke 27, yaitu jumlah yang Anda bayar kepada pengemudi untuk mengemudikan van penitipan. Untuk mengetahui informasi selengkapnya tentang parameter biaya, lihat Model biaya.Untuk memastikan pengoptimal membuat rute dalam jam operasional van, tentukan
startTimeWindowske rentang yang dapat diterima bagi pengemudi untuk mulai mengoperasikan van danendTimeWindowske rentang yang dapat diterima bagi pengemudi untuk kembali ke pusat penitipan anak. Untuk mengetahui informasi selengkapnya tentang periode waktu, lihat Periode waktu.
Untuk mengetahui informasi selengkapnya tentang cara menentukan kendaraan, lihat Kendaraan.
Tetapkan jangka waktu global. Jendela waktu global mewakili jangka waktu saat van dapat melakukan penjemputan dan pengantaran untuk penitipan anak Anda sepanjang hari. Untuk skenario ini, setel
globalStartTimeke pukul 07.00 danglobalEndTimeke pukul 19.00 untuk 13 Februari 2024, yang mewakili jam operasional penitipan Anda.
3. Kirim permintaan
Berikut adalah permintaan curl sederhana berdasarkan skenario penitipan
dan menggunakan metode optimizeTours pemblokiran.
Sebelum mengirim permintaan, ganti PROJECT_NUMBER_OR_ID dalam kode contoh dengan project ID Google Cloud Anda.
curl -X POST 'https://routeoptimization.googleapis.com/v1/projects/PROJECT_NUMBER_OR_ID:optimizeTours' \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth application-default print-access-token)" \
--data @- << EOM
{
"timeout": "2s",
"model": {
"shipments": [
{
"pickups": [
{
"arrivalWaypoint": {
"location": {
"latLng": {
"latitude": 37.802395,
"longitude": -122.405822
}
}
},
"timeWindows": [
{
"startTime": "2024-02-13T07:30:00Z",
"endTime": "2024-02-13T09:30:00Z"
}
]
}
],
"deliveries": [
{
"arrivalWaypoint": {
"location": {
"latLng": {
"latitude": 37.760202,
"longitude": -122.426796
}
}
},
"timeWindows": [
{
"startTime": "2024-02-13T09:30:00Z",
"endTime": "2024-02-13T11:30:00Z"
}
]
}
],
"label": "Bernese mountain dog"
},
{
"pickups": [
{
"arrivalWaypoint": {
"location": {
"latLng": {
"latitude": 37.738067,
"longitude": -122.498593
}
}
},
"timeWindows": [
{
"startTime": "2024-02-13T07:30:00Z",
"endTime": "2024-02-13T09:30:00Z"
}
]
}
],
"deliveries": [
{
"arrivalWaypoint": {
"location": {
"latLng": {
"latitude": 37.760202,
"longitude": -122.426796
}
}
},
"timeWindows": [
{
"startTime": "2024-02-13T09:30:00Z",
"endTime": "2024-02-13T11:30:00Z"
}
]
}
],
"label": "Chihuahua"
}
],
"vehicles": [
{
"startWaypoint": {
"location": {
"latLng": {
"latitude": 37.760202,
"longitude": -122.426796
}
}
},
"endWaypoint": {
"location": {
"latLng": {
"latitude": 37.760202,
"longitude": -122.426796
}
}
},
"costPerHour": 27,
"startTimeWindows": [
{
"startTime": "2024-02-13T07:00:00Z",
"endTime": "2024-02-13T07:15:00Z"
}
],
"endTimeWindows": [
{
"startTime": "2024-02-13T11:45:00Z",
"endTime": "2024-02-13T12:00:00Z"
}
]
}
],
"globalStartTime": "2024-02-13T07:00:00Z",
"globalEndTime": "2024-02-13T19:00:00Z"
}
}
EOM
Parameter permintaan yang digunakan dalam permintaan
Tabel berikut menjelaskan parameter permintaan yang digunakan dalam isi permintaan skenario contoh. Anda dapat memfilter konten menurut induk atau menurut penelusuran teks.
| Orang tua | Parameter | Jenis Properti | Deskripsi |
|---|---|---|---|
OptimizeToursRequest |
model |
objek (ShipmentModel) |
Ini adalah inti permintaan Anda. Objek ini adalah satu objek tempat Anda
menentukan seluruh masalah Anda, termasuk semua yang perlu Anda ambil dan
antar (shipments)
dan van dalam armada Anda
(vehicles).
Anggap saja ini sebagai cetak biru lengkap untuk masalah yang perlu Anda optimalkan. |
timeout |
Durasi | Parameter ini menentukan waktu maksimum server memproses permintaan sebelum menampilkan respons. Gunakan parameter ini untuk mempersingkat waktu tunggu Anda. Untuk permintaan kecil dan cepat, seperti skenario penitipan ini, tetapkan nilai ini ke 2 detik. | |
ShipmentModel |
shipments[] |
array objek (Shipment) |
Ini adalah array objek yang setiap objeknya merepresentasikan yang perlu diambil atau diantar. |
vehicles[] |
array objek (Vehicle) |
Ini adalah array objek yang setiap objeknya menentukan kendaraan dalam armada Anda. Di sini Anda mendeskripsikan resource, seperti van yang melakukan pengambilan dan pengantaran. Anda harus menentukan setidaknya satu kendaraan untuk mendapatkan rute yang dioptimalkan. | |
globalStartTime |
Stempel waktu | Ini adalah waktu paling awal yang memungkinkan untuk terjadinya peristiwa apa pun dalam seluruh model Anda. Parameter ini mempersempit masalah pengoptimalan dari waktu ke waktu, yang sangat penting untuk penghitungan traffic dan perutean yang akurat. Untuk skenario penitipan ini, tetapkan ini ke waktu paling awal pengemudi dapat mengoperasikan van untuk hari itu, yaitu pukul 07.00 untuk 13 Februari 2024. | |
globalEndTime |
Stempel waktu | Ini adalah waktu paling akhir yang memungkinkan untuk terjadinya peristiwa apa pun dalam seluruh model Anda. Untuk skenario penitipan ini, tetapkan waktu saat van diperkirakan akan mengakhiri operasinya, yaitu pukul 19.00 pada 13 Februari 2024. | |
Shipment |
pickups[] |
array objek (VisitRequest) |
Ini adalah daftar semua opsi pengambilan yang mungkin untuk pengiriman. Pengoptimal memilih yang terbaik untuk memecahkan masalah Anda. Untuk skenario penitipan ini, cantumkan lokasi pengambilan dan jangka waktu yang diberikan setiap pemilik untuk setiap. |
deliveries[] |
array objek (VisitRequest) |
Ini adalah daftar semua kemungkinan opsi pengantaran untuk pengiriman. Pengoptimal memilih yang terbaik untuk memecahkan masalah Anda. Untuk skenario penitipan ini, cantumkan lokasi fasilitas penitipan dan jangka waktu saat pengemudi perlu kembali untuk makan siang untuk setiap. | |
label |
string | Ini adalah ID untuk pengiriman tertentu dalam permintaan Anda. Anda dapat menentukan label dalam permintaan untuk mempermudah membaca respons. Untuk skenario penitipan ini, gunakan string deskriptif seperti "Chihuahua", "Bernese mountain dog", atau nama untuk mencocokkan solusi dengan input Anda saat Anda menerima respons API. | |
VisitRequest |
arrivalWaypoint[] |
objek (Waypoint) |
Ini adalah lokasi kunjungan tertentu di rute. Anda dapat menentukan hal ini
menggunakan koordinat lintang dan bujur, ID tempat, atau arah tujuan. Dalam
skenario penitipan ini, tetapkan ini ke lokasi yang diberikan oleh pemilik untuk
pickups
dan ke alamat pusat penitipan untuk
deliveries. |
timeWindows[] |
array objek (TimeWindow) |
Ini adalah array objek yang menentukan batasan waktu untuk pengambilan atau pengiriman. Untuk skenario ini, gunakan ini untuk menentukan jangka waktu pengambilan untuk setiap dan jangka waktu yang dapat diterima untuk mengantar ke pusat penitipan. | |
Vehicle |
startWaypoint[] |
objek (Waypoint) |
Ini adalah lokasi awal rute kendaraan, yang ditentukan dengan koordinat lintang dan bujur atau ID tempat. Parameter ini memberi tahu pengoptimal tempat kendaraan harus memulai rute. Jika Anda tidak menentukan titik jalan ini, pengoptimal akan memilih salah satu lokasi pengambilan atau pengiriman sebagai lokasi awal. Untuk skenario penitipan ini, karena pengemudi memulai hari di fasilitas penitipan, gunakan koordinat Mission Dolores Park. |
endWaypoint[] |
objek (Waypoint) |
Ini adalah tujuan akhir untuk rute kendaraan, yang ditentukan dengan koordinat lintang dan bujur atau ID tempat. Parameter ini memberi tahu pengoptimal tempat kendaraan harus mengakhiri rute. Jika Anda tidak menentukan titik jalan ini, pengoptimal akan memilih salah satu pengambilan atau pengiriman sebagai akhir rute. Untuk skenario penitipan ini, karena pengemudi harus mengakhiri hari di fasilitas penitipan, gunakan koordinat Mission Dolores Park. | |
costPerHour |
angka | Ini adalah biaya yang dikeluarkan untuk setiap jam penggunaan kendaraan, terlepas dari apakah kendaraan sedang berjalan atau berhenti. Untuk skenario penitipan ini, gunakan ini untuk memodelkan upah per jam pengemudi. | |
startTimeWindows[] |
array objek (TimeWindow) |
Ini adalah rentang waktu yang dapat diterima bagi pengemudi untuk mulai mengemudikan van untuk penjemputan pada pagi hari. | |
endTimeWindows[] |
array objek (TimeWindow) |
Ini adalah jangka waktu yang dapat diterima bagi pengemudi untuk menyelesaikan mengemudikan van dan parkir kembali di pusat penitipan. |
