Web Receiver SDK 使用内置的媒体播放器来提供无缝且简单的 。它还为 Google 助理提供开箱即用型支持 作为 Cast 专用功能,所有发送器和 触控设备。随着新功能的发布 无需对发件人进行其他更改即可。
自定义网络接收器是一个定制的 HTML5 应用,必须托管在 在支持 Cast 的设备上显示您的内容。您可能需要创建自定义 Web Receiver(取决于您的业务需求)。如需有关确定接收者的帮助 类型,请参阅 选择一份 Web 接收器指南。
Google Web Receiver SDK
您的 Web 接收器应用使用以下项访问 Web Receiver API 参考:
<script src="//www.gstatic.com/cast/sdk/libs/caf_receiver/v3/cast_receiver_framework.js"></script>
网址协议最佳做法:请注意,上面的网址没有指定
“http:”或“https:”协议。在获取
“cast_receiver_framework.js”资源允许使用以下规则提取此资源:
使用与托管网络接收器应用的服务器相同的协议。这意味着
在开发用的 HTTP 和生产用的 HTTPS 之间切换是透明的
无需更改代码。(必须托管已发布的 Web Receiver 应用
。)
SDK 预览
预发布版本的 Cast Web Receiver SDK 也可用于 测试非正式版应用。详细了解 SDK 预览网址 (网址为 Google Cast Web Receiver SDK Preview 网址)。
应用生命周期
Web Receiver 应用的生命周期从 Web Receiver 的生命周期开始 然后一直进行到 并且 Cast 设备会还原为其默认状态。
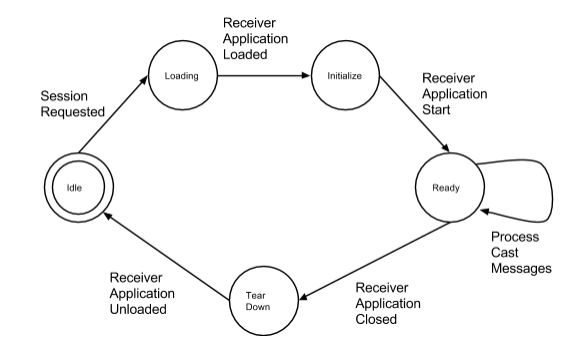
在网络接收器应用的整个生命周期内, Web Receiver 和所有已连接的发送器应用。发送者应用将 向 Google Cast 设备发送一条初始消息,请求创建会话 使用特定的应用 ID。这就开始了网络接收器的生命周期,因为 Google Cast 设备将尝试加载网络接收器应用。假设 没有网络问题,系统会从网络下载 Web Receiver 应用 使用与应用 ID 关联的解析网址。加载完成后,Web Receiver 会 应用将执行其设置操作,并指明其已可处理 来自任何已连接的发件人应用的邮件。
Web 接收器应用可能会自行崩溃(终止其当前生命周期并关闭 应用)执行以下操作:
- Web 接收器应用会收到上次连接的明确消息 发送人来结束应用会话。
- Web Receiver 应用已闲置一定时间,没有任何活动 连接发送者并决定结束应用会话。
- 启动了其他投放会话。
- Web Receiver 在其正常生命周期内遇到严重错误。
Web Receiver SDK 会按照我们的 用户体验指南。
主要课程
Web Receiver SDK 框架有 2 个主要类:
cast.framework.CastReceiverContext- 管理员 并加载所有必要的库。借助此对象,您可以:- 设置应用配置选项
- 处理系统事件(例如发送者连接或断开连接)
- 创建自定义渠道
- 启动投屏通信
cast.framework.PlayerManager- 管理媒体 。它会根据 请求。借助此对象,您可以:- 处理播放操作
- 处理来自发送者的播放相关请求
- 处理与播放相关的事件
注册网络接收器应用
在开发 Web Receiver 应用之前,您需要 包含 Google Cast SDK Developer Console 的接收器应用。请参阅 注册以了解详情。所有网络接收器 应用要求发送者的应用为命令消息提供应用 ID 向网络接收器发送数据当您注册 Web 应用 接收方应用,您将收到要添加到发送者的 API 调用。
创建基本的 Web 接收器应用
以下是基本 Web 接收器应用的主要结构,它没有 自定义:
- 用于表示媒体播放器的
cast-media-playerHTML 元素。 - 用于加载网络接收器框架的脚本 HTML 元素。
- 致电
start()启动 Web Receiver 应用,且不选择任何选项。
以下是使用 Cast 应用的网络接收器应用所需的最低代码 框架,无需任何自定义。您可以将此脚本直接复制并粘贴到 以便创建 Web 接收器应用
<html>
<head>
<script type="text/javascript"
src="//www.gstatic.com/cast/sdk/libs/caf_receiver/v3/cast_receiver_framework.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<cast-media-player></cast-media-player>
<script>
cast.framework.CastReceiverContext.getInstance().start();
</script>
</body>
</html>
此时,用户可以打开发送器应用,连接到 Cast 设备, 然后找到媒体并按“播放”,这会指示网络接收器流式传输 将媒体传输到电视上以供用户观看。
将此基本网络接收器与 自定义的接收器应用。
媒体和播放器
Cast 框架提供了一个内置的媒体播放器,由
cast-media-player HTML 元素。此媒体播放器支持播放
流式传输协议,例如 MPEG-DASH、HLS 和 Smooth Streaming。
下面列出了一组受支持的媒体编解码器和容器:
支持的媒体。通过 Cast 消息传递功能,开发者可以
支持一系列发送者发起的操作,例如加载、播放、暂停和
而 Cast SDK 会处理与媒体的交互。有关
请参阅您应用平台的发送者 API 参考资料:
Android Sender 中的 RemoteMediaClient、
iOS 发件人中的 GCKMediaControlChannel
和
Web Sender 中的Media。
跨源资源共享
Google Cast 完全支持跨域资源共享 (CORS)。流式传输
协议与大多数基于文件的协议不同,
使用 XMLHttpRequest 实现。在 CORS 环境中,这些请求会受到
CORS 标头针对资源所在的服务器进行的不当访问,
来源。这意味着,您的内容的服务器对可能出现的位置有决定权。
包括在内。大多数现代浏览器都完全支持 CORS。iOS 和 Android 设备
访问较低级别的内容,无需查看这些标头。这是
这通常是开发者想要使用流式传输时遇到的第一个问题
内容。如需了解更多详情,请参阅跨域资源共享。
。