データの入手
収集した位置情報を取得する方法は多数あります。ここでは、Roads API の道路にスナップ機能で使用するデータを取得する 2 つの手法について説明します。
GPX
GPX は、GPS デバイスで取得したルート、トラック、ウェイポイントを共有するためのオープンな XML ベースの形式です。この例では、Java サーバーとモバイル環境の両方で使用できる軽量の XML パーサーである XmlPull パーサーを使用します。
/** * Parses the waypoint (wpt tags) data into native objects from a GPX stream. */ private List<LatLng> loadGpxData(XmlPullParser parser, InputStream gpxIn) throws XmlPullParserException, IOException { // We use a List<> as we need subList for paging later List<LatLng> latLngs = new ArrayList<>(); parser.setInput(gpxIn, null); parser.nextTag(); while (parser.next() != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) { if (parser.getEventType() != XmlPullParser.START_TAG) { continue; } if (parser.getName().equals("wpt")) { // Save the discovered latitude/longitude attributes in each <wpt>. latLngs.add(new LatLng( Double.valueOf(parser.getAttributeValue(null, "lat")), Double.valueOf(parser.getAttributeValue(null, "lon")))); } // Otherwise, skip irrelevant data } return latLngs; }
地図に読み込まれた GPX 生データは次のようになります。
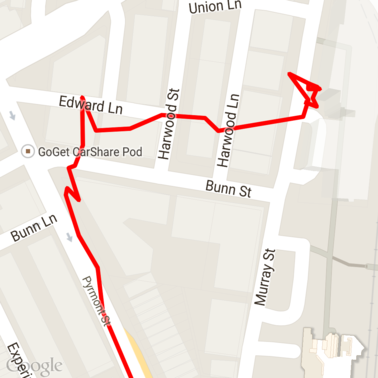
Android 位置情報サービス
Android デバイスから GPS データを取得する最適な方法は、ユースケースによって異なります。位置情報の更新を受け取るに関する Android トレーニング クラスと、GitHub の Google Play 位置情報サンプルをご覧ください。
長いパスを処理する
道路へのスナップ機能は、個々のポイントではなく、完全なパスに基づいて位置を推測するため、長いパス(リクエストあたり 100 ポイントの制限を超えるパス)を処理する場合は注意が必要です。
個々のリクエストを 1 つの長いパスとして扱うには、前のリクエストの最終地点が次のリクエストの最初の地点として含まれるように、ある程度の重複を含める必要があります。含めるポイントの数は、データの精度によって異なります。精度の低いリクエストでは、より多くのポイントを含める必要があります。
この例では、Google Maps Services 用 Java クライアントを使用してページングされたリクエストを送信し、補間されたポイントを含むデータを返されたリストに結合します。
/** * Snaps the points to their most likely position on roads using the Roads API. */ private List<SnappedPoint> snapToRoads(GeoApiContext context) throws Exception { List<SnappedPoint> snappedPoints = new ArrayList<>(); int offset = 0; while (offset < mCapturedLocations.size()) { // Calculate which points to include in this request. We can't exceed the API's // maximum and we want to ensure some overlap so the API can infer a good location for // the first few points in each request. if (offset > 0) { offset -= PAGINATION_OVERLAP; // Rewind to include some previous points. } int lowerBound = offset; int upperBound = Math.min(offset + PAGE_SIZE_LIMIT, mCapturedLocations.size()); // Get the data we need for this page. LatLng[] page = mCapturedLocations .subList(lowerBound, upperBound) .toArray(new LatLng[upperBound - lowerBound]); // Perform the request. Because we have interpolate=true, we will get extra data points // between our originally requested path. To ensure we can concatenate these points, we // only start adding once we've hit the first new point (that is, skip the overlap). SnappedPoint[] points = RoadsApi.snapToRoads(context, true, page).await(); boolean passedOverlap = false; for (SnappedPoint point : points) { if (offset == 0 || point.originalIndex >= PAGINATION_OVERLAP - 1) { passedOverlap = true; } if (passedOverlap) { snappedPoints.add(point); } } offset = upperBound; } return snappedPoints; }
道路へのスナップ リクエストを実行した後の上記のデータは次のとおりです。赤い線は元データ、青い線はスナップされたデータです。
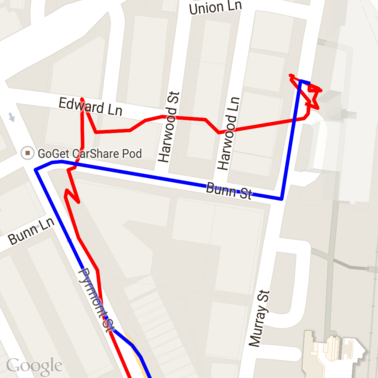
割り当ての効率的な使用
道路にスナップ リクエストのレスポンスには、指定したポイントにマッピングされる場所 ID のリストが含まれます。interpolate=true を設定した場合は、追加のポイントが含まれる可能性があります。
制限速度リクエストの割り当てを効率的に使用するには、リクエストで一意のプレイス ID のみをクエリする必要があります。この例では、Google Maps Services 用の Java クライアントを使用して、プレイス ID のリストから制限速度をクエリしています。
/** * Retrieves speed limits for the previously-snapped points. This method is efficient in terms * of quota usage as it will only query for unique places. * * Note: Speed limit data is only available for requests using an API key enabled for a * Google Maps APIs Premium Plan license. */ private Map<String, SpeedLimit> getSpeedLimits(GeoApiContext context, List<SnappedPoint> points) throws Exception { Map<String, SpeedLimit> placeSpeeds = new HashMap<>(); // Pro tip: Save on quota by filtering to unique place IDs. for (SnappedPoint point : points) { placeSpeeds.put(point.placeId, null); } String[] uniquePlaceIds = placeSpeeds.keySet().toArray(new String[placeSpeeds.keySet().size()]); // Loop through the places, one page (API request) at a time. for (int i = 0; i < uniquePlaceIds.length; i += PAGE_SIZE_LIMIT) { String[] page = Arrays.copyOfRange(uniquePlaceIds, i, Math.min(i + PAGE_SIZE_LIMIT, uniquePlaceIds.length)); // Execute! SpeedLimit[] placeLimits = RoadsApi.speedLimits(context, page).await(); for (SpeedLimit sl : placeLimits) { placeSpeeds.put(sl.placeId, sl); } } return placeSpeeds; }
上のデータに、各一意の場所 ID の制限速度をマークしたものがこちらです。
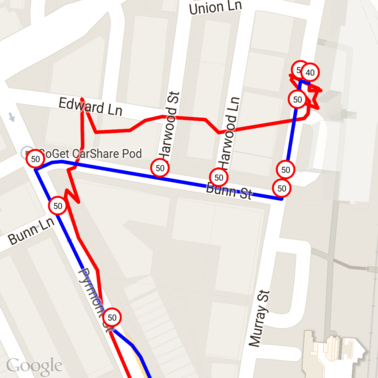
他の API との連携
道路へのスナップ レスポンスでプレイス ID が返されるメリットの 1 つは、多くの Google Maps Platform API でプレイス ID を使用できることです。この例では、Google マップ サービス用 Java クライアントを使用して、上記の道路へのスナップ リクエストから返された場所をジオコーディングします。
/** * Geocodes a snapped point using the place ID. */ private GeocodingResult geocodeSnappedPoint(GeoApiContext context, SnappedPoint point) throws Exception { GeocodingResult[] results = GeocodingApi.newRequest(context) .place(point.placeId) .await(); if (results.length > 0) { return results[0]; } return null; }
ここでは、制限速度マーカーに Geocoding API からの住所がアノテーションされています。
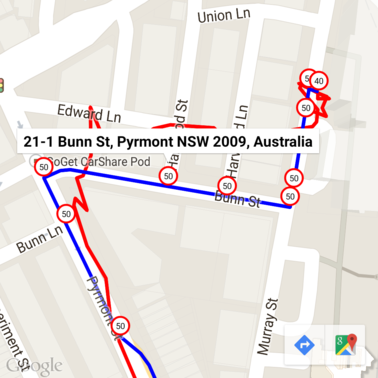
サンプルコード
考慮事項
このドキュメントをサポートするコードは、例示目的で単一の Android アプリとして提供されています。実際には、サードパーティからの不正アクセスから鍵を保護できないため、サーバーサイドの API キーを Android アプリで配布しないでください。代わりに、キーを保護するには、API 向けコードをサーバーサイド プロキシとしてデプロイし、Android アプリがプロキシを使用してリクエストを送信するようにして、リクエストが確実に承認されるようにする必要があります。
ダウンロード
GitHub からコードをダウンロードします。
