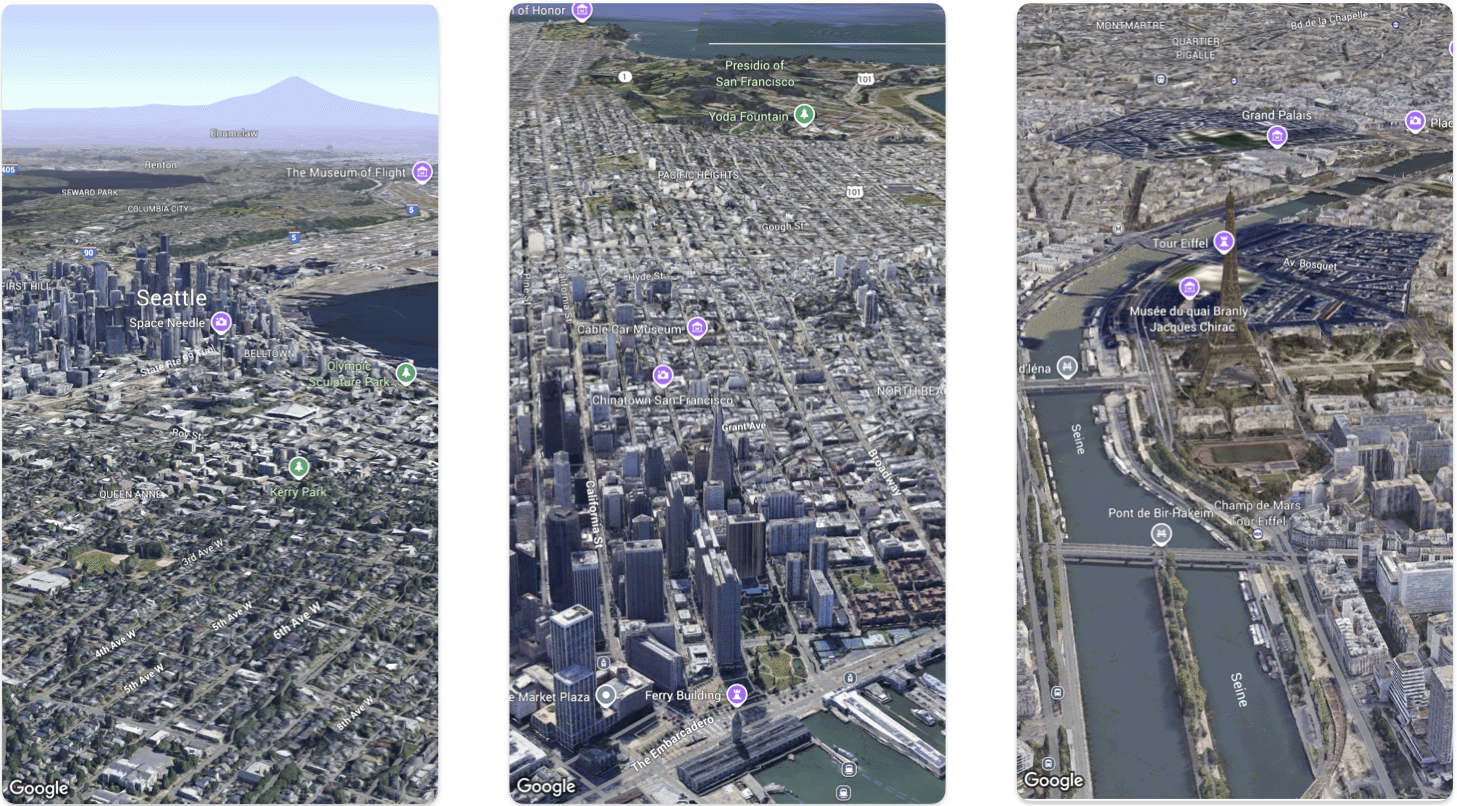
Cette page présente un exemple d'ajout d'une carte 3D de base à une application iOS à l'aide du SDK Maps 3D pour iOS. Les instructions figurant sur cette page supposent que vous avez déjà suivi les étapes de la page Configuration et que vous disposez des éléments suivants :
- Un projet Google Cloud avec le SDK Maps 3D pour iOS activé
- Clé API SDK Maps 3D pour iOS
- Xcode version 16.0 ou ultérieure avec le package SDK Maps 3D pour iOS ajouté.
Pour en savoir plus sur ces prérequis, consultez Configuration.
Suivez un atelier de programmation plus avancé.
Consultez d'autres exemples de code sur GitHub.
Partie 1 : Créer une application SwiftUI de base
- Créez une application dans Xcode.
- Définissez Product Name sur
Hello3DWorld, avec l'identifiant de l'organisation défini surcom.example. Le nom du package doit êtrecom.example.Hello3DWorld. - Choisissez l'interface SwiftUI.
- Ajoutez la bibliothèque Maps 3D à votre application. Consultez les instructions dans la section de configuration.
Partie 2 : Ajouter une carte
Ouvrez le fichier nommé
ContentView.swift. Il s'agit du point d'entrée et de la navigation principale de votre application.Importez
SwiftUIet le packageGoogleMaps3D.Remplacez tout le code à l'intérieur de la déclaration du corps par Map(mode: .hybrid).
La configuration initiale minimale que vous devez fournir pour initialiser un
Mapest leMapMode:- .hybrid ou
- .satellite
Votre fichier
ContentView.swiftdevrait se présenter comme suit :import SwiftUI import GoogleMaps3D struct ContentView: View { var body: some View { Map(mode: .hybrid) } } #Preview { ContentView() }
Partie 3 : Définissez votre clé API.
La clé API doit être définie avant l'initialisation de la carte. Pour ce faire, définissez
Map.apiKeydans le gestionnaire d'événementsinit()duViewcontenant la carte.import SwiftUI import GoogleMaps3D struct ContentView: View { init () { Map.apiKey = "YOUR_API_KEY" } var body: some View { Map(mode: .hybrid) } }
Partie 4 : Utiliser une caméra pour contrôler la vue de la carte
Les vues de carte 3D sont contrôlées par la classe Camera. Dans cette étape, vous allez apprendre à spécifier la position, l'altitude, le cap, l'inclinaison, le roulis et la distance pour personnaliser la vue de la carte.
Modifiez l'appel de fonction
Map()pour inclure une propriétéinitialCamera. InitialisezinitialCamerapour afficher une vue du centre-ville de Manhattan.import SwiftUI import GoogleMaps3D struct ContentView: View { init () { Map.apiKey = "YOUR_API_KEY" } var body: some View { Map(initialCamera: .init( latitude: 40.748339, longitude: -73.985912, altitude: 211.1, heading: 52, tilt: 68, range: 1039 ), mode: .hybrid) } }
Le code ci-dessus définit des valeurs pour les paramètres suivants :
heading: cap en degrés depuis le nord vers lequel pointer la caméra.tilt: angle d'inclinaison en degrés, où 0 correspond à une vue directement au-dessus et 90 à une vue horizontale.roll: angle de roulis autour du plan vertical de la caméra, en degrés.range: distance en mètres de la caméra par rapport à la latitude et à la longitudealtitude: hauteur de la caméra au-dessus du niveau de la mer.
Si vous ne fournissez aucun de ces paramètres supplémentaires, une valeur par défaut sera utilisée.
Pour que la vue de la caméra affiche davantage de données 3D, définissez les paramètres initiaux de manière à afficher une vue plus rapprochée et inclinée.
Partie 6 : Prévisualiser et exécuter votre application

Ajouter un aperçu Xcode
Les aperçus sont une fonctionnalité puissante d'Xcode qui vous permet de voir votre application et d'interagir avec elle sans avoir à utiliser le simulateur ni un appareil externe.
Pour ajouter un aperçu, ajoutez un bloc de code
#Preview {}en dehors de votre struct.#Preview { CameraDemo() }Exécuter l'application
Créez et exécutez l'application.
Félicitations !
Vous avez bien ajouté une carte 3D à une application.
Vous pouvez ensuite explorer les fonctionnalités avancées du SDK Maps 3D pour iOS, comme les animations de chemin de caméra, les repères 3D ou les polygones.
