Dowiedz się, jak znaleźć bieżącą lokalizację urządzenia z Androidem i wyświetlić szczegóły miejsca (firmy lub innego ważnego miejsca) w tej lokalizacji. Postępuj zgodnie z tym samouczkiem, aby utworzyć aplikację na Androida za pomocą Maps SDK na Androida, Places SDK na Androida i zintegrowanego dostawcy lokalizacji w interfejsach API lokalizacji usług Google Play.
Pobierz kod
Sklonuj lub pobierz repozytorium przykładów Google Maps Android API v2 z GitHuba.
Wyświetl wersję działania w Javie:
// Copyright 2020 Google LLC // // Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); // you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. // You may obtain a copy of the License at // // http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 // // Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software // distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, // WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. // See the License for the specific language governing permissions and // limitations under the License. package com.example.currentplacedetailsonmap; import android.content.DialogInterface; import android.content.pm.PackageManager; import android.location.Location; import android.os.Bundle; import android.util.Log; import android.view.Menu; import android.view.MenuItem; import android.view.View; import android.widget.FrameLayout; import android.widget.TextView; import androidx.annotation.NonNull; import androidx.appcompat.app.AlertDialog; import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import androidx.core.app.ActivityCompat; import androidx.core.content.ContextCompat; import com.google.android.gms.location.FusedLocationProviderClient; import com.google.android.gms.location.LocationServices; import com.google.android.gms.maps.CameraUpdateFactory; import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap; import com.google.android.gms.maps.OnMapReadyCallback; import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.CameraPosition; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.LatLng; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Marker; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.MarkerOptions; import com.google.android.gms.tasks.OnCompleteListener; import com.google.android.gms.tasks.Task; import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.Places; import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.model.Place; import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.model.PlaceLikelihood; import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.net.FindCurrentPlaceRequest; import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.net.FindCurrentPlaceResponse; import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.net.PlacesClient; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; /** * An activity that displays a map showing the place at the device's current location. */ public class MapsActivityCurrentPlace extends AppCompatActivity implements OnMapReadyCallback { private static final String TAG = MapsActivityCurrentPlace.class.getSimpleName(); private GoogleMap map; private CameraPosition cameraPosition; // The entry point to the Places API. private PlacesClient placesClient; // The entry point to the Fused Location Provider. private FusedLocationProviderClient fusedLocationProviderClient; // A default location (Sydney, Australia) and default zoom to use when location permission is // not granted. private final LatLng defaultLocation = new LatLng(-33.8523341, 151.2106085); private static final int DEFAULT_ZOOM = 15; private static final int PERMISSIONS_REQUEST_ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION = 1; private boolean locationPermissionGranted; // The geographical location where the device is currently located. That is, the last-known // location retrieved by the Fused Location Provider. private Location lastKnownLocation; // Keys for storing activity state. private static final String KEY_CAMERA_POSITION = "camera_position"; private static final String KEY_LOCATION = "location"; // Used for selecting the current place. private static final int M_MAX_ENTRIES = 5; private String[] likelyPlaceNames; private String[] likelyPlaceAddresses; private List[] likelyPlaceAttributions; private LatLng[] likelyPlaceLatLngs; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // Retrieve location and camera position from saved instance state. if (savedInstanceState != null) { lastKnownLocation = savedInstanceState.getParcelable(KEY_LOCATION); cameraPosition = savedInstanceState.getParcelable(KEY_CAMERA_POSITION); } // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps); // Construct a PlacesClient Places.initialize(getApplicationContext(), BuildConfig.PLACES_API_KEY); placesClient = Places.createClient(this); // Construct a FusedLocationProviderClient. fusedLocationProviderClient = LocationServices.getFusedLocationProviderClient(this); // Build the map. SupportMapFragment mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager() .findFragmentById(R.id.map); mapFragment.getMapAsync(this); } /** * Saves the state of the map when the activity is paused. */ @Override protected void onSaveInstanceState(Bundle outState) { if (map != null) { outState.putParcelable(KEY_CAMERA_POSITION, map.getCameraPosition()); outState.putParcelable(KEY_LOCATION, lastKnownLocation); } super.onSaveInstanceState(outState); } /** * Sets up the options menu. * @param menu The options menu. * @return Boolean. */ @Override public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) { getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.current_place_menu, menu); return true; } /** * Handles a click on the menu option to get a place. * @param item The menu item to handle. * @return Boolean. */ @Override public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) { if (item.getItemId() == R.id.option_get_place) { showCurrentPlace(); } return true; } /** * Manipulates the map when it's available. * This callback is triggered when the map is ready to be used. */ @Override public void onMapReady(GoogleMap map) { this.map = map; // Use a custom info window adapter to handle multiple lines of text in the // info window contents. this.map.setInfoWindowAdapter(new GoogleMap.InfoWindowAdapter() { @Override // Return null here, so that getInfoContents() is called next. public View getInfoWindow(Marker arg0) { return null; } @Override public View getInfoContents(Marker marker) { // Inflate the layouts for the info window, title and snippet. View infoWindow = getLayoutInflater().inflate(R.layout.custom_info_contents, (FrameLayout) findViewById(R.id.map), false); TextView title = infoWindow.findViewById(R.id.title); title.setText(marker.getTitle()); TextView snippet = infoWindow.findViewById(R.id.snippet); snippet.setText(marker.getSnippet()); return infoWindow; } }); // Prompt the user for permission. getLocationPermission(); // Turn on the My Location layer and the related control on the map. updateLocationUI(); // Get the current location of the device and set the position of the map. getDeviceLocation(); } /** * Gets the current location of the device, and positions the map's camera. */ private void getDeviceLocation() { /* * Get the best and most recent location of the device, which may be null in rare * cases when a location is not available. */ try { if (locationPermissionGranted) { Task<Location> locationResult = fusedLocationProviderClient.getLastLocation(); locationResult.addOnCompleteListener(this, new OnCompleteListener<Location>() { @Override public void onComplete(@NonNull Task<Location> task) { if (task.isSuccessful()) { // Set the map's camera position to the current location of the device. lastKnownLocation = task.getResult(); if (lastKnownLocation != null) { map.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom( new LatLng(lastKnownLocation.getLatitude(), lastKnownLocation.getLongitude()), DEFAULT_ZOOM)); } } else { Log.d(TAG, "Current location is null. Using defaults."); Log.e(TAG, "Exception: %s", task.getException()); map.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory .newLatLngZoom(defaultLocation, DEFAULT_ZOOM)); map.getUiSettings().setMyLocationButtonEnabled(false); } } }); } } catch (SecurityException e) { Log.e("Exception: %s", e.getMessage(), e); } } /** * Prompts the user for permission to use the device location. */ private void getLocationPermission() { /* * Request location permission, so that we can get the location of the * device. The result of the permission request is handled by a callback, * onRequestPermissionsResult. */ if (ContextCompat.checkSelfPermission(this.getApplicationContext(), android.Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION) == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) { locationPermissionGranted = true; } else { ActivityCompat.requestPermissions(this, new String[]{android.Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION}, PERMISSIONS_REQUEST_ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION); } } /** * Handles the result of the request for location permissions. */ @Override public void onRequestPermissionsResult(int requestCode, @NonNull String[] permissions, @NonNull int[] grantResults) { locationPermissionGranted = false; if (requestCode == PERMISSIONS_REQUEST_ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION) {// If request is cancelled, the result arrays are empty. if (grantResults.length > 0 && grantResults[0] == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) { locationPermissionGranted = true; } } else { super.onRequestPermissionsResult(requestCode, permissions, grantResults); } updateLocationUI(); } /** * Prompts the user to select the current place from a list of likely places, and shows the * current place on the map - provided the user has granted location permission. */ private void showCurrentPlace() { if (map == null) { return; } if (locationPermissionGranted) { // Use fields to define the data types to return. List<Place.Field> placeFields = Arrays.asList(Place.Field.NAME, Place.Field.ADDRESS, Place.Field.LAT_LNG); // Use the builder to create a FindCurrentPlaceRequest. FindCurrentPlaceRequest request = FindCurrentPlaceRequest.newInstance(placeFields); // Get the likely places - that is, the businesses and other points of interest that // are the best match for the device's current location. @SuppressWarnings("MissingPermission") final Task<FindCurrentPlaceResponse> placeResult = placesClient.findCurrentPlace(request); placeResult.addOnCompleteListener (new OnCompleteListener<FindCurrentPlaceResponse>() { @Override public void onComplete(@NonNull Task<FindCurrentPlaceResponse> task) { if (task.isSuccessful() && task.getResult() != null) { FindCurrentPlaceResponse likelyPlaces = task.getResult(); // Set the count, handling cases where less than 5 entries are returned. int count; if (likelyPlaces.getPlaceLikelihoods().size() < M_MAX_ENTRIES) { count = likelyPlaces.getPlaceLikelihoods().size(); } else { count = M_MAX_ENTRIES; } int i = 0; likelyPlaceNames = new String[count]; likelyPlaceAddresses = new String[count]; likelyPlaceAttributions = new List[count]; likelyPlaceLatLngs = new LatLng[count]; for (PlaceLikelihood placeLikelihood : likelyPlaces.getPlaceLikelihoods()) { // Build a list of likely places to show the user. likelyPlaceNames[i] = placeLikelihood.getPlace().getName(); likelyPlaceAddresses[i] = placeLikelihood.getPlace().getAddress(); likelyPlaceAttributions[i] = placeLikelihood.getPlace() .getAttributions(); likelyPlaceLatLngs[i] = placeLikelihood.getPlace().getLatLng(); i++; if (i > (count - 1)) { break; } } // Show a dialog offering the user the list of likely places, and add a // marker at the selected place. MapsActivityCurrentPlace.this.openPlacesDialog(); } else { Log.e(TAG, "Exception: %s", task.getException()); } } }); } else { // The user has not granted permission. Log.i(TAG, "The user did not grant location permission."); // Add a default marker, because the user hasn't selected a place. map.addMarker(new MarkerOptions() .title(getString(R.string.default_info_title)) .position(defaultLocation) .snippet(getString(R.string.default_info_snippet))); // Prompt the user for permission. getLocationPermission(); } } /** * Displays a form allowing the user to select a place from a list of likely places. */ private void openPlacesDialog() { // Ask the user to choose the place where they are now. DialogInterface.OnClickListener listener = new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) { // The "which" argument contains the position of the selected item. LatLng markerLatLng = likelyPlaceLatLngs[which]; String markerSnippet = likelyPlaceAddresses[which]; if (likelyPlaceAttributions[which] != null) { markerSnippet = markerSnippet + "\n" + likelyPlaceAttributions[which]; } // Add a marker for the selected place, with an info window // showing information about that place. map.addMarker(new MarkerOptions() .title(likelyPlaceNames[which]) .position(markerLatLng) .snippet(markerSnippet)); // Position the map's camera at the location of the marker. map.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(markerLatLng, DEFAULT_ZOOM)); } }; // Display the dialog. AlertDialog dialog = new AlertDialog.Builder(this) .setTitle(R.string.pick_place) .setItems(likelyPlaceNames, listener) .show(); } /** * Updates the map's UI settings based on whether the user has granted location permission. */ private void updateLocationUI() { if (map == null) { return; } try { if (locationPermissionGranted) { map.setMyLocationEnabled(true); map.getUiSettings().setMyLocationButtonEnabled(true); } else { map.setMyLocationEnabled(false); map.getUiSettings().setMyLocationButtonEnabled(false); lastKnownLocation = null; } } catch (SecurityException e) { Log.e("Exception: %s", e.getMessage()); } } }
Wyświetl wersję aktywności w języku Kotlin:
// Copyright 2020 Google LLC // // Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); // you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. // You may obtain a copy of the License at // // http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 // // Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software // distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, // WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. // See the License for the specific language governing permissions and // limitations under the License. package com.example.currentplacedetailsonmap import android.Manifest import android.annotation.SuppressLint import android.content.DialogInterface import android.content.pm.PackageManager import android.location.Location import android.os.Bundle import android.util.Log import android.view.Menu import android.view.MenuItem import android.view.View import android.widget.FrameLayout import android.widget.TextView import androidx.appcompat.app.AlertDialog import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity import androidx.core.app.ActivityCompat import androidx.core.content.ContextCompat import com.google.android.gms.location.FusedLocationProviderClient import com.google.android.gms.location.LocationServices import com.google.android.gms.maps.CameraUpdateFactory import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap.InfoWindowAdapter import com.google.android.gms.maps.OnMapReadyCallback import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.CameraPosition import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.LatLng import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Marker import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.MarkerOptions import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.Places import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.model.Place import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.net.FindCurrentPlaceRequest import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.net.PlacesClient /** * An activity that displays a map showing the place at the device's current location. */ class MapsActivityCurrentPlace : AppCompatActivity(), OnMapReadyCallback { private var map: GoogleMap? = null private var cameraPosition: CameraPosition? = null // The entry point to the Places API. private lateinit var placesClient: PlacesClient // The entry point to the Fused Location Provider. private lateinit var fusedLocationProviderClient: FusedLocationProviderClient // A default location (Sydney, Australia) and default zoom to use when location permission is // not granted. private val defaultLocation = LatLng(-33.8523341, 151.2106085) private var locationPermissionGranted = false // The geographical location where the device is currently located. That is, the last-known // location retrieved by the Fused Location Provider. private var lastKnownLocation: Location? = null private var likelyPlaceNames: Array<String?> = arrayOfNulls(0) private var likelyPlaceAddresses: Array<String?> = arrayOfNulls(0) private var likelyPlaceAttributions: Array<List<*>?> = arrayOfNulls(0) private var likelyPlaceLatLngs: Array<LatLng?> = arrayOfNulls(0) override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // Retrieve location and camera position from saved instance state. if (savedInstanceState != null) { lastKnownLocation = savedInstanceState.getParcelable(KEY_LOCATION) cameraPosition = savedInstanceState.getParcelable(KEY_CAMERA_POSITION) } // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps) // Construct a PlacesClient Places.initialize(applicationContext, BuildConfig.MAPS_API_KEY) placesClient = Places.createClient(this) // Construct a FusedLocationProviderClient. fusedLocationProviderClient = LocationServices.getFusedLocationProviderClient(this) // Build the map. val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager .findFragmentById(R.id.map) as SupportMapFragment? mapFragment?.getMapAsync(this) } /** * Saves the state of the map when the activity is paused. */ override fun onSaveInstanceState(outState: Bundle) { map?.let { map -> outState.putParcelable(KEY_CAMERA_POSITION, map.cameraPosition) outState.putParcelable(KEY_LOCATION, lastKnownLocation) } super.onSaveInstanceState(outState) } /** * Sets up the options menu. * @param menu The options menu. * @return Boolean. */ override fun onCreateOptionsMenu(menu: Menu): Boolean { menuInflater.inflate(R.menu.current_place_menu, menu) return true } /** * Handles a click on the menu option to get a place. * @param item The menu item to handle. * @return Boolean. */ override fun onOptionsItemSelected(item: MenuItem): Boolean { if (item.itemId == R.id.option_get_place) { showCurrentPlace() } return true } /** * Manipulates the map when it's available. * This callback is triggered when the map is ready to be used. */ override fun onMapReady(map: GoogleMap) { this.map = map // Use a custom info window adapter to handle multiple lines of text in the // info window contents. this.map?.setInfoWindowAdapter(object : InfoWindowAdapter { // Return null here, so that getInfoContents() is called next. override fun getInfoWindow(arg0: Marker): View? { return null } override fun getInfoContents(marker: Marker): View { // Inflate the layouts for the info window, title and snippet. val infoWindow = layoutInflater.inflate(R.layout.custom_info_contents, findViewById<FrameLayout>(R.id.map), false) val title = infoWindow.findViewById<TextView>(R.id.title) title.text = marker.title val snippet = infoWindow.findViewById<TextView>(R.id.snippet) snippet.text = marker.snippet return infoWindow } }) // Prompt the user for permission. getLocationPermission() // Turn on the My Location layer and the related control on the map. updateLocationUI() // Get the current location of the device and set the position of the map. getDeviceLocation() } /** * Gets the current location of the device, and positions the map's camera. */ @SuppressLint("MissingPermission") private fun getDeviceLocation() { /* * Get the best and most recent location of the device, which may be null in rare * cases when a location is not available. */ try { if (locationPermissionGranted) { val locationResult = fusedLocationProviderClient.lastLocation locationResult.addOnCompleteListener(this) { task -> if (task.isSuccessful) { // Set the map's camera position to the current location of the device. lastKnownLocation = task.result if (lastKnownLocation != null) { map?.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom( LatLng(lastKnownLocation!!.latitude, lastKnownLocation!!.longitude), DEFAULT_ZOOM.toFloat())) } } else { Log.d(TAG, "Current location is null. Using defaults.") Log.e(TAG, "Exception: %s", task.exception) map?.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory .newLatLngZoom(defaultLocation, DEFAULT_ZOOM.toFloat())) map?.uiSettings?.isMyLocationButtonEnabled = false } } } } catch (e: SecurityException) { Log.e("Exception: %s", e.message, e) } } /** * Prompts the user for permission to use the device location. */ private fun getLocationPermission() { /* * Request location permission, so that we can get the location of the * device. The result of the permission request is handled by a callback, * onRequestPermissionsResult. */ if (ContextCompat.checkSelfPermission(this.applicationContext, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION) == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) { locationPermissionGranted = true } else { ActivityCompat.requestPermissions(this, arrayOf(Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION), PERMISSIONS_REQUEST_ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION) } } /** * Handles the result of the request for location permissions. */ override fun onRequestPermissionsResult(requestCode: Int, permissions: Array<String>, grantResults: IntArray) { locationPermissionGranted = false when (requestCode) { PERMISSIONS_REQUEST_ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION -> { // If request is cancelled, the result arrays are empty. if (grantResults.isNotEmpty() && grantResults[0] == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) { locationPermissionGranted = true } } else -> super.onRequestPermissionsResult(requestCode, permissions, grantResults) } updateLocationUI() } /** * Prompts the user to select the current place from a list of likely places, and shows the * current place on the map - provided the user has granted location permission. */ @SuppressLint("MissingPermission") private fun showCurrentPlace() { if (map == null) { return } if (locationPermissionGranted) { // Use fields to define the data types to return. val placeFields = listOf(Place.Field.NAME, Place.Field.ADDRESS, Place.Field.LAT_LNG) // Use the builder to create a FindCurrentPlaceRequest. val request = FindCurrentPlaceRequest.newInstance(placeFields) // Get the likely places - that is, the businesses and other points of interest that // are the best match for the device's current location. val placeResult = placesClient.findCurrentPlace(request) placeResult.addOnCompleteListener { task -> if (task.isSuccessful && task.result != null) { val likelyPlaces = task.result // Set the count, handling cases where less than 5 entries are returned. val count = if (likelyPlaces != null && likelyPlaces.placeLikelihoods.size < M_MAX_ENTRIES) { likelyPlaces.placeLikelihoods.size } else { M_MAX_ENTRIES } var i = 0 likelyPlaceNames = arrayOfNulls(count) likelyPlaceAddresses = arrayOfNulls(count) likelyPlaceAttributions = arrayOfNulls<List<*>?>(count) likelyPlaceLatLngs = arrayOfNulls(count) for (placeLikelihood in likelyPlaces?.placeLikelihoods ?: emptyList()) { // Build a list of likely places to show the user. likelyPlaceNames[i] = placeLikelihood.place.name likelyPlaceAddresses[i] = placeLikelihood.place.address likelyPlaceAttributions[i] = placeLikelihood.place.attributions likelyPlaceLatLngs[i] = placeLikelihood.place.latLng i++ if (i > count - 1) { break } } // Show a dialog offering the user the list of likely places, and add a // marker at the selected place. openPlacesDialog() } else { Log.e(TAG, "Exception: %s", task.exception) } } } else { // The user has not granted permission. Log.i(TAG, "The user did not grant location permission.") // Add a default marker, because the user hasn't selected a place. map?.addMarker(MarkerOptions() .title(getString(R.string.default_info_title)) .position(defaultLocation) .snippet(getString(R.string.default_info_snippet))) // Prompt the user for permission. getLocationPermission() } } /** * Displays a form allowing the user to select a place from a list of likely places. */ private fun openPlacesDialog() { // Ask the user to choose the place where they are now. val listener = DialogInterface.OnClickListener { dialog, which -> // The "which" argument contains the position of the selected item. val markerLatLng = likelyPlaceLatLngs[which] var markerSnippet = likelyPlaceAddresses[which] if (likelyPlaceAttributions[which] != null) { markerSnippet = """ $markerSnippet ${likelyPlaceAttributions[which]} """.trimIndent() } if (markerLatLng == null) { return@OnClickListener } // Add a marker for the selected place, with an info window // showing information about that place. map?.addMarker(MarkerOptions() .title(likelyPlaceNames[which]) .position(markerLatLng) .snippet(markerSnippet)) // Position the map's camera at the location of the marker. map?.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(markerLatLng, DEFAULT_ZOOM.toFloat())) } // Display the dialog. AlertDialog.Builder(this) .setTitle(R.string.pick_place) .setItems(likelyPlaceNames, listener) .show() } /** * Updates the map's UI settings based on whether the user has granted location permission. */ @SuppressLint("MissingPermission") private fun updateLocationUI() { if (map == null) { return } try { if (locationPermissionGranted) { map?.isMyLocationEnabled = true map?.uiSettings?.isMyLocationButtonEnabled = true } else { map?.isMyLocationEnabled = false map?.uiSettings?.isMyLocationButtonEnabled = false lastKnownLocation = null getLocationPermission() } } catch (e: SecurityException) { Log.e("Exception: %s", e.message, e) } } companion object { private val TAG = MapsActivityCurrentPlace::class.java.simpleName private const val DEFAULT_ZOOM = 15 private const val PERMISSIONS_REQUEST_ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION = 1 // Keys for storing activity state. private const val KEY_CAMERA_POSITION = "camera_position" private const val KEY_LOCATION = "location" // Used for selecting the current place. private const val M_MAX_ENTRIES = 5 } }
Konfigurowanie projektu programistycznego
Aby utworzyć projekt samouczka w Android Studio, wykonaj te czynności.
- Pobierz i zainstaluj Android Studio.
- Dodaj pakiet usług Google Play do Androida Studio.
- Sklonuj lub pobierz repozytorium przykładów Google Maps Android API v2, jeśli nie zostało to zrobione na początku tego samouczka.
Zaimportuj projekt samouczka:
- W Android Studio wybierz Plik > Nowy > Importuj projekt.
- Otwórz lokalizację, w której po pobraniu został zapisany repozytorium przykładów Google Maps Android API v2.
- Projekt CurrentPlaceDetailsOnMap znajdziesz w tej lokalizacji:
PATH-TO-SAVED-REPO/android-samples/tutorials/java/CurrentPlaceDetailsOnMap(Java) lub
PATH-TO-SAVED-REPO/android-samples/tutorials/kotlin/CurrentPlaceDetailsOnMap(Kotlin) - Wybierz katalog projektu, a potem kliknij Otwórz. Android Studio skompiluje teraz Twój projekt za pomocą narzędzia do kompilacji Gradle.
Włączanie niezbędnych interfejsów API i uzyskiwanie klucza interfejsu API
Aby wykonać zadania z tego samouczka, musisz mieć projekt Google Cloud z włączonymi interfejsami API i kluczem interfejsu API, który jest autoryzowany do używania pakietu SDK Map Google na Androida. Więcej informacji znajdziesz w tych artykułach:
Aby wyświetlić włączone interfejsy API, otwórz stronę Google Maps Platform w konsoli Cloud i wybierz projekt:
Otwórz stronę Google Maps PlatformJeśli nie widzisz, że interfejs Places API jest włączony w Twoim projekcie, musisz go włączyć:
Włączanie interfejsu Places APIJeśli dodasz do klucza interfejsu API jakiekolwiek ograniczenia, pamiętaj, aby dodać do niego interfejs Places API. Więcej informacji znajdziesz w artykule Używanie kluczy API.
Dodawanie klucza interfejsu API do aplikacji
- Otwórz plik
local.propertiesprojektu. Dodaj ten ciąg znaków, a potem zastąp
YOUR_API_KEYwartością klucza interfejsu API:MAPS_API_KEY=YOUR_API_KEY
Gdy tworzysz aplikację, wtyczka Gradle obiektów tajnych na Androida kopiuje klucz interfejsu API i udostępnia go jako zmienną kompilacji w pliku manifestu Androida.
Tworzenie i uruchamianie aplikacji
Podłącz urządzenie z Androidem do komputera. Postępuj zgodnie z instrukcjami, aby włączyć opcje programisty na urządzeniu z Androidem i skonfigurować system tak, aby wykrywał urządzenie.
Możesz też użyć menedżera urządzenia wirtualnego z Androidem (AVD), aby skonfigurować urządzenie wirtualne. Podczas wybierania emulatora upewnij się, że wybierasz obraz, który zawiera interfejsy API Google. Więcej informacji znajdziesz w artykule Konfigurowanie projektu w Android Studio.
- W Android Studio kliknij opcję menu Uruchom (lub ikonę przycisku odtwarzania). Wybierz urządzenie zgodnie z instrukcjami.
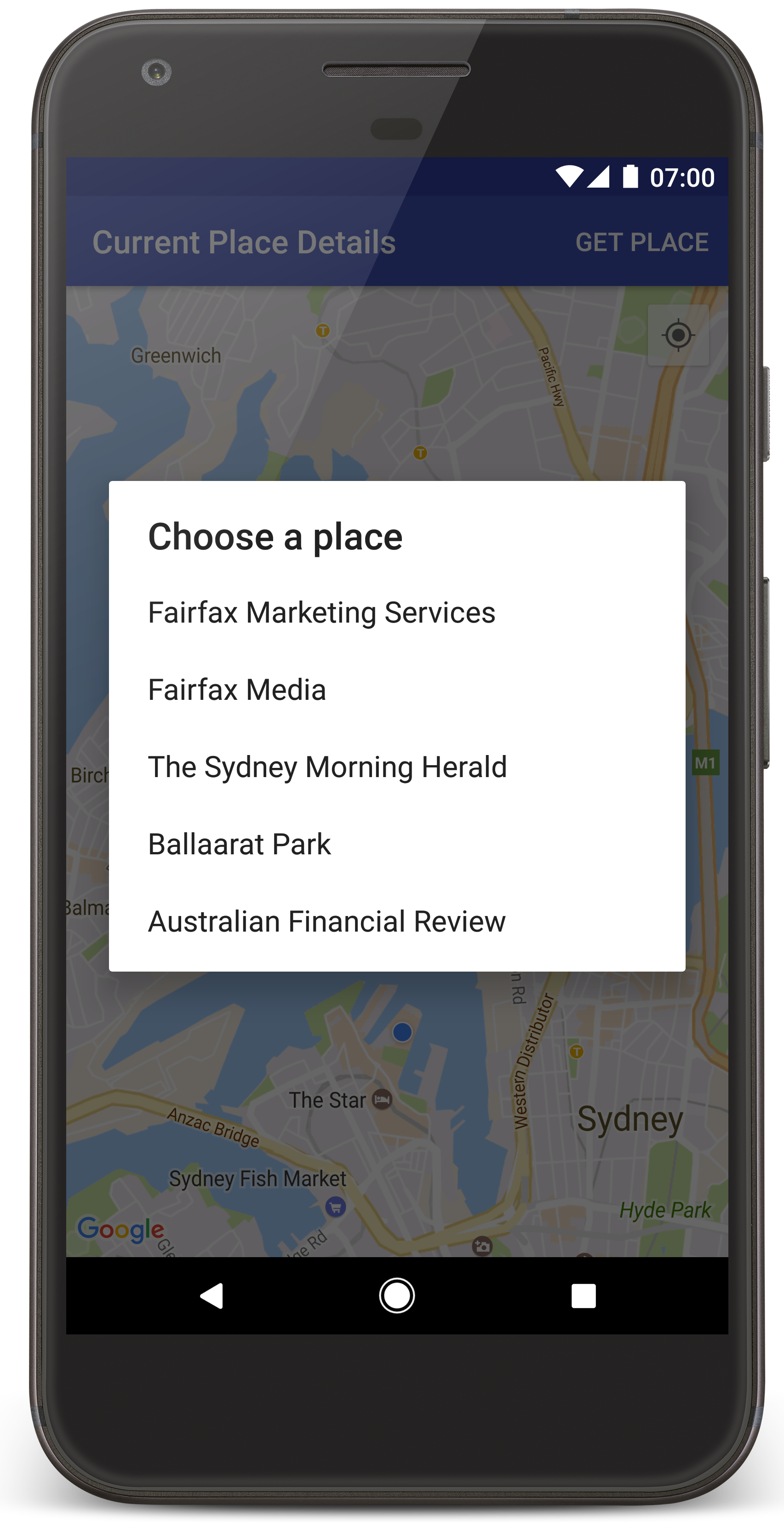
Android Studio wywołuje Gradle, aby skompilować aplikację, a następnie uruchamia ją na urządzeniu lub w emulatorze. Powinna się wyświetlić mapa z kilkoma znacznikami wyśrodkowanymi wokół Twojej bieżącej lokalizacji, podobnie jak na ilustracji na tej stronie.
- Kliknij Pobierz miejsce, aby otworzyć listę miejsc (firm lub innych punktów orientacyjnych) w pobliżu Twojej obecnej lokalizacji.
- Wybierz miejsce z listy. Do mapy zostanie dodany znacznik wybranego miejsca.
Rozwiązywanie problemów:
- Jeśli nie widzisz mapy, sprawdź, czy masz klucz interfejsu API i czy został on dodany do aplikacji w sposób opisany powyżej. Sprawdź dziennik w Monitorze Androida w Android Studio, aby znaleźć komunikaty o błędach dotyczące klucza interfejsu API.
- Jeśli na mapie widać tylko jeden znacznik znajdujący się na moście Sydney Harbour Bridge (domyślna lokalizacja określona w aplikacji), sprawdź, czy aplikacja ma uprawnienia do określania lokalizacji. Aplikacja prosi o uprawnienia do określania lokalizacji w czasie działania, zgodnie ze wzorcem opisanym w przewodniku po uprawnieniach na Androidzie. Pamiętaj, że uprawnienia możesz też ustawić bezpośrednio na urządzeniu, wybierając Ustawienia > Aplikacje > nazwa aplikacji > Uprawnienia > Lokalizacja. Szczegółowe informacje o tym, jak obsługiwać uprawnienia w kodzie, znajdziesz w przewodniku prośba o uprawnienia do lokalizacji w aplikacji.
- Aby wyświetlić logi i debugować aplikację, użyj narzędzi do debugowania w Androidzie Studio.
Zrozumienie kodu
W tej części samouczka omawiamy najważniejsze elementy aplikacji CurrentPlaceDetailsOnMap, aby pomóc Ci zrozumieć, jak utworzyć podobną aplikację.
Utwórz instancję klienta interfejsu Places API
Te obiekty są głównymi punktami wejścia do pakietu SDK Miejsc na Androida:
- Klasa
Placestworzy klientów pakietu Places SDK na Androida i nimi zarządza. - Interfejs
PlacesClientpobiera aktualną lokalizację urządzenia i miejsca w pobliżu.
Interfejs LocationServices jest głównym punktem wejścia do usług lokalizacyjnych na Androidzie.
Aby korzystać z interfejsów API, wykonaj te czynności w metodzie onCreate() fragmentu lub aktywności:
- Zainicjuj obiekt
Places. - Utwórz obiekt
PlacesClient. - Utwórz obiekt
FusedLocationProviderClient.
Na przykład:
Java
@Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // ... // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps); // Construct a PlacesClient Places.initialize(getApplicationContext(), getString(R.string.maps_api_key)); placesClient = Places.createClient(this); // Construct a FusedLocationProviderClient. fusedLocationProviderClient = LocationServices.getFusedLocationProviderClient(this); }
Kotlin
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // ... // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps) // Construct a PlacesClient Places.initialize(applicationContext, getString(R.string.maps_api_key)) placesClient = Places.createClient(this) // Construct a FusedLocationProviderClient. fusedLocationProviderClient = LocationServices.getFusedLocationProviderClient(this) }
Poproś o dostęp do lokalizacji
Aby określić lokalizację urządzenia i umożliwić użytkownikowi kliknięcie przycisku Moja lokalizacja na mapie, aplikacja musi poprosić o uprawnienia dostępu do lokalizacji.
W tym samouczku znajdziesz kod potrzebny do wysłania prośby o uprawnienia do precyzyjnej lokalizacji. Więcej informacji znajdziesz w przewodniku po uprawnieniach na Androidzie.
Dodaj uprawnienie jako element podrzędny elementu
<manifest>w pliku manifestu Androida:<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.example.currentplacedetailsonmap"> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION" /> </manifest>
W aplikacji musisz prosić o uprawnienia w czasie działania, aby użytkownik mógł zezwolić na dostęp do lokalizacji lub odmówić go. Poniższy kod sprawdza, czy użytkownik przyznał uprawnienia do dokładnej lokalizacji. Jeśli nie, prosi o uprawnienia:
Java
private void getLocationPermission() { /* * Request location permission, so that we can get the location of the * device. The result of the permission request is handled by a callback, * onRequestPermissionsResult. */ if (ContextCompat.checkSelfPermission(this.getApplicationContext(), android.Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION) == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) { locationPermissionGranted = true; } else { ActivityCompat.requestPermissions(this, new String[]{android.Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION}, PERMISSIONS_REQUEST_ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION); } }
Kotlin
private fun getLocationPermission() { /* * Request location permission, so that we can get the location of the * device. The result of the permission request is handled by a callback, * onRequestPermissionsResult. */ if (ContextCompat.checkSelfPermission(this.applicationContext, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION) == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) { locationPermissionGranted = true } else { ActivityCompat.requestPermissions(this, arrayOf(Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION), PERMISSIONS_REQUEST_ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION) } }
Zastąp wywołanie zwrotne
onRequestPermissionsResult(), aby obsłużyć wynik prośby o uprawnienia:Java
@Override public void onRequestPermissionsResult(int requestCode, @NonNull String[] permissions, @NonNull int[] grantResults) { locationPermissionGranted = false; if (requestCode == PERMISSIONS_REQUEST_ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION) {// If request is cancelled, the result arrays are empty. if (grantResults.length > 0 && grantResults[0] == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) { locationPermissionGranted = true; } } else { super.onRequestPermissionsResult(requestCode, permissions, grantResults); } updateLocationUI(); }
Kotlin
override fun onRequestPermissionsResult(requestCode: Int, permissions: Array<String>, grantResults: IntArray) { locationPermissionGranted = false when (requestCode) { PERMISSIONS_REQUEST_ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION -> { // If request is cancelled, the result arrays are empty. if (grantResults.isNotEmpty() && grantResults[0] == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) { locationPermissionGranted = true } } else -> super.onRequestPermissionsResult(requestCode, permissions, grantResults) } updateLocationUI() }
W dalszej części tego samouczka opisujemy metodę
updateLocationUI().
Dodawanie mapy
Wyświetlanie mapy za pomocą pakietu Maps SDK na Androida.
Dodaj element
<fragment>do pliku układu aktywności,activity_maps.xml. Ten element definiujeSupportMapFragment, który pełni funkcję kontenera mapy i zapewnia dostęp do obiektuGoogleMap. W samouczku używana jest wersja fragmentu mapy z biblioteki pomocy Androida, aby zapewnić zgodność wsteczną ze starszymi wersjami platformy Androida.<!-- Copyright 2020 Google LLC Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. --> <fragment xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/map" android:name="com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context="com.example.currentplacedetailsonmap.MapsActivityCurrentPlace" />
W metodzie
onCreate()aktywności ustaw plik układu jako widok treści:Java
@Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps); }
Kotlin
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps) }
Zaimplementuj interfejs
OnMapReadyCallbacki zastąp metodęonMapReady(), aby skonfigurować mapę, gdy obiektGoogleMapbędzie dostępny:Java
@Override public void onMapReady(GoogleMap map) { this.map = map; // ... // Turn on the My Location layer and the related control on the map. updateLocationUI(); // Get the current location of the device and set the position of the map. getDeviceLocation(); }
Kotlin
override fun onMapReady(map: GoogleMap) { this.map = map // ... // Turn on the My Location layer and the related control on the map. updateLocationUI() // Get the current location of the device and set the position of the map. getDeviceLocation() }
W metodzie
onCreate()aktywności uzyskaj uchwyt do fragmentu mapy, wywołującFragmentManager.findFragmentById(). Następnie użyjgetMapAsync(), aby zarejestrować wywołanie zwrotne mapy:Java
SupportMapFragment mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager() .findFragmentById(R.id.map); mapFragment.getMapAsync(this);
Kotlin
val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager .findFragmentById(R.id.map) as SupportMapFragment? mapFragment?.getMapAsync(this)
Napisz metodę
updateLocationUI(), która ustawia elementy sterujące lokalizacją na mapie. Jeśli użytkownik zezwolił na dostęp do lokalizacji, włącz warstwę Moja lokalizacja i powiązany z nią element sterujący na mapie. W przeciwnym razie wyłącz warstwę i element sterujący oraz ustaw bieżącą lokalizację na null:Java
private void updateLocationUI() { if (map == null) { return; } try { if (locationPermissionGranted) { map.setMyLocationEnabled(true); map.getUiSettings().setMyLocationButtonEnabled(true); } else { map.setMyLocationEnabled(false); map.getUiSettings().setMyLocationButtonEnabled(false); lastKnownLocation = null; } } catch (SecurityException e) { Log.e("Exception: %s", e.getMessage()); } }
Kotlin
@SuppressLint("MissingPermission") private fun updateLocationUI() { if (map == null) { return } try { if (locationPermissionGranted) { map?.isMyLocationEnabled = true map?.uiSettings?.isMyLocationButtonEnabled = true } else { map?.isMyLocationEnabled = false map?.uiSettings?.isMyLocationButtonEnabled = false lastKnownLocation = null getLocationPermission() } } catch (e: SecurityException) { Log.e("Exception: %s", e.message, e) } }
Pobieranie lokalizacji urządzenia z Androidem i ustawianie pozycji mapy
Użyj dostawcy połączonej lokalizacji, aby znaleźć ostatnią znaną lokalizację urządzenia, a następnie użyj tej lokalizacji do ustawienia pozycji mapy. W samouczku znajdziesz potrzebny kod. Więcej informacji o uzyskiwaniu lokalizacji urządzenia znajdziesz w przewodniku po zintegrowanym dostawcy lokalizacji w interfejsach API lokalizacji w usługach Google Play.
Java
private void getDeviceLocation() { /* * Get the best and most recent location of the device, which may be null in rare * cases when a location is not available. */ try { if (locationPermissionGranted) { Task<Location> locationResult = fusedLocationProviderClient.getLastLocation(); locationResult.addOnCompleteListener(this, new OnCompleteListener<Location>() { @Override public void onComplete(@NonNull Task<Location> task) { if (task.isSuccessful()) { // Set the map's camera position to the current location of the device. lastKnownLocation = task.getResult(); if (lastKnownLocation != null) { map.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom( new LatLng(lastKnownLocation.getLatitude(), lastKnownLocation.getLongitude()), DEFAULT_ZOOM)); } } else { Log.d(TAG, "Current location is null. Using defaults."); Log.e(TAG, "Exception: %s", task.getException()); map.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory .newLatLngZoom(defaultLocation, DEFAULT_ZOOM)); map.getUiSettings().setMyLocationButtonEnabled(false); } } }); } } catch (SecurityException e) { Log.e("Exception: %s", e.getMessage(), e); } }
Kotlin
@SuppressLint("MissingPermission") private fun getDeviceLocation() { /* * Get the best and most recent location of the device, which may be null in rare * cases when a location is not available. */ try { if (locationPermissionGranted) { val locationResult = fusedLocationProviderClient.lastLocation locationResult.addOnCompleteListener(this) { task -> if (task.isSuccessful) { // Set the map's camera position to the current location of the device. lastKnownLocation = task.result if (lastKnownLocation != null) { map?.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom( LatLng(lastKnownLocation!!.latitude, lastKnownLocation!!.longitude), DEFAULT_ZOOM.toFloat())) } } else { Log.d(TAG, "Current location is null. Using defaults.") Log.e(TAG, "Exception: %s", task.exception) map?.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory .newLatLngZoom(defaultLocation, DEFAULT_ZOOM.toFloat())) map?.uiSettings?.isMyLocationButtonEnabled = false } } } } catch (e: SecurityException) { Log.e("Exception: %s", e.message, e) } }
Pobieranie bieżącego miejsca
Użyj pakietu SDK Miejsc na Androida, aby uzyskać listę prawdopodobnych miejsc w bieżącej lokalizacji urządzenia. W tym kontekście miejsce to firma lub inny punkt orientacyjny.
W tym samouczku pokazujemy, jak uzyskać bieżące miejsce, gdy użytkownik kliknie przycisk Pobierz miejsce. Wyświetla użytkownikowi listę prawdopodobnych miejsc do wyboru, a następnie dodaje znacznik na mapie w lokalizacji wybranego miejsca. W samouczku znajdziesz kod potrzebny do interakcji z pakietem SDK Miejsc na Androida. Więcej informacji znajdziesz w przewodniku na temat uzyskiwania bieżącego miejsca.
- Utwórz plik układu (
current_place_menu.xml) dla menu opcji i zastąp metodęonCreateOptionsMenu(), aby skonfigurować menu opcji. Kod znajdziesz w przykładowej aplikacji. - Zastąp metodę
onOptionsItemSelected(), aby uzyskać bieżące miejsce, gdy użytkownik kliknie opcję Pobierz miejsce:Java
@Override public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) { if (item.getItemId() == R.id.option_get_place) { showCurrentPlace(); } return true; }
Kotlin
override fun onOptionsItemSelected(item: MenuItem): Boolean { if (item.itemId == R.id.option_get_place) { showCurrentPlace() } return true }
Utwórz metodę
showCurrentPlace(), aby uzyskać listę prawdopodobnych miejsc w bieżącej lokalizacji urządzenia:Java
private void showCurrentPlace() { if (map == null) { return; } if (locationPermissionGranted) { // Use fields to define the data types to return. List<Place.Field> placeFields = Arrays.asList(Place.Field.NAME, Place.Field.ADDRESS, Place.Field.LAT_LNG); // Use the builder to create a FindCurrentPlaceRequest. FindCurrentPlaceRequest request = FindCurrentPlaceRequest.newInstance(placeFields); // Get the likely places - that is, the businesses and other points of interest that // are the best match for the device's current location. @SuppressWarnings("MissingPermission") final Task<FindCurrentPlaceResponse> placeResult = placesClient.findCurrentPlace(request); placeResult.addOnCompleteListener (new OnCompleteListener<FindCurrentPlaceResponse>() { @Override public void onComplete(@NonNull Task<FindCurrentPlaceResponse> task) { if (task.isSuccessful() && task.getResult() != null) { FindCurrentPlaceResponse likelyPlaces = task.getResult(); // Set the count, handling cases where less than 5 entries are returned. int count; if (likelyPlaces.getPlaceLikelihoods().size() < M_MAX_ENTRIES) { count = likelyPlaces.getPlaceLikelihoods().size(); } else { count = M_MAX_ENTRIES; } int i = 0; likelyPlaceNames = new String[count]; likelyPlaceAddresses = new String[count]; likelyPlaceAttributions = new List[count]; likelyPlaceLatLngs = new LatLng[count]; for (PlaceLikelihood placeLikelihood : likelyPlaces.getPlaceLikelihoods()) { // Build a list of likely places to show the user. likelyPlaceNames[i] = placeLikelihood.getPlace().getName(); likelyPlaceAddresses[i] = placeLikelihood.getPlace().getAddress(); likelyPlaceAttributions[i] = placeLikelihood.getPlace() .getAttributions(); likelyPlaceLatLngs[i] = placeLikelihood.getPlace().getLatLng(); i++; if (i > (count - 1)) { break; } } // Show a dialog offering the user the list of likely places, and add a // marker at the selected place. MapsActivityCurrentPlace.this.openPlacesDialog(); } else { Log.e(TAG, "Exception: %s", task.getException()); } } }); } else { // The user has not granted permission. Log.i(TAG, "The user did not grant location permission."); // Add a default marker, because the user hasn't selected a place. map.addMarker(new MarkerOptions() .title(getString(R.string.default_info_title)) .position(defaultLocation) .snippet(getString(R.string.default_info_snippet))); // Prompt the user for permission. getLocationPermission(); } }
Kotlin
@SuppressLint("MissingPermission") private fun showCurrentPlace() { if (map == null) { return } if (locationPermissionGranted) { // Use fields to define the data types to return. val placeFields = listOf(Place.Field.NAME, Place.Field.ADDRESS, Place.Field.LAT_LNG) // Use the builder to create a FindCurrentPlaceRequest. val request = FindCurrentPlaceRequest.newInstance(placeFields) // Get the likely places - that is, the businesses and other points of interest that // are the best match for the device's current location. val placeResult = placesClient.findCurrentPlace(request) placeResult.addOnCompleteListener { task -> if (task.isSuccessful && task.result != null) { val likelyPlaces = task.result // Set the count, handling cases where less than 5 entries are returned. val count = if (likelyPlaces != null && likelyPlaces.placeLikelihoods.size < M_MAX_ENTRIES) { likelyPlaces.placeLikelihoods.size } else { M_MAX_ENTRIES } var i = 0 likelyPlaceNames = arrayOfNulls(count) likelyPlaceAddresses = arrayOfNulls(count) likelyPlaceAttributions = arrayOfNulls<List<*>?>(count) likelyPlaceLatLngs = arrayOfNulls(count) for (placeLikelihood in likelyPlaces?.placeLikelihoods ?: emptyList()) { // Build a list of likely places to show the user. likelyPlaceNames[i] = placeLikelihood.place.name likelyPlaceAddresses[i] = placeLikelihood.place.address likelyPlaceAttributions[i] = placeLikelihood.place.attributions likelyPlaceLatLngs[i] = placeLikelihood.place.latLng i++ if (i > count - 1) { break } } // Show a dialog offering the user the list of likely places, and add a // marker at the selected place. openPlacesDialog() } else { Log.e(TAG, "Exception: %s", task.exception) } } } else { // The user has not granted permission. Log.i(TAG, "The user did not grant location permission.") // Add a default marker, because the user hasn't selected a place. map?.addMarker(MarkerOptions() .title(getString(R.string.default_info_title)) .position(defaultLocation) .snippet(getString(R.string.default_info_snippet))) // Prompt the user for permission. getLocationPermission() } }
Utwórz metodę
openPlacesDialog(), która wyświetli formularz umożliwiający użytkownikowi wybranie miejsca z listy prawdopodobnych miejsc. Dodaj znacznik na mapie dla wybranego miejsca. Treść znacznika zawiera nazwę i adres miejsca oraz wszelkie atrybucje dostarczane przez interfejs API:Java
private void openPlacesDialog() { // Ask the user to choose the place where they are now. DialogInterface.OnClickListener listener = new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) { // The "which" argument contains the position of the selected item. LatLng markerLatLng = likelyPlaceLatLngs[which]; String markerSnippet = likelyPlaceAddresses[which]; if (likelyPlaceAttributions[which] != null) { markerSnippet = markerSnippet + "\n" + likelyPlaceAttributions[which]; } // Add a marker for the selected place, with an info window // showing information about that place. map.addMarker(new MarkerOptions() .title(likelyPlaceNames[which]) .position(markerLatLng) .snippet(markerSnippet)); // Position the map's camera at the location of the marker. map.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(markerLatLng, DEFAULT_ZOOM)); } }; // Display the dialog. AlertDialog dialog = new AlertDialog.Builder(this) .setTitle(R.string.pick_place) .setItems(likelyPlaceNames, listener) .show(); }
Kotlin
private fun openPlacesDialog() { // Ask the user to choose the place where they are now. val listener = DialogInterface.OnClickListener { dialog, which -> // The "which" argument contains the position of the selected item. val markerLatLng = likelyPlaceLatLngs[which] var markerSnippet = likelyPlaceAddresses[which] if (likelyPlaceAttributions[which] != null) { markerSnippet = """ $markerSnippet ${likelyPlaceAttributions[which]} """.trimIndent() } if (markerLatLng == null) { return@OnClickListener } // Add a marker for the selected place, with an info window // showing information about that place. map?.addMarker(MarkerOptions() .title(likelyPlaceNames[which]) .position(markerLatLng) .snippet(markerSnippet)) // Position the map's camera at the location of the marker. map?.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(markerLatLng, DEFAULT_ZOOM.toFloat())) } // Display the dialog. AlertDialog.Builder(this) .setTitle(R.string.pick_place) .setItems(likelyPlaceNames, listener) .show() }
Utwórz niestandardowy układ treści okna informacyjnego. Dzięki temu w oknie informacji można wyświetlać wiele wierszy treści. Najpierw dodaj plik układu XML,
custom_info_contents.xml, zawierający widok tekstu dla tytułu okna informacyjnego i inny widok tekstu dla fragmentu (czyli treści tekstowej okna informacyjnego):<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!-- Copyright 2020 Google LLC Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. --> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layoutDirection="locale" android:orientation="vertical"> <TextView android:id="@+id/title" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal" android:textColor="#ff000000" android:textStyle="bold" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/snippet" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:textColor="#ff7f7f7f" /> </LinearLayout>
Zaimplementuj interfejs
InfoWindowAdapter, aby rozwinąć układ i wczytać zawartość okna informacji:Java
// Use a custom info window adapter to handle multiple lines of text in the // info window contents. this.map.setInfoWindowAdapter(new GoogleMap.InfoWindowAdapter() { @Override // Return null here, so that getInfoContents() is called next. public View getInfoWindow(Marker arg0) { return null; } @Override public View getInfoContents(Marker marker) { // Inflate the layouts for the info window, title and snippet. View infoWindow = getLayoutInflater().inflate(R.layout.custom_info_contents, (FrameLayout) findViewById(R.id.map), false); TextView title = infoWindow.findViewById(R.id.title); title.setText(marker.getTitle()); TextView snippet = infoWindow.findViewById(R.id.snippet); snippet.setText(marker.getSnippet()); return infoWindow; } });
Kotlin
// Use a custom info window adapter to handle multiple lines of text in the // info window contents. this.map?.setInfoWindowAdapter(object : InfoWindowAdapter { // Return null here, so that getInfoContents() is called next. override fun getInfoWindow(arg0: Marker): View? { return null } override fun getInfoContents(marker: Marker): View { // Inflate the layouts for the info window, title and snippet. val infoWindow = layoutInflater.inflate(R.layout.custom_info_contents, findViewById<FrameLayout>(R.id.map), false) val title = infoWindow.findViewById<TextView>(R.id.title) title.text = marker.title val snippet = infoWindow.findViewById<TextView>(R.id.snippet) snippet.text = marker.snippet return infoWindow } })
Zapisywanie stanu mapy
Zapisz pozycję kamery na mapie i lokalizację urządzenia. Gdy użytkownik obróci urządzenie z Androidem lub wprowadzi zmiany w konfiguracji, platforma Android zniszczy i ponownie utworzy aktywność mapy. Aby zapewnić użytkownikom wygodę, warto przechowywać odpowiedni stan aplikacji i w razie potrzeby go przywracać.
Ten samouczek zawiera cały kod potrzebny do zapisania stanu mapy. Więcej informacji znajdziesz w przewodniku po savedInstanceStatepakiecie.
W aktywności mapy skonfiguruj wartości kluczowe do przechowywania stanu aktywności:
Java
private static final String KEY_CAMERA_POSITION = "camera_position"; private static final String KEY_LOCATION = "location";
Kotlin
private const val KEY_CAMERA_POSITION = "camera_position" private const val KEY_LOCATION = "location"
Zaimplementuj wywołanie zwrotne
onSaveInstanceState(), aby zapisać stan, gdy aktywność zostanie wstrzymana:Java
@Override protected void onSaveInstanceState(Bundle outState) { if (map != null) { outState.putParcelable(KEY_CAMERA_POSITION, map.getCameraPosition()); outState.putParcelable(KEY_LOCATION, lastKnownLocation); } super.onSaveInstanceState(outState); }
Kotlin
override fun onSaveInstanceState(outState: Bundle) { map?.let { map -> outState.putParcelable(KEY_CAMERA_POSITION, map.cameraPosition) outState.putParcelable(KEY_LOCATION, lastKnownLocation) } super.onSaveInstanceState(outState) }
W metodzie
onCreate()aktywności pobierz lokalizację urządzenia i pozycję kamery mapy, jeśli zostały wcześniej zapisane:Java
// Retrieve location and camera position from saved instance state. if (savedInstanceState != null) { lastKnownLocation = savedInstanceState.getParcelable(KEY_LOCATION); cameraPosition = savedInstanceState.getParcelable(KEY_CAMERA_POSITION); }
Kotlin
if (savedInstanceState != null) { lastKnownLocation = savedInstanceState.getParcelable(KEY_LOCATION) cameraPosition = savedInstanceState.getParcelable(KEY_CAMERA_POSITION) }
