Приложения и проекты, использующие API и SDK платформы Google Maps, должны использовать ключи API или, если это поддерживается, OAuth 2.0 для аутентификации.
Эти рекомендации помогут вам обеспечить безопасность доступа к платформе Maps.
Если вы хотите использовать OAuth 2.0 для авторизации трафика между серверами , найдите раздел OAuth в документации к вашему API. Дополнительные сведения см. в разделе «Использование OAuth для серверных приложений» .
Помимо применения ограничений на использование приложений и ключей API, соблюдайте все правила безопасности, применимые к конкретным продуктам платформы Google Maps. Например, см. раздел «Рекомендуемые ограничения на использование приложений и API» для API JavaScript в разделе «Карты».
Если ваши API-ключи уже используются, ознакомьтесь с рекомендациями ниже в разделе «Если вы ограничиваете доступ к используемому API-ключу» .
Более подробную информацию о цифровых подписях, поддерживаемых статическим API карт и статическим API просмотра улиц, см. в Руководстве по цифровым подписям .
Рекомендуемые передовые методы
Для повышения безопасности и во избежание выставления счетов за несанкционированное использование, следуйте этим рекомендациям по обеспечению безопасности API для всех API, SDK и сервисов платформы Google Maps:
Рекомендуется для всех случаев использования API-ключей.
Ограничьте использование ваших API-ключей
Используйте отдельные API-ключи для каждого приложения.
Удалите неиспользуемые ключи API.
Проверьте использование вашего API-ключа.
Будьте осторожны при смене ключей API.
Разделите использование клиентской и серверной частей на отдельные проекты.
Отключить неиспользуемые службы
Дополнительные рекомендации для клиентских приложений
Используйте SDK на стороне клиента.
Безопасные вызовы веб-сервисов на стороне клиента
Дополнительные рекомендации для веб-сайтов или клиентских приложений, использующих статические веб-API.
Защита использования статического веб-API
Дополнительные рекомендации для серверных приложений, использующих веб-сервисы.
Используйте OAuth для серверных приложений.
Если вы ограничиваете или меняете используемый ключ API, который в настоящее время применяется.
Прежде чем менять ключ API, проверьте, как используется ваш ключ API. Этот шаг особенно важен, если вы добавляете ограничения для ключа, который уже используется в рабочем приложении.
После изменения ключа обновите все свои приложения, используя новые API-ключи, по мере необходимости.
Если ваш API-ключ не был скомпрометирован и не используется в злоупотреблениях, вы можете в удобном для вас темпе перенести свои приложения на несколько новых API-ключей, оставив исходный API-ключ нетронутым до тех пор, пока не будет наблюдаться только один тип трафика, и API-ключ можно безопасно ограничить с помощью одного типа ограничений для приложений, не вызывая непредвиденных сбоев в работе сервиса.
Дополнительные инструкции см. в разделе «Переход на использование нескольких ключей API» .
Отслеживайте использование с течением времени и определяйте, когда определенные API, типы платформ и домены перешли на использование старого ключа API, прежде чем ограничивать или удалять старый ключ. Для получения дополнительной информации см. разделы «Отчетность и мониторинг» и «Метрики».
Если ваш API-ключ был скомпрометирован, вам следует как можно быстрее принять меры для его защиты и предотвращения злоупотреблений. В приложениях для Android и iOS ключи не заменяются до тех пор, пока пользователи не обновят свои приложения. Обновление или замена ключей на веб-страницах или в серверных приложениях гораздо проще, но все равно может потребовать тщательного планирования и быстрой работы.
Для получения дополнительной информации см. раздел «Обработка несанкционированного использования ключа API» .
Более подробная информация
Рекомендуемые ограничения для приложений и API.
Ограничьте использование ваших API-ключей
Рекомендуется всегда ограничивать использование API-ключей одним типом ограничений для приложений и одним или несколькими ограничениями для API. Рекомендации по ограничениям для API, SDK или JavaScript-сервисов см. в разделе «Рекомендуемые ограничения для приложений и API» ниже.
Ограничения для приложений. Вы можете ограничить использование ключа API определенными платформами: приложениями Android или iOS, определенными веб-сайтами для клиентских приложений или определенными IP-адресами или подсетями CIDR для серверных приложений, выполняющих вызовы REST API веб-сервисов.
Вы ограничиваете доступ к ключу, добавляя одно или несколько ограничений для приложений тех типов, которые хотите авторизовать, после чего разрешаются только запросы, исходящие из этих источников.
Ограничения API. Вы можете ограничить использование вашего ключа API для определенных API, SDK или сервисов платформы Google Maps. Ограничения API разрешают запросы только к указанным вами API и SDK. Для каждого ключа API можно указать столько ограничений, сколько необходимо. Список доступных API включает все API, включенные в проекте.
Установите ограничение на использование ключа API для конкретного приложения.
Откройте страницу «Учетные данные платформы Google Maps» в консоли Google Cloud.
Выберите ключ API, доступ к которому вы хотите ограничить.
На странице редактирования ключа API в разделе «Ограничения ключа» выберите «Установить ограничение для приложения» .
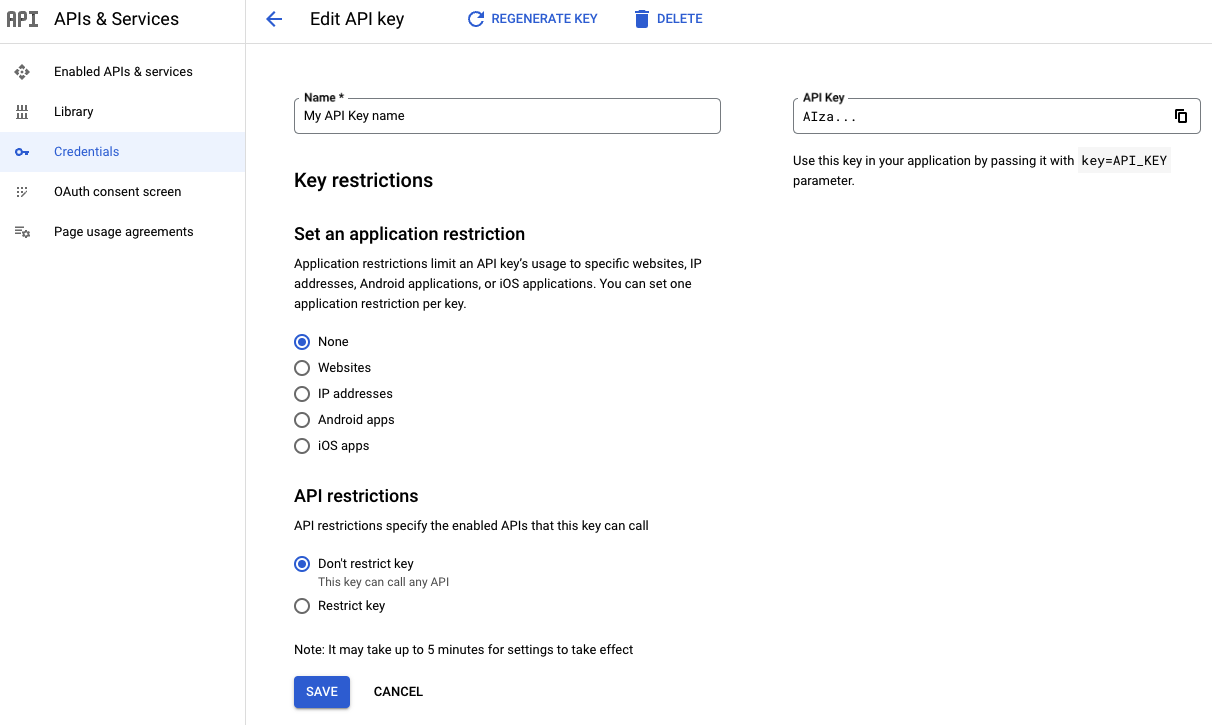
Выберите один из типов ограничений и предоставьте запрашиваемую информацию, следуя списку ограничений.
Тип ограничения Описание Веб-сайты Укажите один или несколько сайтов-источников перехода. - Универсально поддерживаемыми схемами URI для рефереров являются
httpsиhttp. Работа других схем не гарантирует корректной работы, поскольку современные веб-браузеры по соображениям конфиденциальности не отправляют заголовок `Referer` в исходящих запросах. - Всегда указывайте полную строку источника перехода, включая схему протокола, имя хоста и, при необходимости, порт (например,
https://google.com). - Для авторизации всех поддоменов можно использовать символы-заменители. Например,
https://*.google.comпринимает все сайты, заканчивающиеся на.google.com. - Будьте осторожны при авторизации полных путей перехода, например,
https://google.com/some/path, поскольку большинство веб-браузеров по соображениям конфиденциальности удаляют путь из междоменных запросов.
IP-адреса Укажите один или несколько IPv4 или IPv6 адресов, либо подсетей, используя нотацию CIDR. IP-адреса должны совпадать с исходным адресом, который наблюдают серверы платформы Google Maps. Если вы используете трансляцию сетевых адресов (NAT) , этот адрес обычно соответствует публичному IP-адресу вашего компьютера. Приложения для Android Добавьте имя пакета Android (из файла
AndroidManifest.xml) и отпечаток сертификата подписи SHA-1 для каждого приложения Android, которое вы хотите авторизовать.- Выберите приложения для Android .
- Нажмите + Добавить .
- Введите имя пакета и отпечаток сертификата SHA-1. Например:
com.example.android.mapexample
BB:0D:AC:74:D3:21:E1:43:67:71:9B:62:91:AF:A1:66:6E:44:5D:75
- Нажмите « Сохранить ».
Существует два типа сертификатов:
- Отладочный сертификат : Используйте этот тип сертификата только для тестируемых приложений и другого кода, не предназначенного для производственной среды. Не пытайтесь опубликовать приложение, подписанное отладочным сертификатом. Инструменты Android SDK автоматически генерируют этот сертификат при запуске отладочной сборки.
- Сертификат для выпуска : Используйте этот сертификат, когда будете готовы выпустить свое приложение в магазин приложений. Инструменты Android SDK генерируют этот сертификат при запуске сборки для выпуска.
Для получения дополнительной информации о подписании приложений Android и сертификатах см. руководство «Подпишите свое приложение» .
Если вы используете функцию подписи приложений Play , чтобы получить отпечаток сертификата подписи, см. раздел «Работа с поставщиками API» . Если вы управляете собственным ключом подписи, см. раздел «Самоподписание приложения» или обратитесь к инструкциям для вашей среды сборки.
приложения для iOS Добавьте идентификатор пакета каждого iOS-приложения, которое вы хотите авторизовать.
- Выберите приложения для iOS .
- Нажмите + Добавить .
- Добавьте идентификатор пакета, чтобы принимать запросы от iOS-приложения с этим идентификатором.
- Нажмите « Сохранить ».
Рекомендации по ограничению использования приложения см. в разделе «Рекомендуемые ограничения использования приложения» .
- Универсально поддерживаемыми схемами URI для рефереров являются
Выберите «Сохранить» .
Установите ограничения API для ключа API.
Откройте страницу «Учетные данные платформы Google Maps» в консоли Google Cloud.
Выберите ключ API, доступ к которому вы хотите ограничить.
На странице редактирования ключа API , в разделе «Ограничения API» :
Выберите «Ограничить ключ» .
Откройте раздел «Выбрать API» и выберите API или SDK, к которым ваше приложение должно иметь доступ, используя ключ API.
Если API или SDK не указаны в списке, их необходимо включить. Подробнее см. раздел «Включение одного или нескольких API или SDK» .
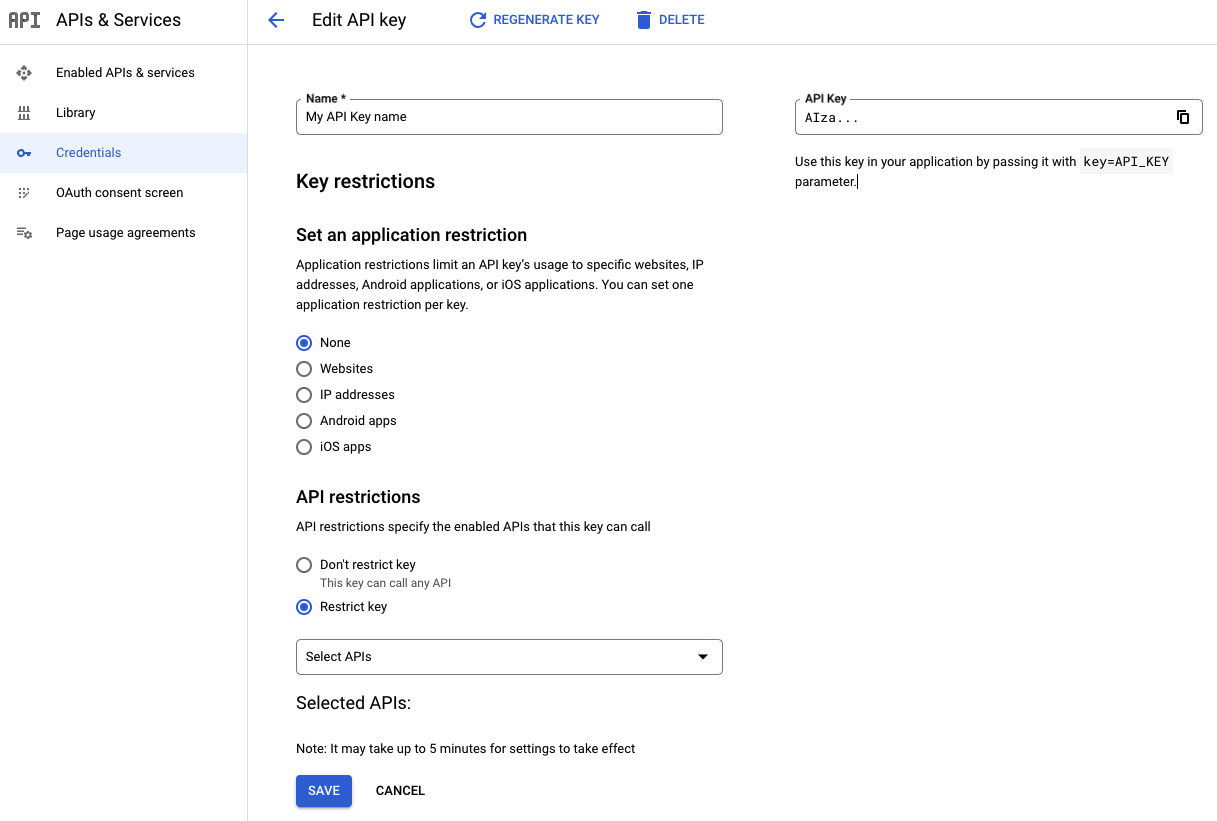
Выберите «Сохранить» .
После этого шага ограничение становится частью определения ключа API. Убедитесь, что вы указали все необходимые данные, и нажмите «Сохранить» , чтобы сохранить ограничения ключа API. Для получения дополнительной информации см. руководство «Получение ключа API» в документации к конкретному API или SDK, который вас интересует.
Рекомендуемые ограничения API см. в разделе «Рекомендуемые ограничения API» .
Проверьте использование вашего API-ключа.
Если вы ограничиваете использование ключей API после их создания или хотите узнать, какие API используются с помощью ключа, чтобы ограничить их использование, вам следует проверить использование вашего ключа API. Эти шаги покажут вам, в каких сервисах и методах API используется ключ API. Если вы видите использование за пределами сервисов платформы Google Maps, проведите расследование, чтобы определить, нужно ли добавить дополнительные ограничения во избежание нежелательного использования. Вы можете использовать инструмент отслеживания метрик в консоли Google Maps Platform Cloud, чтобы определить, какие ограничения API и приложений следует применить к вашему ключу API:
Определите API, которые используют ваш API-ключ.
Следующие отчеты по метрикам позволяют определить, какие API используют ваши API-ключи. Используйте эти отчеты для выполнения следующих действий:
- Узнайте, как используются ваши API-ключи.
- Выявите неожиданное использование
- Помогите проверить, безопасно ли удалять неиспользуемый ключ. Информацию об удалении ключа API см. в разделе «Удаление неиспользуемых ключей API» .
При применении ограничений к API используйте эти отчеты для создания списка авторизуемых API или для проверки автоматически сгенерированных рекомендаций по ограничению ключей API. Дополнительную информацию о рекомендуемых ограничениях см. в разделе « Применение рекомендуемых ограничений» . Дополнительную информацию об использовании обозревателя метрик см. в разделе «Создание диаграмм с помощью обозревателя метрик» .
Перейдите в раздел «Обозреватель метрик» в консоли Google Cloud.
Войдите в систему и выберите проект, для которого хотите проверить ключи API.
Перейдите на страницу обозревателя метрик для вашего типа API:
Для получения ключей API, использующих любой API , кроме API встраивания карт : перейдите на страницу обозревателя метрик .
Для получения ключей API, используемых с Maps Embed API , перейдите в раздел «Обозреватель метрик» .
Проверьте каждый ключ API:
Выберите «ДОБАВИТЬ ФИЛЬТР» .
Выберите метку
credential_id.Выберите значение , соответствующее ключу, который вы хотите проверить.
Обратите внимание, для каких API используется этот ключ API, и убедитесь, что его использование ожидаемо.
После этого выберите «Удалить фильтр» в конце строки активного фильтра, чтобы удалить лишний фильтр.
Повторите то же самое для всех оставшихся ключей.
Используйте в качестве ключа API только те API-интерфейсы, которые используются.
Если вы обнаружили несанкционированное использование, см. раздел «Обработка несанкционированного использования ключа API» .
Выберите правильный тип ограничения для приложений с помощью инструмента «Обозреватель метрик».
После того, как вы проверили и предприняли все необходимые действия, чтобы убедиться, что ваш API-ключ используется только для тех сервисов платформы Google Maps, которые он использует, также убедитесь, что API-ключ имеет правильные ограничения для приложений.
Если для вашего API-ключа установлены рекомендуемые ограничения, примените их. Для получения дополнительной информации см. раздел «Применение рекомендуемых ограничений API-ключа» .
Если для вашего API-ключа отсутствуют рекомендации по ограничениям, определите тип применяемого ограничения для приложения на основе указанного platform_type с помощью инструмента Metrics explorer:
Перейдите в раздел «Обозреватель метрик» в консоли Google Cloud.
Войдите в систему и выберите проект, для которого хотите проверить API.
Перейдите на эту страницу обозревателя метрик: Обозреватель метрик .
Проверьте каждый ключ API:
Выберите «ДОБАВИТЬ ФИЛЬТР» .
Выберите метку
credential_id.Выберите значение , соответствующее ключу, который вы хотите проверить.
После этого выберите «Удалить фильтр» в конце строки активного фильтра, чтобы удалить лишний фильтр.
Повторите то же самое для всех оставшихся ключей.
Получив тип платформы для ваших API-ключей, примените ограничение приложения для этого
platform_type:PLATFORM_TYPE_JS: Применить ограничения веб-сайта к этому ключу.PLATFORM_TYPE_ANDROID: Применить ограничения для приложений Android к этому ключу.PLATFORM_TYPE_IOS: Применить ограничения для iOS-приложений к ключу.PLATFORM_TYPE_WEBSERVICE: Возможно, вам придется полагаться на ограничения по IP-адресу для ключа, чтобы обеспечить его корректное использование.Рекомендации по использованию статического API карт и статического API просмотра улиц см. в разделе «Защита использования статического веб-API» .
Рекомендации по использованию API для встраивания карт см. в разделе «Веб-сайты, использующие API для встраивания карт» .
Мой API-ключ использует несколько типов платформ: ваш трафик не может быть должным образом защищен с помощью одного API-ключа. Вам необходимо перейти на использование нескольких API-ключей. Для получения дополнительной информации см. раздел «Переход на использование нескольких API-ключей» .
Используйте отдельные API-ключи для каждого приложения.
Эта практика ограничивает область действия каждого ключа. Если один из ключей API скомпрометирован, вы можете удалить или заменить затронутый ключ, не обновляя при этом другие ключи API. В одном проекте можно создать до 300 ключей API. Для получения дополнительной информации см. раздел «Ограничения на ключи API» .
Хотя использование одного API-ключа на приложение идеально подходит с точки зрения безопасности, вы можете использовать ограниченные ключи в нескольких приложениях, если они используют один и тот же тип ограничений.
Примените рекомендуемые ограничения на использование API-ключей.
Для некоторых владельцев проектов, редакторов и администраторов ключей API консоль Google Cloud предлагает определенные ограничения для неограниченных ключей API в зависимости от их использования и активности на платформе Google Maps.
Если рекомендации доступны, они отображаются в виде предварительно заполненных полей на странице «Учетные данные платформы Google Maps» .
Автоматизированные рекомендации поддерживают API и SDK платформы Google Maps.
JavaScript API для работы с картами, включая службу построения маршрутов (устаревшая версия), службу матриц расстояний (устаревшая версия), службу высот, службу геокодирования, класс Place, виджет автозаполнения Place (новый), API данных автозаполнения Place, библиотеку Places, службу Places, виджет автозаполнения Place и набор инструментов пользовательского интерфейса Places.
Статический API карт и статический API просмотра улиц
API для встраивания карт
Maps SDK для Android, Navigation SDK для Android, Places SDK для Android и Places UI Kit для Android
Maps SDK для iOS, Navigation SDK для iOS, Places SDK для iOS, Places Swift SDK для iOS и Places UI Kit для iOS.
Причины, по которым вы можете не увидеть рекомендацию или увидеть неполную рекомендацию.
Причины, по которым рекомендация не была принята
Вы также используете ключ API не только на сервисах платформы Google Maps, но и на сервисах платформы Maps, которые еще не поддерживаются автоматическими рекомендациями.
Если вы видите использование сервисов в других средах, не применяйте рекомендацию, не выполнив предварительно следующие действия:
Убедитесь, что информация об использовании API, которую вы видите в окне «Обозреватель метрик» консоли Google Cloud, является достоверной.
Вручную добавьте отсутствующие сервисы в список авторизуемых API.
Вручную добавьте все отсутствующие ограничения для приложений, добавленных в список API. Если для других добавленных сервисов требуются другие типы ограничений, см. раздел «Переход на использование нескольких ключей API» .
Ваш API-ключ не используется в клиентских SDK или API.
Вы используете ключ API в приложении или на веб-сайте с низкой интенсивностью использования, которые не использовались в течение последних 60 дней.
Вы совсем недавно создали новый ключ или совсем недавно развернули существующий ключ в новом приложении. В этом случае просто подождите еще несколько дней, чтобы рекомендации обновились.
Вы используете ключ API в нескольких приложениях, что может привести к конфликтующим типам ограничений, или используете один и тот же ключ API в слишком многих разных приложениях или веб-сайтах. В любом случае, в качестве лучшей практики следует перейти на использование нескольких ключей. Для получения более подробной информации см. раздел «Переход на использование нескольких ключей API» .
Причины, по которым может быть показана неполная рекомендация
Вы используете ключ API в приложении или на веб-сайте с низкой интенсивностью использования, которые не использовались в течение последних 60 дней.
Вы совсем недавно начали использовать существующий ключ в новом API или сервисе, и автоматический конвейер рекомендаций по ограничению использования ключей API еще не обработал обновленные метрики использования. Распространение метрик использования может занять несколько дней.
Если вы видите использование сервисов в других средах, не применяйте рекомендацию, не выполнив предварительно следующие действия:
Убедитесь, что информация об использовании API, которую вы видите в окне «Обозреватель метрик» консоли Google Cloud, является достоверной.
Вручную добавьте отсутствующие сервисы в список авторизуемых API.
Вручную добавьте все отсутствующие ограничения для приложений, добавленных в список API. Если для других добавленных сервисов требуются другие типы ограничений, см. раздел «Переход на использование нескольких ключей API» .
Если вам не требуется срочно ограничить доступ к ключу, например, из-за несанкционированного использования, вы можете подождать день-два, пока рекомендации обновятся.
Причины, по которым вы можете увидеть рекомендации, не отображаемые на графиках.
Ваше приложение или веб-сайт отправляли трафик лишь в очень короткие промежутки времени. В этом случае переключитесь с режима ДИАГРАММЫ на отображение ТАБЛИЦЫ или ОБА режима , поскольку данные об использовании по-прежнему отображаются в легенде. Для получения дополнительной информации см. раздел «Переключение полной легенды диаграммы» .
Ваш трафик поступает от API встраивания карт. Инструкции см. в разделе «Определение API, использующих ваш ключ API» .
Трафик из приложения или веб-сайта выходит за пределы диапазона дат, доступного в инструменте «Обозреватель метрик» консоли Google Cloud.
Для применения рекомендованных ограничений
Откройте страницу «Учетные данные платформы Google Maps» в консоли Google Cloud.
Если доступно, выберите «Применить рекомендуемые ограничения» .
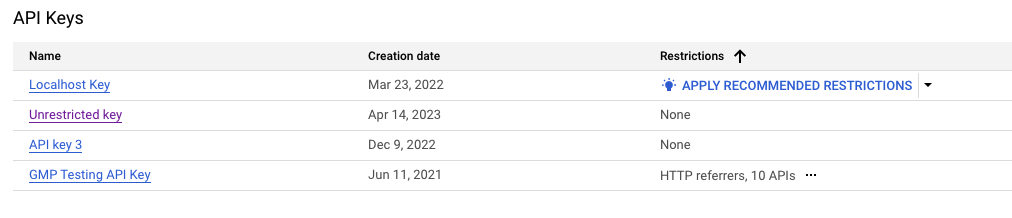
Выберите «Проверить использование API» , чтобы убедиться, для каких сервисов используется ключ API. Если вы видите сервисы, отличные от Google Maps Platform, сделайте паузу и вручную проверьте рекомендации, описанные выше. См. шаги по устранению неполадок в начале раздела «Применение рекомендуемых ограничений для ключа API» .
Убедитесь, что предварительно заполненные ограничения соответствуют веб-сайтам и приложениям, где вы планируете использовать свой API-ключ.
Рекомендации : Документируйте и удаляйте все ограничения на приложения или API, не связанные с вашими сервисами. Если что-то сломается из-за неожиданной зависимости, вы сможете добавить необходимые приложения или API обратно.
Если вы заметили, что приложение, веб-сайт или API явно отсутствуют в ваших рекомендациях, добавьте их вручную или подождите пару дней, чтобы рекомендации обновились.
Если вам потребуется дополнительная помощь с предложенной рекомендацией, обратитесь в службу поддержки .
Выберите «Применить» .
Что делать, если вашу заявку отклонили после предоставления рекомендации?
Если вы заметили, что приложение или веб-сайт отклоняются после применения ограничения, найдите в сообщении об ошибке ответа API ограничение для приложения, которое необходимо добавить.
SDK и API на стороне клиента
- Приложения на основе браузера и веб-просмотра
Современные браузеры обычно удаляют заголовок
Refererв междоменных запросах по соображениям конфиденциальности, часто оставляя толькоOrigin. Однако точное поведение зависит от применяемойreferrer-policyсайта и может также различаться в зависимости от браузера и его версии.Веб-приложения, использующие непрозрачные или локальные URI-схемы для загрузки контента, обычно заставляют браузер или веб-представление полностью скрывать заголовок
Refererиз любых исходящих вызовов, что может привести к сбоям запросов при использовании ключей API с ограничениями веб-сайта.Дополнительные рекомендации см. в разделе «Размещение браузерных приложений на сервере» .
Инструкции по устранению неполадок в приложениях, работающих в браузере и через веб-просмотр:
Для получения подробной информации о том, как авторизовать ваше приложение с помощью JavaScript API для работы с картами, см. консоль отладки браузера.
Поддержка экзотических URI-схем осуществляется частично . Если отдельные части вашего приложения не работают с экзотической URI-схемой, даже после авторизации необходимого реферера, вам, вероятно, потребуется разместить приложение удаленно на сервере и загружать его по протоколу HTTPS (или HTTP).
Если вам нужна помощь с экзотическими схемами URI, обратитесь в службу поддержки .
Другие API картографической платформы обычно возвращают необходимый для авторизации реферер в ответе об ошибке API, при условии, что клиент отправил эту информацию вместе с отклоненным запросом.
Экзотические схемы URI не поддерживаются.
- Приложения для Android
Используйте Android Debug Bridge (adb) или Logcat.
- приложения для iOS
См. раздел «Просмотр сообщений журнала».
Приложения, напрямую обращающиеся к веб-сервисам
Для приложений, напрямую обращающихся к HTTPS REST API или gRPC-конечным точкам платформы Maps без клиентского SDK Google Maps Platform, см. ниже:
- Приложения для Android и iOS
Если ваше приложение для Android или iOS обращается к сервисам платформы карт напрямую, не используя доступные SDK клиента Google Maps Platform, см. разделы «Приложения для Android» и «Приложения для iOS» для получения дополнительных советов по устранению неполадок, а также раздел «Безопасные вызовы веб-сервисов на стороне клиента» для ознакомления с актуальными рекомендациями по обеспечению безопасности в мобильных приложениях.
Если ваше приложение регистрирует ошибки в ответах API платформы карт, приведенные выше инструкции для клиентских SDK также могут оказаться полезными для устранения неполадок с аутентификацией.
- Приложения на стороне сервера
Наилучшая защита серверных приложений, использующих ключи API, достигается за счет ограничений по IP-адресам. Если вы применили ограничения по IP-адресам к своему ключу, и ваш сервис регистрирует ошибки API платформы карт, проверьте системные журналы для получения дополнительной информации. В ответе об ошибке будет указан IP-адрес сервера, который необходимо авторизовать.
- Приложения, работающие в браузере или в режиме просмотра веб-страниц.
Хотя API Maps Static, Street View Static и более новые API платформы Google Maps также поддерживают ограничения по Referrer, следует отметить, что веб-браузеры или веб-представления, скорее всего, ограничат заголовок
RefererтолькоOriginдля междоменных запросов и, вероятно, вообще не будут его отправлять, например, для локально доступных ресурсов или для ресурсов, предоставляемых по протоколам, отличным от HTTP или HTTPS.Если вы не можете использовать API Maps JavaScript в своем приложении, и ограничения веб-сайта не работают, см. раздел «Безопасные вызовы веб-сервисов на стороне клиента», чтобы узнать, как безопасно выполнять вызовы веб-сервисов платформы Maps из вашего клиентского приложения, работающего в браузере.
Советы по проверке ограничений API
Чтобы проверить необходимые ограничения для вашего API, см. раздел «Определение API, использующих ваш ключ API» .
Если вы не можете определить, какие ограничения следует применить:
- Задокументируйте действующие ограничения для дальнейшего использования.
- Временно удалите их, пока вы разбираетесь с проблемой. Вы можете проверить использование API с течением времени, выполнив действия, описанные в разделе «Проверка использования ключа API» .
- При необходимости обратитесь в службу поддержки .
Удалите неиспользуемые ключи API.
Прежде чем удалять ключ API, убедитесь, что он не используется в рабочей среде. Если нет успешного трафика, ключ, скорее всего, можно безопасно удалить. Для получения дополнительной информации см. раздел «Проверка использования ключа API» .
Чтобы удалить ключ API:
Откройте страницу «Учетные данные платформы Google Maps» в консоли Google Cloud.
Выберите ключ API, который хотите удалить.
Нажмите кнопку «Удалить» в верхней части страницы.
На странице «Удалить учетные данные» выберите «Удалить» .
Удаление ключа API занимает несколько минут для распространения изменений. После завершения распространения любой трафик, использующий удаленный ключ API, будет отклонен.
Будьте осторожны при смене ключей API.
Смена API-ключа создает новый ключ, который сохраняет все ограничения старого ключа. В течение этого периода принимаются как старый, так и новый ключ, что дает вам возможность перевести ваши приложения на использование нового ключа.
Перед изменением ключа API :
Сначала попробуйте ограничить доступ к своим API-ключам, как описано в разделе «Ограничение доступа к API-ключам» .
Если ограничение доступа к вашему API-ключу невозможно из-за конфликтующих типов ограничений приложения, выполните миграцию на несколько новых (ограниченных) ключей, как описано в разделе «Миграция на несколько API-ключей» . Миграция позволяет контролировать сроки миграции и развертывания новых API-ключей.
Если предложенные выше варианты не подходят , и вам необходимо сменить API-ключ для предотвращения несанкционированного использования, выполните следующие действия:
Откройте страницу «Учетные данные платформы Google Maps» в консоли Google Cloud.
Откройте API-ключ, который хотите поменять местами.
В верхней части страницы выберите кнопку «Поворот» .
При желании можно изменить имя ключа API.
Выберите «Создать» .
Обновите свои приложения, чтобы использовать новый ключ.
После обновления приложений с использованием нового ключа удалите старый ключ, нажав кнопку «Удалить предыдущий ключ» в разделе «Предыдущий ключ» на странице нового ключа API.
Переход на использование нескольких ключей API
Для перехода от использования одного API-ключа для нескольких приложений к одному уникальному API-ключу для каждого приложения выполните следующие действия:
Определите, каким приложениям нужны новые ключи :
- Веб-приложения обновлять проще всего, поскольку вы контролируете весь код. Запланируйте обновление ключей для всех ваших веб-приложений.
- Разработка мобильных приложений гораздо сложнее, поскольку клиентам необходимо обновить свои приложения, прежде чем новые ключи можно будет использовать.
Создайте и ограничьте новые ключи : добавьте ограничение для приложения и как минимум одно ограничение для API. Для получения дополнительной информации см. раздел «Рекомендуемые лучшие практики» .
Добавьте новые ключи в свои приложения : для мобильных приложений этот процесс может занять несколько месяцев, пока все ваши пользователи не обновят приложение до последней версии с новым API-ключом.
Разделите использование клиентской и серверной частей на отдельные проекты.
Если вам необходимо вызывать сервисы платформы Google Maps как из серверных приложений, так и напрямую из клиентских приложений, работающих на устройствах конечных пользователей, Google рекомендует разделить использование этих сервисов между двумя отдельными проектами.
Этот подход позволяет устанавливать соответствующие поминутные квоты для каждого пользователя на большинстве сервисов платформы Google Maps в вашем клиентском проекте, помогая обеспечить всем конечным пользователям справедливую долю общей квоты проекта без взаимного влияния.
Однако, поскольку ограничения квоты для каждого пользователя влияют как на клиентские, так и на серверные приложения, если вам также требуется высокая пропускная способность для серверных задач, создайте отдельный проект для этого случая, настроив его с более высоким лимитом квоты для каждого пользователя или вообще без ограничений.
Отключить неиспользуемые службы
Не оставляйте неиспользуемые сервисы включенными в проекте, так как эта практика уязвима для злоупотреблений, особенно если вы не ограничили доступ ко всем своим публичным API-ключам. В качестве лучшей практики, включайте сервис в проекте только тогда, когда он действительно необходим вашим приложениям.
Добавление ограничений API к ключу предотвращает его использование в сервисах, для которых он не авторизован, но ограничения API применяются только к этому конкретному ключу. Отключение сервиса на уровне проекта предотвращает несанкционированное использование сервиса с любым ключом, связанным с проектом.
Используйте SDK на стороне клиента.
При использовании предоставленных клиентских SDK платформы Google Maps вы всегда сможете применять соответствующие ограничения к своему API-ключу для обеспечения безопасности использования сервиса.
Использование клиентских SDK также позволит вам внедрить более продвинутые механизмы безопасности, такие как Firebase App Check на тех платформах API, которые его поддерживают. Дополнительные сведения см. в разделе «Использование App Check для защиты вашего ключа API» .
Если для вашей платформы недоступны SDK для клиентской части, см. раздел «Защита вызовов веб-сервисов на стороне клиента» .
Информацию о доступности клиентских SDK Google Maps Platform для различных платформ см. в разделе «Рекомендуемые ограничения для приложений и API» .
Защита использования статического веб-API
Статические веб-API, такие как Maps Static API и Street View Static API, похожи на вызовы API веб-сервисов.
Вы обращаетесь к обоим сервисам, используя HTTPS REST API, и обычно URL-адрес запроса API генерируется на сервере. Однако вместо возврата JSON-ответа статические веб-API генерируют изображение, которое можно встроить в сгенерированный HTML-код. Что еще важнее, как правило, именно конечный пользователь , а не сервер, обращается к сервису Google Maps Platform.
Используйте цифровую подпись
В качестве лучшей практики всегда используйте цифровые подписи в дополнение к ключу API. Также проверьте, сколько неподписанных запросов вы хотите разрешить в день, и скорректируйте квоты на неподписанные запросы соответствующим образом.
Более подробную информацию о цифровых подписях см. в Руководстве по цифровым подписям .
Защитите свой секрет подписания
Для защиты статических веб-API не следует встраивать секреты подписи API непосредственно в код или исходный код, а также не следует раскрывать их в клиентских приложениях. Следуйте этим рекомендациям по защите секретов подписи:
Генерируйте подписанные URL-адреса запросов для статического API карт и статического API просмотра улиц на стороне сервера при отображении веб-страницы или в ответ на запрос из вашего мобильного приложения .
Для статического веб-контента можно использовать виджет «Подписать URL сейчас» на странице «Учетные данные платформы Google Maps» в консоли Cloud Console.
Для динамического веб-контента ознакомьтесь с доступными примерами кода для подписи URL-запросов.
Храните секреты подписи вне исходного кода и дерева исходного кода вашего приложения . Если вы помещаете секреты подписи или любую другую конфиденциальную информацию в переменные окружения или включаемые файлы, которые хранятся отдельно, а затем делитесь своим кодом, то секреты подписи не включаются в общие файлы. Если вы храните секреты подписи или любую другую конфиденциальную информацию в файлах, храните эти файлы вне дерева исходного кода вашего приложения, чтобы ваши секреты подписи не попали в вашу систему контроля версий. Эта мера предосторожности особенно важна, если вы используете общедоступную систему управления исходным кодом, такую как GitHub.
Защита ключей API веб-сервиса
For secure use of Google Maps Platform APIs and services from client-side apps, see Use client-side SDKs and Secure client-side web service calls .
Store API keys outside of your application's source code or source tree . If you put your API keys or any other information in environment variables or include files that are stored separately and then share your code, the API keys are not included in the shared files. This is particularly important if you use a public source code management system, such as GitHub.
To help shield your web service API key against accidental use, Google recommends applying API restrictions to any key used for Maps Platform. Furthermore, also applying IP address restrictions to your web service key will protect it against help protect it against unauthorized use from other source IP addresses, even if the key accidentally leaks.
Use OAuth for server-side apps
OAuth 2.0 is an open standard for access delegation.
While the OAuth 2.0 protocol supports use cases, where an end user authorizes an application to access personal data on their behalf, the intended use case for OAuth 2.0 with Maps Platform is for the developer to utilize temporary access tokens for authorizing their application to call an API on behalf of their Google Cloud project service account with the permissions of the service account.
As a service account may have extremely broad permissions, OAuth 2.0 is recommended for authorizing server-to-server calls between a developer's trusted server-side applications and Google's Maps Platform servers.
For client-side applications running on end user devices, other authentication methods, such as API keys, are recommended.
If you want to use OAuth 2.0 to authorize server-to-server traffic, look for the OAuth topic in your API documentation.
For example, here is the OAuth topic for the Address Validation API .
Secure client-side web service calls
If client-side SDKs are not available, see the recommendations below.
Используйте прокси-сервер
Using a secure proxy server provides a solid source for interacting with a Google Maps Platform web service endpoint from a client-side application without exposing your API key, signing secret or Google Cloud service account to unauthorized users.
Основные моменты:
Construct your Google Maps Platform requests on the proxy server. Don't allow clients to relay arbitrary API calls using the proxy.
Post-process the Google Maps Platform responses on your proxy server. Filter out data that the client doesn't need.
For more information about using a proxy server, see Living Vicariously: Using Proxy Servers with the Google Data API Client Libraries .
Secure direct mobile web service calls
If you are unable to set up a secure proxy server for your client-side app, secure your application using the following steps:
Use HTTP headers:
Android : Use the
X-Android-PackageandX-Android-CertHTTP headers.iOS : Use the
X-Ios-Bundle-IdentifierHTTP header.
Add the corresponding application restrictions to your Android or iOS key.
Before you consider issuing calls directly from your mobile application to a Google Maps Platform REST API web service, verify that requests with incorrect Android or iOS application identifiers are rejected.
If Android and iOS application restrictions are not supported on the tested endpoint, Google strongly recommends that you use a secure proxy server between your mobile clients and the Google Maps Platform web service endpoint.
Tips for Android applications:
Before you integrate your Android application with Google Maps Platform services, verify that your application ID (also called package name) is formatted correctly. For details, see Configure app module . in the Android documentation.
To pass
X-Android-Packagedirectly from your application, look it up programmatically usingContext.getPackageName().To pass
X-Android-Certdirectly from your applications, calculate the required SHA-1 fingerprint of your application signing certificates, accessible throughPackageInfo.signingInfo.If you authorize your Android application using the Google Cloud console, note that the UI expects the SHA-1 fingerprint to be a colon-delimited string, eg,
00:11:22:33:44:55:66:77:88:99:AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF:00:11:22:33. However, thegcloudtool and the API keys API expect the hexadecimal string without delimiters.
Tips for iOS applications:
Before you integrate your iOS application with Google Maps Platform services, verify that your Bundle ID is formatted correctly .
You should typically always pass the Bundle ID of your main bundle in the
X-Ios-Bundle-Identifierheader, when authorizing your iOS application.
For further information, refer to articles Manage API keys and Use API keys to access APIs .
Host your browser based apps on a server
Frameworks, such as Apache Cordova, allow you to conveniently create multi-platform hybrid apps running inside a webview. However, API key website restrictions are not guaranteed to work correctly, unless your web app is loaded using HTTP or HTTPS from a website that you control and have authorized.
Bundled resources, loaded locally from within a hybrid application, or accessed using a local file URL will in many cases prevent referrer based authorization from working as the browser engine powering your webview will omit sending the Referer header. To avoid this, host your web applications server-side, not client-side.
Alternatively, for mobile applications, consider using available native Google Maps Platform Android and iOS SDKs, instead of using a web based SDK.
Use App Check to secure your API key
Certain Maps SDKs and APIs allow you to integrate with Firebase App Check . App Check provides protection for calls from your app to Google Maps Platform by blocking traffic that comes from sources other than legitimate apps. It does this by checking for a token from an attestation provider. Integrating your apps with App Check helps to protect against malicious requests, so you're not charged for unauthorized API calls.
App Check integration instructions:
Handle unauthorized use of an API key
If you detect use of your API key that is unauthorized, do the following to address the problem:
Restrict your keys : If you've used the same key in multiple apps, migrate to multiple API keys, and use separate API keys for each app. For more details, see:
If you use the Places SDK or the Maps Javascript API, you can also use App Check to secure your API Key .
Only replace or rotate keys if the following is true:
You detect unauthorized usage on keys that either cannot be restricted or are already restricted, and App Check is not applicable.
You want to move more quickly to secure your API key and stop the abuse, even if it might impact legitimate traffic from your application.
Before proceeding, read through Be careful when rotating API keys .
If you are still having issues or need help, contact support .
Recommended application and API restrictions
The following sections suggest appropriate application and API restrictions for each Google Maps Platform API, SDK or service.
Recommended API Restrictions
The following guidelines for API restrictions apply to all Google Maps Platform services:
Restrict your API key to only the APIs you are using it for, with the following exceptions:
If your app uses the Places SDK for Android or Places SDK for iOS, authorize Places API (New) or Places API, depending on the SDK versions you use. 1
If your app uses Maps JavaScript API, always authorize it on your key.
If you also use any of the following Maps JavaScript API services, you should also authorize these corresponding APIs:
Услуга API restriction Directions Service (Legacy) Directions API (Legacy) Distance Matrix Service (Legacy) Distance Matrix API (Legacy) Elevation Service Elevation API Geocoding Service API геокодирования Place class, Place Autocomplete Widget (New) & Place Autocomplete Data API Places API (New) 2 Places Library, Places Service & Place Autocomplete Widget Places API 2
1 For more details, see the Places SDK for Android and Places SDK for iOS documentation.
2 If you are unsure if you need to authorize Places API (New) or Places API, see the Maps JavaScript API documentation.
Несколько примеров:
You are using the Maps SDK for Android and Places SDK for Android, so you include the Maps SDK for Android and Places API (New) as API restrictions.
Your website uses the Maps JavaScript API Elevation Service and the Maps Static API, so you add API restrictions for all of the following APIs:
- API карт на JavaScript
- Elevation API
- Maps Static API
Recommended application Restriction
Веб-сайты
For websites using Maps JavaScript API services, Maps Static API or Street View Static API or calling recent Google Maps Platform services directly over the HTTPS REST API or gRPC, use the Websites application restriction:
1 For mobile applications, consider using the native Maps SDK for Android and Maps SDK for iOS .
2 For mobile applications, consider using the native Places SDK for Android and Places SDK for iOS .
3 See also Protect Static Web API usage .
Websites with the Maps Embed API
While using the Maps Embed API is no charge, you should still restrict any used API key to prevent abuse on other services.
Best practice : Create a separate API key for Maps Embed API use, and restrict this key to only the Maps Embed API. This restriction sufficiently secures the key, preventing its unauthorized use on any other Google service. For full control over where your Maps Embed API key can be used from, Google recommends also applying Websites application restrictions.
If you are unable to separate your Maps Embed API usage to a separate API key, secure your existing key using the Websites application restriction.
Apps and servers using web services
For servers and client-side apps from trusted corporate internal networks using web services together with API keys, use the IP addresses application restriction.
Use for apps and servers using these APIs:
4 For mobile applications, consider using the Navigation SDK.
5 For safe mobile usage, use a secure proxy server .
6 For client-side applications, consider using the native geolocation service offered by the platform; for example, W3C Geolocation for web browsers, LocationManager or the Fused Location Provider API for Android, or the Apple Core Location framework for iOS.
7 For mobile applications, consider using the native Places SDK for Android and Places SDK for iOS .
8 For safe client-side usage, use a secure proxy server .
Приложения для Android
For apps on Android, use the Android apps application restriction. Use for apps using these SDKs:
In addition, prevent accidentally checking API keys into version control by using the Secrets Gradle Plugin to inject secrets from a local file rather than storing them in the Android Manifest.
iOS apps
For apps on iOS, use the iOS apps application restriction. Use for apps and servers using these SDKs:
Дополнительная информация
- Управление ключами API
- Use API keys to access APIs
- Optimize your Google Maps Platform usage with quotas (video)
- How to generate and restrict API keys for the Google Maps Platform (video)
- Restricting API keys
- Securing API keys when using Static Maps and Street View APIs
- 15 Google Maps platform Best Practices

