对话型 Action 允许开发者为使用 Google 助理的用户创建自定义体验或对话,从而扩展了 Google 助理的功能。在对话中,对话型 Action 会处理来自 Google 助理的请求,并返回包含音频和视觉组件的响应。对话型 Action 还可以连接到外部服务,以增加对话或业务逻辑,然后再返回响应。
例如,当用户想要查询信息、获得个性化推荐内容或执行涉及电子付款的交易时,可以调用您的对话型 Action,以获得来自外部执行方式服务的响应。

用例
对话型 Action 最适合用于补充另一种体验的简单用例。良好的对话型 Action 通常分为以下几大类:
- 用户可以轻松回答的问题。可以使用时间或日期等熟悉的输入内容来完成的操作,例如预订航班。
- 快速但极具吸引力的实用 Action。通常,用户只需花费很少的时间就能立即享受到优势,比如了解他们喜爱的球队下一场比赛的时间。
- 本身更适合使用语音的操作。这些通常都是您希望无需动手就能完成的操作,例如在瑜伽或轻度锻炼期间接受指导。
对话型 Action 的运作方式
与采用以计算机为中心的范式的传统移动应用和桌面应用不同,用户通过自然流畅的来回对话与适用于 Google 助理的 Action 进行互动。对话型 Action 会在用户调用时开始,并一直持续到用户选择退出(使用预定短语)或您的对话型 Action 表示对话结束。
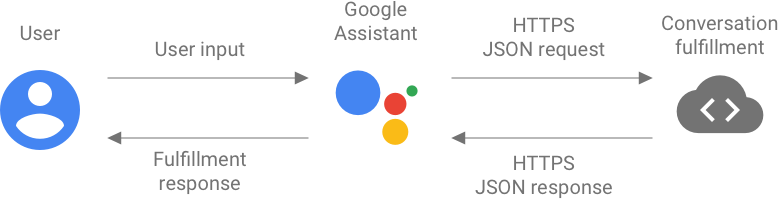
在对话期间,Google 助理会将用户输入的内容从语音转换为文字,并形成 JSON 请求以进行自然语言处理。这些请求会被发送到所谓的“对话执行方式”。
对话执行方式会将用户的查询解析为结构化数据,处理该数据,并向 Google 助理返回网络钩子 JSON 响应。然后,Google 助理会处理您的回复,并将其呈现给用户。
构建您自己的自然语言处理服务可能并非易事,因此我们提供 Dialogflow 作为一种处理方式。对于无法使用 Dialogflow 的开发者,我们还提供 Actions SDK 作为备用选项,并提供一个单独但相关的开发路径。
在 Dialogflow 中设置好代理后,对话执行方式可以通过 Dialogflow 的功能(包括使用 Dialogflow 执行方式)得到增强。通过这种方法,您可以将对话执行方式与可能需要为用户提供预期结果的其他服务隔离开来。
构建对话型 Action
构建对话型 Action 的主要工作就是设计对话和构建对话执行方式。您可以将对话视为对话型 Action 的界面。您需要考虑用户如何调用您的 Actions 项目、他们在对话中可以说的有效内容,以及您的 Actions 项目如何响应它们。
在 Actions 项目中,您需要提供用于发布项目的元数据,并指定对话执行方式的方法。使用 Dialogflow 的开发者将其 Dialogflow 代理与该项目关联,然后通过 Dialogflow 构建 fulfillment。对于使用 Actions SDK 的开发者,构建对话执行方式涉及以对话网络钩子格式进行编码和部署。
在设计对话时,我们建议遵循我们的流程和设计原则。对话式界面仍然是一项相对新技术,了解最佳实践有助于您在未来节省时间。
使用 Dialogflow 的执行方式
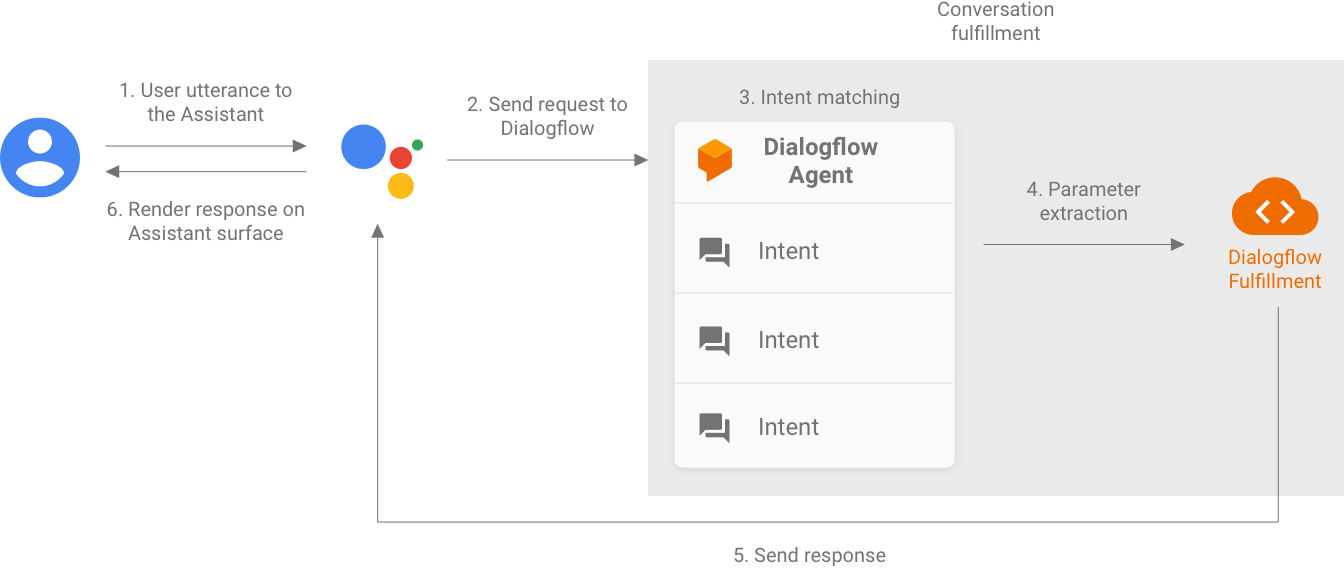
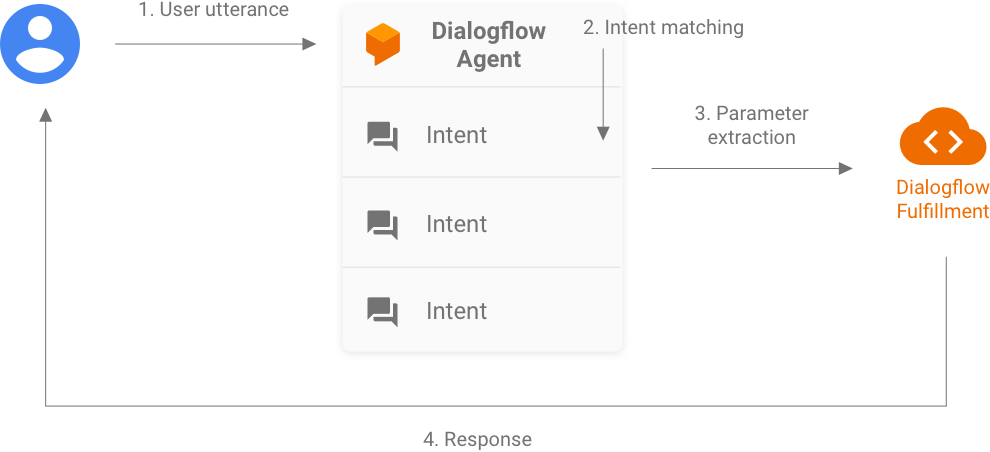
与 Dialogflow 代理集成时,该代理可处理对话型 Action 中的用户查询的 NLU。在此步骤中,您的 Dialogflow 代理会为您执行以下操作:
- 根据您提供的训练短语和对话上下文解析来自 Google 助理的每个传入请求。
- 将每个请求与 Dialogflow intent(也称为事件)匹配。
- 将参数提取到 Dialogflow 实体中。
然后,您的 Dialogflow 代理可以调用自己的 fulfillment(部署为 webhook)来执行某些逻辑,例如调用 REST API 或其他后端服务来生成响应以返回到 Google 助理。此 webhook 也称为 Dialogflow fulfillment,使用 Dialogflow 网络钩子格式。
在使用 Dialogflow 时构建对话 fulfillment 主要包括开发 Dialogflow fulfillment 网络钩子。在 Actions on Google 文档中,您可以找到一些可帮助您设计、构建和测试 Dialogflow 执行方式 webhook 的资源。最值得注意的是,这些资源包括 Node.js 客户端库和 Java 客户端库。
使用 Dialogflow 进行构建时,您可以使用 Dialogflow 控制台创建 Dialogflow 意图、实体和训练短语。
如需了解有关 Dialogflow 的更多常规信息,请参阅 Dialogflow 文档,了解 Actions on Google 集成。
使用 Actions SDK 的执行方式
使用 Actions SDK 构建对话执行方式主要包括创建和部署 Action 软件包。操作软件包以 ActionPackage 格式创建,并使用对话网络钩子格式。Action 包包含给定 Actions 项目的所有 Action。
Google 助理使用 Actions on Google intent 为您的对话执行方式提供用户查询。对于每个 intent,执行方式 webhook 都必须解析 intent,进行处理,然后向用户返回 JSON 响应。
响应
构建适用于 Google 助理的 Action 时,您可以针对各种 surface 设计对话,例如针对声控音响设备的以语音为中心的对话,或在 Google 助理支持的界面上显示视觉对话。这种方法可让用户通过语音或视觉功能快速完成操作。
构建执行方式时,您可以从各种有吸引力的响应类型中进行选择,供 Google 助理向用户显示。从包含简单文本的聊天气泡到媒体响应、轮播界面,甚至使用 Interactive Canvas 的 HTML。
后续步骤
如需了解详细的分步说明,请按照构建适用于 Google 助理的 Action(第 1 级)Codelab 进行操作,开始构建您的第一个对话型 Action。
然后,您可以继续参阅我们的指南,了解如何使用 Dialogflow 或使用 Actions SDK 构建自己的对话执行方式。您还可以探索下面这些有关构建对话型 Action 的其他资源:
- Actions on Google GitHub 代码库:示例代码和库。
- r/GoogleAssistantDev:从事 Google 助理相关工作的开发者的官方 Reddit 社区。