Os parceiros que usam o programa de listas de espera de reservas precisam concluir a configuração da conta antes de começar. No entanto, algumas etapas do guia geral não são necessárias para usar o recurso de lista de espera. As diretrizes desta página explicam quais etapas se aplicam a parceiros interessados em usar o recurso de lista de espera no Reservar com o Google. Sugerimos a leitura da visão geral antes de seguir as etapas de integração.
Processo de lançamento
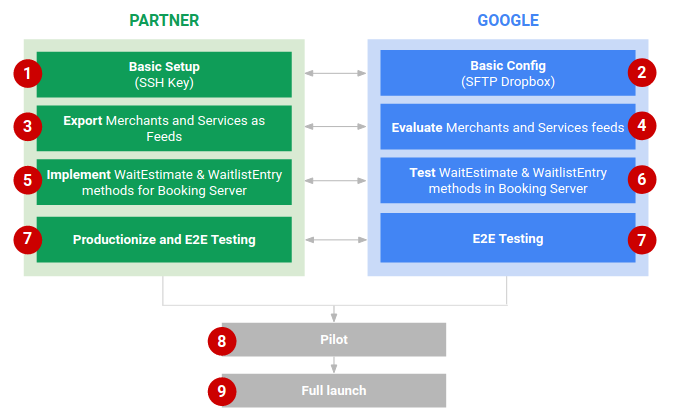
A Figura 1 descreve o processo para lançar os comerciantes que usam listas de espera no Centro de ações.
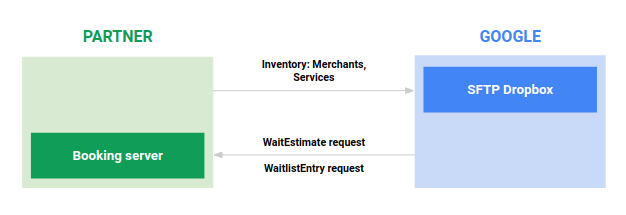
No geral, os principais fluxos de dados entre você (o parceiro) e o Google são mostrados na Figura 2:
Diretrizes para todos os parceiros da lista de espera de reservas
Lembre-se do seguinte ao implementar o recurso de listas de espera para reservas:
- O serviço de cada comerciante que usa a lista de espera de reservas precisa ter o campo
waitlist_rulespreenchido.- É necessário usar o mesmo serviço para a lista de espera e a reserva. Em outras palavras, se o restaurante também permite reservas, basta adicionar os metadados relacionados à lista de espera ao serviço para reserva.
- O envio de atualizações por SMS é necessário para a implementação da lista de espera nos
seguintes casos:
- Para confirmar que o usuário entrou na lista de espera.
- Notificar o usuário de que a mesa está pronta.
- Para notificar o usuário de que a entrada na lista de espera foi cancelada.
- As mensagens SMS precisam conter um link para uma página em que os usuários possam conferir o status da lista de espera.
- Os comerciantes que utilizam somente esse recurso não precisam enviar feeds de disponibilidade ao Centro de ações.
- Seu servidor de agendamento precisa implementar todas as etapas específicas da lista de espera mencionadas em Implementar o servidor de agendamento. Os parceiros que aceitam reservas e listas de espera podem adicionar os novos métodos ao servidor de agendamento.
- O Actions Center executa um conjunto de casos de teste para os métodos da lista de espera no servidor de agendamento.
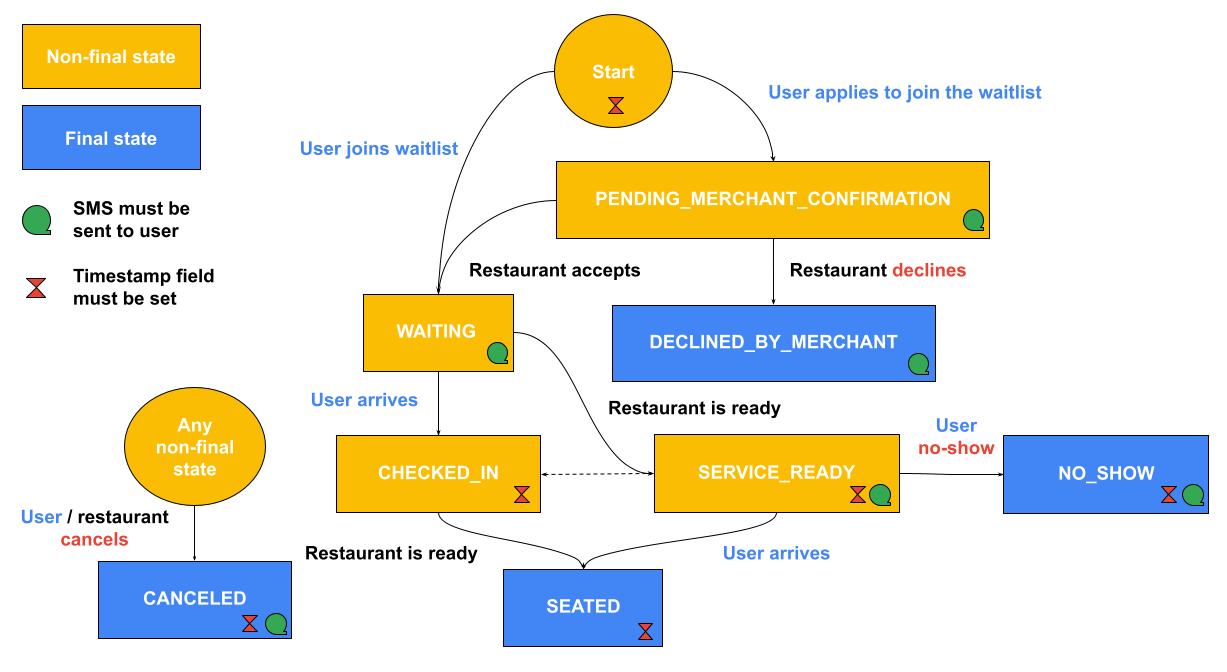
Fluxograma de status
Este gráfico descreve os status que precisam ser informados em
WaitlistEntry.waitlist_entry_state
ao responder a
GetWaitlistEntry
chamadas. O gráfico também indica quando registrar e preencher os campos
WaitlistEntry.waitlist_entry_state_times.*_time_seconds
e quando enviar um SMS para o usuário informando que ele entrou em um novo estado.
Casos extremos comuns
Confira a seguir casos extremos comuns em uma integração de listas de espera de reservas e as soluções preferidas para eles.
-
Se alguns tamanhos de grupo (mas não todos) não aceitarem novas adições à lista de espera
porque atualmente não há tempo de espera para eles, é preferível retornar
WaitEstimatespara todos os grupos na respostaBatchGetWaitEstimatese permitir que os usuários entrem na lista de espera desses grupos sem tempo de espera. Retorne umWaitLengthcom 0parties_ahead_counte/ou com umestimated_seat_time_rangecom 0start_secondse com 0end_secondspara osparty_sizes sem espera -
Caso um ou mais grupos não aceitem essas inclusões porque o tempo de espera ficou muito longo, omita
WaitEstimatespara eles na respostaBatchGetWaitEstimates.
Essas abordagens são preferenciais. Os usuários podem tomar decisões próprias, embora a lista de espera do comerciante não esteja totalmente aberta em alguns casos.
Diretrizes para parceiros que usam apenas listas de espera para reservas
Lembre-se do seguinte se o servidor de agendamento for usado somente para listas de espera:
- Os parceiros que usam apenas esse recurso não enviam feeds de disponibilidade ao Reservar com o Google.
- Os parceiros que usam apenas a lista de espera não implementam os métodos de reserva no servidor de agendamento. Em vez disso, implemente o servidor de agendamento com as instruções para a implementação da lista de espera.
- Os parceiros que usam apenas esse recurso não fazem chamadas de API para o Google. Isso significa que os parceiros que usam apenas a lista de espera não precisam configurar um projeto na nuvem nem fornecer um endereço de e-mail do desenvolvedor. Não é necessário fazer as atualizações em tempo real da API. No entanto, os feeds do comerciante e de serviços ainda precisam ser enviados ao Centro de ações.
Diretrizes para parceiros em que os comerciantes precisam aceitar/recusar manualmente adições à lista de espera
Se os comerciantes precisarem aceitar ou recusar de forma manual novas adições à lista de espera do Google, serão necessárias etapas adicionais:
- Defina o
waitlist_confirmation_modecomoWAITLIST_CONFIRMATION_MODE_ASYNCHRONOUSemwait_estimatepara tamanhos de grupo que exigem confirmação manual. Isso precisa ser definido emBatchGetWaitEstimateResponseeGetWaitlistEntryResponse. - As entradas da lista de espera que foram solicitadas pelo usuário, mas ainda não
foram aceitas pelo comerciante, devem estar no estado
PENDING_MERCHANT_CONFIRMATION.
Casos de teste de listas de espera de reservas
O Google testa os seguintes casos de uso para garantir a funcionalidade dos métodos da lista de espera na implementação do servidor de agendamento. O Google também testa e monitora a latência. Todos esses testes precisam ser aprovados antes do lançamento.
Recuperação de WaitEstimate
- As estimativas de espera são retornadas para cada tamanho de grupo solicitado em uma
BatchGetWaitEstimatesRequest. - No caso de grupos em que o comerciante pode aceitar ou recusar
novas adições à lista de espera, defina waitlist_confirmation_mode como
WAITLIST_CONFIRMATION_MODE_ASYNCHRONOUS.
Criação de entradas da lista de espera
- Uma entrada da lista de espera pode ser criada diretamente de uma
solicitação
CreateWaitlistEntry. - Se essa operação falhar, um erro de lógica de negócios será exibido na resposta.
- Se uma tentativa de
CreateWaitlistEntryfor bem-sucedida, a mesma resposta será retornada quando a mesmaCreateWaitlistEntryfor recebida novamente. - Se uma tentativa de
CreateWaitlistEntryfalhar, o servidor tentará de novo quando a mesmaCreateWaitlistEntryfor recebida novamente. - As entradas da lista de espera são exibidas na interface do comerciante.
- As chamadas para
GetWaitlistEntryretornam a entrada da lista de espera criada.
Estados e carimbos de data/hora das entradas da lista de espera
- Verifique se cada estado é retornado corretamente na entrada da lista de espera das
respostas de
GetWaitlistEntry. - Verifique se os carimbos de data/hora dos estados foram definidos no campo de carimbo de data/hora
apropriado da entrada na lista de espera nas respostas de
GetWaitlistEntry.
Exclusão de entradas da lista de espera
- É possível remover as entradas da lista de espera. A resposta a uma exclusão
bem-sucedida precisa ser o proto vazio
{}.
Desativar
- Verifique se os comerciantes que recusaram o uso das listas de espera são tratados conforme descrito em Como os comerciantes recusam o uso das listas de espera.
Exemplo de feed de serviços da lista de espera (JSON)
Feed de serviços da lista de esperaDesativação do comerciante
O Google espera determinadas respostas para comerciantes que usavam listas de espera, mas decidiram desativá-las.
Desativação imediata
- Retorne
CLOSED_OTHERpara solicitaçõesBatchGetWaitEstimates. - Retorne
WAITLIST_CLOSEDpara solicitaçõesCreateWaitlistEntry. - Retorne
solicitações
GetWaitlistEntrycorretamente para usuários que já estão na lista de espera.
Desativação estendida
- Remova o
waitlist_rulesdo feed de serviços do comerciante se ele não quiser desativar as reservas. - Remova o comerciante do feed do comerciante se ele desativar todas as integrações do Google.