במדריך הזה נסביר איך להוסיף מפה של Google לאפליקציית Android, ואיך להשתמש בקווי פוליגון ובפוליגונים כדי לייצג מסלולים ואזורים במפה.
פועלים לפי ההוראות במדריך כדי לפתח אפליקציית Android באמצעות Maps SDK ל-Android. סביבת הפיתוח המומלצת היא Android Studio.
קבל את הקוד
משכפלים או מורידים את מאגר הדוגמאות של Google Maps Android API v2 מ-GitHub.
כדי לראות את גרסת ה-Java של הפעילות:
// Copyright 2020 Google LLC // // Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); // you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. // You may obtain a copy of the License at // // http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 // // Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software // distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, // WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. // See the License for the specific language governing permissions and // limitations under the License. package com.example.polygons; import android.os.Bundle; import android.widget.Toast; import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import com.google.android.gms.maps.CameraUpdateFactory; import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap; import com.google.android.gms.maps.OnMapReadyCallback; import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.BitmapDescriptorFactory; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.CustomCap; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Dash; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Dot; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Gap; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.JointType; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.LatLng; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.PatternItem; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Polygon; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.PolygonOptions; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Polyline; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.PolylineOptions; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.RoundCap; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; /** * An activity that displays a Google map with polylines to represent paths or routes, * and polygons to represent areas. */ public class PolyActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements OnMapReadyCallback, GoogleMap.OnPolylineClickListener, GoogleMap.OnPolygonClickListener { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps); // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. SupportMapFragment mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager() .findFragmentById(R.id.map); mapFragment.getMapAsync(this); } /** * Manipulates the map when it's available. * The API invokes this callback when the map is ready to be used. * This is where we can add markers or lines, add listeners or move the camera. * In this tutorial, we add polylines and polygons to represent routes and areas on the map. */ @Override public void onMapReady(GoogleMap googleMap) { // Add polylines to the map. // Polylines are useful to show a route or some other connection between points. Polyline polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(new PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), new LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), new LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), new LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), new LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), new LatLng(-32.491, 147.309))); // Store a data object with the polyline, used here to indicate an arbitrary type. polyline1.setTag("A"); // Style the polyline. stylePolyline(polyline1); Polyline polyline2 = googleMap.addPolyline(new PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-29.501, 119.700), new LatLng(-27.456, 119.672), new LatLng(-25.971, 124.187), new LatLng(-28.081, 126.555), new LatLng(-28.848, 124.229), new LatLng(-28.215, 123.938))); polyline2.setTag("B"); stylePolyline(polyline2); // Add polygons to indicate areas on the map. Polygon polygon1 = googleMap.addPolygon(new PolygonOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-27.457, 153.040), new LatLng(-33.852, 151.211), new LatLng(-37.813, 144.962), new LatLng(-34.928, 138.599))); // Store a data object with the polygon, used here to indicate an arbitrary type. polygon1.setTag("alpha"); // Style the polygon. stylePolygon(polygon1); Polygon polygon2 = googleMap.addPolygon(new PolygonOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-31.673, 128.892), new LatLng(-31.952, 115.857), new LatLng(-17.785, 122.258), new LatLng(-12.4258, 130.7932))); polygon2.setTag("beta"); stylePolygon(polygon2); // Position the map's camera near Alice Springs in the center of Australia, // and set the zoom factor so most of Australia shows on the screen. googleMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(new LatLng(-23.684, 133.903), 4)); // Set listeners for click events. googleMap.setOnPolylineClickListener(this); googleMap.setOnPolygonClickListener(this); } private static final int COLOR_BLACK_ARGB = 0xff000000; private static final int POLYLINE_STROKE_WIDTH_PX = 12; /** * Styles the polyline, based on type. * @param polyline The polyline object that needs styling. */ private void stylePolyline(Polyline polyline) { String type = ""; // Get the data object stored with the polyline. if (polyline.getTag() != null) { type = polyline.getTag().toString(); } switch (type) { // If no type is given, allow the API to use the default. case "A": // Use a custom bitmap as the cap at the start of the line. polyline.setStartCap( new CustomCap( BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromResource(R.drawable.ic_arrow), 10)); break; case "B": // Use a round cap at the start of the line. polyline.setStartCap(new RoundCap()); break; } polyline.setEndCap(new RoundCap()); polyline.setWidth(POLYLINE_STROKE_WIDTH_PX); polyline.setColor(COLOR_BLACK_ARGB); polyline.setJointType(JointType.ROUND); } private static final int PATTERN_GAP_LENGTH_PX = 20; private static final PatternItem DOT = new Dot(); private static final PatternItem GAP = new Gap(PATTERN_GAP_LENGTH_PX); // Create a stroke pattern of a gap followed by a dot. private static final List<PatternItem> PATTERN_POLYLINE_DOTTED = Arrays.asList(GAP, DOT); /** * Listens for clicks on a polyline. * @param polyline The polyline object that the user has clicked. */ @Override public void onPolylineClick(Polyline polyline) { // Flip from solid stroke to dotted stroke pattern. if ((polyline.getPattern() == null) || (!polyline.getPattern().contains(DOT))) { polyline.setPattern(PATTERN_POLYLINE_DOTTED); } else { // The default pattern is a solid stroke. polyline.setPattern(null); } Toast.makeText(this, "Route type " + polyline.getTag().toString(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } /** * Listens for clicks on a polygon. * @param polygon The polygon object that the user has clicked. */ @Override public void onPolygonClick(Polygon polygon) { // Flip the values of the red, green, and blue components of the polygon's color. int color = polygon.getStrokeColor() ^ 0x00ffffff; polygon.setStrokeColor(color); color = polygon.getFillColor() ^ 0x00ffffff; polygon.setFillColor(color); Toast.makeText(this, "Area type " + polygon.getTag().toString(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } private static final int COLOR_WHITE_ARGB = 0xffffffff; private static final int COLOR_DARK_GREEN_ARGB = 0xff388E3C; private static final int COLOR_LIGHT_GREEN_ARGB = 0xff81C784; private static final int COLOR_DARK_ORANGE_ARGB = 0xffF57F17; private static final int COLOR_LIGHT_ORANGE_ARGB = 0xffF9A825; private static final int POLYGON_STROKE_WIDTH_PX = 8; private static final int PATTERN_DASH_LENGTH_PX = 20; private static final PatternItem DASH = new Dash(PATTERN_DASH_LENGTH_PX); // Create a stroke pattern of a gap followed by a dash. private static final List<PatternItem> PATTERN_POLYGON_ALPHA = Arrays.asList(GAP, DASH); // Create a stroke pattern of a dot followed by a gap, a dash, and another gap. private static final List<PatternItem> PATTERN_POLYGON_BETA = Arrays.asList(DOT, GAP, DASH, GAP); /** * Styles the polygon, based on type. * @param polygon The polygon object that needs styling. */ private void stylePolygon(Polygon polygon) { String type = ""; // Get the data object stored with the polygon. if (polygon.getTag() != null) { type = polygon.getTag().toString(); } List<PatternItem> pattern = null; int strokeColor = COLOR_BLACK_ARGB; int fillColor = COLOR_WHITE_ARGB; switch (type) { // If no type is given, allow the API to use the default. case "alpha": // Apply a stroke pattern to render a dashed line, and define colors. pattern = PATTERN_POLYGON_ALPHA; strokeColor = COLOR_DARK_GREEN_ARGB; fillColor = COLOR_LIGHT_GREEN_ARGB; break; case "beta": // Apply a stroke pattern to render a line of dots and dashes, and define colors. pattern = PATTERN_POLYGON_BETA; strokeColor = COLOR_DARK_ORANGE_ARGB; fillColor = COLOR_LIGHT_ORANGE_ARGB; break; } polygon.setStrokePattern(pattern); polygon.setStrokeWidth(POLYGON_STROKE_WIDTH_PX); polygon.setStrokeColor(strokeColor); polygon.setFillColor(fillColor); } }
כדי לראות את גרסת הפעילות ב-Kotlin:
// Copyright 2020 Google LLC // // Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); // you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. // You may obtain a copy of the License at // // http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 // // Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software // distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, // WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. // See the License for the specific language governing permissions and // limitations under the License. package com.example.polygons import android.os.Bundle import android.widget.Toast import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity import com.google.android.gms.maps.CameraUpdateFactory import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap.OnPolygonClickListener import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap.OnPolylineClickListener import com.google.android.gms.maps.OnMapReadyCallback import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.BitmapDescriptorFactory import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.CustomCap import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Dash import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Dot import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Gap import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.JointType import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.LatLng import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.PatternItem import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Polygon import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.PolygonOptions import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Polyline import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.PolylineOptions import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.RoundCap /** * An activity that displays a Google map with polylines to represent paths or routes, * and polygons to represent areas. */ class PolyActivity : AppCompatActivity(), OnMapReadyCallback, OnPolylineClickListener, OnPolygonClickListener { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps) // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager .findFragmentById(R.id.map) as SupportMapFragment? mapFragment?.getMapAsync(this) } /** * Manipulates the map when it's available. * The API invokes this callback when the map is ready to be used. * This is where we can add markers or lines, add listeners or move the camera. * In this tutorial, we add polylines and polygons to represent routes and areas on the map. */ override fun onMapReady(googleMap: GoogleMap) { // Add polylines to the map. // Polylines are useful to show a route or some other connection between points. val polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), LatLng(-32.491, 147.309))) // Store a data object with the polyline, used here to indicate an arbitrary type. polyline1.tag = "A" // Style the polyline. stylePolyline(polyline1) val polyline2 = googleMap.addPolyline(PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-29.501, 119.700), LatLng(-27.456, 119.672), LatLng(-25.971, 124.187), LatLng(-28.081, 126.555), LatLng(-28.848, 124.229), LatLng(-28.215, 123.938))) polyline2.tag = "B" stylePolyline(polyline2) // Add polygons to indicate areas on the map. val polygon1 = googleMap.addPolygon(PolygonOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-27.457, 153.040), LatLng(-33.852, 151.211), LatLng(-37.813, 144.962), LatLng(-34.928, 138.599))) // Store a data object with the polygon, used here to indicate an arbitrary type. polygon1.tag = "alpha" // Style the polygon. stylePolygon(polygon1) val polygon2 = googleMap.addPolygon(PolygonOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-31.673, 128.892), LatLng(-31.952, 115.857), LatLng(-17.785, 122.258), LatLng(-12.4258, 130.7932))) polygon2.tag = "beta" stylePolygon(polygon2) // Position the map's camera near Alice Springs in the center of Australia, // and set the zoom factor so most of Australia shows on the screen. googleMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(LatLng(-23.684, 133.903), 4f)) // Set listeners for click events. googleMap.setOnPolylineClickListener(this) googleMap.setOnPolygonClickListener(this) } private val COLOR_BLACK_ARGB = -0x1000000 private val POLYLINE_STROKE_WIDTH_PX = 12 /** * Styles the polyline, based on type. * @param polyline The polyline object that needs styling. */ private fun stylePolyline(polyline: Polyline) { // Get the data object stored with the polyline. val type = polyline.tag?.toString() ?: "" when (type) { "A" -> { // Use a custom bitmap as the cap at the start of the line. polyline.startCap = CustomCap( BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromResource(R.drawable.ic_arrow), 10f) } "B" -> { // Use a round cap at the start of the line. polyline.startCap = RoundCap() } } polyline.endCap = RoundCap() polyline.width = POLYLINE_STROKE_WIDTH_PX.toFloat() polyline.color = COLOR_BLACK_ARGB polyline.jointType = JointType.ROUND } private val PATTERN_GAP_LENGTH_PX = 20 private val DOT: PatternItem = Dot() private val GAP: PatternItem = Gap(PATTERN_GAP_LENGTH_PX.toFloat()) // Create a stroke pattern of a gap followed by a dot. private val PATTERN_POLYLINE_DOTTED = listOf(GAP, DOT) /** * Listens for clicks on a polyline. * @param polyline The polyline object that the user has clicked. */ override fun onPolylineClick(polyline: Polyline) { // Flip from solid stroke to dotted stroke pattern. if (polyline.pattern == null || !polyline.pattern!!.contains(DOT)) { polyline.pattern = PATTERN_POLYLINE_DOTTED } else { // The default pattern is a solid stroke. polyline.pattern = null } Toast.makeText(this, "Route type " + polyline.tag.toString(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show() } /** * Listens for clicks on a polygon. * @param polygon The polygon object that the user has clicked. */ override fun onPolygonClick(polygon: Polygon) { // Flip the values of the red, green, and blue components of the polygon's color. var color = polygon.strokeColor xor 0x00ffffff polygon.strokeColor = color color = polygon.fillColor xor 0x00ffffff polygon.fillColor = color Toast.makeText(this, "Area type ${polygon.tag?.toString()}", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show() } private val COLOR_WHITE_ARGB = -0x1 private val COLOR_DARK_GREEN_ARGB = -0xc771c4 private val COLOR_LIGHT_GREEN_ARGB = -0x7e387c private val COLOR_DARK_ORANGE_ARGB = -0xa80e9 private val COLOR_LIGHT_ORANGE_ARGB = -0x657db private val POLYGON_STROKE_WIDTH_PX = 8 private val PATTERN_DASH_LENGTH_PX = 20 private val DASH: PatternItem = Dash(PATTERN_DASH_LENGTH_PX.toFloat()) // Create a stroke pattern of a gap followed by a dash. private val PATTERN_POLYGON_ALPHA = listOf(GAP, DASH) // Create a stroke pattern of a dot followed by a gap, a dash, and another gap. private val PATTERN_POLYGON_BETA = listOf(DOT, GAP, DASH, GAP) /** * Styles the polygon, based on type. * @param polygon The polygon object that needs styling. */ private fun stylePolygon(polygon: Polygon) { // Get the data object stored with the polygon. val type = polygon.tag?.toString() ?: "" var pattern: List<PatternItem>? = null var strokeColor = COLOR_BLACK_ARGB var fillColor = COLOR_WHITE_ARGB when (type) { "alpha" -> { // Apply a stroke pattern to render a dashed line, and define colors. pattern = PATTERN_POLYGON_ALPHA strokeColor = COLOR_DARK_GREEN_ARGB fillColor = COLOR_LIGHT_GREEN_ARGB } "beta" -> { // Apply a stroke pattern to render a line of dots and dashes, and define colors. pattern = PATTERN_POLYGON_BETA strokeColor = COLOR_DARK_ORANGE_ARGB fillColor = COLOR_LIGHT_ORANGE_ARGB } } polygon.strokePattern = pattern polygon.strokeWidth = POLYGON_STROKE_WIDTH_PX.toFloat() polygon.strokeColor = strokeColor polygon.fillColor = fillColor } }
הגדרת פרויקט הפיתוח
כדי ליצור את פרויקט ההדרכה ב-Android Studio, פועלים לפי השלבים הבאים.
- מורידים ומתקינים את Android Studio.
- מוסיפים את חבילת Google Play services ל-Android Studio.
- משכפלים או מורידים את מאגר הדוגמאות של Google Maps Android API v2 אם לא עשיתם את זה כשקראתם את המדריך הזה.
מייבאים את פרויקט המדריך:
- ב-Android Studio, בוחרים באפשרות File > New > Import Project (קובץ > חדש > ייבוא פרויקט).
- עוברים למיקום שבו שמרתם את מאגר הדוגמאות של Google Maps Android API v2 אחרי ההורדה.
- מחפשים את הפרויקט Polygons במיקום הבא:
PATH-TO-SAVED-REPO/android-samples/tutorials/java/Polygons(Java) או
PATH-TO-SAVED-REPO/android-samples/tutorials/kotlin/Polygons(Kotlin) - בוחרים את ספריית הפרויקט ולוחצים על פתיחה. מערכת Android Studio תבצע עכשיו build של הפרויקט באמצעות כלי ה-build של Gradle.
הפעלת ממשקי ה-API הנדרשים וקבלת מפתח API
כדי להשלים את המדריך הזה, אתם צריכים פרויקט ב-Google Cloud עם ממשקי ה-API הדרושים שמופעלים בו, ומפתח API שמאושר לשימוש ב-SDK של מפות ל-Android. פרטים נוספים זמינים במאמרים הבאים:
הוספת מפתח ה-API לאפליקציה
- פותחים את הקובץ
local.propertiesשל הפרויקט. מוסיפים את המחרוזת הבאה ומחליפים את הערך
YOUR_API_KEYבערך של מפתח ה-API:MAPS_API_KEY=YOUR_API_KEYכשאתם בונים את האפליקציה, הפלאגין של Secrets Gradle ל-Android מעתיק את מפתח ה-API והופך אותו לזמין כמשתנה build במניפסט של Android, כמו שמוסבר בהמשך.
איך יוצרים ומריצים את האפליקציה
כדי לבנות ולהריץ את האפליקציה:
מחברים מכשיר Android למחשב. פועלים לפי ההוראות כדי להפעיל את האפשרויות למפתחים במכשיר Android ולהגדיר את המערכת כך שתזהה את המכשיר.
אפשרות נוספת היא להשתמש במנהל המכשירים הווירטואליים (AVD) של Android כדי להגדיר מכשיר וירטואלי. כשבוחרים אמולטור, חשוב לבחור תמונה שכוללת את Google APIs. פרטים נוספים זמינים במאמר הגדרת פרויקט ב-Android Studio .
ב-Android Studio, לוחצים על האפשרות Run בתפריט (או על סמל ההפעלה). בוחרים מכשיר לפי ההנחיות.
Android Studio מפעיל את Gradle כדי לבנות את האפליקציה, ואז מריץ את האפליקציה במכשיר או באמולטור.
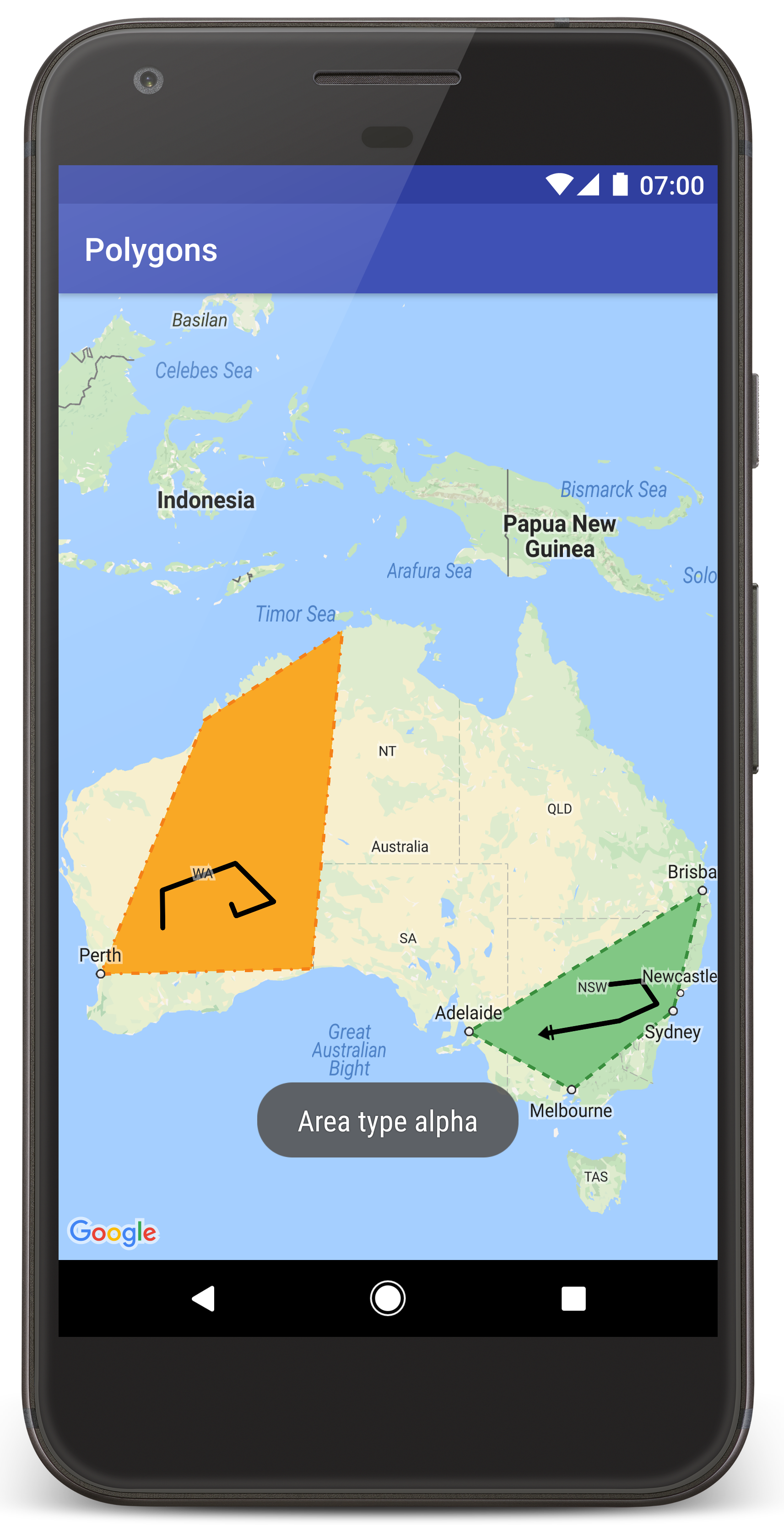
אמורה להופיע מפה עם שני מצולעים שמוצגים מעל אוסטרליה, בדומה לתמונה בדף הזה.
פתרון בעיות:
- אם לא רואים מפה, צריך לוודא שהשגתם מפתח API והוספתם אותו לאפליקציה, כמו שמתואר למעלה. בודקים את היומן בAndroid Monitor ב-Android Studio כדי לראות הודעות שגיאה לגבי מפתח ה-API.
- אפשר להשתמש בכלים לניפוי באגים ב-Android Studio כדי לראות את היומנים ולנפות באגים באפליקציה.
הסבר על הקוד
בחלק הזה של המדריך מוסברים החלקים הכי חשובים באפליקציית Polygons, כדי לעזור לכם להבין איך לבנות אפליקציה דומה.
בדיקת מניפסט Android
שימו לב לרכיבים הבאים בקובץ AndroidManifest.xml של האפליקציה:
מוסיפים רכיב
meta-dataכדי להטמיע את הגרסה של Google Play Services שהאפליקציה קומפלה איתה.<meta-data android:name="com.google.android.gms.version" android:value="@integer/google_play_services_version" />מוסיפים רכיב
meta-dataשמציין את מפתח ה-API. בדוגמה שמצורפת למדריך הזה, הערך של מפתח ה-API ממופה למשתנה build שתואם לשם המפתח שהגדרתם קודם,MAPS_API_KEY. כשמבצעים build לאפליקציה, הפלאגין Secrets Gradle ל-Android הופך את המפתחות בקובץlocal.propertiesלזמינים כמשתני build של המניפסט.<meta-data android:name="com.google.android.geo.API_KEY" android:value="${MAPS_API_KEY}" />בקובץ
build.gradle, השורה הבאה מעבירה את מפתח ה-API למניפסט של Android.id 'com.google.android.libraries.mapsplatform.secrets-gradle-plugin'
דוגמה מלאה למניפסט:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!-- Copyright 2020 Google LLC Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. --> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:supportsRtl="true" android:theme="@style/AppTheme"> <meta-data android:name="com.google.android.gms.version" android:value="@integer/google_play_services_version" /> <!-- The API key for Google Maps-based APIs. --> <meta-data android:name="com.google.android.geo.API_KEY" android:value="${MAPS_API_KEY}" /> <activity android:name="com.example.polygons.PolyActivity" android:exported="true" android:label="@string/title_activity_maps"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> </application> </manifest>
הוספת מפה
הצגת מפה באמצעות Maps SDK ל-Android.
מוסיפים רכיב
<fragment>לקובץ הפריסה של הפעילות,activity_maps.xml. האלמנט הזה מגדירSupportMapFragmentשישמש כקונטיינר למפה ויספק גישה לאובייקטGoogleMap. במדריך נעשה שימוש בגרסה של ספריית התמיכה של Android של קטע המפה, כדי להבטיח תאימות לאחור עם גרסאות קודמות של מסגרת Android.<!-- Copyright 2020 Google LLC Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. --> <fragment xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/map" android:name="com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context="com.example.polygons.PolyActivity" />
ב-method
onCreate()של הפעילות, מגדירים את קובץ הפריסה כתצוגת התוכן. כדי לקבל הפניה אל קטע המפה, צריך להתקשר אלFragmentManager.findFragmentById(). אחר כך משתמשים ב-getMapAsync()כדי להירשם לקריאה חוזרת של המפה:Java
@Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps); // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. SupportMapFragment mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager() .findFragmentById(R.id.map); mapFragment.getMapAsync(this); }
Kotlin
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps) // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager .findFragmentById(R.id.map) as SupportMapFragment? mapFragment?.getMapAsync(this) }
מטמיעים את הממשק
OnMapReadyCallbackומבטלים את ה-methodonMapReady(). ה-API מפעיל את פונקציית הקריאה החוזרת הזו כשאובייקטGoogleMapזמין, כך שאפשר להוסיף אובייקטים למפה ולהתאים אותה אישית לאפליקציה:Java
public class PolyActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements OnMapReadyCallback, GoogleMap.OnPolylineClickListener, GoogleMap.OnPolygonClickListener { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps); // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. SupportMapFragment mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager() .findFragmentById(R.id.map); mapFragment.getMapAsync(this); } /** * Manipulates the map when it's available. * The API invokes this callback when the map is ready to be used. * This is where we can add markers or lines, add listeners or move the camera. * In this tutorial, we add polylines and polygons to represent routes and areas on the map. */ @Override public void onMapReady(GoogleMap googleMap) { // Add polylines to the map. // Polylines are useful to show a route or some other connection between points. Polyline polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(new PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), new LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), new LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), new LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), new LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), new LatLng(-32.491, 147.309))); // Position the map's camera near Alice Springs in the center of Australia, // and set the zoom factor so most of Australia shows on the screen. googleMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(new LatLng(-23.684, 133.903), 4)); // Set listeners for click events. googleMap.setOnPolylineClickListener(this); googleMap.setOnPolygonClickListener(this); }
Kotlin
class PolyActivity : AppCompatActivity(), OnMapReadyCallback, OnPolylineClickListener, OnPolygonClickListener { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps) // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager .findFragmentById(R.id.map) as SupportMapFragment? mapFragment?.getMapAsync(this) } /** * Manipulates the map when it's available. * The API invokes this callback when the map is ready to be used. * This is where we can add markers or lines, add listeners or move the camera. * In this tutorial, we add polylines and polygons to represent routes and areas on the map. */ override fun onMapReady(googleMap: GoogleMap) { // Add polylines to the map. // Polylines are useful to show a route or some other connection between points. val polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), LatLng(-32.491, 147.309))) // Position the map's camera near Alice Springs in the center of Australia, // and set the zoom factor so most of Australia shows on the screen. googleMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(LatLng(-23.684, 133.903), 4f)) // Set listeners for click events. googleMap.setOnPolylineClickListener(this) googleMap.setOnPolygonClickListener(this) }
הוספת קו שבור כדי לשרטט קו במפה
Polyline הוא סדרה של קטעי קו מחוברים. קווי פוליגון שימושיים לייצוג של מסלולים, נתיבים או קשרים אחרים בין מיקומים במפה.
יוצרים אובייקט
PolylineOptionsומוסיפים אליו נקודות. כל נקודה מייצגת מיקום במפה, שמוגדר באמצעות אובייקטLatLngשמכיל ערכים של קו רוחב וקו אורך. בדוגמת הקוד הבאה נוצרת קו פוליגוני עם 6 נקודות.מתקשרים אל
GoogleMap.addPolyline()כדי להוסיף את הקו למפה.Java
Polyline polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(new PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), new LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), new LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), new LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), new LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), new LatLng(-32.491, 147.309)));
Kotlin
val polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), LatLng(-32.491, 147.309)))
מגדירים את האפשרות clickable של הקו המקוטע ל-true אם רוצים לטפל באירועי לחיצה על הקו המקוטע. בהמשך המדריך הזה יש מידע נוסף על טיפול באירועים.
אחסון נתונים שרירותיים באמצעות קו פוליגוני
אפשר לאחסן אובייקטים שרירותיים של נתונים עם קווים פוליגוניים ואובייקטים גיאומטריים אחרים.
שולחים קריאה אל
Polyline.setTag()כדי לאחסן אובייקט נתונים עם הקו המרוסקע. הקוד שלמטה מגדיר תג שרירותי (A) שמציין סוג של קו פוליגוני.Java
Polyline polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(new PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), new LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), new LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), new LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), new LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), new LatLng(-32.491, 147.309))); // Store a data object with the polyline, used here to indicate an arbitrary type. polyline1.setTag("A");
Kotlin
val polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), LatLng(-32.491, 147.309))) // Store a data object with the polyline, used here to indicate an arbitrary type. polyline1.tag = "A
אפשר לאחזר את הנתונים באמצעות
Polyline.getTag(), כמו שמוסבר בקטע הבא.
הוספת סגנון מותאם אישית לקו הפוליגוני
אפשר לציין מאפייני סגנון שונים באובייקט PolylineOptions. אפשרויות העיצוב כוללות את צבע הקו, רוחב הקו, דפוס הקו, סוגי החיבורים וסוגי הקצוות. אם לא מציינים מאפיין מסוים, ה-API משתמש בברירת מחדל עבור המאפיין הזה.
הקוד הבא מוסיף קצה מעוגל לסוף הקו, וקצה התחלתי שונה בהתאם לסוג הקו הפוליגוני. הסוג הוא מאפיין שרירותי שמאוחסן באובייקט הנתונים של הקו הפוליגוני. בדוגמה מוגדרים גם רוחב קו, צבע קו וסוג חיבור:
Java
private static final int COLOR_BLACK_ARGB = 0xff000000; private static final int POLYLINE_STROKE_WIDTH_PX = 12; /** * Styles the polyline, based on type. * @param polyline The polyline object that needs styling. */ private void stylePolyline(Polyline polyline) { String type = ""; // Get the data object stored with the polyline. if (polyline.getTag() != null) { type = polyline.getTag().toString(); } switch (type) { // If no type is given, allow the API to use the default. case "A": // Use a custom bitmap as the cap at the start of the line. polyline.setStartCap( new CustomCap( BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromResource(R.drawable.ic_arrow), 10)); break; case "B": // Use a round cap at the start of the line. polyline.setStartCap(new RoundCap()); break; } polyline.setEndCap(new RoundCap()); polyline.setWidth(POLYLINE_STROKE_WIDTH_PX); polyline.setColor(COLOR_BLACK_ARGB); polyline.setJointType(JointType.ROUND); }
Kotlin
private val COLOR_BLACK_ARGB = -0x1000000 private val POLYLINE_STROKE_WIDTH_PX = 12 /** * Styles the polyline, based on type. * @param polyline The polyline object that needs styling. */ private fun stylePolyline(polyline: Polyline) { // Get the data object stored with the polyline. val type = polyline.tag?.toString() ?: "" when (type) { "A" -> { // Use a custom bitmap as the cap at the start of the line. polyline.startCap = CustomCap( BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromResource(R.drawable.ic_arrow), 10f) } "B" -> { // Use a round cap at the start of the line. polyline.startCap = RoundCap() } } polyline.endCap = RoundCap() polyline.width = POLYLINE_STROKE_WIDTH_PX.toFloat() polyline.color = COLOR_BLACK_ARGB polyline.jointType = JointType.ROUND }
הקוד שלמעלה מציין מפת סיביות מותאמת אישית לכיסוי הקצה של קו פוליגון מסוג A, ומציין רוחב קו התייחסות של 10 פיקסלים. ממשק ה-API משנה את גודל מפת הביטים בהתאם לרוחב קו הייחוס. כשמציינים את רוחב הקו של התמונה לדוגמה, צריך לספק את הרוחב שבו השתמשתם כשעיצבתם את תמונת ה-Bitmap, במימד המקורי של התמונה. טיפ: פותחים את תמונת ה-Bitmap בהגדלה של 100% בכלי לעריכת תמונות, ומשרטטים את הרוחב הרצוי של קו המשיכה ביחס לתמונה.
מידע נוסף על קצוות קוים ואפשרויות אחרות להתאמה אישית של צורות
טיפול באירועי קליקים בקו פוליגוני
כדי להפוך את הקו המרובה לניתן ללחיצה, שולחים קריאה אל
Polyline.setClickable(). (כברירת מחדל, אי אפשר ללחוץ על קווים פוליגוניים, והאפליקציה לא תקבל התראה כשהמשתמש יקיש על קו פוליגוני).מטמיעים את הממשק
OnPolylineClickListenerוקוראים ל-GoogleMap.setOnPolylineClickListener()כדי להגדיר את מאזין המפה:Java
public class PolyActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements OnMapReadyCallback, GoogleMap.OnPolylineClickListener, GoogleMap.OnPolygonClickListener { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps); // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. SupportMapFragment mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager() .findFragmentById(R.id.map); mapFragment.getMapAsync(this); } /** * Manipulates the map when it's available. * The API invokes this callback when the map is ready to be used. * This is where we can add markers or lines, add listeners or move the camera. * In this tutorial, we add polylines and polygons to represent routes and areas on the map. */ @Override public void onMapReady(GoogleMap googleMap) { // Add polylines to the map. // Polylines are useful to show a route or some other connection between points. Polyline polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(new PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), new LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), new LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), new LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), new LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), new LatLng(-32.491, 147.309))); // Position the map's camera near Alice Springs in the center of Australia, // and set the zoom factor so most of Australia shows on the screen. googleMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(new LatLng(-23.684, 133.903), 4)); // Set listeners for click events. googleMap.setOnPolylineClickListener(this); googleMap.setOnPolygonClickListener(this); }
Kotlin
class PolyActivity : AppCompatActivity(), OnMapReadyCallback, OnPolylineClickListener, OnPolygonClickListener { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps) // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager .findFragmentById(R.id.map) as SupportMapFragment? mapFragment?.getMapAsync(this) } /** * Manipulates the map when it's available. * The API invokes this callback when the map is ready to be used. * This is where we can add markers or lines, add listeners or move the camera. * In this tutorial, we add polylines and polygons to represent routes and areas on the map. */ override fun onMapReady(googleMap: GoogleMap) { // Add polylines to the map. // Polylines are useful to show a route or some other connection between points. val polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), LatLng(-32.491, 147.309))) // Position the map's camera near Alice Springs in the center of Australia, // and set the zoom factor so most of Australia shows on the screen. googleMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(LatLng(-23.684, 133.903), 4f)) // Set listeners for click events. googleMap.setOnPolylineClickListener(this) googleMap.setOnPolygonClickListener(this) }
מבטלים את שיטת הקריאה החוזרת
onPolylineClick(). בדוגמה הבאה, דפוס הקו משתנה בין קו רציף לקו מקווקו בכל פעם שהמשתמש לוחץ על הקו המרובה:Java
private static final int PATTERN_GAP_LENGTH_PX = 20; private static final PatternItem DOT = new Dot(); private static final PatternItem GAP = new Gap(PATTERN_GAP_LENGTH_PX); // Create a stroke pattern of a gap followed by a dot. private static final List<PatternItem> PATTERN_POLYLINE_DOTTED = Arrays.asList(GAP, DOT); /** * Listens for clicks on a polyline. * @param polyline The polyline object that the user has clicked. */ @Override public void onPolylineClick(Polyline polyline) { // Flip from solid stroke to dotted stroke pattern. if ((polyline.getPattern() == null) || (!polyline.getPattern().contains(DOT))) { polyline.setPattern(PATTERN_POLYLINE_DOTTED); } else { // The default pattern is a solid stroke. polyline.setPattern(null); } Toast.makeText(this, "Route type " + polyline.getTag().toString(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); }
Kotlin
private val PATTERN_GAP_LENGTH_PX = 20 private val DOT: PatternItem = Dot() private val GAP: PatternItem = Gap(PATTERN_GAP_LENGTH_PX.toFloat()) // Create a stroke pattern of a gap followed by a dot. private val PATTERN_POLYLINE_DOTTED = listOf(GAP, DOT) /** * Listens for clicks on a polyline. * @param polyline The polyline object that the user has clicked. */ override fun onPolylineClick(polyline: Polyline) { // Flip from solid stroke to dotted stroke pattern. if (polyline.pattern == null || !polyline.pattern!!.contains(DOT)) { polyline.pattern = PATTERN_POLYLINE_DOTTED } else { // The default pattern is a solid stroke. polyline.pattern = null } Toast.makeText(this, "Route type " + polyline.tag.toString(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show() }
הוספת פוליגונים לייצוג אזורים במפה
Polygon הוא צורה שמורכבת מסדרה של קואורדינטות ברצף מסודר, בדומה לPolyline. ההבדל הוא שפוליגון מגדיר אזור סגור עם פנים שאפשר למלא, בעוד שקו פוליגוני הוא פתוח.
יוצרים אובייקט
PolygonOptionsומוסיפים אליו נקודות. כל נקודה מייצגת מיקום במפה, שמוגדר באמצעות אובייקטLatLngשמכיל ערכים של קו רוחב וקו אורך. בדוגמה הבאה של קוד נוצר פוליגון עם 4 נקודות.כדי להפוך את הפוליגון לניתן ללחיצה, קוראים לפונקציה
Polygon.setClickable(). (כברירת מחדל, אי אפשר ללחוץ על מצולעים והאפליקציה לא תקבל התראה כשהמשתמש יקיש על מצולע). הטיפול באירועי קליק על מצולעים דומה לטיפול באירועים על קווים שבורים, שמתואר בהמשך המדריך הזה.מתקשרים למספר
GoogleMap.addPolygon()כדי להוסיף את הפוליגון למפה.שולחים קריאה אל
Polygon.setTag()כדי לאחסן אובייקט נתונים עם הפוליגון. הקוד שלמטה מגדיר סוג שרירותי (alpha) למצולע.Java
// Add polygons to indicate areas on the map. Polygon polygon1 = googleMap.addPolygon(new PolygonOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-27.457, 153.040), new LatLng(-33.852, 151.211), new LatLng(-37.813, 144.962), new LatLng(-34.928, 138.599))); // Store a data object with the polygon, used here to indicate an arbitrary type. polygon1.setTag("alpha");
Kotlin
// Add polygons to indicate areas on the map. val polygon1 = googleMap.addPolygon(PolygonOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-27.457, 153.040), LatLng(-33.852, 151.211), LatLng(-37.813, 144.962), LatLng(-34.928, 138.599))) // Store a data object with the polygon, used here to indicate an arbitrary type. polygon1.tag = "alpha" // Style the polygon.
הוספת סגנון מותאם אישית לפוליגון
אפשר לציין מספר מאפייני סגנון באובייקט PolygonOptions. אפשרויות העיצוב כוללות את צבע הקו, רוחב הקו, דוגמת הקו, סוגי החיבורים של הקו וצבע המילוי. אם לא מציינים מאפיין מסוים, ה-API משתמש בברירת מחדל עבור המאפיין הזה.
הקוד הבא מחיל צבעים ספציפיים ודפוסי קו בהתאם לסוג של הפוליגון, כאשר הסוג הוא מאפיין שרירותי שמאוחסן באובייקט הנתונים של הפוליגון:
Java
private static final int COLOR_WHITE_ARGB = 0xffffffff; private static final int COLOR_DARK_GREEN_ARGB = 0xff388E3C; private static final int COLOR_LIGHT_GREEN_ARGB = 0xff81C784; private static final int COLOR_DARK_ORANGE_ARGB = 0xffF57F17; private static final int COLOR_LIGHT_ORANGE_ARGB = 0xffF9A825; private static final int POLYGON_STROKE_WIDTH_PX = 8; private static final int PATTERN_DASH_LENGTH_PX = 20; private static final PatternItem DASH = new Dash(PATTERN_DASH_LENGTH_PX); // Create a stroke pattern of a gap followed by a dash. private static final List<PatternItem> PATTERN_POLYGON_ALPHA = Arrays.asList(GAP, DASH); // Create a stroke pattern of a dot followed by a gap, a dash, and another gap. private static final List<PatternItem> PATTERN_POLYGON_BETA = Arrays.asList(DOT, GAP, DASH, GAP); /** * Styles the polygon, based on type. * @param polygon The polygon object that needs styling. */ private void stylePolygon(Polygon polygon) { String type = ""; // Get the data object stored with the polygon. if (polygon.getTag() != null) { type = polygon.getTag().toString(); } List<PatternItem> pattern = null; int strokeColor = COLOR_BLACK_ARGB; int fillColor = COLOR_WHITE_ARGB; switch (type) { // If no type is given, allow the API to use the default. case "alpha": // Apply a stroke pattern to render a dashed line, and define colors. pattern = PATTERN_POLYGON_ALPHA; strokeColor = COLOR_DARK_GREEN_ARGB; fillColor = COLOR_LIGHT_GREEN_ARGB; break; case "beta": // Apply a stroke pattern to render a line of dots and dashes, and define colors. pattern = PATTERN_POLYGON_BETA; strokeColor = COLOR_DARK_ORANGE_ARGB; fillColor = COLOR_LIGHT_ORANGE_ARGB; break; } polygon.setStrokePattern(pattern); polygon.setStrokeWidth(POLYGON_STROKE_WIDTH_PX); polygon.setStrokeColor(strokeColor); polygon.setFillColor(fillColor); }
Kotlin
private val COLOR_WHITE_ARGB = -0x1 private val COLOR_DARK_GREEN_ARGB = -0xc771c4 private val COLOR_LIGHT_GREEN_ARGB = -0x7e387c private val COLOR_DARK_ORANGE_ARGB = -0xa80e9 private val COLOR_LIGHT_ORANGE_ARGB = -0x657db private val POLYGON_STROKE_WIDTH_PX = 8 private val PATTERN_DASH_LENGTH_PX = 20 private val DASH: PatternItem = Dash(PATTERN_DASH_LENGTH_PX.toFloat()) // Create a stroke pattern of a gap followed by a dash. private val PATTERN_POLYGON_ALPHA = listOf(GAP, DASH) // Create a stroke pattern of a dot followed by a gap, a dash, and another gap. private val PATTERN_POLYGON_BETA = listOf(DOT, GAP, DASH, GAP) /** * Styles the polygon, based on type. * @param polygon The polygon object that needs styling. */ private fun stylePolygon(polygon: Polygon) { // Get the data object stored with the polygon. val type = polygon.tag?.toString() ?: "" var pattern: List<PatternItem>? = null var strokeColor = COLOR_BLACK_ARGB var fillColor = COLOR_WHITE_ARGB when (type) { "alpha" -> { // Apply a stroke pattern to render a dashed line, and define colors. pattern = PATTERN_POLYGON_ALPHA strokeColor = COLOR_DARK_GREEN_ARGB fillColor = COLOR_LIGHT_GREEN_ARGB } "beta" -> { // Apply a stroke pattern to render a line of dots and dashes, and define colors. pattern = PATTERN_POLYGON_BETA strokeColor = COLOR_DARK_ORANGE_ARGB fillColor = COLOR_LIGHT_ORANGE_ARGB } } polygon.strokePattern = pattern polygon.strokeWidth = POLYGON_STROKE_WIDTH_PX.toFloat() polygon.strokeColor = strokeColor polygon.fillColor = fillColor }
מידע נוסף על דפוסי קו ואפשרויות אחרות להתאמה אישית של צורות
השלבים הבאים
מידע נוסף על אובייקט Circle מעגלים דומים לפוליגונים, אבל יש להם מאפיינים שמשקפים את הצורה של מעגל.
