Hướng dẫn này cho bạn biết cách thêm bản đồ Google vào ứng dụng Android, đồng thời sử dụng nhiều đường và đa giác để biểu thị các tuyến đường và khu vực trên bản đồ.
Làm theo hướng dẫn để tạo một ứng dụng Android bằng Maps SDK dành cho Android. Môi trường phát triển được đề xuất là Android Studio.
Lấy mã
Sao chép hoặc tải kho lưu trữ Mẫu Google Maps Android API phiên bản 2 xuống từ GitHub.
Xem phiên bản Java của hoạt động:
// Copyright 2020 Google LLC // // Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); // you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. // You may obtain a copy of the License at // // http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 // // Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software // distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, // WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. // See the License for the specific language governing permissions and // limitations under the License. package com.example.polygons; import android.os.Bundle; import android.widget.Toast; import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import com.google.android.gms.maps.CameraUpdateFactory; import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap; import com.google.android.gms.maps.OnMapReadyCallback; import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.BitmapDescriptorFactory; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.CustomCap; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Dash; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Dot; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Gap; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.JointType; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.LatLng; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.PatternItem; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Polygon; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.PolygonOptions; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Polyline; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.PolylineOptions; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.RoundCap; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; /** * An activity that displays a Google map with polylines to represent paths or routes, * and polygons to represent areas. */ public class PolyActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements OnMapReadyCallback, GoogleMap.OnPolylineClickListener, GoogleMap.OnPolygonClickListener { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps); // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. SupportMapFragment mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager() .findFragmentById(R.id.map); mapFragment.getMapAsync(this); } /** * Manipulates the map when it's available. * The API invokes this callback when the map is ready to be used. * This is where we can add markers or lines, add listeners or move the camera. * In this tutorial, we add polylines and polygons to represent routes and areas on the map. */ @Override public void onMapReady(GoogleMap googleMap) { // Add polylines to the map. // Polylines are useful to show a route or some other connection between points. Polyline polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(new PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), new LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), new LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), new LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), new LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), new LatLng(-32.491, 147.309))); // Store a data object with the polyline, used here to indicate an arbitrary type. polyline1.setTag("A"); // Style the polyline. stylePolyline(polyline1); Polyline polyline2 = googleMap.addPolyline(new PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-29.501, 119.700), new LatLng(-27.456, 119.672), new LatLng(-25.971, 124.187), new LatLng(-28.081, 126.555), new LatLng(-28.848, 124.229), new LatLng(-28.215, 123.938))); polyline2.setTag("B"); stylePolyline(polyline2); // Add polygons to indicate areas on the map. Polygon polygon1 = googleMap.addPolygon(new PolygonOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-27.457, 153.040), new LatLng(-33.852, 151.211), new LatLng(-37.813, 144.962), new LatLng(-34.928, 138.599))); // Store a data object with the polygon, used here to indicate an arbitrary type. polygon1.setTag("alpha"); // Style the polygon. stylePolygon(polygon1); Polygon polygon2 = googleMap.addPolygon(new PolygonOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-31.673, 128.892), new LatLng(-31.952, 115.857), new LatLng(-17.785, 122.258), new LatLng(-12.4258, 130.7932))); polygon2.setTag("beta"); stylePolygon(polygon2); // Position the map's camera near Alice Springs in the center of Australia, // and set the zoom factor so most of Australia shows on the screen. googleMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(new LatLng(-23.684, 133.903), 4)); // Set listeners for click events. googleMap.setOnPolylineClickListener(this); googleMap.setOnPolygonClickListener(this); } private static final int COLOR_BLACK_ARGB = 0xff000000; private static final int POLYLINE_STROKE_WIDTH_PX = 12; /** * Styles the polyline, based on type. * @param polyline The polyline object that needs styling. */ private void stylePolyline(Polyline polyline) { String type = ""; // Get the data object stored with the polyline. if (polyline.getTag() != null) { type = polyline.getTag().toString(); } switch (type) { // If no type is given, allow the API to use the default. case "A": // Use a custom bitmap as the cap at the start of the line. polyline.setStartCap( new CustomCap( BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromResource(R.drawable.ic_arrow), 10)); break; case "B": // Use a round cap at the start of the line. polyline.setStartCap(new RoundCap()); break; } polyline.setEndCap(new RoundCap()); polyline.setWidth(POLYLINE_STROKE_WIDTH_PX); polyline.setColor(COLOR_BLACK_ARGB); polyline.setJointType(JointType.ROUND); } private static final int PATTERN_GAP_LENGTH_PX = 20; private static final PatternItem DOT = new Dot(); private static final PatternItem GAP = new Gap(PATTERN_GAP_LENGTH_PX); // Create a stroke pattern of a gap followed by a dot. private static final List<PatternItem> PATTERN_POLYLINE_DOTTED = Arrays.asList(GAP, DOT); /** * Listens for clicks on a polyline. * @param polyline The polyline object that the user has clicked. */ @Override public void onPolylineClick(Polyline polyline) { // Flip from solid stroke to dotted stroke pattern. if ((polyline.getPattern() == null) || (!polyline.getPattern().contains(DOT))) { polyline.setPattern(PATTERN_POLYLINE_DOTTED); } else { // The default pattern is a solid stroke. polyline.setPattern(null); } Toast.makeText(this, "Route type " + polyline.getTag().toString(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } /** * Listens for clicks on a polygon. * @param polygon The polygon object that the user has clicked. */ @Override public void onPolygonClick(Polygon polygon) { // Flip the values of the red, green, and blue components of the polygon's color. int color = polygon.getStrokeColor() ^ 0x00ffffff; polygon.setStrokeColor(color); color = polygon.getFillColor() ^ 0x00ffffff; polygon.setFillColor(color); Toast.makeText(this, "Area type " + polygon.getTag().toString(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } private static final int COLOR_WHITE_ARGB = 0xffffffff; private static final int COLOR_DARK_GREEN_ARGB = 0xff388E3C; private static final int COLOR_LIGHT_GREEN_ARGB = 0xff81C784; private static final int COLOR_DARK_ORANGE_ARGB = 0xffF57F17; private static final int COLOR_LIGHT_ORANGE_ARGB = 0xffF9A825; private static final int POLYGON_STROKE_WIDTH_PX = 8; private static final int PATTERN_DASH_LENGTH_PX = 20; private static final PatternItem DASH = new Dash(PATTERN_DASH_LENGTH_PX); // Create a stroke pattern of a gap followed by a dash. private static final List<PatternItem> PATTERN_POLYGON_ALPHA = Arrays.asList(GAP, DASH); // Create a stroke pattern of a dot followed by a gap, a dash, and another gap. private static final List<PatternItem> PATTERN_POLYGON_BETA = Arrays.asList(DOT, GAP, DASH, GAP); /** * Styles the polygon, based on type. * @param polygon The polygon object that needs styling. */ private void stylePolygon(Polygon polygon) { String type = ""; // Get the data object stored with the polygon. if (polygon.getTag() != null) { type = polygon.getTag().toString(); } List<PatternItem> pattern = null; int strokeColor = COLOR_BLACK_ARGB; int fillColor = COLOR_WHITE_ARGB; switch (type) { // If no type is given, allow the API to use the default. case "alpha": // Apply a stroke pattern to render a dashed line, and define colors. pattern = PATTERN_POLYGON_ALPHA; strokeColor = COLOR_DARK_GREEN_ARGB; fillColor = COLOR_LIGHT_GREEN_ARGB; break; case "beta": // Apply a stroke pattern to render a line of dots and dashes, and define colors. pattern = PATTERN_POLYGON_BETA; strokeColor = COLOR_DARK_ORANGE_ARGB; fillColor = COLOR_LIGHT_ORANGE_ARGB; break; } polygon.setStrokePattern(pattern); polygon.setStrokeWidth(POLYGON_STROKE_WIDTH_PX); polygon.setStrokeColor(strokeColor); polygon.setFillColor(fillColor); } }
Xem phiên bản Kotlin của hoạt động này:
// Copyright 2020 Google LLC // // Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); // you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. // You may obtain a copy of the License at // // http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 // // Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software // distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, // WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. // See the License for the specific language governing permissions and // limitations under the License. package com.example.polygons import android.os.Bundle import android.widget.Toast import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity import com.google.android.gms.maps.CameraUpdateFactory import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap.OnPolygonClickListener import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap.OnPolylineClickListener import com.google.android.gms.maps.OnMapReadyCallback import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.BitmapDescriptorFactory import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.CustomCap import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Dash import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Dot import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Gap import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.JointType import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.LatLng import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.PatternItem import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Polygon import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.PolygonOptions import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Polyline import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.PolylineOptions import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.RoundCap /** * An activity that displays a Google map with polylines to represent paths or routes, * and polygons to represent areas. */ class PolyActivity : AppCompatActivity(), OnMapReadyCallback, OnPolylineClickListener, OnPolygonClickListener { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps) // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager .findFragmentById(R.id.map) as SupportMapFragment? mapFragment?.getMapAsync(this) } /** * Manipulates the map when it's available. * The API invokes this callback when the map is ready to be used. * This is where we can add markers or lines, add listeners or move the camera. * In this tutorial, we add polylines and polygons to represent routes and areas on the map. */ override fun onMapReady(googleMap: GoogleMap) { // Add polylines to the map. // Polylines are useful to show a route or some other connection between points. val polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), LatLng(-32.491, 147.309))) // Store a data object with the polyline, used here to indicate an arbitrary type. polyline1.tag = "A" // Style the polyline. stylePolyline(polyline1) val polyline2 = googleMap.addPolyline(PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-29.501, 119.700), LatLng(-27.456, 119.672), LatLng(-25.971, 124.187), LatLng(-28.081, 126.555), LatLng(-28.848, 124.229), LatLng(-28.215, 123.938))) polyline2.tag = "B" stylePolyline(polyline2) // Add polygons to indicate areas on the map. val polygon1 = googleMap.addPolygon(PolygonOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-27.457, 153.040), LatLng(-33.852, 151.211), LatLng(-37.813, 144.962), LatLng(-34.928, 138.599))) // Store a data object with the polygon, used here to indicate an arbitrary type. polygon1.tag = "alpha" // Style the polygon. stylePolygon(polygon1) val polygon2 = googleMap.addPolygon(PolygonOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-31.673, 128.892), LatLng(-31.952, 115.857), LatLng(-17.785, 122.258), LatLng(-12.4258, 130.7932))) polygon2.tag = "beta" stylePolygon(polygon2) // Position the map's camera near Alice Springs in the center of Australia, // and set the zoom factor so most of Australia shows on the screen. googleMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(LatLng(-23.684, 133.903), 4f)) // Set listeners for click events. googleMap.setOnPolylineClickListener(this) googleMap.setOnPolygonClickListener(this) } private val COLOR_BLACK_ARGB = -0x1000000 private val POLYLINE_STROKE_WIDTH_PX = 12 /** * Styles the polyline, based on type. * @param polyline The polyline object that needs styling. */ private fun stylePolyline(polyline: Polyline) { // Get the data object stored with the polyline. val type = polyline.tag?.toString() ?: "" when (type) { "A" -> { // Use a custom bitmap as the cap at the start of the line. polyline.startCap = CustomCap( BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromResource(R.drawable.ic_arrow), 10f) } "B" -> { // Use a round cap at the start of the line. polyline.startCap = RoundCap() } } polyline.endCap = RoundCap() polyline.width = POLYLINE_STROKE_WIDTH_PX.toFloat() polyline.color = COLOR_BLACK_ARGB polyline.jointType = JointType.ROUND } private val PATTERN_GAP_LENGTH_PX = 20 private val DOT: PatternItem = Dot() private val GAP: PatternItem = Gap(PATTERN_GAP_LENGTH_PX.toFloat()) // Create a stroke pattern of a gap followed by a dot. private val PATTERN_POLYLINE_DOTTED = listOf(GAP, DOT) /** * Listens for clicks on a polyline. * @param polyline The polyline object that the user has clicked. */ override fun onPolylineClick(polyline: Polyline) { // Flip from solid stroke to dotted stroke pattern. if (polyline.pattern == null || !polyline.pattern!!.contains(DOT)) { polyline.pattern = PATTERN_POLYLINE_DOTTED } else { // The default pattern is a solid stroke. polyline.pattern = null } Toast.makeText(this, "Route type " + polyline.tag.toString(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show() } /** * Listens for clicks on a polygon. * @param polygon The polygon object that the user has clicked. */ override fun onPolygonClick(polygon: Polygon) { // Flip the values of the red, green, and blue components of the polygon's color. var color = polygon.strokeColor xor 0x00ffffff polygon.strokeColor = color color = polygon.fillColor xor 0x00ffffff polygon.fillColor = color Toast.makeText(this, "Area type ${polygon.tag?.toString()}", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show() } private val COLOR_WHITE_ARGB = -0x1 private val COLOR_DARK_GREEN_ARGB = -0xc771c4 private val COLOR_LIGHT_GREEN_ARGB = -0x7e387c private val COLOR_DARK_ORANGE_ARGB = -0xa80e9 private val COLOR_LIGHT_ORANGE_ARGB = -0x657db private val POLYGON_STROKE_WIDTH_PX = 8 private val PATTERN_DASH_LENGTH_PX = 20 private val DASH: PatternItem = Dash(PATTERN_DASH_LENGTH_PX.toFloat()) // Create a stroke pattern of a gap followed by a dash. private val PATTERN_POLYGON_ALPHA = listOf(GAP, DASH) // Create a stroke pattern of a dot followed by a gap, a dash, and another gap. private val PATTERN_POLYGON_BETA = listOf(DOT, GAP, DASH, GAP) /** * Styles the polygon, based on type. * @param polygon The polygon object that needs styling. */ private fun stylePolygon(polygon: Polygon) { // Get the data object stored with the polygon. val type = polygon.tag?.toString() ?: "" var pattern: List<PatternItem>? = null var strokeColor = COLOR_BLACK_ARGB var fillColor = COLOR_WHITE_ARGB when (type) { "alpha" -> { // Apply a stroke pattern to render a dashed line, and define colors. pattern = PATTERN_POLYGON_ALPHA strokeColor = COLOR_DARK_GREEN_ARGB fillColor = COLOR_LIGHT_GREEN_ARGB } "beta" -> { // Apply a stroke pattern to render a line of dots and dashes, and define colors. pattern = PATTERN_POLYGON_BETA strokeColor = COLOR_DARK_ORANGE_ARGB fillColor = COLOR_LIGHT_ORANGE_ARGB } } polygon.strokePattern = pattern polygon.strokeWidth = POLYGON_STROKE_WIDTH_PX.toFloat() polygon.strokeColor = strokeColor polygon.fillColor = fillColor } }
Thiết lập dự án phát triển
Hãy làm theo các bước sau để tạo dự án hướng dẫn trong Android Studio.
- Tải xuống và cài đặt Android Studio.
- Thêm gói Dịch vụ Google Play vào Android Studio.
- Sao chép hoặc tải kho lưu trữ Mẫu API Google Maps cho Android phiên bản 2 xuống nếu bạn chưa làm việc đó khi bắt đầu đọc hướng dẫn này.
Nhập dự án hướng dẫn:
- Trong Android Studio, hãy chọn File > New > Import Project (Tệp > Mới > Nhập dự án).
- Chuyển đến vị trí mà bạn đã lưu kho lưu trữ Google Maps Android API phiên bản 2 Samples sau khi tải xuống.
- Tìm dự án Polygons tại vị trí này:
PATH-TO-SAVED-REPO/android-samples/tutorials/java/Polygons(Java) hoặc
PATH-TO-SAVED-REPO/android-samples/tutorials/kotlin/Polygons(Kotlin) - Chọn thư mục dự án, rồi nhấp vào Mở. Giờ đây, Android Studio sẽ tạo dự án của bạn bằng công cụ bản dựng Gradle.
Bật các API cần thiết và lấy khoá API
Để hoàn tất hướng dẫn này, bạn cần có một dự án trên Google Cloud đã bật các API cần thiết và một khoá API được phép sử dụng Maps SDK cho Android. Để biết thêm thông tin, hãy xem:
Thêm khoá API vào ứng dụng
- Mở tệp
local.propertiescủa dự án. Thêm chuỗi sau, rồi thay thế
YOUR_API_KEYbằng giá trị khoá API của bạn:MAPS_API_KEY=YOUR_API_KEYKhi bạn tạo ứng dụng, Trình bổ trợ Secrets Gradle cho Android sẽ sao chép khoá API và cung cấp khoá này dưới dạng một biến bản dựng trong tệp kê khai Android, như giải thích bên dưới.
Tạo và chạy ứng dụng
Cách tạo bản dựng và chạy ứng dụng:
Kết nối thiết bị Android với máy tính. Làm theo hướng dẫn để bật tuỳ chọn cho nhà phát triển trên thiết bị Android và định cấu hình hệ thống để phát hiện thiết bị.
Ngoài ra, bạn có thể sử dụng Trình quản lý thiết bị ảo Android (AVD) để định cấu hình một thiết bị ảo. Khi chọn trình mô phỏng, hãy nhớ chọn một hình ảnh có chứa các API của Google. Để biết thêm thông tin chi tiết, hãy xem bài viết Thiết lập dự án Android Studio .
Trong Android Studio, hãy nhấp vào lựa chọn Run (Chạy) trong trình đơn (hoặc biểu tượng nút phát). Chọn một thiết bị theo lời nhắc.
Android Studio sẽ gọi Gradle để tạo ứng dụng, sau đó chạy ứng dụng trên thiết bị hoặc trên trình mô phỏng.
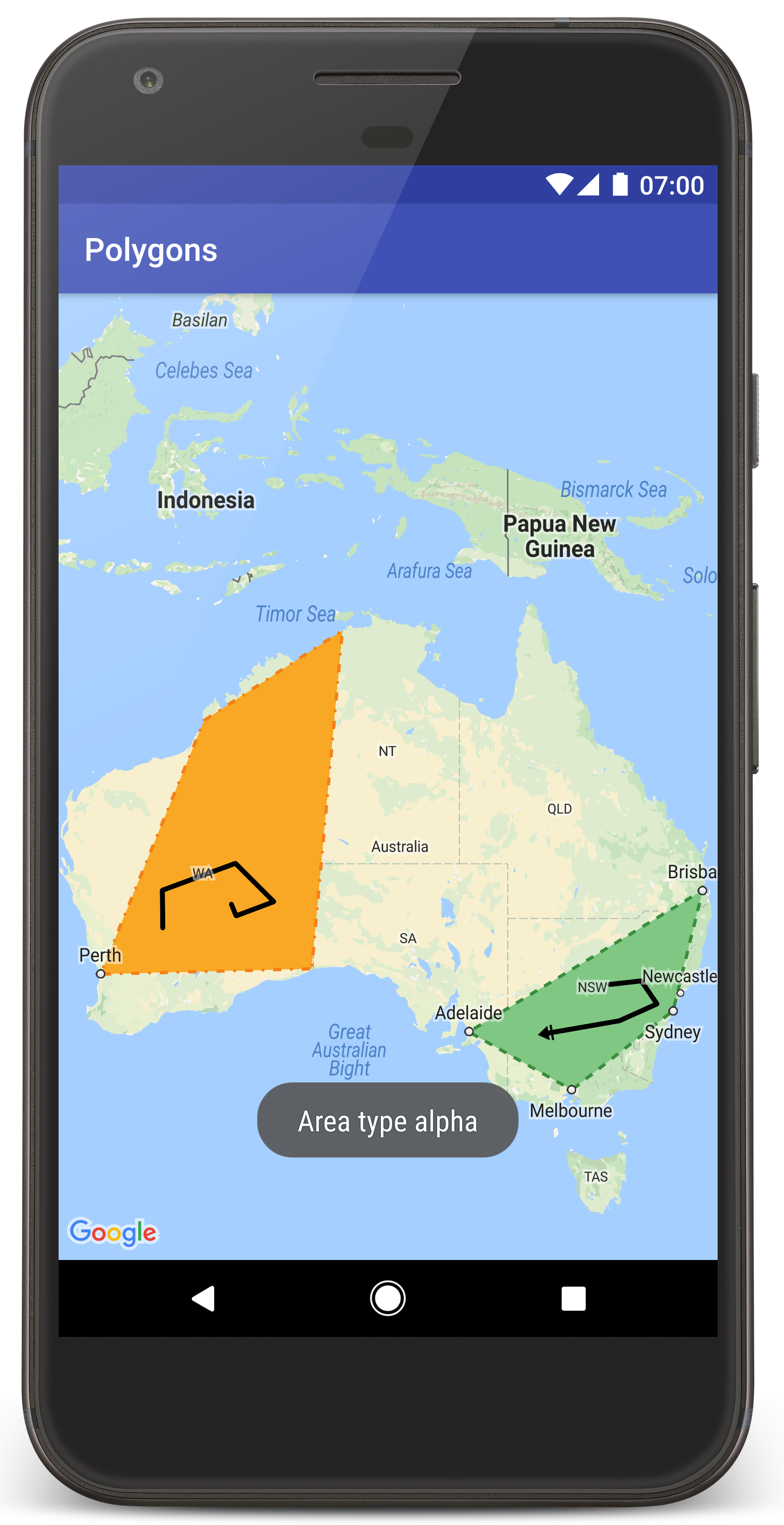
Bạn sẽ thấy một bản đồ có 2 đa giác phủ lên trên nước Úc, tương tự như hình ảnh trên trang này.
Gỡ rối:
- Nếu bạn không thấy bản đồ, hãy kiểm tra để đảm bảo bạn đã lấy khoá API và thêm khoá đó vào ứng dụng, như mô tả ở trên. Kiểm tra nhật ký trong Android Monitor (Trình theo dõi Android) của Android Studio để xem thông báo lỗi về khoá API.
- Sử dụng công cụ gỡ lỗi của Android Studio để xem nhật ký và gỡ lỗi ứng dụng.
Tìm hiểu về mã
Phần này của hướng dẫn giải thích những phần quan trọng nhất của ứng dụng Polygons (Đa giác) để giúp bạn hiểu cách tạo một ứng dụng tương tự.
Kiểm tra tệp kê khai Android
Lưu ý các phần tử sau trong tệp AndroidManifest.xml của ứng dụng:
Thêm một phần tử
meta-datađể nhúng phiên bản Dịch vụ Google Play mà ứng dụng đã được biên dịch.<meta-data android:name="com.google.android.gms.version" android:value="@integer/google_play_services_version" />Thêm một phần tử
meta-datachỉ định khoá API của bạn. Mẫu đi kèm với hướng dẫn này sẽ liên kết giá trị cho khoá API với một biến bản dựng khớp với tên của khoá mà bạn đã xác định trước đó,MAPS_API_KEY. Khi bạn tạo ứng dụng, Trình bổ trợ Secrets Gradle cho Android sẽ cung cấp các khoá trong tệplocal.propertiesdưới dạng các biến bản dựng kê khai.<meta-data android:name="com.google.android.geo.API_KEY" android:value="${MAPS_API_KEY}" />Trong tệp
build.gradle, dòng sau sẽ truyền khoá API của bạn đến tệp kê khai Android.id 'com.google.android.libraries.mapsplatform.secrets-gradle-plugin'
Dưới đây là ví dụ đầy đủ về một tệp kê khai:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!-- Copyright 2020 Google LLC Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. --> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:supportsRtl="true" android:theme="@style/AppTheme"> <meta-data android:name="com.google.android.gms.version" android:value="@integer/google_play_services_version" /> <!-- The API key for Google Maps-based APIs. --> <meta-data android:name="com.google.android.geo.API_KEY" android:value="${MAPS_API_KEY}" /> <activity android:name="com.example.polygons.PolyActivity" android:exported="true" android:label="@string/title_activity_maps"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> </application> </manifest>
Thêm bản đồ
Hiển thị bản đồ bằng Maps SDK cho Android.
Thêm phần tử
<fragment>vào tệp bố cục của hoạt động,activity_maps.xml. Phần tử này xác định mộtSupportMapFragmentđể đóng vai trò là vùng chứa cho bản đồ và cung cấp quyền truy cập vào đối tượngGoogleMap. Hướng dẫn này sử dụng phiên bản thư viện hỗ trợ Android của mảnh bản đồ để đảm bảo khả năng tương thích ngược với các phiên bản trước của khung Android.<!-- Copyright 2020 Google LLC Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. --> <fragment xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/map" android:name="com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context="com.example.polygons.PolyActivity" />
Trong phương thức
onCreate()của hoạt động, hãy đặt tệp bố cục làm khung hiển thị nội dung. Xử lý mảnh bản đồ bằng cách gọiFragmentManager.findFragmentById(). Sau đó, hãy dùnggetMapAsync()để đăng ký lệnh gọi lại bản đồ:Java
@Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps); // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. SupportMapFragment mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager() .findFragmentById(R.id.map); mapFragment.getMapAsync(this); }
Kotlin
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps) // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager .findFragmentById(R.id.map) as SupportMapFragment? mapFragment?.getMapAsync(this) }
Triển khai giao diện
OnMapReadyCallbackvà ghi đè phương thứconMapReady(). API này sẽ gọi lệnh gọi lại này khi đối tượngGoogleMapcó sẵn, vì vậy, bạn có thể thêm các đối tượng vào bản đồ và tuỳ chỉnh thêm cho ứng dụng của mình:Java
public class PolyActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements OnMapReadyCallback, GoogleMap.OnPolylineClickListener, GoogleMap.OnPolygonClickListener { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps); // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. SupportMapFragment mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager() .findFragmentById(R.id.map); mapFragment.getMapAsync(this); } /** * Manipulates the map when it's available. * The API invokes this callback when the map is ready to be used. * This is where we can add markers or lines, add listeners or move the camera. * In this tutorial, we add polylines and polygons to represent routes and areas on the map. */ @Override public void onMapReady(GoogleMap googleMap) { // Add polylines to the map. // Polylines are useful to show a route or some other connection between points. Polyline polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(new PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), new LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), new LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), new LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), new LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), new LatLng(-32.491, 147.309))); // Position the map's camera near Alice Springs in the center of Australia, // and set the zoom factor so most of Australia shows on the screen. googleMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(new LatLng(-23.684, 133.903), 4)); // Set listeners for click events. googleMap.setOnPolylineClickListener(this); googleMap.setOnPolygonClickListener(this); }
Kotlin
class PolyActivity : AppCompatActivity(), OnMapReadyCallback, OnPolylineClickListener, OnPolygonClickListener { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps) // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager .findFragmentById(R.id.map) as SupportMapFragment? mapFragment?.getMapAsync(this) } /** * Manipulates the map when it's available. * The API invokes this callback when the map is ready to be used. * This is where we can add markers or lines, add listeners or move the camera. * In this tutorial, we add polylines and polygons to represent routes and areas on the map. */ override fun onMapReady(googleMap: GoogleMap) { // Add polylines to the map. // Polylines are useful to show a route or some other connection between points. val polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), LatLng(-32.491, 147.309))) // Position the map's camera near Alice Springs in the center of Australia, // and set the zoom factor so most of Australia shows on the screen. googleMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(LatLng(-23.684, 133.903), 4f)) // Set listeners for click events. googleMap.setOnPolylineClickListener(this) googleMap.setOnPolygonClickListener(this) }
Thêm một đường nhiều đoạn để vẽ một đường kẻ trên bản đồ
Polyline là một chuỗi các đoạn thẳng được kết nối. Đường nhiều đoạn rất hữu ích để biểu thị các tuyến đường, đường dẫn hoặc các mối kết nối khác giữa các vị trí trên bản đồ.
Tạo một đối tượng
PolylineOptionsvà thêm các điểm vào đối tượng đó. Mỗi điểm đại diện cho một vị trí trên bản đồ mà bạn xác định bằng một đối tượngLatLngchứa các giá trị vĩ độ và kinh độ. Mã mẫu bên dưới tạo một đường nhiều đoạn có 6 điểm.Gọi
GoogleMap.addPolyline()để thêm đường nhiều đoạn vào bản đồ.Java
Polyline polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(new PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), new LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), new LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), new LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), new LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), new LatLng(-32.491, 147.309)));
Kotlin
val polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), LatLng(-32.491, 147.309)))
Đặt lựa chọn clickable của đường nhiều đoạn thành true nếu bạn muốn xử lý các sự kiện nhấp vào đường nhiều đoạn. Bạn có thể tìm hiểu thêm về cách xử lý sự kiện ở phần sau của hướng dẫn này.
Lưu trữ dữ liệu tuỳ ý bằng một đường nhiều đoạn
Bạn có thể lưu trữ các đối tượng dữ liệu tuỳ ý bằng đường nhiều đoạn và các đối tượng hình học khác.
Gọi
Polyline.setTag()để lưu trữ một đối tượng dữ liệu bằng đường nhiều đoạn. Đoạn mã dưới đây xác định một thẻ tuỳ ý (A) cho biết một loại đường nhiều đoạn.Java
Polyline polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(new PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), new LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), new LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), new LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), new LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), new LatLng(-32.491, 147.309))); // Store a data object with the polyline, used here to indicate an arbitrary type. polyline1.setTag("A");
Kotlin
val polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), LatLng(-32.491, 147.309))) // Store a data object with the polyline, used here to indicate an arbitrary type. polyline1.tag = "A
Truy xuất dữ liệu bằng cách sử dụng
Polyline.getTag(), như phần tiếp theo cho thấy.
Thêm kiểu tuỳ chỉnh vào đường nhiều đoạn
Bạn có thể chỉ định nhiều thuộc tính tạo kiểu trong đối tượng PolylineOptions. Các lựa chọn tạo kiểu bao gồm màu nét vẽ, chiều rộng nét vẽ, mẫu nét vẽ, loại dấu nối, cũng như dấu đầu và dấu cuối. Nếu bạn không chỉ định một thuộc tính cụ thể, API sẽ sử dụng giá trị mặc định cho thuộc tính đó.
Mã sau đây áp dụng một nắp tròn cho cuối đường và một nắp bắt đầu khác tuỳ thuộc vào loại của đường nhiều đoạn, trong đó loại là một thuộc tính tuỳ ý được lưu trữ trong đối tượng dữ liệu cho đường nhiều đoạn. Mẫu này cũng chỉ định độ rộng nét vẽ, màu nét vẽ và loại khớp:
Java
private static final int COLOR_BLACK_ARGB = 0xff000000; private static final int POLYLINE_STROKE_WIDTH_PX = 12; /** * Styles the polyline, based on type. * @param polyline The polyline object that needs styling. */ private void stylePolyline(Polyline polyline) { String type = ""; // Get the data object stored with the polyline. if (polyline.getTag() != null) { type = polyline.getTag().toString(); } switch (type) { // If no type is given, allow the API to use the default. case "A": // Use a custom bitmap as the cap at the start of the line. polyline.setStartCap( new CustomCap( BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromResource(R.drawable.ic_arrow), 10)); break; case "B": // Use a round cap at the start of the line. polyline.setStartCap(new RoundCap()); break; } polyline.setEndCap(new RoundCap()); polyline.setWidth(POLYLINE_STROKE_WIDTH_PX); polyline.setColor(COLOR_BLACK_ARGB); polyline.setJointType(JointType.ROUND); }
Kotlin
private val COLOR_BLACK_ARGB = -0x1000000 private val POLYLINE_STROKE_WIDTH_PX = 12 /** * Styles the polyline, based on type. * @param polyline The polyline object that needs styling. */ private fun stylePolyline(polyline: Polyline) { // Get the data object stored with the polyline. val type = polyline.tag?.toString() ?: "" when (type) { "A" -> { // Use a custom bitmap as the cap at the start of the line. polyline.startCap = CustomCap( BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromResource(R.drawable.ic_arrow), 10f) } "B" -> { // Use a round cap at the start of the line. polyline.startCap = RoundCap() } } polyline.endCap = RoundCap() polyline.width = POLYLINE_STROKE_WIDTH_PX.toFloat() polyline.color = COLOR_BLACK_ARGB polyline.jointType = JointType.ROUND }
Đoạn mã trên chỉ định một bitmap tuỳ chỉnh cho phần đầu của đường nhiều đoạn loại A và chỉ định chiều rộng nét vẽ tham chiếu là 10 pixel. API này sẽ điều chỉnh tỷ lệ bitmap dựa trên độ rộng nét vẽ tham chiếu. Khi chỉ định chiều rộng nét vẽ tham chiếu, hãy cung cấp chiều rộng mà bạn đã dùng khi thiết kế hình ảnh bitmap, theo kích thước ban đầu của hình ảnh. Lưu ý: Mở hình ảnh bitmap ở chế độ thu phóng 100% trong một trình chỉnh sửa hình ảnh và vẽ chiều rộng mong muốn của nét vẽ đường thẳng so với hình ảnh.
Đọc thêm về đầu đường kẻ và các lựa chọn khác để tuỳ chỉnh hình dạng.
Xử lý các sự kiện nhấp vào đường nhiều đoạn
Tạo đường nhiều đoạn có thể nhấp bằng cách gọi
Polyline.setClickable(). (Theo mặc định, người dùng không thể nhấp vào các đường nhiều đoạn và ứng dụng của bạn sẽ không nhận được thông báo khi người dùng nhấn vào một đường nhiều đoạn.)Triển khai giao diện
OnPolylineClickListenervà gọiGoogleMap.setOnPolylineClickListener()để thiết lập trình nghe trên bản đồ:Java
public class PolyActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements OnMapReadyCallback, GoogleMap.OnPolylineClickListener, GoogleMap.OnPolygonClickListener { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps); // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. SupportMapFragment mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager() .findFragmentById(R.id.map); mapFragment.getMapAsync(this); } /** * Manipulates the map when it's available. * The API invokes this callback when the map is ready to be used. * This is where we can add markers or lines, add listeners or move the camera. * In this tutorial, we add polylines and polygons to represent routes and areas on the map. */ @Override public void onMapReady(GoogleMap googleMap) { // Add polylines to the map. // Polylines are useful to show a route or some other connection between points. Polyline polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(new PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), new LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), new LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), new LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), new LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), new LatLng(-32.491, 147.309))); // Position the map's camera near Alice Springs in the center of Australia, // and set the zoom factor so most of Australia shows on the screen. googleMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(new LatLng(-23.684, 133.903), 4)); // Set listeners for click events. googleMap.setOnPolylineClickListener(this); googleMap.setOnPolygonClickListener(this); }
Kotlin
class PolyActivity : AppCompatActivity(), OnMapReadyCallback, OnPolylineClickListener, OnPolygonClickListener { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps) // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager .findFragmentById(R.id.map) as SupportMapFragment? mapFragment?.getMapAsync(this) } /** * Manipulates the map when it's available. * The API invokes this callback when the map is ready to be used. * This is where we can add markers or lines, add listeners or move the camera. * In this tutorial, we add polylines and polygons to represent routes and areas on the map. */ override fun onMapReady(googleMap: GoogleMap) { // Add polylines to the map. // Polylines are useful to show a route or some other connection between points. val polyline1 = googleMap.addPolyline(PolylineOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-35.016, 143.321), LatLng(-34.747, 145.592), LatLng(-34.364, 147.891), LatLng(-33.501, 150.217), LatLng(-32.306, 149.248), LatLng(-32.491, 147.309))) // Position the map's camera near Alice Springs in the center of Australia, // and set the zoom factor so most of Australia shows on the screen. googleMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(LatLng(-23.684, 133.903), 4f)) // Set listeners for click events. googleMap.setOnPolylineClickListener(this) googleMap.setOnPolygonClickListener(this) }
Ghi đè phương thức gọi lại
onPolylineClick(). Ví dụ sau đây sẽ thay đổi mẫu nét của đường giữa nét liền và nét đứt mỗi khi người dùng nhấp vào đường nhiều đoạn:Java
private static final int PATTERN_GAP_LENGTH_PX = 20; private static final PatternItem DOT = new Dot(); private static final PatternItem GAP = new Gap(PATTERN_GAP_LENGTH_PX); // Create a stroke pattern of a gap followed by a dot. private static final List<PatternItem> PATTERN_POLYLINE_DOTTED = Arrays.asList(GAP, DOT); /** * Listens for clicks on a polyline. * @param polyline The polyline object that the user has clicked. */ @Override public void onPolylineClick(Polyline polyline) { // Flip from solid stroke to dotted stroke pattern. if ((polyline.getPattern() == null) || (!polyline.getPattern().contains(DOT))) { polyline.setPattern(PATTERN_POLYLINE_DOTTED); } else { // The default pattern is a solid stroke. polyline.setPattern(null); } Toast.makeText(this, "Route type " + polyline.getTag().toString(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); }
Kotlin
private val PATTERN_GAP_LENGTH_PX = 20 private val DOT: PatternItem = Dot() private val GAP: PatternItem = Gap(PATTERN_GAP_LENGTH_PX.toFloat()) // Create a stroke pattern of a gap followed by a dot. private val PATTERN_POLYLINE_DOTTED = listOf(GAP, DOT) /** * Listens for clicks on a polyline. * @param polyline The polyline object that the user has clicked. */ override fun onPolylineClick(polyline: Polyline) { // Flip from solid stroke to dotted stroke pattern. if (polyline.pattern == null || !polyline.pattern!!.contains(DOT)) { polyline.pattern = PATTERN_POLYLINE_DOTTED } else { // The default pattern is a solid stroke. polyline.pattern = null } Toast.makeText(this, "Route type " + polyline.tag.toString(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show() }
Thêm đa giác để biểu thị các khu vực trên bản đồ
Polygon là một hình dạng bao gồm một chuỗi toạ độ theo một trình tự có thứ tự, tương tự như Polyline. Điểm khác biệt là đa giác xác định một vùng khép kín có phần bên trong có thể điền, trong khi đường nhiều đoạn là đường hở.
Tạo một đối tượng
PolygonOptionsvà thêm các điểm vào đối tượng đó. Mỗi điểm đại diện cho một vị trí trên bản đồ mà bạn xác định bằng một đối tượngLatLngchứa các giá trị vĩ độ và kinh độ. Mã mẫu bên dưới tạo một đa giác có 4 điểm.Hãy làm cho đa giác có thể nhấp vào bằng cách gọi
Polygon.setClickable(). (Theo mặc định, đa giác không thể nhấp vào và ứng dụng của bạn sẽ không nhận được thông báo khi người dùng nhấn vào một đa giác.) Việc xử lý các sự kiện nhấp vào đa giác cũng tương tự như việc xử lý các sự kiện trên đường nhiều đoạn, như đã mô tả trước đó trong hướng dẫn này.Gọi
GoogleMap.addPolygon()để thêm đa giác vào bản đồ.Gọi
Polygon.setTag()để lưu trữ một đối tượng dữ liệu bằng đa giác. Đoạn mã bên dưới xác định một loại tuỳ ý (alpha) cho đa giác.Java
// Add polygons to indicate areas on the map. Polygon polygon1 = googleMap.addPolygon(new PolygonOptions() .clickable(true) .add( new LatLng(-27.457, 153.040), new LatLng(-33.852, 151.211), new LatLng(-37.813, 144.962), new LatLng(-34.928, 138.599))); // Store a data object with the polygon, used here to indicate an arbitrary type. polygon1.setTag("alpha");
Kotlin
// Add polygons to indicate areas on the map. val polygon1 = googleMap.addPolygon(PolygonOptions() .clickable(true) .add( LatLng(-27.457, 153.040), LatLng(-33.852, 151.211), LatLng(-37.813, 144.962), LatLng(-34.928, 138.599))) // Store a data object with the polygon, used here to indicate an arbitrary type. polygon1.tag = "alpha" // Style the polygon.
Thêm kiểu tuỳ chỉnh vào đa giác
Bạn có thể chỉ định một số thuộc tính tạo kiểu trong đối tượng PolygonOptions. Các lựa chọn về kiểu bao gồm màu nét vẽ, độ rộng nét vẽ, mẫu nét vẽ, loại dấu nối nét vẽ và màu tô. Nếu bạn không chỉ định một thuộc tính cụ thể, API sẽ sử dụng giá trị mặc định cho thuộc tính đó.
Đoạn mã sau đây áp dụng các màu và mẫu nét vẽ cụ thể tuỳ thuộc vào loại đa giác, trong đó loại là một thuộc tính tuỳ ý được lưu trữ trong đối tượng dữ liệu cho đa giác:
Java
private static final int COLOR_WHITE_ARGB = 0xffffffff; private static final int COLOR_DARK_GREEN_ARGB = 0xff388E3C; private static final int COLOR_LIGHT_GREEN_ARGB = 0xff81C784; private static final int COLOR_DARK_ORANGE_ARGB = 0xffF57F17; private static final int COLOR_LIGHT_ORANGE_ARGB = 0xffF9A825; private static final int POLYGON_STROKE_WIDTH_PX = 8; private static final int PATTERN_DASH_LENGTH_PX = 20; private static final PatternItem DASH = new Dash(PATTERN_DASH_LENGTH_PX); // Create a stroke pattern of a gap followed by a dash. private static final List<PatternItem> PATTERN_POLYGON_ALPHA = Arrays.asList(GAP, DASH); // Create a stroke pattern of a dot followed by a gap, a dash, and another gap. private static final List<PatternItem> PATTERN_POLYGON_BETA = Arrays.asList(DOT, GAP, DASH, GAP); /** * Styles the polygon, based on type. * @param polygon The polygon object that needs styling. */ private void stylePolygon(Polygon polygon) { String type = ""; // Get the data object stored with the polygon. if (polygon.getTag() != null) { type = polygon.getTag().toString(); } List<PatternItem> pattern = null; int strokeColor = COLOR_BLACK_ARGB; int fillColor = COLOR_WHITE_ARGB; switch (type) { // If no type is given, allow the API to use the default. case "alpha": // Apply a stroke pattern to render a dashed line, and define colors. pattern = PATTERN_POLYGON_ALPHA; strokeColor = COLOR_DARK_GREEN_ARGB; fillColor = COLOR_LIGHT_GREEN_ARGB; break; case "beta": // Apply a stroke pattern to render a line of dots and dashes, and define colors. pattern = PATTERN_POLYGON_BETA; strokeColor = COLOR_DARK_ORANGE_ARGB; fillColor = COLOR_LIGHT_ORANGE_ARGB; break; } polygon.setStrokePattern(pattern); polygon.setStrokeWidth(POLYGON_STROKE_WIDTH_PX); polygon.setStrokeColor(strokeColor); polygon.setFillColor(fillColor); }
Kotlin
private val COLOR_WHITE_ARGB = -0x1 private val COLOR_DARK_GREEN_ARGB = -0xc771c4 private val COLOR_LIGHT_GREEN_ARGB = -0x7e387c private val COLOR_DARK_ORANGE_ARGB = -0xa80e9 private val COLOR_LIGHT_ORANGE_ARGB = -0x657db private val POLYGON_STROKE_WIDTH_PX = 8 private val PATTERN_DASH_LENGTH_PX = 20 private val DASH: PatternItem = Dash(PATTERN_DASH_LENGTH_PX.toFloat()) // Create a stroke pattern of a gap followed by a dash. private val PATTERN_POLYGON_ALPHA = listOf(GAP, DASH) // Create a stroke pattern of a dot followed by a gap, a dash, and another gap. private val PATTERN_POLYGON_BETA = listOf(DOT, GAP, DASH, GAP) /** * Styles the polygon, based on type. * @param polygon The polygon object that needs styling. */ private fun stylePolygon(polygon: Polygon) { // Get the data object stored with the polygon. val type = polygon.tag?.toString() ?: "" var pattern: List<PatternItem>? = null var strokeColor = COLOR_BLACK_ARGB var fillColor = COLOR_WHITE_ARGB when (type) { "alpha" -> { // Apply a stroke pattern to render a dashed line, and define colors. pattern = PATTERN_POLYGON_ALPHA strokeColor = COLOR_DARK_GREEN_ARGB fillColor = COLOR_LIGHT_GREEN_ARGB } "beta" -> { // Apply a stroke pattern to render a line of dots and dashes, and define colors. pattern = PATTERN_POLYGON_BETA strokeColor = COLOR_DARK_ORANGE_ARGB fillColor = COLOR_LIGHT_ORANGE_ARGB } } polygon.strokePattern = pattern polygon.strokeWidth = POLYGON_STROKE_WIDTH_PX.toFloat() polygon.strokeColor = strokeColor polygon.fillColor = fillColor }
Đọc thêm về mẫu nét vẽ và các lựa chọn khác để tuỳ chỉnh hình dạng.
Các bước tiếp theo
Tìm hiểu về đối tượng Circle. Đường tròn tương tự như đa giác nhưng có các thuộc tính phản ánh hình dạng của đường tròn.
