W tym samouczku pokazujemy, jak dodać mapę Google do aplikacji na Androida. Mapa zawiera znacznik, zwany też pinezką, wskazujący konkretną lokalizację.
Postępuj zgodnie z samouczkiem, aby utworzyć aplikację na Androida za pomocą pakietu Maps SDK na Androida. Zalecane środowisko programistyczne to Android Studio.
Pobierz kod
Sklonuj lub pobierz repozytorium przykładów Google Maps Android API v2 z GitHuba.
Wyświetl wersję działania w Javie:
// Copyright 2020 Google LLC // // Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); // you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. // You may obtain a copy of the License at // // http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 // // Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software // distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, // WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. // See the License for the specific language governing permissions and // limitations under the License. package com.example.mapwithmarker; import android.os.Bundle; import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import com.google.android.gms.maps.CameraUpdateFactory; import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap; import com.google.android.gms.maps.OnMapReadyCallback; import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.LatLng; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.MarkerOptions; /** * An activity that displays a Google map with a marker (pin) to indicate a particular location. */ public class MapsMarkerActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements OnMapReadyCallback { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps); // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. SupportMapFragment mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager() .findFragmentById(R.id.map); mapFragment.getMapAsync(this); } /** * Manipulates the map when it's available. * The API invokes this callback when the map is ready to be used. * This is where we can add markers or lines, add listeners or move the camera. In this case, * we just add a marker near Sydney, Australia. * If Google Play services is not installed on the device, the user receives a prompt to install * Play services inside the SupportMapFragment. The API invokes this method after the user has * installed Google Play services and returned to the app. */ @Override public void onMapReady(GoogleMap googleMap) { // Add a marker in Sydney, Australia, // and move the map's camera to the same location. LatLng sydney = new LatLng(-33.852, 151.211); googleMap.addMarker(new MarkerOptions() .position(sydney) .title("Marker in Sydney")); googleMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLng(sydney)); } }
Wyświetl wersję aktywności w języku Kotlin:
// Copyright 2020 Google LLC // // Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); // you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. // You may obtain a copy of the License at // // http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 // // Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software // distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, // WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. // See the License for the specific language governing permissions and // limitations under the License. package com.example.mapwithmarker import android.os.Bundle import android.widget.Toast import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity import com.google.android.gms.maps.CameraUpdateFactory import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap import com.google.android.gms.maps.OnMapReadyCallback import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.LatLng import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.MarkerOptions /** * An activity that displays a Google map with a marker (pin) to indicate a particular location. */ class MapsMarkerActivity : AppCompatActivity(), OnMapReadyCallback { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps) // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.map) as? SupportMapFragment mapFragment?.getMapAsync(this) } override fun onMapReady(googleMap: GoogleMap) { val sydney = LatLng(-33.852, 151.211) googleMap.addMarker( MarkerOptions() .position(sydney) .title("Marker in Sydney") ) googleMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLng(sydney)) } }
Konfigurowanie projektu programistycznego
Aby utworzyć projekt samouczka w Android Studio, wykonaj te czynności.
- Pobierz i zainstaluj Android Studio.
- Dodaj pakiet usług Google Play do Androida Studio.
- Sklonuj lub pobierz repozytorium przykładów Google Maps Android API v2, jeśli nie zrobisz tego na początku tego samouczka.
Zaimportuj projekt samouczka:
- W Android Studio wybierz Plik > Nowy > Importuj projekt.
- Otwórz miejsce, w którym po pobraniu został zapisany repozytorium przykładów Google Maps Android API v2.
- Znajdź projekt MapWithMarker w tej lokalizacji:
PATH-TO-SAVED-REPO/android-samples/tutorials/java/MapWithMarker(Java) lub
PATH-TO-SAVED-REPO/android-samples/tutorials/kotlin/MapWithMarker(Kotlin) - Wybierz katalog projektu, a następnie kliknij Otwórz. Android Studio skompiluje teraz Twój projekt za pomocą narzędzia Gradle.
Włączanie niezbędnych interfejsów API i uzyskiwanie klucza interfejsu API
Aby wykonać zadania z tego samouczka, musisz mieć projekt Google Cloud z włączonymi interfejsami API i kluczem interfejsu API, który jest autoryzowany do używania pakietu SDK Map Google na Androida. Więcej informacji znajdziesz w tych artykułach:
Dodawanie klucza interfejsu API do aplikacji
- Otwórz plik
local.propertiesprojektu. Dodaj ten ciąg znaków, a potem zastąp symbol
YOUR_API_KEYwartością klucza API:MAPS_API_KEY=YOUR_API_KEYGdy skompilujesz aplikację, wtyczka Gradle obiektów tajnych dla Androida skopiuje klucz interfejsu API i udostępni go jako zmienną kompilacji w manifeście Androida, jak opisano poniżej.
Tworzenie i uruchamianie aplikacji
Aby skompilować i uruchomić aplikację:
Podłącz urządzenie z Androidem do komputera. Postępuj zgodnie z instrukcjami, aby włączyć opcje programisty na urządzeniu z Androidem i skonfigurować system tak, aby wykrywał urządzenie.
Możesz też użyć menedżera urządzenia wirtualnego z Androidem (AVD), aby skonfigurować urządzenie wirtualne. Wybierając emulator, upewnij się, że wybierasz obraz, który zawiera interfejsy API Google. Więcej informacji znajdziesz w artykule Konfigurowanie projektu w Android Studio .
W Android Studio kliknij opcję menu Uruchom (lub ikonę przycisku odtwarzania). Wybierz urządzenie zgodnie z instrukcjami.
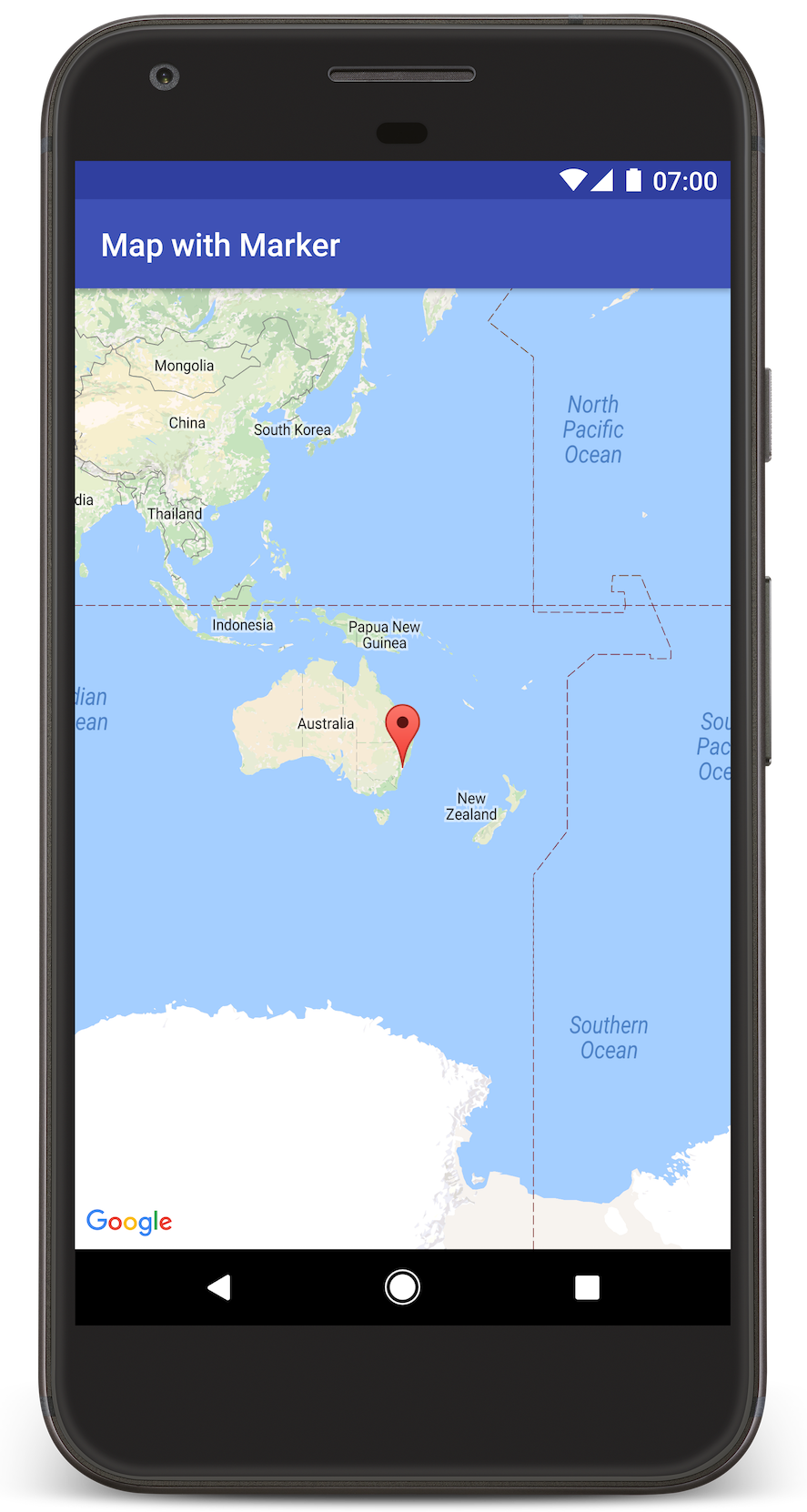
Android Studio wywołuje Gradle, aby skompilować aplikację, a następnie uruchamia ją na urządzeniu lub w emulatorze. Powinna się wyświetlić mapa ze znacznikiem wskazującym Sydney na wschodnim wybrzeżu Australii, podobna do obrazu na tej stronie.
Rozwiązywanie problemów:
- Jeśli nie widzisz mapy, sprawdź, czy masz klucz interfejsu API i czy został on dodany do aplikacji w sposób opisany powyżej. Sprawdź dziennik w Monitorze Androida w Android Studio pod kątem komunikatów o błędach dotyczących klucza interfejsu API.
- Użyj narzędzi do debugowania w Android Studio, aby wyświetlić logi i debugować aplikację.
Zrozumienie kodu
W tej części samouczka wyjaśniamy najważniejsze elementy aplikacji MapWithMarker, aby pomóc Ci w utworzeniu podobnej aplikacji.
Sprawdzanie pliku manifestu Androida
Zwróć uwagę na te elementy w pliku AndroidManifest.xml aplikacji:
Dodaj element
meta-data, aby osadzić wersję Usług Google Play, z którą skompilowano aplikację.<meta-data android:name="com.google.android.gms.version" android:value="@integer/google_play_services_version" />Dodaj element
meta-dataokreślający klucz interfejsu API. Przykładowy kod dołączony do tego samouczka mapuje wartość klucza interfejsu API na zmienną kompilacji pasującą do nazwy zdefiniowanego wcześniej klucza, czyliMAPS_API_KEY. Podczas kompilowania aplikacji wtyczka Gradle obiektów tajnych na Androida udostępni klucze w plikulocal.propertiesjako zmienne kompilacji manifestu.<meta-data android:name="com.google.android.geo.API_KEY" android:value="${MAPS_API_KEY}" />W pliku
build.gradleten wiersz przekazuje klucz interfejsu API do manifestu Androida.id 'com.google.android.libraries.mapsplatform.secrets-gradle-plugin'
Oto przykład pełnego pliku manifestu:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!-- Copyright 2020 Google LLC Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. --> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:supportsRtl="true" android:theme="@style/AppTheme"> <meta-data android:name="com.google.android.gms.version" android:value="@integer/google_play_services_version" /> <!-- The API key for Google Maps-based APIs. --> <meta-data android:name="com.google.android.geo.API_KEY" android:value="${MAPS_API_KEY}" /> <activity android:name=".MapsMarkerActivity" android:label="@string/title_activity_maps" android:exported="true"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> </application> </manifest>
Dodawanie mapy
Wyświetlanie mapy za pomocą pakietu Maps SDK na Androida.
Dodaj element
<fragment>do pliku układu aktywności,activity_maps.xml. Ten element definiujeSupportMapFragment, który działa jako kontener mapy i zapewnia dostęp do obiektuGoogleMap. W samouczku używamy wersji fragmentu mapy z biblioteki pomocy Androida, aby zapewnić wsteczną zgodność ze starszymi wersjami platformy Android.<!-- Copyright 2020 Google LLC Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. --> <fragment xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/map" android:name="com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context="com.example.mapwithmarker.MapsMarkerActivity" />
W metodzie
onCreate()aktywności ustaw plik układu jako widok treści. Pobierz uchwyt do fragmentu mapy, wywołującFragmentManager.findFragmentById(). Następnie użyjgetMapAsync(), aby zarejestrować wywołanie zwrotne mapy:Java
@Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps); // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. SupportMapFragment mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager() .findFragmentById(R.id.map); mapFragment.getMapAsync(this); }
Kotlin
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps) // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.map) as? SupportMapFragment mapFragment?.getMapAsync(this) }
Zaimplementuj interfejs
OnMapReadyCallbacki zastąp metodęonMapReady(), aby skonfigurować mapę, gdy dostępny jest obiektGoogleMap:Java
public class MapsMarkerActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements OnMapReadyCallback { // ... @Override public void onMapReady(GoogleMap googleMap) { LatLng sydney = new LatLng(-33.852, 151.211); googleMap.addMarker(new MarkerOptions() .position(sydney) .title("Marker in Sydney")); } }
Kotlin
class MapsMarkerActivity : AppCompatActivity(), OnMapReadyCallback { // ... override fun onMapReady(googleMap: GoogleMap) { val sydney = LatLng(-33.852, 151.211) googleMap.addMarker( MarkerOptions() .position(sydney) .title("Marker in Sydney") ) } }
Domyślnie pakiet SDK Map Google na Androida wyświetla zawartość okna informacji, gdy użytkownik kliknie znacznik. Jeśli chcesz używać domyślnego działania, nie musisz dodawać odbiornika kliknięć znacznika.
Dalsze kroki
Dowiedz się więcej o obiekcie mapy i o tym, co możesz zrobić z markerami.

