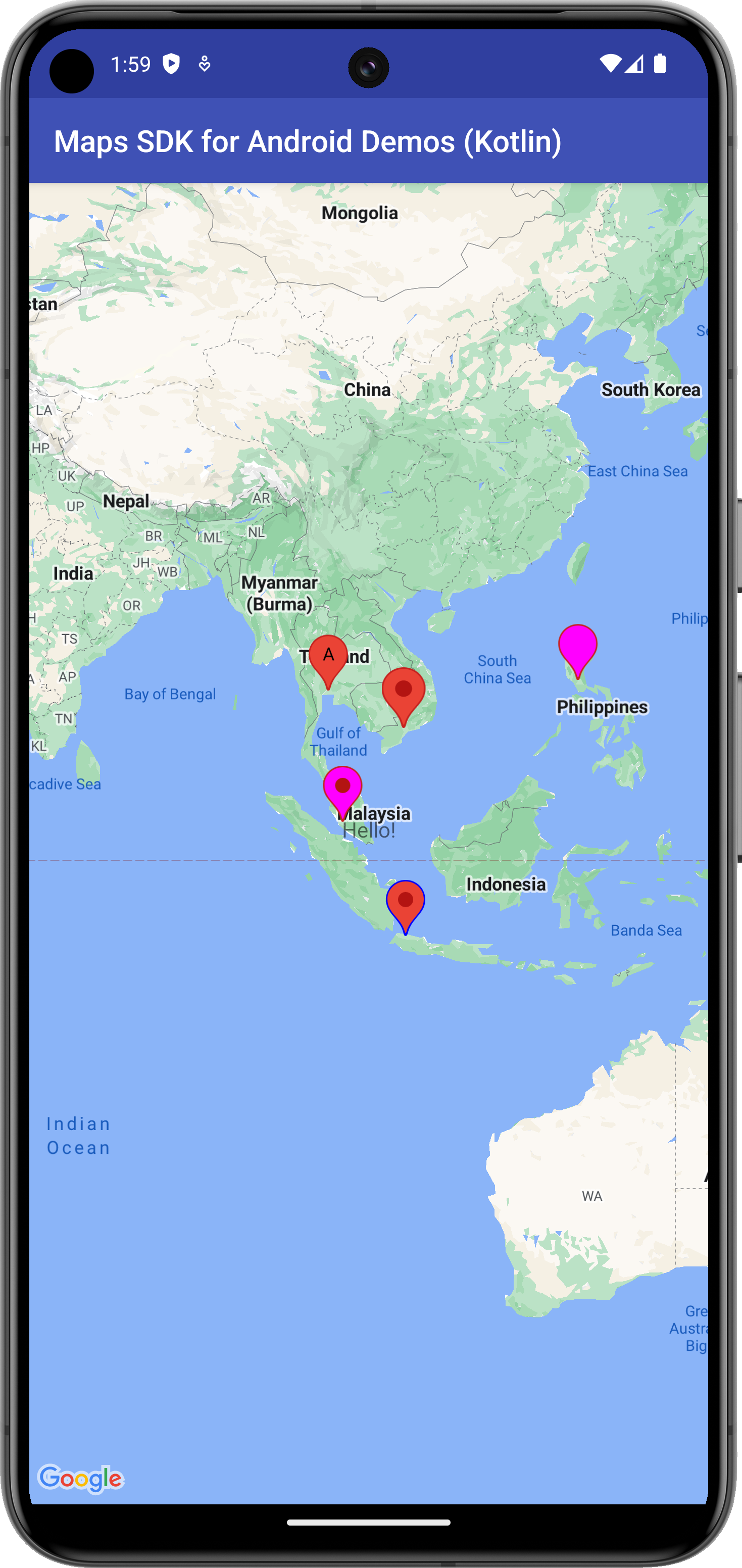
Questo esempio identifica una posizione sulla mappa con un indicatore avanzato e dimostra alcune delle funzionalità degli indicatori avanzati.
Per ulteriori informazioni, consulta la documentazione.
Inizia
Prima di poter provare il codice di esempio, devi configurare il tuo ambiente di sviluppo. Per ulteriori informazioni, consulta gli esempi di codice di Maps SDK for Android.
Visualizza il codice
Kotlin
class AdvancedMarkersDemoActivity : SamplesBaseActivity(), OnMapReadyCallback { /** * This method is called when the activity is first created. * * It sets up the activity's layout and then initializes the map. * * The key logic here is to check if the developer has provided a Map ID in the * `strings.xml` file. * * If the `R.string.map_id` value is not the default "DEMO_MAP_ID", it means a * custom Map ID has been provided. In this case, we can rely on the simpler setup * where the `SupportMapFragment` is inflated directly from the XML layout, and it * will automatically use the Map ID from the string resource. * * However, if the `R.string.map_id` is still the default value, we fall back to a * programmatic setup. This involves: * 1. Retrieving the Map ID from the `secrets.properties` file, which is managed by the * `ApiDemoApplication` class. * 2. Creating a `GoogleMapOptions` object. * 3. Explicitly setting the retrieved `mapId` on the `GoogleMapOptions`. This step is * **critical** because Advanced Markers will not work without a valid Map ID. * 4. Creating a new `SupportMapFragment` instance with these options and replacing the * placeholder fragment in the layout. * * This dual approach ensures that the demo can run seamlessly while also providing a * clear path for developers to use their own Map IDs, which is a requirement for using * Advanced Markers. */ /** * This method is called when the activity is first created. * * It sets up the activity's layout and then initializes the map. * * The key logic here is to check if the developer has provided a Map ID in the * `strings.xml` file. * * If the `R.string.map_id` value is not the default "DEMO_MAP_ID", it means a * custom Map ID has been provided. In this case, we can rely on the simpler setup * where the `SupportMapFragment` is inflated directly from the XML layout, and it * will automatically use the Map ID from the string resource. * * However, if the `R.string.map_id` is still the default value, we fall back to a * programmatic setup. This involves: * 1. Retrieving the Map ID from the `secrets.properties` file, via the * `ApiDemoApplication.mapId` property. * 2. Creating a `GoogleMapOptions` object. * 3. Explicitly setting the retrieved `mapId` on the `GoogleMapOptions`. This step is * **critical** because Advanced Markers will not work without a valid Map ID. * 4. Creating a new `SupportMapFragment` instance with these options and replacing the * placeholder fragment in the layout. * * This dual approach ensures that the demo can run seamlessly while also providing a * clear path for developers to use their own Map IDs, which is a requirement for using * Advanced Markers. */ override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(com.example.common_ui.R.layout.advanced_markers_demo) if (getString(com.example.common_ui.R.string.map_id) != "DEMO_MAP_ID") { val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(com.example.common_ui.R.id.map) as SupportMapFragment? mapFragment?.getMapAsync(this) } else { val mapId = (application as ApiDemoApplication).mapId // --- Map ID Check --- if (mapId == null) { finish() return // Exit early if no valid Map ID } // --- Programmatically create and add the map fragment --- val mapOptions = GoogleMapOptions().apply { mapId(mapId) } val mapFragment = SupportMapFragment.newInstance(mapOptions) supportFragmentManager.beginTransaction() .replace(R.id.map, mapFragment) // Use the container ID .commit() mapFragment.getMapAsync(this) } applyInsets(findViewById(com.example.common_ui.R.id.map_container)) } override fun onMapReady(map: GoogleMap) { with(map) { moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(SINGAPORE, ZOOM_LEVEL)) } val capabilities: MapCapabilities = map.mapCapabilities Log.d(TAG, "are advanced marker enabled?" + capabilities.isAdvancedMarkersAvailable) // This sample sets a view as the iconView for the Advanced Marker val textView = TextView(this) textView.text = "Hello!" val advancedMarkerView: Marker? = map.addMarker( AdvancedMarkerOptions().position(SINGAPORE).iconView(textView).zIndex(1f) ) // This uses PinConfig.Builder to create an instance of PinConfig. val pinConfigBuilder: PinConfig.Builder = PinConfig.builder() pinConfigBuilder.setBackgroundColor(Color.MAGENTA) val pinConfig: PinConfig = pinConfigBuilder.build() // Use the PinConfig instance to set the icon for AdvancedMarkerOptions. val advancedMarkerOptions: AdvancedMarkerOptions = AdvancedMarkerOptions().icon(BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromPinConfig(pinConfig)) .position(KUALA_LUMPUR) // Pass the AdvancedMarkerOptions instance to addMarker(). val marker: Marker? = map.addMarker(advancedMarkerOptions) // This sample changes the border color of the advanced marker val pinConfigBuilder2: PinConfig.Builder = PinConfig.builder() pinConfigBuilder2.setBorderColor(Color.BLUE) val pinConfig2: PinConfig = pinConfigBuilder2.build() val advancedMarkerOptions2: AdvancedMarkerOptions = AdvancedMarkerOptions() .icon(BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromPinConfig(pinConfig2)) .position(JAKARTA) val marker2: Marker? = map.addMarker(advancedMarkerOptions2) // Set the glyph text. val pinConfigBuilder3: PinConfig.Builder = PinConfig.builder() val glyphText = PinConfig.Glyph("A") // Alternatively, you can set the text color: // Glyph glyphText = new Glyph("A", Color.GREEN); pinConfigBuilder3.setGlyph(glyphText) val pinConfig3: PinConfig = pinConfigBuilder3.build() val advancedMarkerOptions3: AdvancedMarkerOptions = AdvancedMarkerOptions() .icon(BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromPinConfig(pinConfig3)) .position(BANGKOK) val marker3: Marker? = map.addMarker(advancedMarkerOptions3) // Create a transparent glyph. val pinConfigBuilder4: PinConfig.Builder = PinConfig.builder() pinConfigBuilder4.setBackgroundColor(Color.MAGENTA) pinConfigBuilder4.setGlyph(PinConfig.Glyph(Color.TRANSPARENT)) val pinConfig4: PinConfig = pinConfigBuilder4.build() val advancedMarkerOptions4: AdvancedMarkerOptions = AdvancedMarkerOptions() .icon(BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromPinConfig(pinConfig4)) .position(MANILA) val marker4: Marker? = map.addMarker(advancedMarkerOptions4) // Collision behavior can only be changed in the AdvancedMarkerOptions object. // Changes to collision behavior after a marker has been created are not possible val collisionBehavior: Int = AdvancedMarkerOptions.CollisionBehavior.REQUIRED_AND_HIDES_OPTIONAL val advancedMarkerOptions5: AdvancedMarkerOptions = AdvancedMarkerOptions() .position(HO_CHI_MINH_CITY) .collisionBehavior(collisionBehavior) val marker5: Marker? = map.addMarker(advancedMarkerOptions5) } }
Java
public class AdvancedMarkersDemoActivity extends SamplesBaseActivity implements OnMapReadyCallback { private static final LatLng SINGAPORE = new LatLng(1.3521, 103.8198); private static final LatLng KUALA_LUMPUR = new LatLng(3.1390, 101.6869); private static final LatLng JAKARTA = new LatLng(-6.2088, 106.8456); private static final LatLng BANGKOK = new LatLng(13.7563, 100.5018); private static final LatLng MANILA = new LatLng(14.5995, 120.9842); private static final LatLng HO_CHI_MINH_CITY = new LatLng(10.7769, 106.7009); private static final float ZOOM_LEVEL = 3.5f; private static final String TAG = AdvancedMarkersDemoActivity.class.getName(); /** * This method is called when the activity is first created. * * It sets up the activity's layout and then initializes the map. * * The key logic here is to check if the developer has provided a Map ID in the * `strings.xml` file. * * If the `R.string.map_id` value is not the default "DEMO_MAP_ID", it means a * custom Map ID has been provided. In this case, we can rely on the simpler setup * where the `SupportMapFragment` is inflated directly from the XML layout, and it * will automatically use the Map ID from the string resource. * * However, if the `R.string.map_id` is still the default value, we fall back to a * programmatic setup. This involves: * 1. Retrieving the Map ID from the `secrets.properties` file, which is managed by the * `ApiDemoApplication` class. * 2. Creating a `GoogleMapOptions` object. * 3. Explicitly setting the retrieved `mapId` on the `GoogleMapOptions`. This step is * **critical** because Advanced Markers will not work without a valid Map ID. * 4. Creating a new `SupportMapFragment` instance with these options and replacing the * placeholder fragment in the layout. * * This dual approach ensures that the demo can run seamlessly while also providing a * clear path for developers to use their own Map IDs, which is a requirement for using * Advanced Markers. */ @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(com.example.common_ui.R.layout.advanced_markers_demo); if (!getString(com.example.common_ui.R.string.map_id).equals("DEMO_MAP_ID")) { SupportMapFragment mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager().findFragmentById(com.example.common_ui.R.id.map); if (mapFragment != null) { mapFragment.getMapAsync(this); } } else { String mapId = ((ApiDemoApplication) getApplication()).getMapId(); if (mapId == null) { finish(); return; } GoogleMapOptions mapOptions = new GoogleMapOptions().mapId(mapId); SupportMapFragment mapFragment = SupportMapFragment.newInstance(mapOptions); getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction() .replace(com.example.common_ui.R.id.map, mapFragment) .commit(); mapFragment.getMapAsync(this); } applyInsets(findViewById(com.example.common_ui.R.id.map_container)); } @Override public void onMapReady(GoogleMap map) { map.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(SINGAPORE, ZOOM_LEVEL)); MapCapabilities capabilities = map.getMapCapabilities(); Log.d(TAG, "Are advanced markers enabled? " + capabilities.isAdvancedMarkersAvailable()); // This sample sets a view as the iconView for the Advanced Marker TextView textView = new TextView(this); textView.setText("Hello!"); Marker advancedMarkerView = map.addMarker(new AdvancedMarkerOptions() .position(SINGAPORE) .iconView(textView) .zIndex(1f)); // This uses PinConfig.Builder to create an instance of PinConfig. PinConfig.Builder pinConfigBuilder = PinConfig.builder(); pinConfigBuilder.setBackgroundColor(Color.MAGENTA); PinConfig pinConfig = pinConfigBuilder.build(); // Use the PinConfig instance to set the icon for AdvancedMarkerOptions. AdvancedMarkerOptions advancedMarkerOptions = new AdvancedMarkerOptions() .icon(BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromPinConfig(pinConfig)) .position(KUALA_LUMPUR); // Pass the AdvancedMarkerOptions instance to addMarker(). Marker marker = map.addMarker(advancedMarkerOptions); // This sample changes the border color of the advanced marker PinConfig.Builder pinConfigBuilder2 = PinConfig.builder(); pinConfigBuilder2.setBorderColor(Color.BLUE); PinConfig pinConfig2 = pinConfigBuilder2.build(); AdvancedMarkerOptions advancedMarkerOptions2 = new AdvancedMarkerOptions() .icon(BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromPinConfig(pinConfig2)) .position(JAKARTA); Marker marker2 = map.addMarker(advancedMarkerOptions2); // Set the glyph text. PinConfig.Builder pinConfigBuilder3 = PinConfig.builder(); PinConfig.Glyph glyphText = new PinConfig.Glyph("A"); // Alternatively, you can set the text color: // Glyph glyphText = new Glyph("A", Color.GREEN); pinConfigBuilder3.setGlyph(glyphText); PinConfig pinConfig3 = pinConfigBuilder3.build(); AdvancedMarkerOptions advancedMarkerOptions3 = new AdvancedMarkerOptions() .icon(BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromPinConfig(pinConfig3)) .position(BANGKOK); Marker marker3 = map.addMarker(advancedMarkerOptions3); // Create a transparent glyph. PinConfig.Builder pinConfigBuilder4 = PinConfig.builder(); pinConfigBuilder4.setBackgroundColor(Color.MAGENTA); pinConfigBuilder4.setGlyph(new PinConfig.Glyph(Color.TRANSPARENT)); PinConfig pinConfig4 = pinConfigBuilder4.build(); AdvancedMarkerOptions advancedMarkerOptions4 = new AdvancedMarkerOptions() .icon(BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromPinConfig(pinConfig4)) .position(MANILA); Marker marker4 = map.addMarker(advancedMarkerOptions4); // Collision behavior can only be changed in the AdvancedMarkerOptions object. // Changes to collision behavior after a marker has been created are not possible int collisionBehavior = AdvancedMarkerOptions.CollisionBehavior.REQUIRED_AND_HIDES_OPTIONAL; AdvancedMarkerOptions advancedMarkerOptions5 = new AdvancedMarkerOptions() .position(HO_CHI_MINH_CITY) .collisionBehavior(collisionBehavior); Marker marker5 = map.addMarker(advancedMarkerOptions5); } }
Clona ed esegui i sample
Per eseguire questo esempio localmente è necessario Git. Il comando seguente clona il repository dell'applicazione di esempio.
git clone git@github.com:googlemaps-samples/android-samples.git
Importa il progetto di esempio in Android Studio:
- In Android Studio, seleziona File > Nuovo > Importa progetto.
Vai alla posizione in cui hai salvato il repository e seleziona la directory del progetto per Kotlin o Java:
- Kotlin:
PATH-REPO/android-samples/ApiDemos/kotlin - Java:
PATH-REPO/android-samples/ApiDemos/java
- Kotlin:
- Seleziona Apri. Android Studio compila il progetto utilizzando lo strumento di compilazione Gradle.
- Crea un file
secrets.propertiesvuoto nella stessa directory del filelocal.propertiesdel progetto. Per ulteriori informazioni su questo file, consulta Aggiungere la chiave API al progetto. - Genera una chiave API dal tuo progetto con l'SDK Maps per Android abilitato.
Aggiungi la seguente stringa a
secrets.properties, sostituendo YOUR_API_KEY con il valore della tua chiave API:MAPS_API_KEY=YOUR_API_KEY- Esegui l'app.
