Der OAuth-Verknüpfungstyp unterstützt zwei branchenübliche OAuth 2.0-Vorgänge: den impliziten und den Autorisierungscode-Vorgang.
In the implicit code flow, Google opens your authorization endpoint in the user's browser. After successful sign in, you return a long-lived access token to Google. This access token is now included in every request sent from the Assistant to your Action.
In the authorization code flow, you need two endpoints:
- The authorization endpoint, which is responsible for presenting the sign-in UI to your users that aren't already signed in and recording consent to the requested access in the form of a short-lived authorization code.
- The token exchange endpoint, which is responsible for two types of exchanges:
- Exchanges an authorization code for a long-lived refresh token and a short-lived access token. This exchange happens when the user goes through the account linking flow.
- Exchanges a long-lived refresh token for a short-lived access token. This exchange happens when Google needs a new access token because the one it had expired.
Although the implicit code flow is simpler to implement, Google recommends that access tokens issued using the implicit flow never expire, because using token expiration with the implicit flow forces the user to link their account again. If you need token expiration for security reasons, you should strongly consider using the auth code flow instead.
OAuth-Kontoverknüpfung implementieren
Projekt konfigurieren
So konfigurieren Sie Ihr Projekt für die Verwendung der OAuth-Verknüpfung:
- Öffnen Sie die Actions Console und wählen Sie das gewünschte Projekt aus.
- Klicken Sie auf den Tab Entwickeln und wählen Sie Kontoverknüpfung aus.
- Aktiviere den Schalter neben Kontoverknüpfung.
- Wählen Sie im Bereich Kontoerstellung die Option Nein, ich möchte die Kontoerstellung nur auf meiner Website zulassen aus.
Wählen Sie unter Linking type (Verknüpfungstyp) die Optionen OAuth und Authorization code (Autorisierungscode) aus.
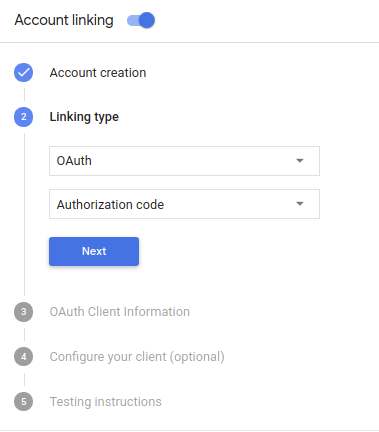
Unter Client Information (Client-Informationen):
- Weisen Sie Client-ID, die von Ihren Actions an Google ausgegeben wird einen Wert zu, um Anfragen von Google zu identifizieren.
- Notieren Sie sich den Wert von Client-ID, die von Google für Ihre Aktionen ausgestellt wurde:
- Fügen Sie die URLs für Ihre Autorisierungs- und Token-Austausch-Endpunkte ein.
- Klicken Sie auf Speichern.
OAuth-Server implementieren
An OAuth 2.0 server implementation of the authorization code flow consists of two endpoints, which your service makes available by HTTPS. The first endpoint is the authorization endpoint, which is responsible for finding or obtaining consent from users for data access. The authorization endpoint presents a sign-in UI to your users that aren't already signed in and records consent to the requested access. The second endpoint is the token exchange endpoint, which is used to obtain encrypted strings called tokens that authorize the Action user to access your service.
When your Action needs to call one of your service's APIs, Google uses these endpoints together to get permission from your users to call these APIs on their behalf.
OAuth 2.0 auth code flow session initiated by Google has the following flow:
- Google opens your authorization endpoint in the user's browser. If the flow started on a voice-only device for an Action, Google would transfer the execution to a phone.
The user signs in (if not signed in already) and grants Google permission to access their data with your API if they haven't already granted permission.
Your service creates an authorization code and returns it to Google by redirecting the user's browser back to Google with the authorization code attached to the request.
Google sends the authorization code to your token exchange endpoint, which verifies the authenticity of the code and returns an access token and a refresh token. The access token is a short-lived token that your service accepts as credentials to access APIs. The refresh token is a long-lived token that Google can store and use to acquire new access tokens when they expire.
After the user has completed the account linking flow, every subsequent request sent from the Assistant to your fulfillment webhook contains an access token.
Handle authorization requests
When your Action needs to perform account linking via an OAuth 2.0 authorization code flow, Google sends the user to your authorization endpoint with a request that includes the following parameters:
| Authorization endpoint parameters | |
|---|---|
client_id |
The Google client ID you registered with Google. |
redirect_uri |
The URL to which you send the response to this request. |
state |
A bookkeeping value that is passed back to Google unchanged in the redirect URI. |
scope |
Optional: A space-delimited set of scope strings that specify the data Google is requesting authorization for. |
response_type |
The string code. |
For example, if your authorization endpoint is available at https://myservice.example.com/auth,
a request might look like:
GET https://myservice.example.com/auth?client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&redirect_uri=REDIRECT_URI&state=STATE_STRING&scope=REQUESTED_SCOPES&response_type=code
For your authorization endpoint to handle sign-in requests, do the following steps:
Verify that the
client_idmatches the Google client ID you registered with Google, and that theredirect_urimatches the redirect URL provided by Google for your service. These checks are important to prevent granting access to unintended or misconfigured client apps.If you support multiple OAuth 2.0 flows, also confirm that the
response_typeiscode.Check if the user is signed in to your service. If the user isn't signed in, complete your service's sign-in or sign-up flow.
Generate an authorization code that Google will use to access your API. The authorization code can be any string value, but it must uniquely represent the user, the client the token is for, and the code's expiration time, and it must not be guessable. You typically issue authorization codes that expire after approximately 10 minutes.
Confirm that the URL specified by the
redirect_uriparameter has the following form:https://oauth-redirect.googleusercontent.com/r/YOUR_PROJECT_ID
Redirect the user's browser to the URL specified by the
redirect_uriparameter. Include the authorization code you just generated and the original, unmodified state value when you redirect by appending thecodeandstateparameters. The following is an example of the resulting URL:https://oauth-redirect.googleusercontent.com/r/YOUR_PROJECT_ID?code=AUTHORIZATION_CODE&state=STATE_STRING
Handle token exchange requests
Your service's token exchange endpoint is responsible for two kinds of token exchanges:
- Exchange authorization codes for access tokens and refresh tokens
- Exchange refresh tokens for access tokens
Token exchange requests include the following parameters:
| Token exchange endpoint parameters | |
|---|---|
client_id |
A string that identifies the request origin as Google. This string must be registered within your system as Google's unique identifier. |
client_secret |
A secret string that you registered with Google for your service. |
grant_type |
The type of token being exchanged. Either
authorization_code or refresh_token. |
code |
When grant_type=authorization_code, the code Google
received from either your sign-in or token exchange endpoint. |
redirect_uri |
When grant_type=authorization_code, this parameter is the
URL used in the initial authorization request. |
refresh_token |
When grant_type=refresh_token, the refresh token Google
received from your token exchange endpoint. |
Exchange authorization codes for access tokens and refresh tokens
After the user signs in and your authorization endpoint returns a short-lived authorization code to Google, Google sends a request to your token exchange endpoint to exchange the authorization code for an access token and a refresh token.
For these requests, the value of grant_type is authorization_code, and the value
of code is the value of the authorization code you previously granted to Google.
The following is an example of a request to exchange an authorization code for an
access token and a refresh token:
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET&grant_type=authorization_code&code=AUTHORIZATION_CODE&redirect_uri=REDIRECT_URI
To exchange authorization codes for an access token and a refresh token, your
token exchange endpoint responds to POST requests executing the following steps:
- Verify that the
client_ididentifies the request origin as an authorized origin, and that theclient_secretmatches the expected value. - Verify the following:
- The authorization code is valid and not expired, and the client ID specified in the request matches the client ID associated with the authorization code.
- The URL specified by the
redirect_uriparameter is identical to the value used in the initial authorization request.
- If you cannot verify all of the above criteria, return an HTTP
400 Bad Request error with
{"error": "invalid_grant"}as the body. - Otherwise, using the user ID from the authorization code, generate a refresh token and an access token. These tokens can be any string value, but they must uniquely represent the user and the client the token is for, and they must not be guessable. For access tokens, also record the expiration time of the token (typically an hour after you issue the token). Refresh tokens do not expire.
- Return the following JSON object in the body of the HTTPS response:
{ "token_type": "Bearer", "access_token": "ACCESS_TOKEN", "refresh_token": "REFRESH_TOKEN", "expires_in": SECONDS_TO_EXPIRATION }
Google stores the access token and the refresh token for the user and records the expiration of the access token. When the access token expires, Google uses the refresh token to get a new access token from your token exchange endpoint.
Exchange refresh tokens for access tokens
When an access token expires, Google sends a request to your token exchange endpoint to exchange a refresh token for a new access token.
For these requests, the value of grant_type is refresh_token, and the value
of refresh_token is the value of the refresh token you previously granted to Google.
The following is an example of a request to exchange a refresh token for an
access token:
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET&grant_type=refresh_token&refresh_token=REFRESH_TOKEN
To exchange a refresh token for an access token, your token exchange endpoint
responds to POST requests executing the following steps:
- Verify that the
client_ididentifies the request origin as Google, and that theclient_secretmatches the expected value. - Verify that the refresh token is valid, and that the client ID specified in the request matches the client ID associated with the refresh token.
- If you cannot verify all of the above criteria, return an HTTP
400 Bad Request error with
{"error": "invalid_grant"}as the body. - Otherwise, use the user ID from the refresh token to generate an access token. These tokens can be any string value, but they must uniquely represent the user and the client the token is for, and they must not be guessable. For access tokens, also record the expiration time of the token (typically an hour after you issue the token).
- Return the following JSON object in the body of the HTTPS
response:
{ "token_type": "Bearer", "access_token": "ACCESS_TOKEN", "expires_in": SECONDS_TO_EXPIRATION }
Sprachbenutzeroberfläche für den Authentifizierungsvorgang entwerfen
Prüfen, ob der Nutzer bestätigt ist, und den Kontoverknüpfungsvorgang starten
- Öffnen Sie Ihr Actions Builder-Projekt in der Actions Console.
- Erstellen Sie eine neue Szene, um die Kontoverknüpfung in Ihrer Aktion zu starten:
- Klicken Sie auf Szenen.
- Klicken Sie auf das Hinzufügen-Symbol (+), um eine neue Szene hinzuzufügen.
- Klicken Sie in der neu erstellten Szene auf das Symbol zum Hinzufügen add für Bedingungen.
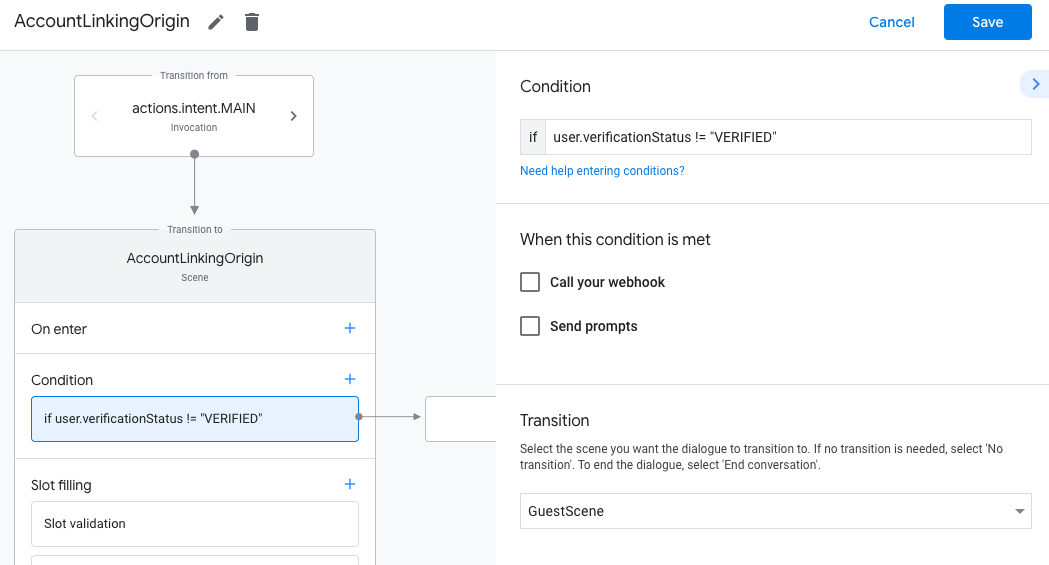
- Fügen Sie eine Bedingung hinzu, die prüft, ob der mit der Unterhaltung verknüpfte Nutzer ein bestätigter Nutzer ist. Wenn die Prüfung fehlschlägt, kann für Ihre Aktion während der Unterhaltung keine Kontoverknüpfung durchgeführt werden. In diesem Fall sollte auf Funktionen zurückgegriffen werden, für die keine Kontoverknüpfung erforderlich ist.
- Geben Sie im Feld
Enter new expressionunter Bedingung die folgende Logik ein:user.verificationStatus != "VERIFIED" - Wählen Sie unter Übergang eine Szene aus, für die keine Kontoverknüpfung erforderlich ist, oder eine Szene, die den Einstiegspunkt für Funktionen ist, die nur für Gäste verfügbar sind.
- Geben Sie im Feld
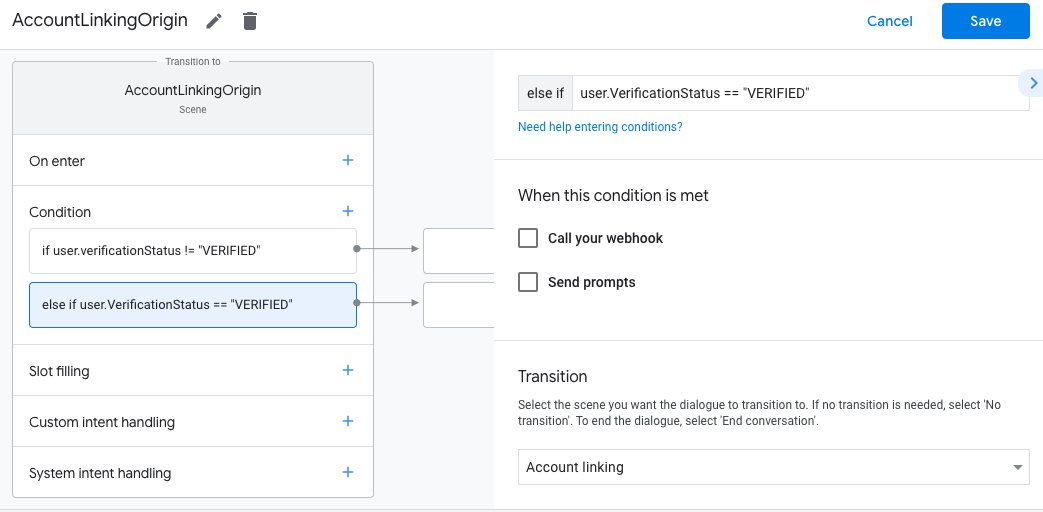
- Klicken Sie für Bedingungen auf das Symbol zum Hinzufügen add.
- Fügen Sie eine Bedingung hinzu, um einen Vorgang für die Kontoverknüpfung auszulösen, wenn der Nutzer keine zugehörige Identität hat.
- Geben Sie im Feld
Enter new expressionunter Bedingung die folgende Logik ein::user.verificationStatus == "VERIFIED" - Wählen Sie unter Übergang die Systemszene Kontoverknüpfung aus.
- Klicken Sie auf Speichern.
- Geben Sie im Feld
Nach dem Speichern wird Ihrem Projekt eine neue Szene für die Kontoverknüpfung mit dem Namen <SceneName>_AccountLinking hinzugefügt.
Szene für die Kontoverknüpfung anpassen
- Wählen Sie unter Szenen die Systemszene für die Kontoverknüpfung aus.
- Klicken Sie auf Prompt senden und fügen Sie einen kurzen Satz hinzu, um dem Nutzer zu erklären, warum die Action auf seine Identität zugreifen muss (z. B. „Zum Speichern Ihrer Einstellungen“).
- Klicken Sie auf Speichern.
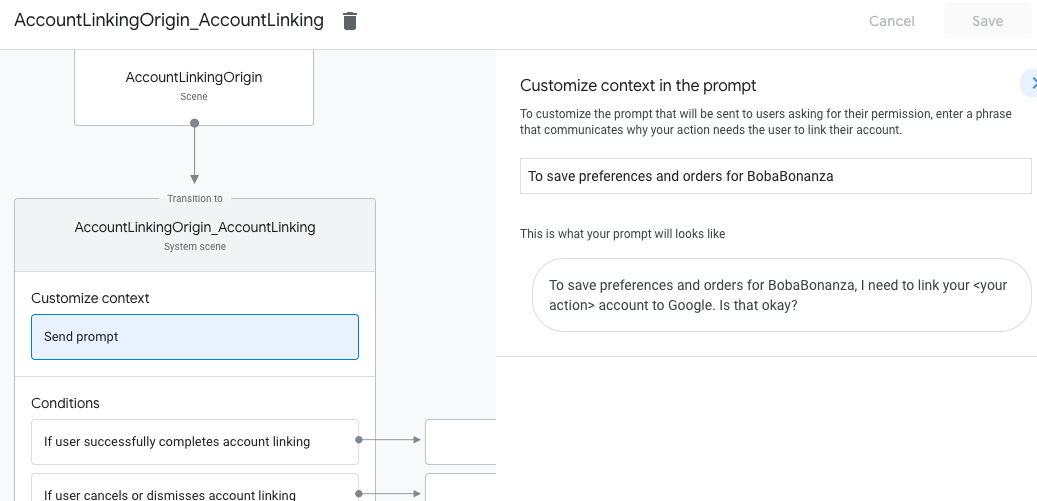
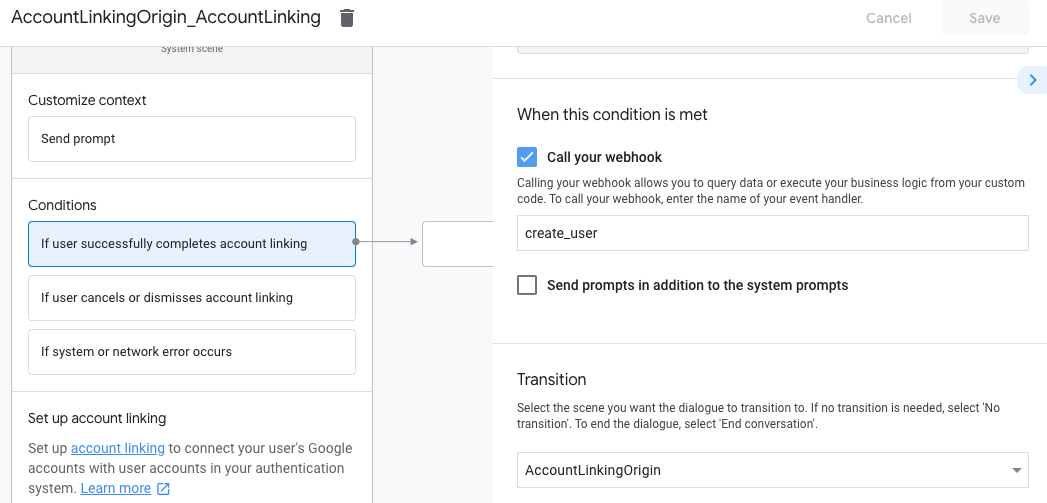
- Klicken Sie unter Bedingungen auf Wenn der Nutzer die Kontoverknüpfung erfolgreich abschließt.
- Konfigurieren Sie, wie der Ablauf fortgesetzt werden soll, wenn der Nutzer der Verknüpfung seines Kontos zustimmt. Rufen Sie den Webhook beispielsweise auf, um die erforderliche benutzerdefinierte Geschäftslogik zu verarbeiten und zur ursprünglichen Szene zurückzukehren.
- Klicken Sie auf Speichern.
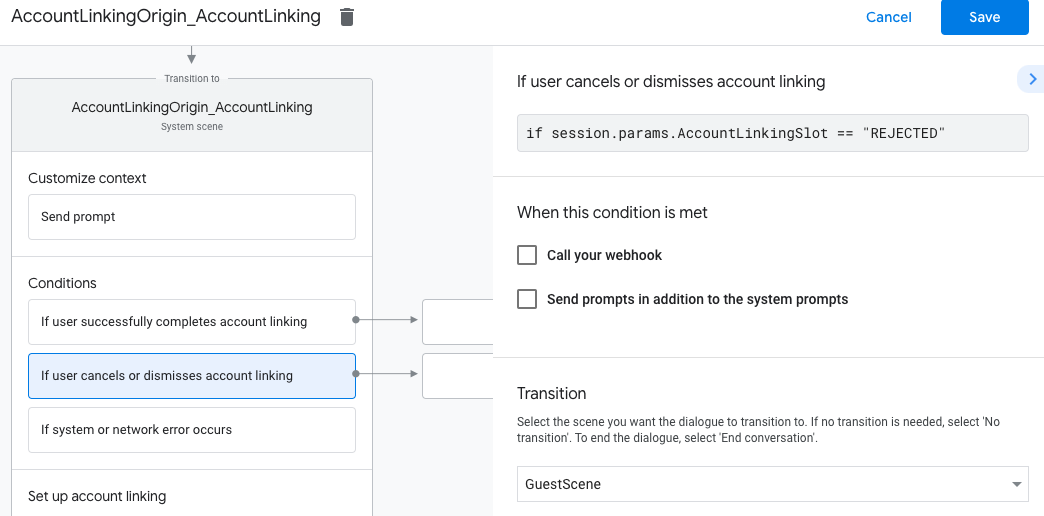
- Klicken Sie unter Bedingungen auf Wenn der Nutzer die Kontoverknüpfung abbricht oder schließt.
- Konfigurieren Sie, wie der Vorgang fortgesetzt werden soll, wenn der Nutzer der Verknüpfung seines Kontos nicht zustimmt. Senden Sie beispielsweise eine Bestätigungsnachricht und leiten Sie Nutzer zu Szenen weiter, die Funktionen bieten, für die keine Kontoverknüpfung erforderlich ist.
- Klicken Sie auf Speichern.
- Klicken Sie unter Bedingungen auf Bei System- oder Netzwerkfehler.
- Konfigurieren Sie, wie der Ablauf fortgesetzt werden soll, wenn der Ablauf für die Kontoverknüpfung aufgrund von System- oder Netzwerkfehlern nicht abgeschlossen werden kann. Senden Sie beispielsweise eine Bestätigungsnachricht und leiten Sie Nutzer zu Szenen weiter, die Funktionen bieten, für die keine Kontoverknüpfung erforderlich ist.
- Klicken Sie auf Speichern.
Datenzugriffsanfragen bearbeiten
Wenn die Assistant-Anfrage ein Zugriffstoken enthält, prüfen Sie zuerst, ob das Zugriffstoken gültig (und nicht abgelaufen) ist, und rufen Sie dann das zugehörige Nutzerkonto aus Ihrer Datenbank ab.