Adaptive banners let you specify the width of an ad to determine the optimal ad size. Adaptive banners also maximize performance by optimizing the ad size for each device. This approach results in opportunities for improved performance.
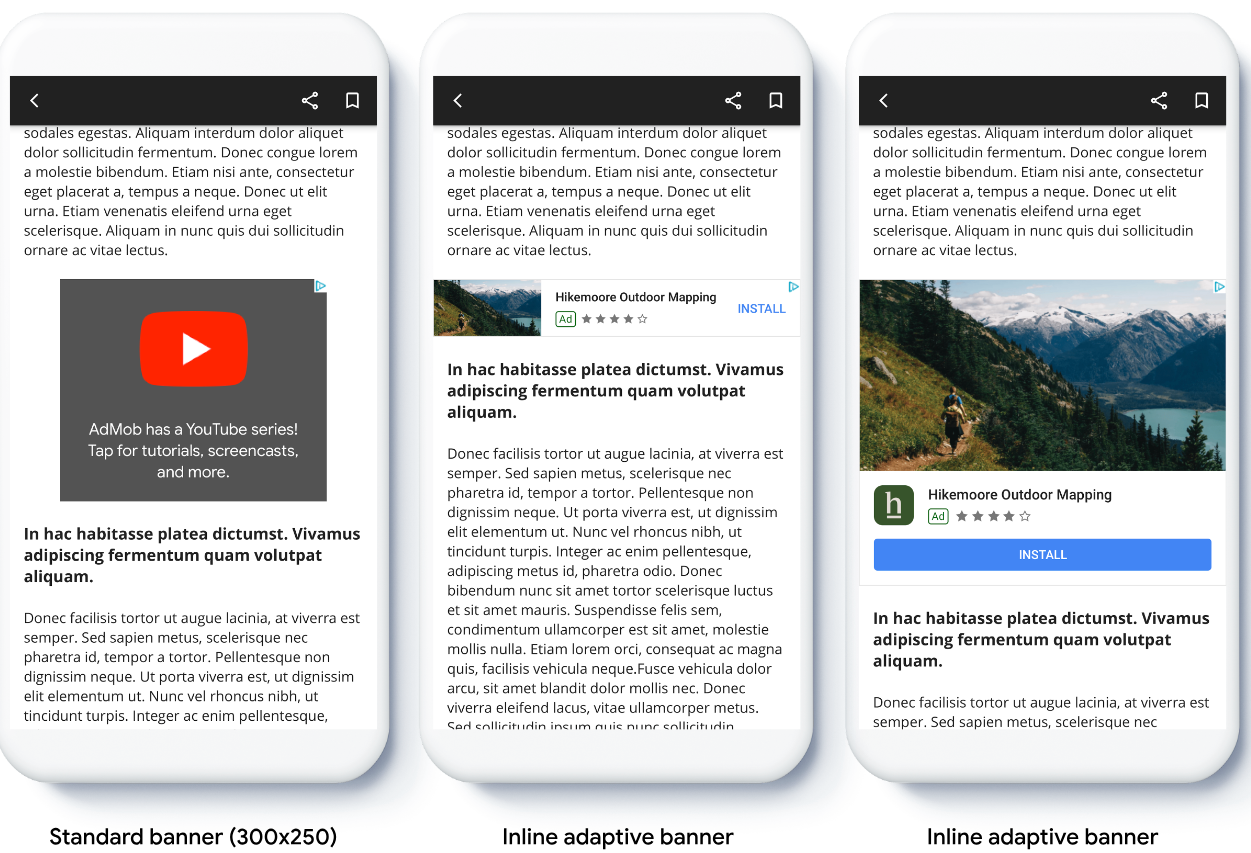
Compared to anchored adaptive banners, inline adaptive banners are larger, taller, and use variable instead of fixed heights. Inline adaptive banners are of variable height, and might encompass the entire screen or a maximum height that you specify.
You place inline adaptive banners in scrolling content, for example:
Before you begin
Before continuing, make sure you have completed the getting started guide, Banner ads.
Implement inline adaptive banners
The following example demonstrates these steps:
Kotlin
private fun loadAd() {
// Create an inline adaptive ad size. 320 is a placeholder value.
// Replace 320 with your banner container width.
val adSize = AdSize.getCurrentOrientationInlineAdaptiveBannerAdSize(this, 320)
// Step 1 - Create a BannerAdRequest object with ad unit ID and size.
val adRequest = BannerAdRequest.Builder("AD_UNIT_ID", adSize).build()
// Step 2 - Load the ad.
BannerAd.load(
adRequest,
object : AdLoadCallback<BannerAd> {
override fun onAdLoaded(ad: BannerAd) {
// Assign the loaded ad to the BannerAd object.
bannerAd = ad
// Step 3 - Call BannerAd.getView() to get the View and add it
// to view hierarchy on the UI thread.
activity?.runOnUiThread {
binding.bannerViewContainer.addView(ad.getView(requireActivity()))
}
}
override fun onAdFailedToLoad(loadAdError: LoadAdError) {
bannerAd = null
}
}
)
}
Java
private void loadAd() {
// Create an inline adaptive ad size. 320 is a placeholder value.
// Replace 320 with your banner container width.
AdSize adSize = AdSize.getCurrentOrientationInlineAdaptiveBannerAdSize(this, 320);
// Step 1 - Create a BannerAdRequest object with ad unit ID and size.
BannerAdRequest adRequest = new BannerAdRequest.Builder("AD_UNIT_ID",
adSize).build();
// Step 2 - Load the ad.
BannerAd.load(
adRequest,
new AdLoadCallback<BannerAd>() {
@Override
public void onAdLoaded(@NonNull BannerAd ad) {
// Assign the loaded ad to the BannerAd object.
bannerAd = ad;
// Step 3 - Call BannerAd.getView() to get the View and add it
// to view hierarchy on the UI thread.
if (getActivity() != null) {
getActivity()
.runOnUiThread(() ->
binding.bannerViewContainer.addView(ad.getView(getActivity())));
}
}
@Override
public void onAdFailedToLoad(@NonNull LoadAdError adError) {
bannerAd = null;
}
});
}
When implementing adaptive banners in your app, note these points:
- The inline adaptive banner sizes work best when using the full available width. In most cases, this size is the full width of the device screen in use, or the full width of the banner's parent content. You must know the width of the view to place in the ad, the device width, the parent content width, and applicable safe areas.
- You may need to update or create new line items to work with adaptive sizes. Learn more.
Orient inline adaptive banner size
To preload an inline adaptive banner ad for a specific orientation, use the following methods:
AdSize.getPortraitInlineAdaptiveBannerAdSize(Context context, int width)AdSize.getLandscapeInlineAdaptiveBannerAdSize(Context context, int width)
If your app supports both portrait and landscape views, and you want to preload
an adaptive banner ad in the current orientation, use
AdSize.getCurrentOrientationInlineAdaptiveBannerAdSize(Context context, int width)
This method loads an ad in the current orientation.
Limit inline adaptive banner height
By default, inline adaptive banners instantiated without a maxHeight value
have a maxHeight equal to the device height. To limit the inline adaptive
banner height, use the
AdSize.getInlineAdaptiveBannerAdSize(int width, int maxHeight)
method.

