取得資料
您可以透過多種方式取得蒐集到的位置資料,以下說明兩種取得資料的技術,可用於 Roads API 的「貼齊道路」功能。
GPX
GPX 是開放的 XML 格式,可分享 GPS 裝置擷取的路線、軌跡和航點。這個範例使用 XmlPull 剖析器,這是一種輕量型 XML 剖析器,適用於 Java 伺服器和行動環境。
/** * Parses the waypoint (wpt tags) data into native objects from a GPX stream. */ private List<LatLng> loadGpxData(XmlPullParser parser, InputStream gpxIn) throws XmlPullParserException, IOException { // We use a List<> as we need subList for paging later List<LatLng> latLngs = new ArrayList<>(); parser.setInput(gpxIn, null); parser.nextTag(); while (parser.next() != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) { if (parser.getEventType() != XmlPullParser.START_TAG) { continue; } if (parser.getName().equals("wpt")) { // Save the discovered latitude/longitude attributes in each <wpt>. latLngs.add(new LatLng( Double.valueOf(parser.getAttributeValue(null, "lat")), Double.valueOf(parser.getAttributeValue(null, "lon")))); } // Otherwise, skip irrelevant data } return latLngs; }
以下是載入地圖的原始 GPX 資料。
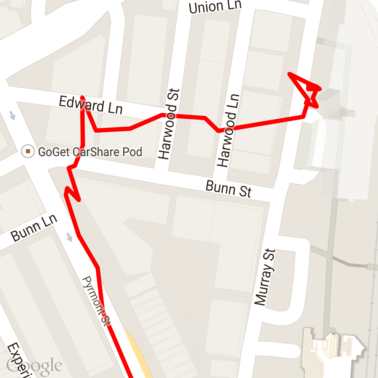
Android 定位服務
從 Android 裝置擷取 GPS 資料的最佳方式會因用途而異。請參閱「接收位置資訊更新」Android 訓練課程,以及 GitHub 上的 Google Play 位置資訊範例。
處理長路徑
由於「貼齊道路」功能會根據完整路徑推斷位置,而非個別點,因此處理長路徑 (即超出每個要求 100 個點的限制) 時,請務必小心。
如要將個別要求視為一條長路徑,您應加入部分重疊,讓前一個要求的終點成為後續要求的起點。要納入多少個點取決於資料的準確度。如果要求準確度較低,請加入更多點。
這個範例使用 Google 地圖服務適用的 Java 用戶端傳送分頁要求,然後將資料 (包括內插點) 重新加入傳回的清單。
/** * Snaps the points to their most likely position on roads using the Roads API. */ private List<SnappedPoint> snapToRoads(GeoApiContext context) throws Exception { List<SnappedPoint> snappedPoints = new ArrayList<>(); int offset = 0; while (offset < mCapturedLocations.size()) { // Calculate which points to include in this request. We can't exceed the API's // maximum and we want to ensure some overlap so the API can infer a good location for // the first few points in each request. if (offset > 0) { offset -= PAGINATION_OVERLAP; // Rewind to include some previous points. } int lowerBound = offset; int upperBound = Math.min(offset + PAGE_SIZE_LIMIT, mCapturedLocations.size()); // Get the data we need for this page. LatLng[] page = mCapturedLocations .subList(lowerBound, upperBound) .toArray(new LatLng[upperBound - lowerBound]); // Perform the request. Because we have interpolate=true, we will get extra data points // between our originally requested path. To ensure we can concatenate these points, we // only start adding once we've hit the first new point (that is, skip the overlap). SnappedPoint[] points = RoadsApi.snapToRoads(context, true, page).await(); boolean passedOverlap = false; for (SnappedPoint point : points) { if (offset == 0 || point.originalIndex >= PAGINATION_OVERLAP - 1) { passedOverlap = true; } if (passedOverlap) { snappedPoints.add(point); } } offset = upperBound; } return snappedPoints; }
以下是執行「將點對應至道路」要求後,上述資料的結果。紅線是原始資料,藍線則是經過對齊的資料。
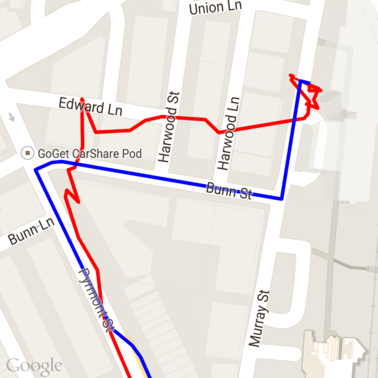
有效運用配額
道路對齊要求的回應會包含地點 ID 清單,這些 ID 會對應到您提供的點,如果您設定 interpolate=true,可能還會包含其他點。
為有效運用速限要求允許的配額,您應只在要求中查詢不重複的地點 ID。這個範例使用 Google 地圖服務的 Java 用戶端,從地點 ID 清單查詢速限。
/** * Retrieves speed limits for the previously-snapped points. This method is efficient in terms * of quota usage as it will only query for unique places. * * Note: Speed limit data is only available for requests using an API key enabled for a * Google Maps APIs Premium Plan license. */ private Map<String, SpeedLimit> getSpeedLimits(GeoApiContext context, List<SnappedPoint> points) throws Exception { Map<String, SpeedLimit> placeSpeeds = new HashMap<>(); // Pro tip: Save on quota by filtering to unique place IDs. for (SnappedPoint point : points) { placeSpeeds.put(point.placeId, null); } String[] uniquePlaceIds = placeSpeeds.keySet().toArray(new String[placeSpeeds.keySet().size()]); // Loop through the places, one page (API request) at a time. for (int i = 0; i < uniquePlaceIds.length; i += PAGE_SIZE_LIMIT) { String[] page = Arrays.copyOfRange(uniquePlaceIds, i, Math.min(i + PAGE_SIZE_LIMIT, uniquePlaceIds.length)); // Execute! SpeedLimit[] placeLimits = RoadsApi.speedLimits(context, page).await(); for (SpeedLimit sl : placeLimits) { placeSpeeds.put(sl.placeId, sl); } } return placeSpeeds; }
以下是上述資料,並在每個不重複的地點 ID 標示速限。
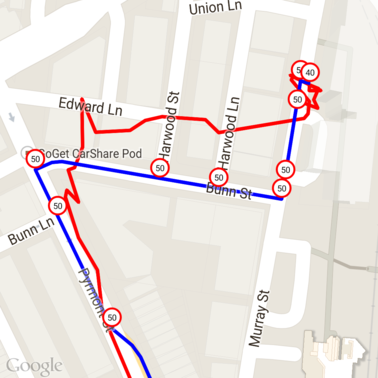
與其他 API 的互動
在道路貼合回應中傳回地點 ID 的優點之一,是您可以在許多 Google 地圖平台 API 中使用地點 ID。這個範例使用 Google 地圖服務適用的 Java 用戶端,將上述「將點對應至道路」要求傳回的地點進行地理編碼。
/** * Geocodes a snapped point using the place ID. */ private GeocodingResult geocodeSnappedPoint(GeoApiContext context, SnappedPoint point) throws Exception { GeocodingResult[] results = GeocodingApi.newRequest(context) .place(point.placeId) .await(); if (results.length > 0) { return results[0]; } return null; }
這裡的速限標記已使用 Geocoding API 的地址進行註解。
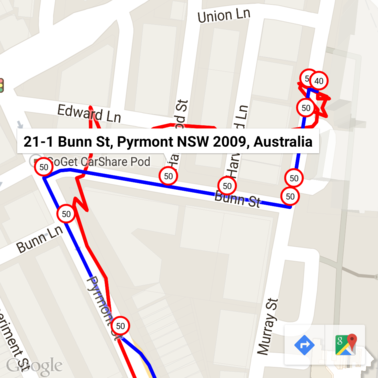
程式碼範例
注意事項
為說明用途,支援這份文件的程式碼會以單一 Android 應用程式的形式提供。實務上,您不應在 Android 應用程式中發布伺服器端 API 金鑰,因為您的金鑰無法防範第三方未經授權的存取行為。為確保金鑰安全,請改為將面向 API 的程式碼部署為伺服器端 Proxy,並讓 Android 應用程式使用 Proxy 傳送要求,確保要求已獲得授權。
下載
從 GitHub 下載程式碼。

