La función PLACES_COUNT devuelve un solo valor de recuento de lugares según el área de búsqueda y los filtros de búsqueda especificados. Debes especificar el área de búsqueda en la función PLACES_COUNT y, de manera opcional, puedes especificar parámetros de filtro adicionales, como el tipo de lugar, el estado operativo, el nivel de precios y mucho más.
Dado que la función PLACES_COUNT devuelve un solo valor, llámala con una cláusula SELECT.
Parámetros de entrada:
Obligatorio: El parámetro de filtro
geographyque especifica el área de búsqueda. El parámetrogeographytoma un valor definido por el tipo de datosGEOGRAPHYde BigQuery, que admite puntos, cadenas de líneas y polígonos.Opcional: Son parámetros de filtro adicionales para definir mejor tu búsqueda.
Se muestra lo siguiente:
- Un solo valor de
countcomoINT64.
- Un solo valor de
Ejemplo: Calcula la cantidad de lugares en un radio de búsqueda
La llamada a la función PLACES_COUNT más simple devuelve un solo recuento de todos los lugares en un área geográfica. En este ejemplo, se muestra el recuento de todos los lugares operativos en un radio de 1,000 metros del Empire State Building.
En este ejemplo, se usa la función ST_GEOGPOINT de BigQuery para devolver un valor de GEOGRAPHY a partir de un punto.
SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000 -- Radius in meters ) ) as count;
La respuesta contiene un solo recuento:
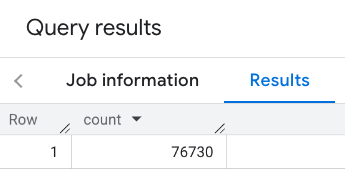
Una llamada más típica aplica filtros al área de búsqueda. En el siguiente ejemplo, se usan filtros para limitar la búsqueda y mostrar solo un recuento de lo siguiente:
- Lugares del tipo
restaurantcon una calificación mínima de 3 - Un nivel de precios económico o medio
- Actualmente operativo
- Se permiten perros
SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'types', ["restaurant"], 'min_rating', 3, 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE', 'PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE'], 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'allows_dogs', TRUE ) ) as count;
La respuesta filtrada:
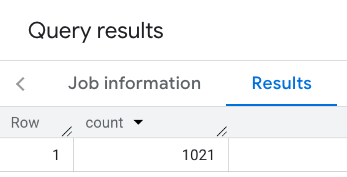
Recuerda que las consultas de conjuntos de datos de lugares aplican un umbral de recuento mínimo de 5. Una de las ventajas de las funciones de recuento de lugares es que pueden devolver cualquier recuento, incluido el 0. Por ejemplo, la siguiente llamada devuelve un recuento de 1:
SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 500, -- Radius in meters 'types', ["restaurant"], 'min_rating', 4.0, 'free_parking_lot', TRUE, 'good_for_watching_sports', TRUE ) ) as count;
Ejemplo: Calcula la cantidad de restaurantes con un polígono
Puedes usar un polígono para especificar el área de búsqueda. Cuando se usa un polígono, sus puntos deben definir un bucle cerrado en el que el primer punto del polígono sea el mismo que el último.
En este ejemplo, se usa la función ST_GEOGFROMTEXT de BigQuery para devolver un valor GEOGRAPHY de un polígono.
DECLARE geo GEOGRAPHY; SET geo = ST_GEOGFROMTEXT('''POLYGON((-73.985708 40.75773,-73.993324 40.750298, -73.9857 40.7484,-73.9785 40.7575, -73.985708 40.75773))'''); -- NYC viewport SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography',geo, -- viewport 'types', ["restaurant"], 'min_rating', 1.0, 'max_rating', 4.5, 'min_user_rating_count', 1, 'max_user_rating_count', 10000, 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE', 'PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE'], 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'allows_dogs', TRUE ) ) as count;
Respuesta del viewport:
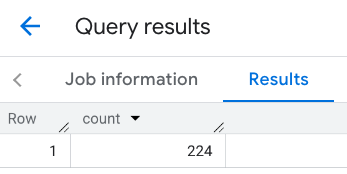
Ejemplo: Calcula la cantidad de restaurantes con una línea
En el siguiente ejemplo, definirás el área de búsqueda con una línea de puntos conectados con un radio de búsqueda de 100 metros alrededor de la línea. La línea es similar a una ruta de viaje calculada por la API de Routes. La ruta puede ser para un vehículo, una bicicleta o un peatón:
DECLARE geo GEOGRAPHY; SET geo = ST_GEOGFROMTEXT('LINESTRING(-73.98903537033028 40.73655649223003,-73.93580216278471 40.80955538843361)'); -- NYC line SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography',geo, -- line 'geography_radius', 100, -- Radius around line 'types', ["restaurant"], 'min_rating', 1.0, 'max_rating', 4.5, 'min_user_rating_count', 1, 'max_user_rating_count', 10000, 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE', 'PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE'], 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'allows_dogs', TRUE ) ) as count;
La respuesta de la línea:
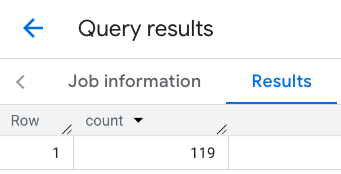
Ejemplo: Combina los resultados de varias llamadas
Puedes combinar los resultados de varias llamadas a la función PLACES_COUNT.
Por ejemplo, deseas un solo resultado que muestre la cantidad de restaurantes para los siguientes niveles de precios dentro de un área específica:
PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVEPRICE_LEVEL_MODERATEPRICE_LEVEL_EXPENSIVEPRICE_LEVEL_VERY_EXPENSIVE"
En este ejemplo, crearás un bucle para llamar a la función PLACES_COUNT para cada nivel de precios y, luego, insertarás los resultados de cada llamada en una tabla temporal. Luego, consultas la tabla temporal para mostrar los resultados:
-- Create a temp table to hold the results. CREATE TEMP TABLE results (type STRING, count INT64); -- Create a loop that calls PLACES_COUNT for each price level. FOR types IN (SELECT type FROM UNNEST(["PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE", "PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE", "PRICE_LEVEL_EXPENSIVE", "PRICE_LEVEL_VERY_EXPENSIVE"]) as type) DO INSERT INTO results VALUES (types.type, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', [types.type] ))); END FOR; -- Query the table of results. SELECT * FROM results;
La respuesta combinada:
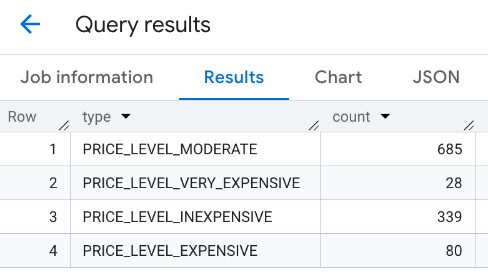
Otra opción es usar el comando UNION ALL para combinar los resultados de varias instrucciones SELECT. En el siguiente ejemplo, se muestran los mismos resultados que en el ejemplo anterior:
SELECT "PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE" as price_level, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE'] ) ) as count UNION ALL SELECT "PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE" as price_level, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE'] ) ) as count UNION ALL SELECT "PRICE_LEVEL_EXPENSIVE" as price_level, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_EXPENSIVE'] ) ) as count UNION ALL SELECT "PRICE_LEVEL_VERY_EXPENSIVE" as price_level, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_VERY_EXPENSIVE'] ) ) as count
