הפונקציה PLACES_COUNT מחזירה ערך יחיד של מספר המקומות על סמך אזור החיפוש ומסנני החיפוש שצוינו. צריך לציין את אזור החיפוש בפונקציה PLACES_COUNT, ואפשר גם לציין פרמטרים נוספים לסינון, כמו סוג המקום, סטטוס הפעילות, רמת המחיר ועוד.
מכיוון שהפונקציה PLACES_COUNT מחזירה ערך יחיד, צריך להפעיל אותה באמצעות פסוקית SELECT.
פרמטרים של קלט:
חובה:
geographyפרמטר הסינון שמציין את אזור החיפוש. הפרמטרgeographyמקבל ערך שמוגדר על ידי סוג הנתוניםGEOGRAPHYב-BigQuery, שתומך בנקודות, בקווי שבר ובמצולעים.אופציונלי: פרמטרים נוספים של מסנן לחידוד החיפוש.
החזרות:
- ערך יחיד של
countבתורINT64.
- ערך יחיד של
דוגמה: חישוב מספר המקומות ברדיוס חיפוש
הקריאה הפשוטה ביותר לפונקציה PLACES_COUNT מחזירה ספירה אחת של כל המקומות באזור גיאוגרפי. בדוגמה הזו, הפונקציה מחזירה את מספר המקומות הפעילים ברדיוס של 1,000 מטר מבניין אמפייר סטייט.
בדוגמה הזו נעשה שימוש בפונקציה ST_GEOGPOINT של BigQuery כדי להחזיר ערך GEOGRAPHY מנקודה.
SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000 -- Radius in meters ) ) as count;
התשובה מכילה ספירה אחת:
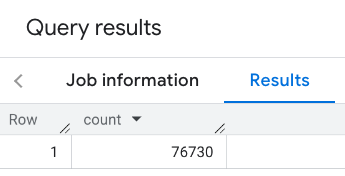
בשיחה טיפוסית יותר, המערכת מחילה מסננים על אזור החיפוש. בדוגמה הבאה נעשה שימוש במסננים כדי להגביל את החיפוש כך שיוחזר רק מספר של:
- מקומות מסוג
restaurantעם דירוג מינימלי של 3 - רמת מחיר זולה או בינונית
- בפעולה כרגע
- מותר להכניס כלבים למקום
SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'types', ["restaurant"], 'min_rating', 3, 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE', 'PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE'], 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'allows_dogs', TRUE ) ) as count;
התשובה המסוננת:
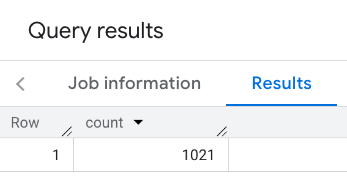
חשוב לזכור שבשאילתות של מערך נתונים של מקומות יש סף מינימלי של 5. אחד היתרונות של פונקציות ספירת המקומות הוא שהן יכולות להחזיר כל ספירה, כולל 0. לדוגמה, הקריאה הבאה מחזירה את הערך 1:
SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 500, -- Radius in meters 'types', ["restaurant"], 'min_rating', 4.0, 'free_parking_lot', TRUE, 'good_for_watching_sports', TRUE ) ) as count;
דוגמה: חישוב מספר המסעדות באמצעות מצולע
אפשר להשתמש במצולע כדי לציין את אזור החיפוש. כשמשתמשים בפוליגון, הנקודות של הפוליגון צריכות להגדיר לולאה סגורה שבה הנקודה הראשונה בפוליגון זהה לנקודה האחרונה.
בדוגמה הזו נעשה שימוש בפונקציה ST_GEOGFROMTEXT של BigQuery כדי להחזיר ערך GEOGRAPHY ממצולע.
DECLARE geo GEOGRAPHY; SET geo = ST_GEOGFROMTEXT('''POLYGON((-73.985708 40.75773,-73.993324 40.750298, -73.9857 40.7484,-73.9785 40.7575, -73.985708 40.75773))'''); -- NYC viewport SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography',geo, -- viewport 'types', ["restaurant"], 'min_rating', 1.0, 'max_rating', 4.5, 'min_user_rating_count', 1, 'max_user_rating_count', 10000, 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE', 'PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE'], 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'allows_dogs', TRUE ) ) as count;
התגובה לאזור התצוגה:
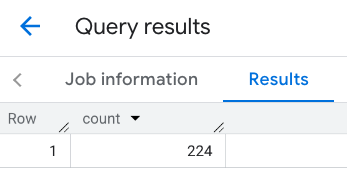
דוגמה: חישוב מספר המסעדות באמצעות קו
בדוגמה הבאה, אזור החיפוש מוגדר באמצעות קו של נקודות מחוברות עם רדיוס חיפוש של 100 מטרים סביב הקו. הקו דומה למסלול נסיעה שמחושב על ידי Routes API. המסלול יכול להיות לרכב, לאופניים או להולכי רגל:
DECLARE geo GEOGRAPHY; SET geo = ST_GEOGFROMTEXT('LINESTRING(-73.98903537033028 40.73655649223003,-73.93580216278471 40.80955538843361)'); -- NYC line SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography',geo, -- line 'geography_radius', 100, -- Radius around line 'types', ["restaurant"], 'min_rating', 1.0, 'max_rating', 4.5, 'min_user_rating_count', 1, 'max_user_rating_count', 10000, 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE', 'PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE'], 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'allows_dogs', TRUE ) ) as count;
התגובה לשורה:
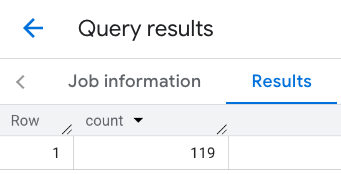
דוגמה: שילוב התוצאות של כמה שיחות
אפשר לשלב את התוצאות של כמה קריאות לפונקציה PLACES_COUNT.
לדוגמה, אתם רוצים לקבל תוצאה אחת שמציגה את מספר המסעדות ברמות המחירים הבאות באזור מסוים:
PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVEPRICE_LEVEL_MODERATEPRICE_LEVEL_EXPENSIVEPRICE_LEVEL_VERY_EXPENSIVE"
בדוגמה הזו, יוצרים לולאה כדי לקרוא לפונקציה PLACES_COUNT לכל רמת מחיר, ומכניסים את התוצאות של כל קריאה לטבלה זמנית. לאחר מכן, שולחים שאילתה לטבלה הזמנית כדי להציג את התוצאות:
-- Create a temp table to hold the results. CREATE TEMP TABLE results (type STRING, count INT64); -- Create a loop that calls PLACES_COUNT for each price level. FOR types IN (SELECT type FROM UNNEST(["PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE", "PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE", "PRICE_LEVEL_EXPENSIVE", "PRICE_LEVEL_VERY_EXPENSIVE"]) as type) DO INSERT INTO results VALUES (types.type, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', [types.type] ))); END FOR; -- Query the table of results. SELECT * FROM results;
התשובה המשולבת:
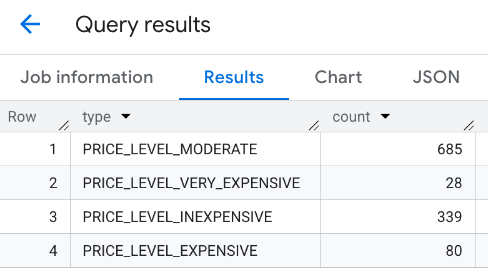
אפשרות נוספת היא להשתמש בפקודה UNION ALL כדי לשלב את התוצאות של כמה הצהרות SELECT. בדוגמה הבאה מוצגות אותן תוצאות כמו בדוגמה הקודמת:
SELECT "PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE" as price_level, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE'] ) ) as count UNION ALL SELECT "PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE" as price_level, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE'] ) ) as count UNION ALL SELECT "PRICE_LEVEL_EXPENSIVE" as price_level, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_EXPENSIVE'] ) ) as count UNION ALL SELECT "PRICE_LEVEL_VERY_EXPENSIVE" as price_level, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_VERY_EXPENSIVE'] ) ) as count
