OAuth 連結類型支援兩種符合業界標準的 OAuth 2.0 流程,分別是隱含和授權碼流程。
在隱式程式碼流程中,Google 會在使用者的瀏覽器中開啟您的授權端點。成功登入後,系統會將長期存取權杖傳回 Google。從現在起,每次透過 Google 助理傳送給您動作的要求中,都會包含這個存取權杖。
在授權碼流程中,您需要兩個端點:
- 授權端點,該端點負責將登入 UI 提供給未登入的使用者,並以簡碼授權代碼的形式,記錄使用者要求的存取權。
- 權杖交換端點,負責以下兩種交換類型:
- 交換長期更新權杖的授權碼和短期存取權杖。這項交換作業會在使用者完成帳戶連結流程時進行。
- 對短期存取權杖交換交換憑證。當 Google 需要新的存取權杖,因為更新權杖已過期時,就會發生此交換行為。
雖然隱含程式碼流程的實作方式較簡單,但 Google 建議使用隱含流程發布的存取權杖不會過期,因為若權杖與隱含流程搭配使用,就會強制使用者重新連結帳戶。如果基於安全考量而需要權杖過期,您應該考慮改用授權碼流程。
實作 OAuth 帳戶連結
設定專案
如要設定專案以使用 OAuth 連結,請按照下列步驟操作:
- 開啟 Actions 管理中心,然後選取要使用的專案。
- 按一下「開發」分頁,然後選擇「帳戶連結」。
- 啟用「帳戶連結」旁的切換鈕。
- 在「帳戶建立」部分,選取「否,我只想允許在我的網站上建立帳戶」。
在「連結類型」中,選取「OAuth」和「授權碼」。
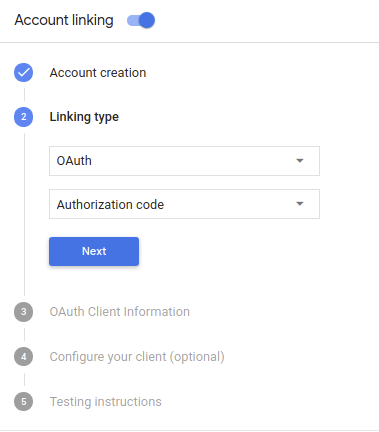
在「用戶端資訊」中:
- 為「Google 簽發給動作的用戶端 ID」指派值,以識別來自 Google 的要求。
- 請記下 Google 為 Actions 核發的 Client ID 值;
- 插入授權和權杖交換端點的網址。
- 按一下 [儲存]。
導入 OAuth 伺服器
授權碼流程的 OAuth 2.0 伺服器實作包括 服務透過 HTTPS 提供第一個端點 是授權端點,負責尋找或取得 徵得使用者同意並授予資料存取權授權端點會顯示登入活動 讓尚未登入的使用者顯示使用者介面,並記錄 要求存取權。第二個端點是權杖交換端點 用於取得加密字串 (稱為「權杖」),授權動作使用者 存取您的服務。
當您的動作需要呼叫服務的其中一個 API 時,Google 會使用這些 多個端點,藉此向使用者取得權限,讓他們能在自己的
Google 啟動的 OAuth 2.0 授權碼流程工作階段如下:
- Google 會在使用者的瀏覽器中開啟授權端點。如果流程 透過純語音裝置啟動一項動作,則 Google 會將 到手機上
使用者登入 (如果尚未登入) 並將權限授予 Google 如果他們尚未授予權限,可以透過您的 API 存取資料。
您的服務會建立授權碼,並由 透過授權碼將使用者的瀏覽器重新導向回 Google 附加在要求中
Google 將授權碼傳送至權杖交換端點 驗證程式碼的真實性,並傳回存取權杖和 更新權杖。存取權杖是服務 以憑證存取 API。更新權杖存在長期 憑證,可供 Google 儲存,用於取得新的存取權杖 過期。
使用者完成帳戶連結流程後, 要求 Google 助理傳送給您的執行要求 Webhook,當中會包含 存取權杖
處理授權要求
你的動作需透過 OAuth 2.0 授權碼進行帳戶連結時 流程時,Google 會透過以下要求將使用者傳送到您的授權端點 包含下列參數:
| 授權端點參數 | |
|---|---|
client_id |
您向 Google 註冊的 Google 用戶端 ID。 |
redirect_uri |
您傳送回應到這項要求的網址。 |
state |
傳回給 Google 的記帳金額,值維持不變 重新導向 URI |
scope |
選用:一組以空格分隔的範圍字串,指定 也就是 Google 要求授權的資料 |
response_type |
字串 code。 |
舉例來說,如果您的授權端點位於 https://myservice.example.com/auth,
要求看起來可能像這樣:
GET https://myservice.example.com/auth?client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&redirect_uri=REDIRECT_URI&state=STATE_STRING&scope=REQUESTED_SCOPES&response_type=code
如要讓授權端點處理登入要求,請按照下列步驟操作:
確認
client_id與您註冊時使用的 Google 用戶端 ID 相符 Google,且redirect_uri與 Google 提供的重新導向網址相符 以及 SLI這些檢查至關重要,是為了避免授予存取權 非預期或設定錯誤的用戶端應用程式。如果您支援多個 OAuth 2.0 流程,請一併確認
response_type為code。檢查使用者是否已登入您的服務。如果使用者未登入, 完成服務的登入或註冊流程。
產生 Google 用來存取 API 的授權碼。 授權碼可以是任何字串值,但必須不重複 代表使用者、該權杖所屬的用戶端,以及代碼的到期時間 而且您無法憑空猜測您通常會核發授權 驗證碼會在大約 10 分鐘後失效
確認
redirect_uri參數指定的網址 格式如下:https://oauth-redirect.googleusercontent.com/r/YOUR_PROJECT_ID
將使用者的瀏覽器重新導向至
redirect_uri參數。附上 產生的原始值,以及您在重新導向時 方法是附加code和state參數。以下為 的結果:https://oauth-redirect.googleusercontent.com/r/YOUR_PROJECT_ID?code=AUTHORIZATION_CODE&state=STATE_STRING
處理權杖交換要求
服務的權杖交換端點負責兩種權杖 廣告交易平台:
- 交換存取權杖和更新權杖的授權碼
- 交換存取權杖的更新權杖
權杖交換要求包含下列參數:
| 權杖交換端點參數 | |
|---|---|
client_id |
用來識別要求來源為 Google 的字串。此字串必須 在您的系統中註冊為 Google 專屬識別碼。 |
client_secret |
您向 Google 註冊的服務專用密鑰。 |
grant_type |
要交換的權杖類型。兩者皆可
authorization_code 或 refresh_token。 |
code |
如果是 grant_type=authorization_code,程式碼會由 Google
接收的驗證憑證。 |
redirect_uri |
如果 grant_type=authorization_code,這個參數是
用於初始授權要求的網址。 |
refresh_token |
如果為 grant_type=refresh_token,Google 更新憑證權杖會由 Google
從權杖交換端點收到的文字 |
交換存取權杖和更新權杖的授權碼
使用者登入,且您的授權端點傳回短期授權後 程式碼給 Google,Google 會向您的權杖交換端點傳送要求 存取權杖的授權碼和更新權杖。
在這些要求的 grant_type 值為 authorization_code,其值為
code 是您之前授予 Google 的授權碼值。
以下是以
存取權杖和更新權杖:
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET&grant_type=authorization_code&code=AUTHORIZATION_CODE&redirect_uri=REDIRECT_URI
如要交換存取權杖和更新權杖的授權碼,您的
權杖交換端點會回應執行下列步驟的 POST 要求:
- 驗證
client_id會將要求來源識別為授權來源。client_secret與預期值相符 - 驗證以下內容:
- 授權碼有效且未過期,且用戶端 要求中指定的 ID 與 授權碼。
redirect_uri參數指定的網址相同 設為初始授權要求使用的值。
- 如果您無法驗證上述所有條件,請傳回 HTTP
400 「Bad Request」錯誤,內文為
{"error": "invalid_grant"}。 - 否則,請使用授權碼中的使用者 ID 產生重新整理 權杖和存取權杖這些符記可以是任何字串值,但必須 可明確代表憑證所屬的使用者和用戶端, 容易猜中如果是存取權杖,請一併記錄權杖的到期時間 (通常是在您核發權杖後一小時)。重新整理權杖沒有期限。
- 在 HTTPS 回應的內文中傳回下列 JSON 物件:
{ "token_type": "Bearer", "access_token": "ACCESS_TOKEN", "refresh_token": "REFRESH_TOKEN", "expires_in": SECONDS_TO_EXPIRATION }
Google 會儲存使用者的存取權杖和更新權杖,並記錄 存取權杖存取權杖到期時,Google 會使用更新項目 取得新的存取權杖。
交換存取權杖的更新權杖
存取權杖到期時,Google 會傳送要求至您的權杖交換端點 來交換更新憑證給新的存取權杖。
在這些要求的 grant_type 值為 refresh_token,其值為
refresh_token 是您先前授予 Google 的更新權杖值。
以下是以
存取權杖:
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET&grant_type=refresh_token&refresh_token=REFRESH_TOKEN
如要將更新權杖換成存取權杖,權杖交換端點
回應 POST 要求,執行下列步驟:
- 驗證
client_id會將要求來源識別為 且client_secret符合預期 值。 - 驗證更新權杖是否有效,以及 此請求會與更新權杖關聯的用戶端 ID 相符。
- 如果您無法驗證上述所有條件,請傳回 HTTP
400 「Bad Request」錯誤,內文為
{"error": "invalid_grant"}。 - 否則,請使用更新權杖的使用者 ID 產生存取權 產生下一個符記這些符記可以是任何字串值,但必須專門用來 和用戶端,您無法猜測該權杖的用途。 如果是存取權杖,請一併記錄權杖的到期時間 (通常是在您核發權杖後一小時)。
- 在 HTTPS 內文中傳回下列 JSON 物件
回應:
{ "token_type": "熊", "access_token": "ACCESS_TOKEN", 「expires_in」:SECONDS_TO_EXPIRATION }
設計驗證流程的語音使用者介面
檢查使用者是否已通過驗證,然後開始帳戶連結流程
- 在 Actions Console 中開啟 Actions Builder 專案。
- 在動作中建立新場景,開始連結帳戶:
- 按一下「場景」。
- 按一下「新增」 (+) 圖示,即可新增場景。
- 在新建立的場景中,按一下「條件」的「新增」圖示 add。
- 新增條件,檢查與對話相關聯的使用者是否為已驗證使用者。如果檢查失敗,動作就無法在對話期間執行帳戶連結,且應改為提供不需要帳戶連結的功能存取權。
- 在「條件」下方的
Enter new expression欄位中,輸入下列邏輯:user.verificationStatus != "VERIFIED" - 在「轉場效果」下方,選取不需要連結帳戶的場景,或是僅限訪客使用的功能進入點場景。
- 在「條件」下方的
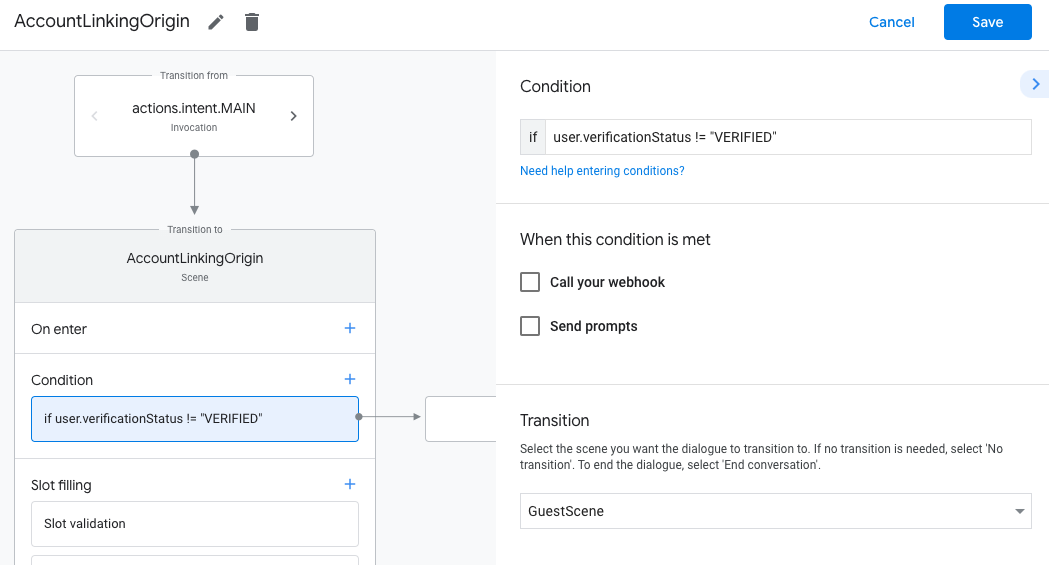
- 按一下「條件」的「新增」add圖示。
- 新增條件,在使用者沒有相關聯的身分時觸發帳戶連結流程。
- 在「條件」下方的
Enter new expression欄位中,輸入下列邏輯:user.verificationStatus == "VERIFIED" - 在「Transition」下方,選取「Account Linking」系統場景。
- 按一下 [儲存]。
- 在「條件」下方的
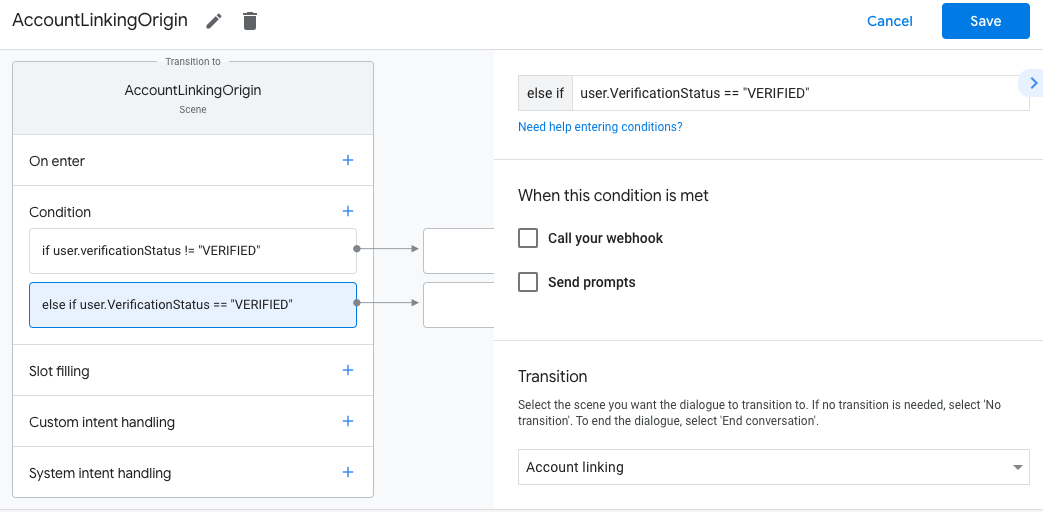
儲存後,專案中會新增名為「<SceneName>_AccountLinking」的帳戶連結系統場景。
自訂帳戶連結場景
- 在「場景」下方,選取帳戶連結系統場景。
- 按一下「傳送提示」,並新增簡短句子,向使用者說明動作為何需要存取身分識別資訊 (例如「儲存偏好設定」)。
- 按一下 [儲存]。
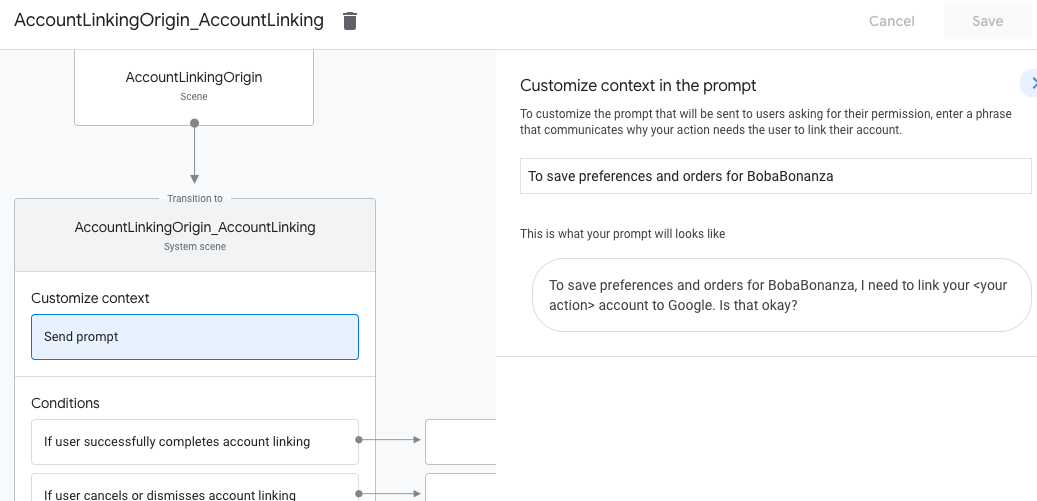
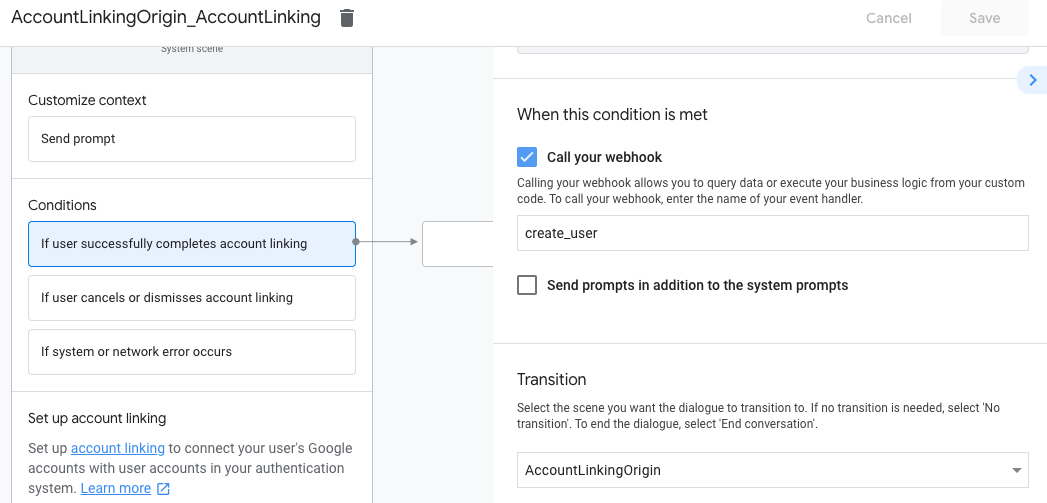
- 按一下「條件」下方的「如果使用者成功完成帳戶連結」。
- 設定使用者同意連結帳戶時,流程應如何繼續進行。 舉例來說,呼叫 Webhook 來處理任何必要的自訂商業邏輯,然後返回原始場景。
- 按一下 [儲存]。
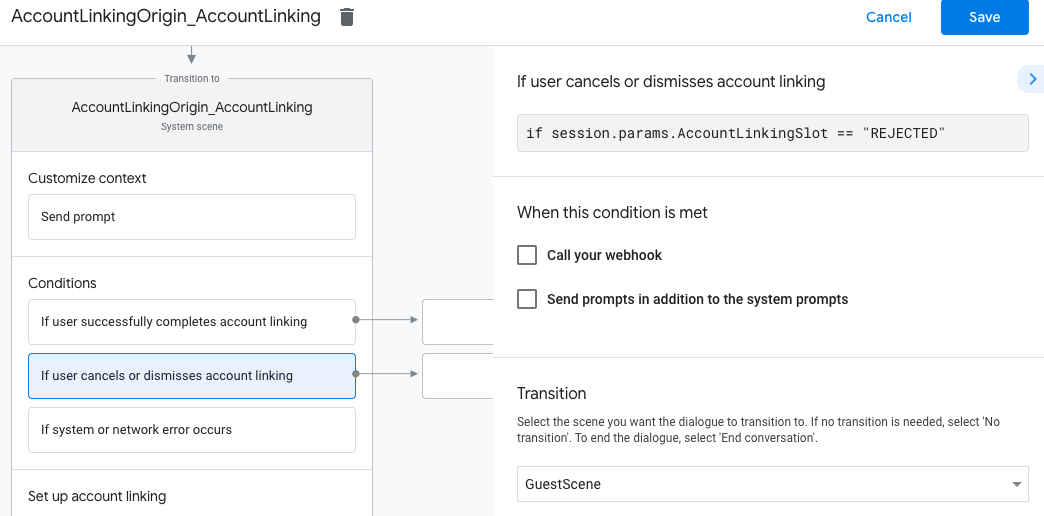
- 在「條件」下方,按一下「如果使用者取消或關閉帳戶連結」。
- 設定使用者不同意連結帳戶時,流程應如何進行。舉例來說,傳送確認訊息,然後重新導向至不需要帳戶連結的功能場景。
- 按一下 [儲存]。
- 在「條件」下方,按一下「如果發生系統或網路錯誤」。
- 設定帳戶連結流程因系統或網路錯誤而無法完成時,流程應如何繼續。舉例來說,傳送確認訊息,然後重新導向至不需要帳戶連結的功能場景。
- 按一下 [儲存]。
處理資料存取要求
如果Google 助理要求包含存取權杖,請先檢查存取權杖是否有效 (未過期),然後從資料庫中擷取相關聯的使用者帳戶。