O tipo vinculação do OAuth é compatível com dois fluxos padrão do setor do OAuth 2.0: os fluxos de código implícito e de autorização.
No fluxo de código implícito, o Google abre o endpoint de autorização no navegador do usuário. Após o login, você retorna um token de acesso de longa duração para o Google. Esse token de acesso agora está incluído em todas as solicitações enviadas do Assistente para sua ação.
No fluxo do código de autorização, você precisa de dois endpoints:
- O endpoint de autorização, responsável por apresentar a IU de login aos usuários que ainda não fizeram login e registrar o consentimento para o acesso solicitado na forma de um código de autorização de curta duração.
- O endpoint de troca de token, que é responsável por dois tipos de trocas:
- troca um código de autorização por um token de atualização de longa duração e um token de acesso de curta duração. Essa troca acontece quando o usuário passa pelo fluxo de vinculação da conta.
- Troca um token de atualização de longa duração por um token de acesso de curta duração. Essa troca acontece quando o Google precisa de um novo token de acesso porque ele expirou.
Embora o fluxo do código implícito seja mais simples de implementar, o Google recomenda que os tokens de acesso emitidos usando o fluxo implícito nunca expirem, porque o uso do token com o fluxo implícito força o usuário a vincular a conta novamente. Se você precisar da validade do token por motivos de segurança, considere o uso do fluxo do código de autenticação.
Implementar a vinculação de contas OAuth
Configurar o projeto
Para configurar seu projeto para usar a vinculação do OAuth, siga estas etapas:
- Abra o Actions Console e selecione o projeto que você quer usar.
- Clique na guia Desenvolver e escolha Vinculação de contas.
- Ative a chave ao lado de Vinculação de contas.
- Na seção Criação de conta, selecione Não, quero permitir a criação de contas apenas no meu site.
Em Tipo de vinculação, selecione OAuth e Código de autorização.
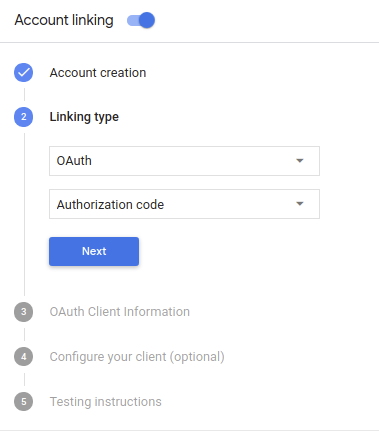
Em Informações do cliente:
- Atribua um valor a ID do cliente emitido pelo Actions on Google para identificar solicitações do Google.
- Anote o valor do ID do cliente emitido pelo Google para suas ações.
- Insira os URLs dos endpoints de autorização e troca de token.
- Clique em Salvar.
Implementar seu servidor OAuth
Uma implementação do servidor OAuth 2.0 do fluxo do código de autorização consiste em dois endpoints, que seu serviço disponibiliza por HTTPS. O primeiro endpoint é o endpoint de autorização, responsável por encontrar ou conseguir o consentimento dos usuários para acesso aos dados. O endpoint de autorização apresenta um interface para seus usuários que ainda não estão conectados e registra o consentimento para o solicitou acesso. O segundo endpoint é a de troca de token, usada para obter strings criptografadas, chamadas de tokens, que autorizam o usuário da ação para acessar seu serviço.
Quando sua Ação precisa chamar uma das APIs do seu serviço, o Google usa essas endpoints juntos para obter a permissão de seus usuários para chamar essas APIs em seus nome de usuário.
A sessão do fluxo do código de autenticação do OAuth 2.0 iniciada pelo Google tem o seguinte fluxo:
- O Google abre seu endpoint de autorização no navegador do usuário. Se o fluxo em um dispositivo somente de voz para uma ação, o Google transferia a execução em um smartphone.
O usuário faz login (se ainda não tiver feito) e concede ao Google permissão para acessar os dados com a API, caso ainda não tenham concedido permissão.
Seu serviço cria um código de autorização e o retorna ao Google: redirecionando o navegador do usuário de volta para o Google com o código de autorização anexada à solicitação.
O Google envia o código de autorização para seu endpoint de troca de token, verifica a autenticidade do código e retorna um token de acesso e um token de atualização. O token de acesso é um token de curta duração que seu serviço aceita como credenciais para acessar APIs. O token de atualização é um token de atualização token que o Google pode armazenar e usar para adquirir novos tokens de acesso e depois ela expira.
Depois que o usuário tiver concluído o fluxo de vinculação à conta, todas as enviada do Assistente para o webhook de fulfillment contém uma token de acesso.
Processar solicitações de autorização
Quando sua Ação precisar realizar a vinculação de contas usando um código de autorização OAuth 2.0. fluxo, o Google envia o usuário para seu endpoint de autorização com uma solicitação que inclui os seguintes parâmetros:
| Parâmetros de endpoint de autorização | |
|---|---|
client_id |
O ID do cliente do Google registrado no Google. |
redirect_uri |
O URL para o qual você envia a resposta para essa solicitação. |
state |
Um valor de contabilidade que é retornado ao Google inalterado na URI de redirecionamento. |
scope |
Opcional: um conjunto delimitado por espaços de strings de escopo que especificam o dados para os quais o Google está solicitando autorização. |
response_type |
A string code. |
Por exemplo, se o endpoint de autorização estiver disponível em https://myservice.example.com/auth,
uma solicitação será semelhante a esta:
GET https://myservice.example.com/auth?client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&redirect_uri=REDIRECT_URI&state=STATE_STRING&scope=REQUESTED_SCOPES&response_type=code
Para que o endpoint de autorização processe solicitações de login, siga estas etapas:
Verifique se o
client_idcorresponde ao ID do cliente do Google com que você se registrou. Google, e se oredirect_uricorresponde ao URL de redirecionamento fornecido pelo Google para seu serviço. Essas verificações são importantes para impedir que você conceda acesso apps clientes não intencionais ou configurados incorretamente.Se você oferecer suporte a vários fluxos do OAuth 2.0, confirme também se o
response_typeécode.Verifique se o usuário está conectado ao seu serviço. Se o usuário não estiver conectado, para concluir o fluxo de login ou inscrição do serviço.
Gere um código de autorização que o Google usará para acessar sua API. O código de autorização pode ser qualquer valor de string, mas deve ser representar o usuário, o cliente a que o token se destina e a expiração do código tempo de resposta e não deve ser adivinhado. Você normalmente emite uma autorização que expiram após aproximadamente 10 minutos.
Confirme se o URL especificado pelo parâmetro
redirect_uritem o seguinte formato:https://oauth-redirect.googleusercontent.com/r/YOUR_PROJECT_ID
Redirecione o navegador do usuário para o URL especificado pelo parâmetro
redirect_uri. Inclua o código de autorização que você e o valor do estado original e inalterado ao redirecionar anexando os parâmetroscodeestate. Confira um exemplo do URL resultante:https://oauth-redirect.googleusercontent.com/r/YOUR_PROJECT_ID?code=AUTHORIZATION_CODE&state=STATE_STRING
Processar solicitações de troca de token
O endpoint de troca de token do seu serviço é responsável por dois tipos de token trocas:
- Trocar códigos de autorização por tokens de acesso e de atualização
- Trocar tokens de atualização por tokens de acesso
As solicitações de troca de token incluem os seguintes parâmetros:
| Parâmetros de endpoint de troca de token | |
|---|---|
client_id |
Uma string que identifica a origem da solicitação como o Google. Essa string precisa ser registrado em seu sistema como identificador exclusivo do Google. |
client_secret |
Uma string secreta que você registrou no Google para seu serviço. |
grant_type |
O tipo de token que está sendo trocado. De qualquer
authorization_code ou refresh_token. |
code |
Quando grant_type=authorization_code, o código do Google
recebidos do endpoint de login ou de troca de token. |
redirect_uri |
Quando grant_type=authorization_code, esse parâmetro é o
URL usado na solicitação de autorização inicial. |
refresh_token |
Quando grant_type=refresh_token, o token de atualização do Google
recebidos do endpoint de troca de token. |
Trocar códigos de autorização por tokens de acesso e de atualização
Depois que o usuário fizer login e o endpoint de autorização retornar uma autorização de curta duração código ao Google, ele envia uma solicitação ao seu endpoint de troca de token para troca o código de autorização para um token de acesso e um token de atualização.
Para essas solicitações, o valor de grant_type é authorization_code, e o valor
code é o valor do código de autorização concedido anteriormente ao Google.
O exemplo a seguir mostra uma solicitação para trocar um código de autorização por um
token de acesso e um token de atualização:
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET&grant_type=authorization_code&code=AUTHORIZATION_CODE&redirect_uri=REDIRECT_URI
Para trocar códigos de autorização por um token de acesso e um token de atualização, seu
o endpoint de troca de token responde a solicitações POST executando as seguintes etapas:
- Verifique se o
client_ididentifica a origem da solicitação como uma origem autorizada. e se oclient_secretcorresponde ao valor esperado. - Verifique o seguinte:
- O código de autorização é válido e não expirou, e o cliente O ID especificado na solicitação corresponde ao ID do cliente associado à código de autorização.
- O URL especificado pelo parâmetro
redirect_urié idêntico ao valor usado na solicitação de autorização inicial.
- Se não for possível verificar todos os critérios acima, retorne uma solicitação HTTP
Erro 400 Solicitação inválida com
{"error": "invalid_grant"}como o corpo. - Caso contrário, com o ID do usuário informado no código de autorização, gere uma atualização e um token de acesso. Esses tokens podem ser de qualquer valor de string, mas devem representam exclusivamente o usuário e o cliente a que o token se destina, e eles não devem pode ser adivinhado. Para tokens de acesso, registre também o tempo de expiração do token (normalmente uma hora após a emissão do token). Os tokens de atualização não expiram.
- Retorne o seguinte objeto JSON no corpo da resposta HTTPS:
{ "token_type": "Bearer", "access_token": "ACCESS_TOKEN", "refresh_token": "REFRESH_TOKEN", "expires_in": SECONDS_TO_EXPIRATION }
O Google armazena o token de acesso e de atualização do usuário e registra a a expiração do token de acesso. Quando o token de acesso expira, o Google usa a para receber um novo token de acesso do endpoint de troca de tokens.
Trocar tokens de atualização por tokens de acesso
Quando um token de acesso expira, o Google envia uma solicitação para seu endpoint de troca de token para trocar um token de atualização por um novo token de acesso.
Para essas solicitações, o valor de grant_type é refresh_token, e o valor
de refresh_token é o valor do token de atualização que você concedeu anteriormente ao Google.
Veja a seguir um exemplo de solicitação para trocar um token de atualização por um
token de acesso:
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET&grant_type=refresh_token&refresh_token=REFRESH_TOKEN
Para trocar um token de atualização por um de acesso, o endpoint de troca de token
responde a solicitações POST executando as seguintes etapas:
- Verifique se o
client_ididentifica a origem da solicitação como no Google, e que oclient_secretcorresponde ao . - Verifique se o token de atualização é válido e se o ID do cliente especificado em a solicitação corresponde ao ID do cliente associado ao token de atualização.
- Se não for possível verificar todos os critérios acima, retorne uma solicitação HTTP
Erro 400 Solicitação inválida com
{"error": "invalid_grant"}como o corpo. - Caso contrário, use o ID de usuário do token de atualização para gerar um acesso com base no token correto anterior. Esses tokens podem ser de qualquer valor de string, mas devem representar exclusivamente o usuário e o cliente ao qual o token se destina e eles não podem ser adivinhados. Para tokens de acesso, registre também o tempo de expiração do token (normalmente uma hora após a emissão do token).
- Retorne o seguinte objeto JSON no corpo da solicitação
resposta:
{ "token_type": "Bearer", "access_token": "ACCESS_TOKEN", "expires_in": SECONDS_TO_EXPIRATION }
Projetar a interface de usuário de voz para o fluxo de autenticação
Verificar se o usuário está verificado e iniciar o fluxo de vinculação da conta
- Abra seu projeto do Actions Builder no Console do Actions.
- Crie uma nova cena para iniciar a vinculação de contas na sua ação:
- Clique em Cenas.
- Clique no ícone de adição (+) para adicionar uma nova cena.
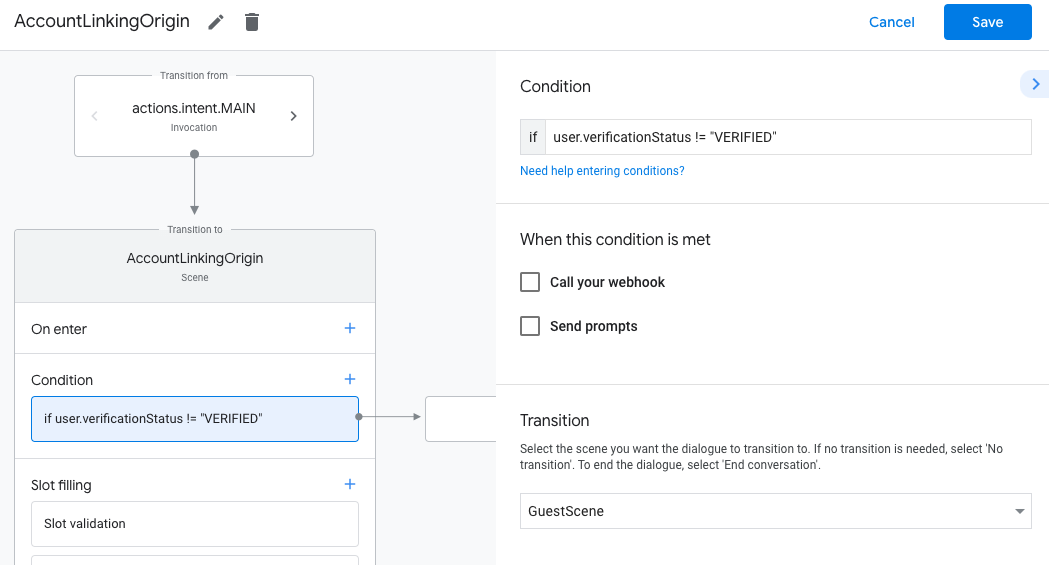
- Na cena recém-criada, clique no ícone de adição add para Condições.
- Adicione uma condição que verifique se o usuário associado à conversa é um usuário verificado. Se a verificação falhar, a Ação não poderá vincular contas
durante a conversa e precisará oferecer acesso a
funcionalidades que não exigem vinculação de contas.
- No campo
Enter new expressionem Condição, insira a seguinte lógica:user.verificationStatus != "VERIFIED" - Em Transição, selecione uma cena que não exija vinculação de conta ou uma cena que seja o ponto de entrada para a funcionalidade somente para convidados.
- No campo
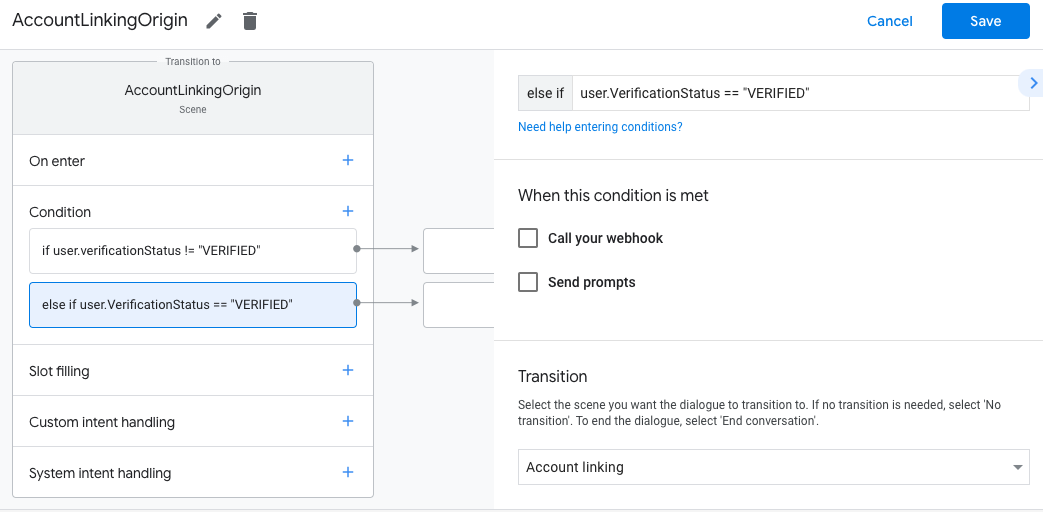
- Clique no ícone de adição add em Condições.
- Adicione uma condição para acionar um fluxo de vinculação de contas se o usuário não tiver
uma identidade associada.
- No campo
Enter new expressionem Condição, insira a seguinte lógica:user.verificationStatus == "VERIFIED" - Em Transição, selecione a cena do sistema Vinculação de conta.
- Clique em Salvar.
- No campo
Depois de salvar, uma nova cena do sistema de vinculação de contas chamada <SceneName>_AccountLinking
será adicionada ao seu projeto.
Personalizar a cena de vinculação de conta
- Em Cenas, selecione a cena do sistema de vinculação de contas.
- Clique em Enviar solicitação e adicione uma frase curta para descrever ao usuário por que a ação precisa acessar a identidade dele (por exemplo, "Para salvar suas preferências").
- Clique em Salvar.
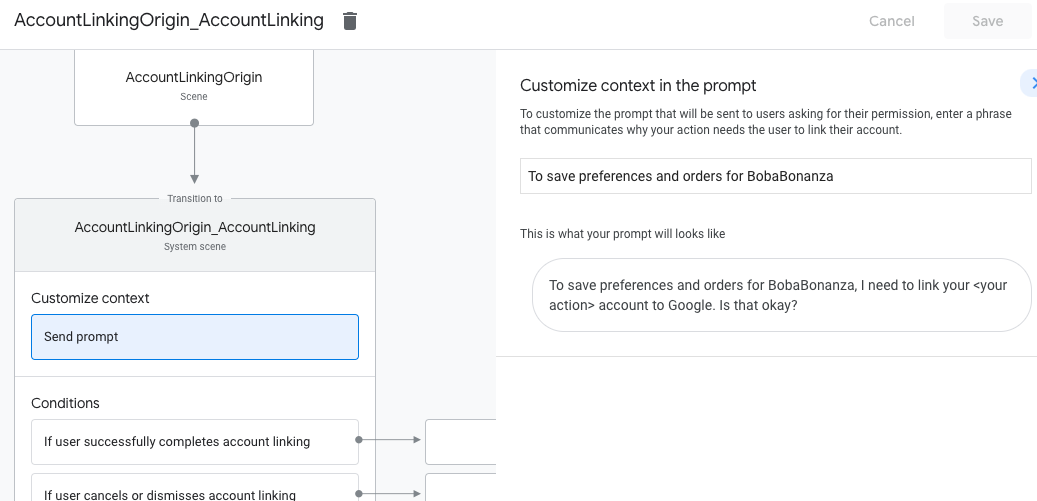
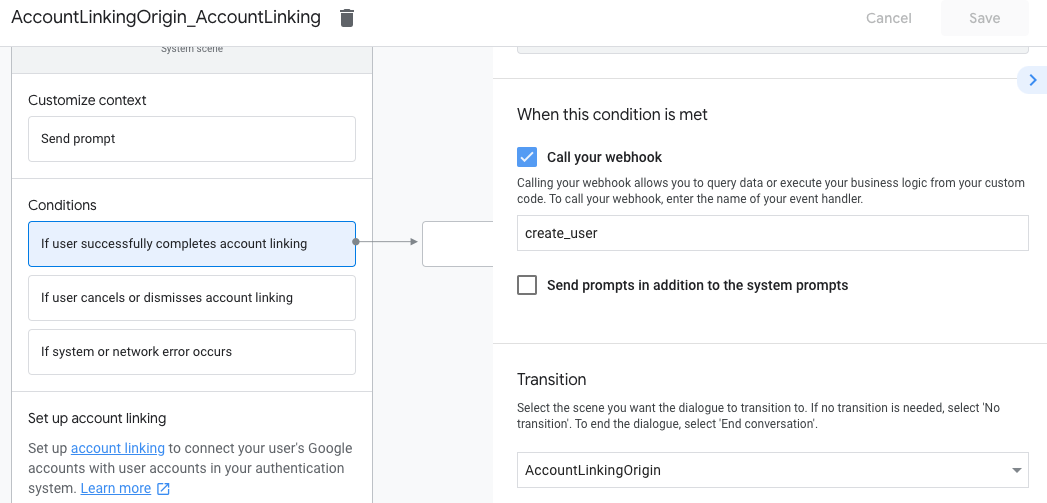
- Em Condições, clique em Se o usuário concluir a vinculação de contas.
- Configure como o fluxo vai prosseguir se o usuário concordar em vincular a conta. Por exemplo, chame o webhook para processar qualquer lógica de negócios personalizada necessária e volte para a cena de origem.
- Clique em Salvar.
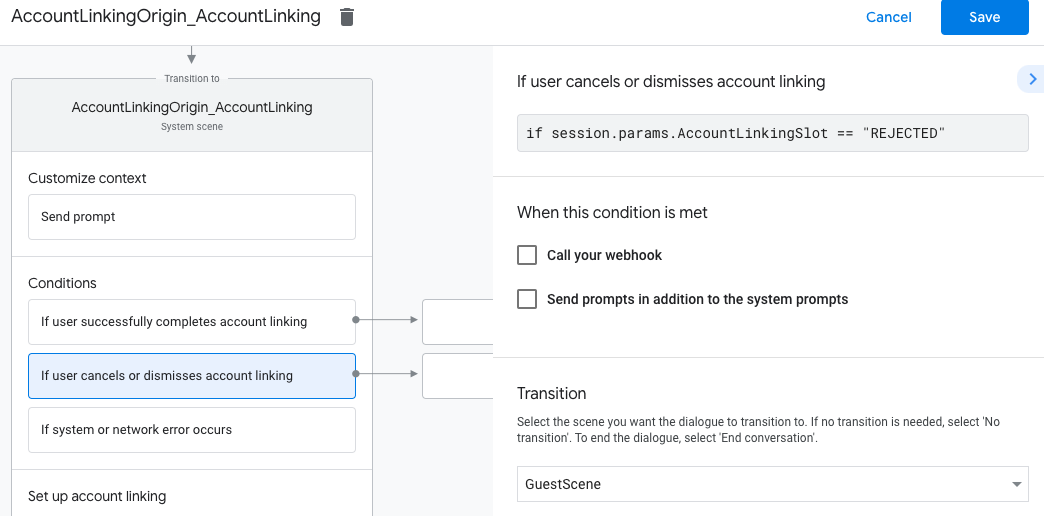
- Em Condições, clique em Se o usuário cancelar ou dispensar a vinculação de contas.
- Configure como o fluxo deve prosseguir se o usuário não concordar em vincular a conta. Por exemplo, envie uma mensagem de confirmação e redirecione para cenas que oferecem funcionalidades que não exigem vinculação de contas.
- Clique em Salvar.
- Em Condições, clique em Se ocorrer um erro de sistema ou de rede.
- Configure como o fluxo deve prosseguir se a vinculação de conta não puder ser concluída devido a erros de sistema ou de rede. Por exemplo, envie uma mensagem de confirmação e redirecione para cenas que oferecem funcionalidades que não exigem vinculação de contas.
- Clique em Salvar.
Processar solicitações de acesso a dados
Se a solicitação do Google Assistente contiver um token de acesso, primeiro verifique se o token de acesso é válido (e não expirou) e recupere a conta de usuário associada do seu banco de dados.