Logowanie przez Google w Asystencie to najprostsza i najłatwiejsza metoda dla użytkownika zarówno użytkownikom, jak i deweloperom. Twoja akcja podczas rozmowy mogą poprosić o dostęp do Twojego profilu Google użytkownika, w tym imię i nazwisko, adres e-mail i zdjęcie profilowe użytkownika.
Informacje profilowe mogą być używane do personalizowania usług w akcji. Jeśli masz aplikacje na innych platformach i używają one Logowania przez Google, Możesz też znaleźć i połączyć istniejące konto użytkownika, utworzyć nowe i ustanowienie kanału bezpośredniej komunikacji z użytkownikiem.
Aby połączyć konta z użyciem Logowania przez Google, musisz poprosić użytkownika o zgodę aby uzyskać dostęp do swojego profilu Google. Następnie używasz tych informacji do celów np. jego adres e-mail, aby zidentyfikować użytkownika w swoim systemie.
Wdrażanie łączenia konta Logowania przez Google
Wykonaj czynności opisane w sekcjach poniżej, aby dodać połączenie z kontem Logowania przez Google do Akcja.
Konfigurowanie projektu
Aby skonfigurować projekt do korzystania z funkcji łączenia kont za pomocą Logowania przez Google, wykonaj te czynności:
- Otwórz konsolę Actions i wybierz projekt.
- Kliknij kartę Programowanie i wybierz Łączenie kont.
- Włącz przełącznik obok opcji Łączenie kont.
- W sekcji Tworzenie konta wybierz Tak.
W sekcji Typ połączenia wybierz Logowanie przez Google.
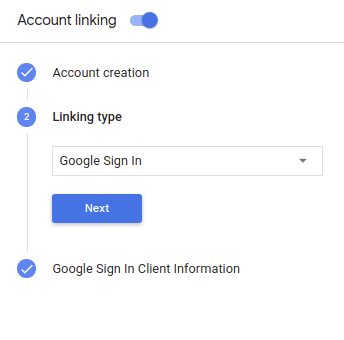
Otwórz Informacje o kliencie i zanotuj wartość identyfikatora klienta nadanego przez Google dla Twoich działań.
Kliknij Zapisz.
Zaprojektuj interfejs głosowy na potrzeby procesu uwierzytelniania
.Sprawdź, czy użytkownik został zweryfikowany, i rozpocznij proces łączenia kont
- Otwórz projekt Actions Builder w Konsoli Actions.
- Utwórz nową scenę, aby rozpocząć łączenie kont w akcji:
- Kliknij Sceny.
- Aby dodać nową scenę, kliknij ikonę dodaj (+).
- W nowo utworzonej scenie kliknij przycisk dodawania add. obok warunków.
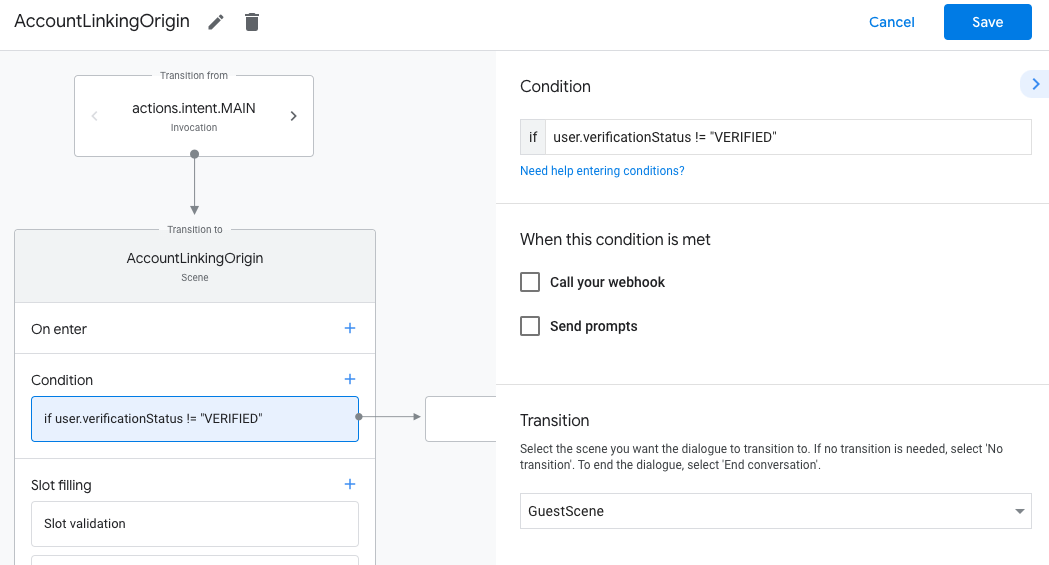
- Dodaj warunek, który sprawdza, czy użytkownik powiązany z rozmową jest
zweryfikowanego użytkownika. Jeśli weryfikacja się nie powiedzie, akcja nie może połączyć kont
podczas rozmowy i powinien wrócić do przyznania dostępu
funkcję, która nie wymaga połączenia kont.
- W polu
Enter new expressionw sekcji Warunek wpisz tę logikę:user.verificationStatus != "VERIFIED" - W sekcji Przejście wybierz scenę, która nie wymaga łączenia kont, lub scenę, która stanowi punkt dostępu do funkcji dostępnych tylko dla gości.
- W polu
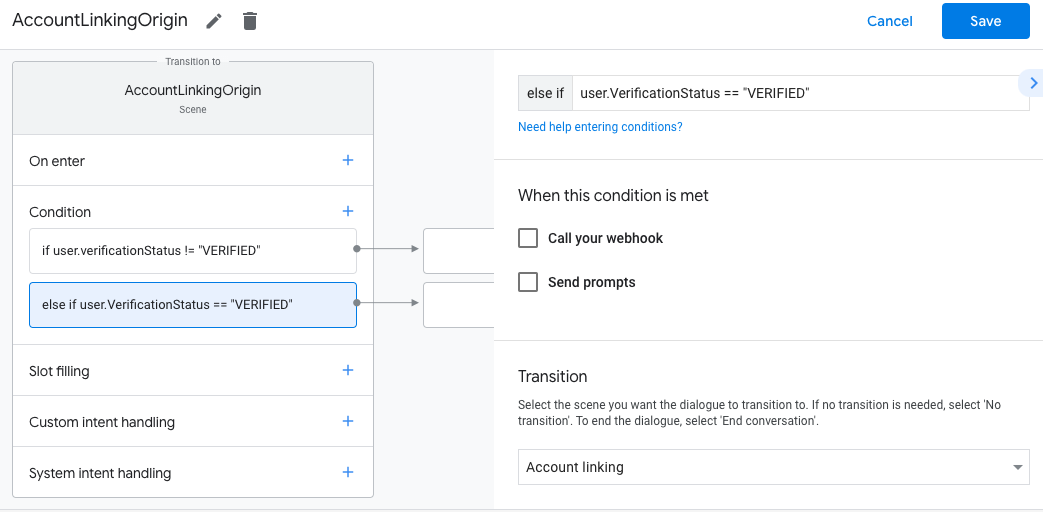
- Kliknij ikonę dodawania add przy warunkach.
- Dodaj warunek, aby uruchomić proces łączenia kont, jeśli użytkownik nie
z powiązaną tożsamością.
- W polu
Enter new expressionw sekcji Warunek wpisz tę logikę:user.verificationStatus == "VERIFIED" - W sekcji Przenoszenie wybierz scenę systemową Łączenie kont.
- Kliknij Zapisz.
- W polu
Po zapisaniu nowa scena systemowa o nazwie <SceneName>_AccountLinking do łączenia kont
zostanie dodana do projektu.
Dostosowywanie punktu łączenia kont
- W sekcji Sceny wybierz scenę systemową łączącą konto.
- Kliknij Wyślij prompt i dodaj krótkie zdanie, które opisze użytkownikowi. dlaczego akcja musi uzyskać dostęp do swojej tożsamości (np. „Aby zapisać preferencje”).
- Kliknij Zapisz.
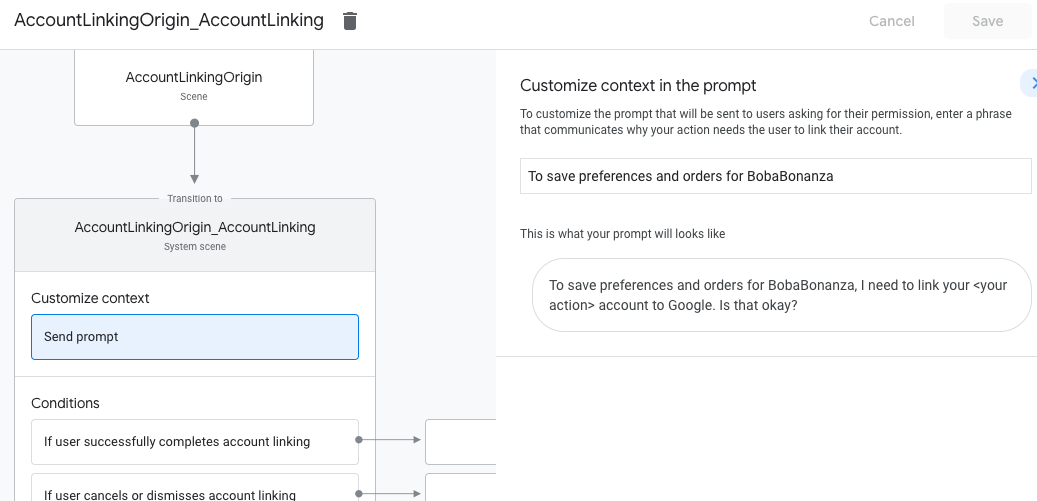
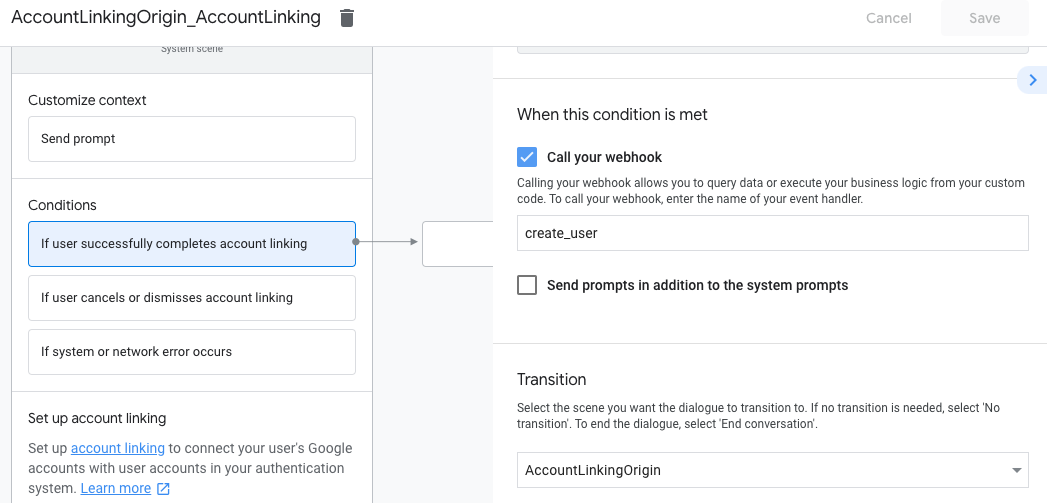
- W sekcji Warunki kliknij Jeśli użytkownik ukończy łączenie kont.
- Określ, co ma być kontynuowane, jeśli użytkownik zgodzi się na połączenie swojego konta. Na przykład wywołaj webhooka, aby przetworzyć wymaganą logikę biznesową i powrót do sceny początkowej.
- Kliknij Zapisz.
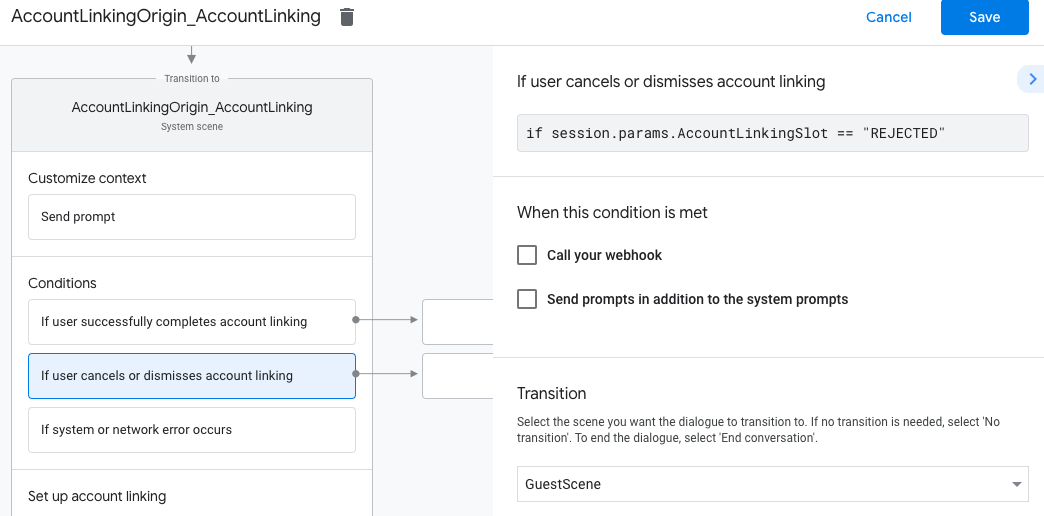
- W sekcji Warunki kliknij Jeśli użytkownik anuluje lub odrzuci połączenie kont.
- Określ, co ma być kontynuowane, jeśli użytkownik nie zgodzi się na połączenie swojego konta koncie. Na przykład wyślij wiadomość z potwierdzeniem i przekieruj do scen które oferują funkcje, które nie wymagają połączenia kont.
- Kliknij Zapisz.
- W sekcji Warunki kliknij W przypadku błędu systemu lub sieci.
- Określ, jak ma być kontynuowany proces, gdy nie można połączyć kont zostało ukończone z powodu błędów systemu lub sieci. Na przykład wyślij wiadomość z potwierdzeniem i przekieruj do scen które oferują funkcje, które nie wymagają połączenia kont.
- Kliknij Zapisz.
Uzyskiwanie dostępu do informacji o profilu w backendzie
Gdy użytkownik zezwoli użytkownikowi na dostęp do jego profilu Google, otrzymasz token tożsamości Google, który zawiera informacje z profilu Google użytkownika w każdym kolejnym do Twojego działania.
Aby uzyskać dostęp do informacji o profilu użytkownika, musisz najpierw zweryfikować i zdekodować token wykonując te czynności:
- Użyj biblioteki dekodowania JWT w swoim języku, aby zdekodować i użyj kluczy publicznych Google (dostępnych w JWK). lub PEM), aby zweryfikować podpis tokena.
- Sprawdź, czy wydawca tokena (pole
issw zdekodowanym tokenie) tohttps://accounts.google.coma lista odbiorców (poleaudw zdekodowanym tokenie) to wartość Identyfikator klienta nadany przez Google dla Działań, który jest przypisany do Twojego projektu w Konsoli Actions.
Oto przykład zdekodowanego tokena:
{ "sub": 1234567890, // The unique ID of the user's Google Account "iss": "https://accounts.google.com", // The token's issuer "aud": "123-abc.apps.googleusercontent.com", // Client ID assigned to your Actions project "iat": 233366400, // Unix timestamp of the token's creation time "exp": 233370000, // Unix timestamp of the token's expiration time "name": "Jan Jansen", "given_name": "Jan", "family_name": "Jansen", "email": "jan@gmail.com", // If present, the user's email address "locale": "en_US" }
Jeśli używasz biblioteki Actions on Google Fulfillment na potrzeby Node.js, zajmuje się weryfikacją i dekodowaniem tokena za Ciebie, a Ty masz dostęp do jak widać w poniższych fragmentach kodu.
... const app = conversation({ // REPLACE THE PLACEHOLDER WITH THE CLIENT_ID OF YOUR ACTIONS PROJECT clientId: CLIENT_ID, }); ... // Invoked on successful completion of account linking flow, check if we need to // create a Firebase user. app.handle('linkAccount', async conv => { let payload = conv.headers.authorization; if (payload) { // Get UID for Firebase auth user using the email of the user const email = payload.email; if (!conv.user.params.uid && email) { try { conv.user.params.uid = (await auth.getUserByEmail(email)).uid; } catch (e) { if (e.code !== 'auth/user-not-found') { throw e; } // If the user is not found, create a new Firebase auth user // using the email obtained from Google Assistant conv.user.params.uid = (await auth.createUser({email})).uid; } } } });
Obsługa żądań dostępu do danych
Aby obsłużyć żądanie dostępu do danych, sprawdź, czy użytkownik potwierdził to za pomocą identyfikatora Google token znajduje się już w bazie danych. Następujący fragment kodu pokazuje: Oto przykład, jak sprawdzić, czy zamówienia danego użytkownika istnieją już w bazie danych Firestore:
... app.handle('Place_Order', async conv => { const order = conv.session.params.order; const userDoc = dbs.user.doc(conv.user.params.uid); const orderHistory = userDoc.collection("orderHistory"); if (orderHistory) { // Order history exists, so the user already placed an order. // Update counter for order type. await orderHistory.doc(order).update({ count: admin.firestore.FieldValue.increment(1)}); } else { // First order they place await orderHistory.doc(order).set({ option: order, count: 1}); options.forEach(opt => { if (opt != order) { orderHistory.doc(opt).set({ option: opt, count: 0}); } }); } return conv.add(`Your ${order} has been placed. ` + 'Thanks for using Boba Bonanza, see you soon!'); });