Find Hub Precision Finding
The Find Hub Precision Finding (FHPF) specification contains implementation requirements for enabling devices that support ranging technologies to support the Precision Finding feature using Google's Find My Device app.
The type of precision finding depends on the type of the ranging technologies supported on devices engaged in precision finding. Supported ranging technologies can be found in the Ranging: Out-of-band message sequence and payload specification. Later sections explore what kind of precision finding experience can be expected based on the used ranging technology.
Find Hub Network Accessory
This specification is an extension of the Find Hub Network Accessory specification (FHNA). The same rules for GATT characteristic and Authentication apply here as defined in the FHNA document. This document defines new operation types, in addition to already existing operations in the FHNA specification.
Ranging Technologies specific payload
This specification also refers to the Ranging: Out-of-band message sequence and payload specification for defining ranging technology specific payload contained in the Additional Data fields of individual operations.
Precision Finding flow
This section explores the FHNA message flow for Precision Finding. Figure 1 shows the flow of the messages, and the paragraphs explain each message in more detail.
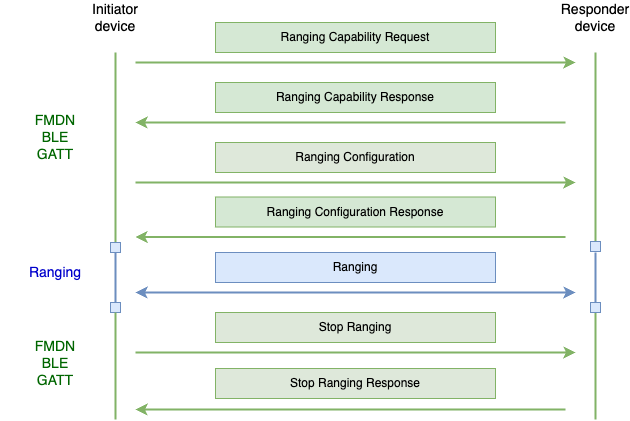
Fig. 1 Typical Precision Finding message flow
The Initiator device is the device that has the Find Hub app, and where the Precision Finding feature was engaged from. The initiator is the device that is trying to find the other device.
The Responder device is the device that is trying to be found by the Initiator device.
The Initiator device sends a Ranging Capability Request message to the Responder device, where it will list the ranging technologies that it's interested in learning about from the Responder device. The responder device will reply back with the Ranging Capability Response notification, containing information about which ranging technologies are supported and what are their capabilities. The responder will include information only requested by the initiator. The list of capabilities will be sorted based on the priority of the ranging technology the Responder device favors, with first in the list having the highest priority.
The Initiator device will then follow up with a Ranging Configuration message, where it will define the configuration for each ranging technology it wants to range with. Upon receiving this message, the Responder device must start ranging for applicable technologies using the provided configurations. The responder device will send back a Ranging Configuration response notification, which contains the results of whether each individual ranging technology started successfully. Some ranging technologies have to be started on both the Initiator and the Responder device in order to have a successful ranging session, while for others it is only necessary that it is started on the Initiator device, still, the Responder device must reply back with a success result for such technologies. More about specific ranging technology behavior can be found in later sections.
Once the Initiator device is ready to stop the Precision Finding session, it will send a Stop Ranging message to the responder, indicating which ranging technologies must stop ranging. The Responder device will respond with a Stop Ranging Response notification, indicating that it successfully stopped ranging with the requested ranging technologies.
In the case of FHNA BLE GATT communication channel disconnecting mid Precision Finding session, but while some of the ranging technologies are still ranging, the responder device will implement a timeout mechanism to ensure that it doesn't range indefinitely. Details will depend on each use case.
Note, the responder device mustn't assume the order of the operations will always be the same. E.g. the responder device must be able to handle multiple Ranging Capability requests operations in a row, or even a direct Ranging Configuration operation without the preceding capability request.
Operations
Table 1 shows FHNA operations defined by this document that are required for Precision Finding. Each subsection defines the FHNA message for each of the operations, while the Additional Data field contents refer to Ranging: Out-of-band message sequence and payload specification.
Table 1: Operations
| Operation | Data Id | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Ranging Capability Request | 0x0A | The capability request operation that will be sent by the Initiator device to the Responder device. Data contents of this operation will list all ranging technologies the Initiator wants to know about from the Responder device. |
| Ranging Capability Response | 0x0A | This is the notification response to the Ranging Capability Request operation. It contains information about capabilities for each supported ranging technology that were requested by the initiator. |
| Ranging Configuration | 0x0B | Ranging Configuration operation contains the configurations for ranging technologies the Initiator device wants to start ranging with the Responder device. |
| Ranging Configuration Response | 0x0B | This is the notification response to the Ranging Configuration operation. It contains data about whether the Responder device successfully started ranging with the requested ranging technologies based on the provided configuration. |
| RFU | 0x0C | The operation with this Data Id is not used and it's reserved for future use. |
| Stop Ranging | 0x0D | The Stop Ranging operation sent by the Initiator device contains information about which ranging technologies the Responder device must stop ranging with. |
| Stop Ranging Response | 0x0D | This is the notification response to the Stop Ranging operation. It contains data whether the stop operation for specific ranging technology was successful or not. |
Ranging Capability Request message
Table 2 defines the Ranging Capability Request message.
Table 2: Ranging Capability Request
| Octet | Data type | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | uint8 | Data ID | 0x0A - Ranging Capability Request operation |
| 1 | uint8 | Data length | varies |
| 2 | byte array | One-time authentication key | The first 8 bytes of HMAC-SHA256(Account Key, Protocol major version number || the last nonce read from the characteristic || Data ID || Data length || Additional Data). |
| 10 | byte array | Additional Data | Ranging Capability Request message as defined in the Ranging: Out-of-band message sequence and payload specification (both header and payload) |
Ranging Capability Response message
Table 3 defines the Ranging Capability Response message.
Table 3: Ranging Capability Response
| Octet | Data type | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | uint8 | Data ID | 0x0A: Ranging Capability Response |
| 1 | uint8 | Data length | varies |
| 2 | byte array | One-time authentication key | The first 8 bytes of HMAC-SHA256(Account Key, Protocol major version number || the last nonce read from the characteristic || Data ID || Data length || Additional Data || 0x01). |
| 10 | byte array | Additional Data | Ranging Capability Response message as defined in the Ranging: Out-of-band message sequence and payload specification (both header and payload) |
Ranging Configuration message
Table 4 defines the Ranging Configuration message.
Table 4: Ranging Configuration
| Octet | Data type | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | uint8 | Data ID | 0x0B - Set Ranging Configuration |
| 1 | uint8 | Data length | varies |
| 2 | byte array | One-time authentication key | The first 8 bytes of HMAC-SHA256(Account Key, Protocol major version number || the last nonce read from the characteristic || Data ID || Data length || Additional Data). |
| 10 | byte array | Additional Data | Ranging Configuration message as defined in the Ranging: Out-of-band message sequence and payload specification (both header and payload) |
Ranging Configuration Response message
Table 5 defines the Ranging Configuration Response message.
Table 5: Ranging Configuration Response
| Octet | Data type | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | uint8 | Data ID | 0x0B - Set Ranging Configuration Response |
| 1 | uint8 | Data length | varies |
| 2 | byte array | One-time authentication key | The first 8 bytes of HMAC-SHA256(Account Key, Protocol major version number || the last nonce read from the characteristic || Data ID || Data length || Additional Data || 0x01). |
| 10 | byte array | Additional Data | Ranging Configuration Response message as defined in the Ranging: Out-of-band message sequence and payload specification (both header and payload) |
Stop Ranging message
Table 6 defines the Stop Ranging message.
Table 6: Stop Ranging
| Octet | Data type | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | uint8 | Data ID | 0x0D - Ranging Stop |
| 1 | uint8 | Data length | varies |
| 2 | byte array | One-time authentication key | The first 8 bytes of HMAC-SHA256(Account Key, Protocol major version number || the last nonce read from the characteristic || Data ID || Data length). |
| 10 | byte array | Additional Data | Stop Ranging message as defined in the Ranging: Out-of-band message sequence and payload specification (both header and payload) |
Stop Ranging Response message
Table 7 defines the Stop Ranging Response message.
Table 7: Stop Ranging Response
| Octet | Data type | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | uint8 | Data ID | 0x0D - Ranging Stop Response |
| 1 | uint8 | Data length | varies |
| 2 | byte array | One-time authentication key | The first 8 bytes of HMAC-SHA256(Account Key, Protocol major version number || the last nonce read from the characteristic || Data ID || Data length || Additional Data || 0x01). |
| 10 | byte array | Additional Data | Stop Ranging Response message as defined in the Ranging: Out-of-band message sequence and payload specification (both header and payload) |
Unwanted tracking protection
When unwanted tracking protection mode is activated, as described in the FHNA specification, the same flow that applies to skipping authentication checks for ringing messages also applies for all Precision Finding messages defined in this document for devices that want to support this feature.
From FHNA specification:
If the Provider isn't provisioned as an FHNA beacon or verification fails, it returns an unauthenticated error. However, if the Provider has unwanted tracking protection active, and the triggering unwanted tracking protection request had the skip ringing authentication flag turned on, the Provider should skip that check. The authentication data is still expected to be provided by the Seeker, but it could be set to an arbitrary value.
Ranging Technology specifics
This section contains details that are ranging technology specific.
Ultra-wideband (UWB) specifics
UWB specific details.
Precision Finding level
Precision Finding sessions using UWB as the ranging technology can expect to see both distance and direction information. The ranging interval needs to be at least 240ms, with 96ms preferred for optimal guidance.
Config Ids
Out-of-band configuration data exchanged for UWB doesn't contain a full set of available configurable parameters that UWB requires to start an UWB ranging session. Some parameters are implicitly selected by the chosen config Id.
Each config Id is a set of predefined UWB configuration parameters that is publicly documented. For the Precision Finding use case, the responder device must support config Id 6, and optionally config Id 3.
UWB Initiator and Responder
For the Precision Finding use case, the device noted as the Initiator device in this document will be the UWB responder, and the device noted as the Responder device in this document will be the UWB initiator. This is because the UWB initiator device consumes less power than UWB responder does, and in most cases the Responder device will be a peripheral with limited battery.
This means that the Responder device needs to indicate that it supports being a UWB initiator role in the Ranging Capability Response message.
Other UWB related parameters
- Channel 9 must be supported
- For optimal guidance, a 96ms ranging interval is recommended, otherwise 240ms must be supported.
- Slot duration of 1ms is recommended for battery savings, but 2ms is also supported.
- The UWB chip must be at least FIRA v1.2 + P-STS compliant.
- BPRF is mandatory, HPRF is recommended but optional. The supported or selected mode is determined by the supported or selected preamble index.
- Session security type: P-STS
BLE Channel Sounding (CS) specifics
BLE CS specific details.
Precision Finding level
Precision Finding sessions using CS as the ranging technology will cause distance only measurements, directionality is not provided at this moment.
Required bond between devices
Precision Finding sessions using Channel Sounding won't work if devices are not bonded. An existing bond between the initiator and the responder device is required. This specification does not provide a way for creating a bond between the devices. Instead, it is up to the developer of the use case to establish this bond between the devices.
Action required by the responder side for CS
Unlike UWB, where both devices are required to call the UWB start ranging and stop ranging API explicitly, for CS, only the initiator device is required to start CS ranging by calling the Bluetooth stack, the rest of the initialization on the responder side happens in-band using Bluetooth (BT). This means that upon receiving the Ranging Configuration message or the Stop Ranging message for CS, the responder side doesn't have to do anything if BT is enabled, other than reply with the Ranging Configuration Response message notification. The responder device could potentially use those messages as a trigger to update the UI where a screen is present, or regardless of having a screen it could be used for visual feedback on the devices state, for example blink the device LEDs.
Wi-Fi NAN RTT
Wi-Fi NAN RTT specific details.
Precision Finding level
Precision Finding sessions using Wi-Fi NAN RTT as the ranging technology will cause distance only measurements, directionality is not provided at this moment.
BLE RSSI
BLE RSSI specific details.
Precision Finding level
Precision Finding sessions using only BLE RSSI as the ranging technology won't be able to get either the distance or the direction information, due to BLE RSSI not being an accurate ranging technology. Instead, the user will see guidance indicating that device is close or device is far.
