Statyczny interfejs API Map Google może zwrócić błąd lub ostrzeżenie, gdy coś się stanie źle. W tym przewodniku objaśniamy każdy komunikat o błędzie i podajemy więcej jak usuwać błędy.
Nieprawidłowe żądania
W przypadku nieprawidłowego żądania interfejs Maps Static API zwraca kod stanu HTTP 4xx i komunikat opisujący problem. Poniżej znajdziesz przykłady takich błędów. Uwaga: to nie jest
pełną listę możliwych błędów. Sprawdź rzeczywisty kod błędu
i komunikat zwracany przez interfejs API
zawierający szczegółowe informacje na temat konkretnych problemów.
| Przykład błędu | Kod stanu |
|---|---|
Żądanie zawiera nieprawidłowy parametr lub wymagany parametr to
brak. Na przykład parametr size nie mieści się w oczekiwanym zakresie wartości liczbowych lub brakuje go w żądaniu. |
400 BAD REQUEST |
| Klucz interfejsu API podany w żądaniu jest nieprawidłowy. | 403 FORBIDDEN |
Błędy, które uniemożliwiają wyświetlenie mapy
Jeśli żądanie jest prawidłowe, ale występuje inny błąd, który uniemożliwia mapę nie jest wyświetlany, interfejs Maps Static API zwraca tekst lub błąd. obraz zamiast mapy zależnie od błędu. Przykładem takiej sytuacji jest przekroczenie limitu wykorzystania przez aplikację.

Błędy związane z kluczami API i płatnościami
Jeśli używasz statycznego interfejsu API Map Google bez klucza interfejsu API lub jeśli korzystasz z rozliczeń nie jest włączona na Twoim koncie, zamiast z linkiem do typu błędu. Na przykład „g.co/staticmaperror/key”.
| Błędy związane z otwieraniem bez użycia klucza i ich rozwiązania | |
|---|---|
 |
Używasz statycznego interfejsu API Map Google bez klucza interfejsu API. Aby rozwiązać ten problem: |
 |
W Twoim żądaniu brakuje podpisu cyfrowego (wymagany). Aby rozwiązać ten problem, Podpisz URL |
Ostrzeżenia
W przypadku niektórych błędów interfejs API zwraca mapę, ale niektóre informacje mogą których nie ma na mapie. W takim przypadku powiadomienie ostrzeże Cię o tym w 2 sposobach.
- 1. Mapa wyświetla się, ale z nałożonym żółtym paskiem błędu górną część mapy z tekstem „Błąd mapy: g.co/staticmaperror”.
- Po drugie, interfejs API zwraca ostrzeżenie w postaci nagłówka HTTP o nazwie
X-Staticmap-API-Warning.
Na przykład poniższy URL zawiera nieoczekiwaną wartość w polu
Parametr markers:
https://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/staticmap?center=Williamsburg,Brooklyn,NY&zoom=13&scale=1&size=400x400&markers=sdgaags&key=YOUR_API_KEY
Interfejs API zwraca mapę, ale wyświetla nałożony żółty pasek błędu. nad obrazem z komunikatem „Błąd mapy: g.co/staticmaperror”:
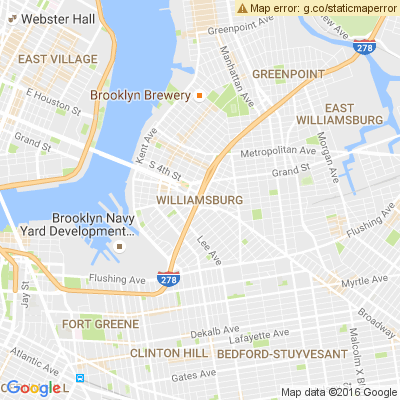
Interfejs API zwraca też ten nagłówek HTTP:
X-Staticmap-API-Warning:Error geocoding: marker 1
W tej tabeli opisano ostrzeżenia, które interfejs API może wyświetlać jako HTTP nagłówki:
Ostrzeżenia w nagłówkach X-Staticmap-API-Warning
|
|
|---|---|
Error geocoding:
[center, ][marker #number, ][visible #num, ][path #num, ]* |
Podczas próby geokodowania żądania wystąpił błąd. Istnieje wiele wersji tego komunikatu, w zależności od elementu, w przypadku którego geokodowanie się nie powiodło (centrum, znacznik, widoczność lub ścieżka) oraz liczby elementów, które nie zostały zgeokodowane. Przykładem takiego ostrzeżenia jest X-Staticmap-API-Warning:Error geocoding: marker 1, jak pokazano w przykładzie powyżej. |
Too many geocoded markers requested (max is 15). |
żądanie określa większą niż dozwolona maksymalną liczbę znaczników z czytelnym adresem; Maksymalna liczba to 15. Pamiętaj, że ten limit dotyczy tylko znaczników określonych jako adresy zrozumiałe dla człowieka, które wymagają geokodowania. Nie dotyczy znaczników określonych za pomocą długości i szerokości geograficznej. |
Too many geocoded polyline vertices requested (max is 15). |
Żądanie określa więcej linii łamanych niż dozwolona maksymalna liczba z adresem zrozumiałym dla człowieka. Maksymalna liczba to 15. Pamiętaj, że ten limit dotyczy tylko polilinii z wierzchołkami określonymi jako adresy zrozumiałe dla człowieka, które wymagają geokodowania. Nie dotyczy ścieżek wielokątów określonych za pomocą współrzędnych geograficznych. |
Ostrzeżenia dotyczące nagłówka HTTP są widoczne w sekcji w konsoli Chrome DevTools, Firefox Konsola internetowa lub inne równoważne narzędzia w przeglądarce.
