برنامهها و پروژههایی که از APIها و SDKهای پلتفرم نقشههای گوگل استفاده میکنند، باید از کلیدهای API یا در صورت پشتیبانی، از OAuth 2.0 برای احراز هویت خود استفاده کنند.
این بهترین شیوهها به شما نشان میدهند که چگونه دسترسی به پلتفرم نقشههای خود را ایمن کنید.
اگر میخواهید از OAuth 2.0 برای تأیید ترافیک سرور به سرور استفاده کنید، موضوع OAuth را در مستندات API خود جستجو کنید. برای جزئیات بیشتر به بخش «استفاده از OAuth برای برنامههای سمت سرور» مراجعه کنید.
علاوه بر اعمال محدودیتهای کلید برنامه و API، از هرگونه رویه امنیتی که برای محصولات خاص پلتفرم نقشههای گوگل اعمال میشود، پیروی کنید. برای مثال، به API جاوا اسکریپت نقشهها در زیر در محدودیتهای پیشنهادی برنامه و API مراجعه کنید.
اگر کلیدهای API شما از قبل در حال استفاده هستند، توصیههای زیر را در بخش «اگر میخواهید یک کلید API در حال استفاده را محدود کنید» مرور کنید.
برای جزئیات بیشتر در مورد امضاهای دیجیتال، که توسط Maps Static API و Street View Static API پشتیبانی میشوند، به راهنمای امضای دیجیتال مراجعه کنید.
بهترین شیوههای توصیهشده
برای افزایش امنیت و جلوگیری از پرداخت هزینه برای استفاده غیرمجاز، این شیوههای برتر امنیتی API را برای همه APIها، SDKها یا سرویسهای پلتفرم نقشههای گوگل دنبال کنید:
برای همه کاربردهای کلید API توصیه میشود
برای هر برنامه از کلیدهای API جداگانه استفاده کنید
کلیدهای API استفاده نشده را حذف کنید
میزان استفاده از کلید API خود را بررسی کنید
هنگام چرخاندن کلیدهای API مراقب باشید
تقسیم استفاده از سمت کلاینت و سمت سرور به پروژههای جداگانه
غیرفعال کردن سرویسهای بلااستفاده
توصیههای اضافی برای برنامههای سمت کلاینت
ایمنسازی فراخوانیهای سرویس وب سمت کلاینت
توصیههای بیشتر برای وبسایتها یا برنامههای سمت کلاینت که از APIهای وب استاتیک استفاده میکنند
محافظت از استفاده از API وب استاتیک
توصیههای اضافی برای برنامههای سمت سرور با استفاده از سرویسهای وب
محافظت از کلیدهای API سرویس وب
استفاده از OAuth برای برنامههای سمت سرور
اگر در حال محدود کردن یا تغییر کلید API در حال استفاده هستید
قبل از تغییر کلید API، میزان استفاده از کلید API خود را بررسی کنید. این مرحله به ویژه در صورتی اهمیت دارد که بخواهید محدودیتهایی را برای کلیدی که از قبل در یک برنامه کاربردی در حال استفاده است، اضافه کنید.
پس از تغییر کلید، در صورت نیاز، تمام برنامههای خود را با کلیدهای API جدید بهروزرسانی کنید.
اگر کلید API شما لو نرفته و مورد سوءاستفادهی فعال قرار نگرفته باشد، میتوانید برنامههای خود را با سرعت دلخواه خود به چندین کلید API جدید منتقل کنید و کلید API اصلی را تا زمانی که فقط یک نوع ترافیک مشاهده نکنید، دستنخورده باقی بگذارید و کلید API را میتوان با خیال راحت با یک نوع محدودیت برنامه محدود کرد، بدون اینکه باعث ایجاد اختلالات ناخواسته در سرویس شود.
برای دستورالعملهای بیشتر، به Migrate to multiple API keys مراجعه کنید.
قبل از اینکه تصمیم به محدود کردن یا حذف کلید قدیمی بگیرید، میزان استفاده را در طول زمان رصد کنید و ببینید چه زمانی APIهای خاص، انواع پلتفرمها و دامنهها از کلید API قدیمی مهاجرت کردهاند. برای اطلاعات بیشتر، به گزارشدهی و نظارت و معیارها مراجعه کنید.
اگر کلید API شما لو رفته است، میخواهید سریعتر برای ایمنسازی کلید API خود و جلوگیری از سوءاستفاده اقدام کنید. در برنامههای اندروید و iOS، کلیدها تا زمانی که مشتریان برنامههای خود را بهروزرسانی نکنند، جایگزین نمیشوند. بهروزرسانی یا جایگزینی کلیدها در صفحات وب یا برنامههای سمت سرور بسیار سادهتر است، اما هنوز هم ممکن است نیاز به برنامهریزی دقیق و کار سریع داشته باشد.
برای اطلاعات بیشتر، به بخش «مدیریت استفاده غیرمجاز از کلید API» مراجعه کنید.
اطلاعات بیشتر
محدودیتهای پیشنهادی برای برنامهها و API
کلیدهای API خود را محدود کنید
بهترین روش این است که همیشه کلیدهای API خود را با یک نوع محدودیت برنامه و یک یا چند محدودیت API محدود کنید. برای محدودیتهای پیشنهادی بر اساس API، SDK یا سرویس جاوا اسکریپت، به محدودیتهای پیشنهادی برنامه و API در زیر مراجعه کنید.
محدودیتهای برنامه شما میتوانید استفاده از کلید API را به پلتفرمهای خاصی محدود کنید: برنامههای اندروید یا iOS، یا وبسایتهای خاص برای برنامههای سمت کلاینت، یا آدرسهای IP خاص یا زیرشبکههای CIDR برای برنامههای سمت سرور که فراخوانیهای REST API سرویس وب را صادر میکنند.
شما با اضافه کردن یک یا چند محدودیت کاربردی از انواعی که میخواهید مجاز کنید، یک کلید را محدود میکنید، و پس از آن فقط درخواستهای ارسالی از این منابع مجاز میشوند.
محدودیتهای API شما میتوانید APIها، SDKها یا سرویسهای پلتفرم نقشههای گوگل را که کلید API شما میتواند در آنها استفاده شود، محدود کنید. محدودیتهای API فقط درخواستها را به APIها و SDKهایی که شما مشخص میکنید، مجاز میدانند. برای هر کلید API مشخص، میتوانید هر تعداد محدودیت API که لازم باشد، تعیین کنید. لیست APIهای موجود شامل تمام APIهای فعال در یک پروژه است.
تنظیم محدودیت برنامه برای کلید API
صفحه اعتبارنامههای پلتفرم نقشههای گوگل (Google Maps Platform Credentials) در کنسول گوگل کلود (Google Cloud console) را باز کنید.
کلید API مورد نظر برای محدود کردن را انتخاب کنید.
در صفحه ویرایش کلید API ، در قسمت محدودیتهای کلید ، گزینه تنظیم محدودیت برنامه را انتخاب کنید.
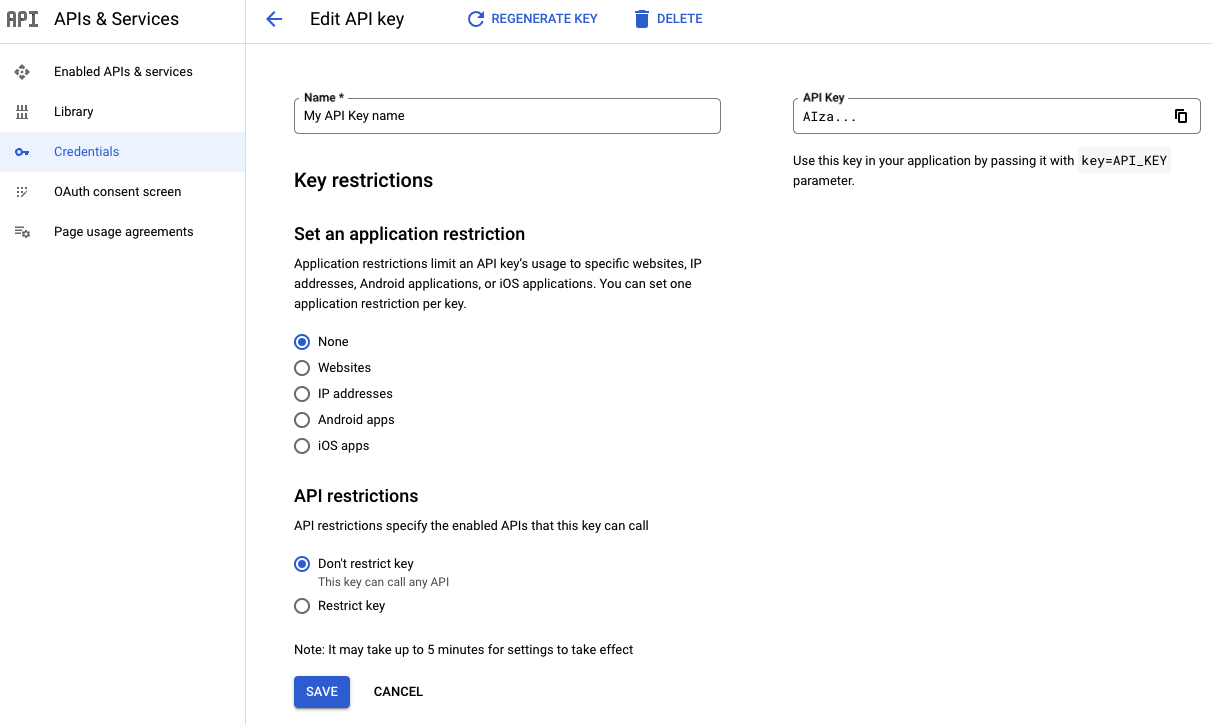
یکی از انواع محدودیتها را انتخاب کنید و اطلاعات درخواستی را مطابق فهرست محدودیتها ارائه دهید.
نوع محدودیت توضیحات وبسایتها یک یا چند وبسایت ارجاعدهنده را مشخص کنید. - طرحهای URI ارجاعدهنده که به طور جهانی پشتیبانی میشوند،
httpsوhttpهستند. تضمینی برای عملکرد صحیح طرحهای دیگر وجود ندارد، زیرا مرورگرهای وب مدرن به دلایل حفظ حریم خصوصی، هدر «ارجاعدهنده» را در درخواستهای خروجی ارسال نمیکنند. - همیشه کل رشته ارجاع، شامل طرح پروتکل، نام میزبان و پورت اختیاری (مثلاً
https://google.com) را ارائه دهید. - شما میتوانید از کاراکترهای wildcard برای تأیید همه زیر دامنهها استفاده کنید. برای مثال،
https://*.google.comهمه سایتهایی را که به.google.comختم میشوند، میپذیرد. - هنگام تأیید ارجاعدهندههای مسیر کامل، مثلاً
https://google.com/some/path، مراقب باشید، زیرا اکثر مرورگرهای وب به دلایل حفظ حریم خصوصی، مسیر را از درخواستهای بینمرجعی حذف میکنند.
آدرسهای IP یک یا چند آدرس IPv4 یا IPv6 یا زیرشبکهها را با استفاده از نمادگذاری CIDR مشخص کنید. آدرسهای IP باید با آدرس منبعی که سرورهای پلتفرم نقشههای گوگل مشاهده میکنند، مطابقت داشته باشند. اگر از ترجمه آدرس شبکه (NAT) استفاده میکنید، این آدرس معمولاً با آدرس IP عمومی دستگاه شما مطابقت دارد. برنامههای اندروید نام بسته اندروید (از فایل
AndroidManifest.xml) و اثر انگشت گواهی امضای SHA-1 هر برنامه اندرویدی که میخواهید مجاز کنید را اضافه کنید.- برنامههای اندروید را انتخاب کنید.
- روی + افزودن کلیک کنید.
- نام بسته و اثر انگشت گواهی SHA-1 خود را وارد کنید. برای مثال:
com.example.android.mapexample
BB:0D:AC:74:D3:21:E1:43:67:71:9B:62:91:AF:A1:66:6E:44:5D:75
- روی ذخیره کلیک کنید.
دو نوع گواهی وجود دارد:
- گواهی اشکالزدایی : فقط از این نوع گواهی برای برنامههایی که آزمایش میکنید و سایر کدهای غیرتولیدی استفاده کنید. سعی نکنید برنامهای را که با گواهی اشکالزدایی امضا شده است منتشر کنید. ابزارهای SDK اندروید هنگام اجرای یک نسخه اشکالزدایی، این گواهی را بهطور خودکار تولید میکنند.
- گواهی انتشار : از این گواهی زمانی استفاده کنید که آماده انتشار برنامه خود در یک فروشگاه برنامه هستید. ابزارهای SDK اندروید این گواهی را هنگام اجرای نسخه آزمایشی تولید میکنند.
برای اطلاعات بیشتر در مورد امضای برنامه اندروید و گواهینامهها، به راهنمای امضای برنامه خود مراجعه کنید.
اگر از امضای برنامه Play برای دریافت اثر انگشت گواهی امضا استفاده میکنید، به بخش «کار با ارائهدهندگان API» مراجعه کنید. اگر کلید امضای خود را مدیریت میکنید، به «امضای خودکار برنامه» مراجعه کنید یا به دستورالعملهای محیط ساخت خود مراجعه کنید.
اپلیکیشنهای iOS شناسه بسته نرمافزاری هر برنامه iOS که میخواهید مجاز کنید را اضافه کنید.
- برنامههای iOS را انتخاب کنید.
- روی + افزودن کلیک کنید.
- شناسه بسته (bundle ID) را برای پذیرش درخواستها از برنامه iOS با آن شناسه اضافه کنید.
- روی ذخیره کلیک کنید.
برای توصیههایی برای محدودیت برنامه، به محدودیت برنامه پیشنهادی مراجعه کنید.
- طرحهای URI ارجاعدهنده که به طور جهانی پشتیبانی میشوند،
ذخیره را انتخاب کنید.
تنظیم محدودیتهای API برای یک کلید API
صفحه اعتبارنامههای پلتفرم نقشههای گوگل (Google Maps Platform Credentials) در کنسول گوگل کلود (Google Cloud console) را باز کنید.
کلید API مورد نظر برای محدود کردن را انتخاب کنید.
در صفحه ویرایش کلید API ، در قسمت محدودیتهای API :
کلید محدود کردن را انتخاب کنید.
بخش Select APIs را باز کنید و APIها یا SDKهایی را که میخواهید برنامهتان با استفاده از کلید API به آنها دسترسی داشته باشد، انتخاب کنید.
اگر API یا SDK مورد نظر در لیست نیست، باید آن را فعال کنید. برای جزئیات بیشتر، به بخش فعال کردن یک یا چند API یا SDK مراجعه کنید.
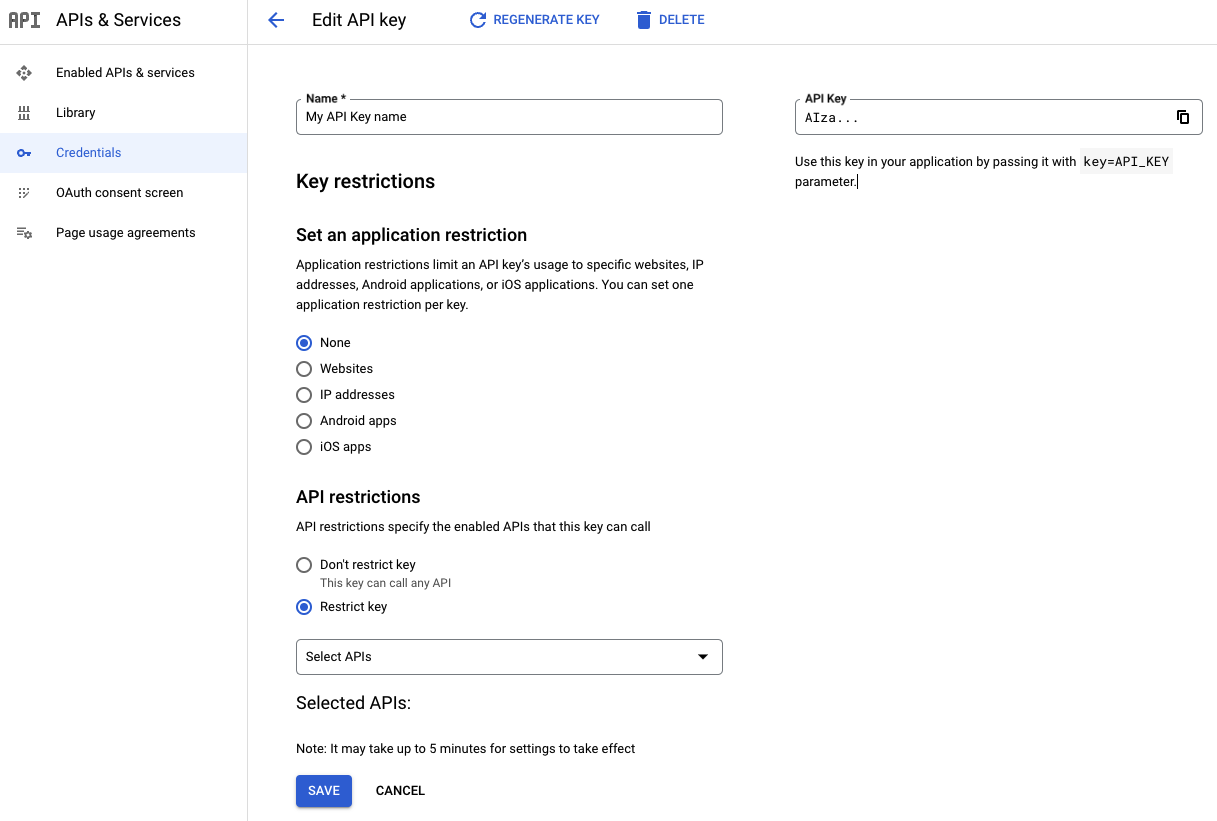
ذخیره را انتخاب کنید.
این محدودیت پس از این مرحله بخشی از تعریف کلید API میشود. مطمئن شوید که جزئیات مناسب را ارائه میدهید و برای ذخیره محدودیتهای کلید API خود، گزینه «ذخیره» را انتخاب کنید. برای اطلاعات بیشتر، به راهنمای «دریافت کلید API» در مستندات مربوط به API یا SDK خاص مورد نظر خود مراجعه کنید.
برای محدودیتهای توصیهشده API، به محدودیتهای توصیهشده API مراجعه کنید.
میزان استفاده از کلید API خود را بررسی کنید
اگر میخواهید کلیدهای API را پس از ایجاد محدود کنید، یا اگر میخواهید ببینید چه APIهایی توسط یک کلید استفاده میشوند تا بتوانید آنها را محدود کنید، باید میزان استفاده از کلید API خود را بررسی کنید. این مراحل به شما نشان میدهد که یک کلید API در کدام سرویسها و روشهای API استفاده میشود. اگر هرگونه استفادهای فراتر از سرویسهای پلتفرم نقشههای گوگل مشاهده کردید، بررسی کنید تا مشخص شود که آیا برای جلوگیری از استفاده ناخواسته نیاز به اضافه کردن محدودیتهای بیشتر دارید یا خیر. میتوانید از کاوشگر معیارهای کنسول ابری پلتفرم نقشههای گوگل برای تعیین محدودیتهای API و برنامههایی که باید برای کلید API شما اعمال شوند، استفاده کنید:
APIهایی که از کلید API شما استفاده میکنند را تعیین کنید
گزارشهای معیارهای زیر به شما امکان میدهند تعیین کنید کدام APIها از کلیدهای API شما استفاده میکنند. از این گزارشها برای انجام موارد زیر استفاده کنید:
- ببینید چگونه از کلیدهای API شما استفاده میشود
- استفاده غیرمنتظره را تشخیص دهید
- به بررسی ایمن بودن حذف یک کلید استفاده نشده کمک کنید. برای اطلاعات بیشتر در مورد حذف یک کلید API، به «حذف کلیدهای API استفاده نشده» مراجعه کنید.
هنگام اعمال محدودیتهای API، از این گزارشها برای ایجاد فهرستی از APIها برای تأیید یا اعتبارسنجی توصیههای محدودیت کلید API که به صورت خودکار ایجاد شدهاند، استفاده کنید. برای اطلاعات بیشتر در مورد محدودیتهای توصیهشده، به اعمال محدودیتهای توصیهشده مراجعه کنید. برای اطلاعات بیشتر در مورد استفاده از کاوشگر Metrics، به ایجاد نمودار با کاوشگر Metrics مراجعه کنید.
به جستجوگر معیارهای کنسول گوگل کلود بروید
وارد سیستم شوید و پروژه مربوط به کلیدهای API مورد نظر خود را انتخاب کنید.
برای نوع API خود به صفحه کاوشگر معیارها بروید:
برای کلیدهای API که از هر API به جز Maps Embed API استفاده میکنند : به صفحه کاوشگر معیارها بروید.
برای کلیدهای API با استفاده از Maps Embed API : به Metrics Explorer بروید.
هر کلید API را بررسی کنید:
گزینه افزودن فیلتر را انتخاب کنید.
برچسب
credential_idرا انتخاب کنید.مقدار مربوط به کلیدی که میخواهید بررسی کنید را انتخاب کنید.
توجه داشته باشید که این کلید API برای کدام APIها استفاده میشود و تأیید کنید که این استفاده مورد انتظار است.
پس از انجام این کار، در انتهای خط فیلتر فعال، گزینه Remove filter انتخاب کنید تا فیلتر اضافی حذف شود.
برای کلیدهای باقی مانده تکرار کنید.
کلیدهای API خود را فقط به APIهایی که استفاده میشوند محدود کنید.
اگر متوجه استفاده غیرمجاز شدید، به بخش «مدیریت استفاده غیرمجاز از کلید API» مراجعه کنید.
با استفاده از کاوشگر معیارها، نوع صحیح محدودیت برنامه را انتخاب کنید
پس از تأیید و انجام هرگونه اقدام لازم برای اطمینان از اینکه کلید API شما فقط برای سرویسهای پلتفرم نقشههای گوگل که از آنها استفاده میکند، استفاده میشود، بررسی کنید که کلید API محدودیتهای برنامه صحیحی را نیز داشته باشد.
اگر کلید API شما محدودیتهای کلید API توصیهشدهای دارد، آنها را اعمال کنید. برای اطلاعات بیشتر، به «اعمال محدودیتهای کلید API توصیهشده» مراجعه کنید.
اگر کلید API شما توصیههای محدودیتی ندارد، نوع محدودیت برنامهای که میخواهید اعمال کنید را بر اساس platform_type گزارششده با استفاده از کاوشگر Metrics تعیین کنید:
به جستجوگر معیارهای کنسول گوگل کلود بروید
وارد سیستم شوید و پروژه مربوط به APIهایی که میخواهید بررسی کنید را انتخاب کنید.
به این صفحهی جستجوگر معیارها بروید: جستجوگر معیارها .
هر کلید API را بررسی کنید:
گزینه افزودن فیلتر را انتخاب کنید.
برچسب
credential_idرا انتخاب کنید.مقدار مربوط به کلیدی که میخواهید بررسی کنید را انتخاب کنید.
پس از انجام این کار، در انتهای خط فیلتر فعال، گزینه Remove filter انتخاب کنید تا فیلتر اضافی حذف شود.
برای کلیدهای باقی مانده تکرار کنید.
وقتی نوع پلتفرم را برای کلیدهای API خود مشخص کردید، محدودیت برنامه را برای آن
platform_typeاعمال کنید:PLATFORM_TYPE_JS: محدودیتهای وبسایت را روی کلید اعمال میکند.PLATFORM_TYPE_ANDROID: محدودیتهای برنامههای اندروید را روی کلید اعمال میکند.PLATFORM_TYPE_IOS: محدودیتهای برنامههای iOS را روی کلید اعمال میکند.PLATFORM_TYPE_WEBSERVICE: برای محدود کردن صحیح کلید، ممکن است مجبور شوید به محدودیتهای آدرس IP روی آن تکیه کنید.برای توصیههایی در مورد API استاتیک نقشهها و API استاتیک نمای خیابان، به بخش «حفاظت از کاربرد API استاتیک وب» مراجعه کنید.
برای توصیههای مربوط به API جاسازی نقشهها، به وبسایتهای دارای API جاسازی نقشهها مراجعه کنید.
کلید API من از چندین نوع پلتفرم استفاده میکند: ترافیک شما نمیتواند به درستی با یک کلید API واحد ایمن شود. شما باید به چندین کلید API مهاجرت کنید. برای اطلاعات بیشتر، به «مهاجرت به چندین کلید API» مراجعه کنید.
برای هر برنامه از کلیدهای API جداگانه استفاده کنید
این روش، دامنه هر کلید را محدود میکند. اگر یک کلید API به خطر بیفتد، میتوانید کلید آسیبدیده را بدون نیاز به بهروزرسانی سایر کلیدهای API خود حذف یا تغییر دهید. میتوانید تا ۳۰۰ کلید API در هر پروژه ایجاد کنید. برای اطلاعات بیشتر، به محدودیتهای کلیدهای API مراجعه کنید.
اگرچه یک کلید API برای هر برنامه برای اهداف امنیتی ایدهآل است، اما میتوانید از کلیدهای محدود شده در چندین برنامه استفاده کنید، مادامی که از همان نوع محدودیت برنامه استفاده کنند.
محدودیتهای توصیهشده برای کلید API را اعمال کنید
برای برخی از صاحبان پروژه، ویراستاران و مدیران کلید API، کنسول Google Cloud محدودیتهای خاصی را برای کلید API بدون محدودیت بر اساس میزان استفاده و فعالیت آنها در پلتفرم Google Maps پیشنهاد میدهد.
در صورت وجود، توصیهها به صورت گزینههای از پیش پر شده در صفحه اعتبارنامههای پلتفرم نقشههای گوگل نمایش داده میشوند.
APIها و SDKهای پلتفرم نقشههای گوگل که توسط توصیههای خودکار پشتیبانی میشوند
API جاوا اسکریپت نقشهها، شامل سرویس مسیرها (قدیمی)، سرویس ماتریس فاصله (قدیمی)، سرویس ارتفاع، سرویس ژئوکدینگ کلاس مکان، ویجت تکمیل خودکار مکان (جدید)، API دادههای تکمیل خودکار مکان، کتابخانه مکانها، سرویس مکانها، ویجت تکمیل خودکار مکان و کیت رابط کاربری مکانها
API استاتیک نقشهها و API استاتیک نمای خیابان
API جاسازی نقشهها
کیت توسعه نرمافزار نقشهها برای اندروید، کیت توسعه نرمافزار ناوبری برای اندروید، کیت توسعه نرمافزار مکانها برای اندروید و کیت رابط کاربری مکانها در اندروید
کیت توسعه نرمافزار نقشهها برای iOS، کیت توسعه نرمافزار ناوبری برای iOS، کیت توسعه نرمافزار مکانها برای iOS، کیت توسعه نرمافزار سوئیفت مکانها برای iOS و کیت رابط کاربری مکانها در iOS.
دلایلی که ممکن است یک توصیه را نبینید یا یک توصیه ناقص را ببینید
دلایل عدم مشاهده توصیه
شما (همچنین) در حال استفاده از کلید API در سرویسهایی غیر از سرویسهای پلتفرم نقشههای گوگل یا سرویسهای پلتفرم نقشههایی هستید که هنوز توسط توصیههای خودکار پشتیبانی نمیشوند .
اگر در سرویسهای دیگر شاهد استفاده از آن هستید، بدون انجام موارد زیر، این توصیه را اعمال نکنید :
تأیید کنید که استفاده از API که در مرورگر معیارهای کنسول Google Cloud مشاهده میکنید، قانونی است.
سرویسهای ناموجود را به صورت دستی به لیست APIهایی که باید مجاز شوند اضافه کنید .
هرگونه محدودیت برنامهای که برای سرویسهای اضافه شده به لیست API وجود ندارد را به صورت دستی اضافه کنید . اگر مورد اضافه شده شما به نوع متفاوتی از محدودیتهای برنامه نیاز دارد، به Migrate to multiple API keys مراجعه کنید.
کلید API شما در SDKها یا APIهای سمت کلاینت استفاده نمیشود.
شما از کلید API در یک برنامه یا وبسایت کمحجم استفاده میکنید که در ۶۰ روز گذشته هیچ کاربردی نداشته است.
شما اخیراً یک کلید جدید ایجاد کردهاید، یا اخیراً یک کلید موجود را در یک برنامه جدید مستقر کردهاید. در این صورت، فقط چند روز دیگر صبر کنید تا توصیهها بهروزرسانی شوند.
شما از کلید API در چندین برنامه استفاده میکنید که به انواع متناقضی از محدودیتهای برنامه نیاز دارند، یا از یک کلید API مشابه در برنامهها یا وبسایتهای مختلف زیادی استفاده میکنید. در هر دو صورت، به عنوان بهترین روش، باید به چندین کلید مهاجرت کنید. برای جزئیات بیشتر، به «مهاجرت به چندین کلید API» مراجعه کنید.
دلایل مشاهده یک توصیهنامه ناقص
شما از کلید API در یک برنامه یا وبسایت کمحجم استفاده میکنید که در ۶۰ روز گذشته هیچ کاربردی نداشته است.
شما اخیراً شروع به استفاده از یک کلید موجود در یک API یا سرویس جدید کردهاید، و خط لوله توصیه محدودیت کلید API خودکار، هنوز معیارهای استفاده بهروز شده را پردازش نکرده است. انتشار معیارهای استفاده ممکن است چند روز طول بکشد.
اگر در سرویسهای دیگر شاهد استفاده از آن هستید، بدون انجام موارد زیر، این توصیه را اعمال نکنید :
تأیید کنید که استفاده از API که در مرورگر معیارهای کنسول Google Cloud مشاهده میکنید، قانونی است.
سرویسهای ناموجود را به صورت دستی به لیست APIهایی که باید مجاز شوند اضافه کنید .
هرگونه محدودیت برنامهای که برای سرویسهای اضافه شده به لیست API وجود ندارد را به صورت دستی اضافه کنید . اگر مورد اضافه شده شما به نوع متفاوتی از محدودیتهای برنامه نیاز دارد، به Migrate to multiple API keys مراجعه کنید.
مگر اینکه فوراً نیاز به محدود کردن یک کلید داشته باشید، مثلاً به دلیل استفاده غیرمجاز، میتوانید یک یا دو روز صبر کنید تا توصیهها به نتیجه برسند.
دلایلی که ممکن است توصیههایی را ببینید که در نمودارها قابل مشاهده نیستند
برنامه یا وبسایت شما فقط ترافیک بسیار کوتاهی ارسال کرده است. در این حالت، از نمای CHART به نمایش TABLE یا هر دو تغییر دهید، زیرا میزان استفاده هنوز در راهنما قابل مشاهده است. برای اطلاعات بیشتر، به بخش تغییر راهنمای کامل نمودار مراجعه کنید.
ترافیک شما از API نقشههای جاسازیشده است. برای دستورالعملها، به تعیین APIهایی که از کلید API شما استفاده میکنند ، مراجعه کنید.
ترافیک برنامه یا وبسایت خارج از محدوده تاریخ موجود در مرورگر معیارهای کنسول Google Cloud است.
برای اعمال محدودیتهای توصیهشده
صفحه اعتبارنامههای پلتفرم نقشههای گوگل (Google Maps Platform Credentials) در کنسول گوگل کلود (Google Cloud console) را باز کنید.
در صورت وجود، اعمال محدودیتهای توصیهشده را انتخاب کنید.
برای تأیید اینکه کلید API در کدام سرویسها استفاده میشود، گزینه «بررسی میزان استفاده از API» را انتخاب کنید. اگر سرویسهایی غیر از سرویسهای پلتفرم نقشههای گوگل را مشاهده کردید، مکث کنید تا مراحل پیشنهادی بالا را به صورت دستی بررسی کنید. مراحل عیبیابی را در ابتدای بخش «اعمال محدودیتهای کلید API توصیهشده» مشاهده کنید.
دوباره بررسی کنید که محدودیتهای از پیش پر شده با وبسایتها و برنامههایی که انتظار دارید از کلید API شما در آنها استفاده شود، مطابقت داشته باشند.
بهترین روش : هرگونه محدودیت برنامه یا API که به سرویسهای شما وابسته نیست را مستندسازی و حذف کنید. اگر به دلیل وابستگی غیرمنتظره چیزی از کار افتاد، میتوانید برنامهها یا APIهای مورد نیاز را دوباره اضافه کنید.
اگر متوجه شدید که یک برنامه، وبسایت یا API به وضوح در پیشنهاد شما وجود ندارد، آن را به صورت دستی اضافه کنید یا چند روز صبر کنید تا پیشنهاد بهروزرسانی شود.
اگر در مورد پیشنهاد پیشنهادی خود به کمک بیشتری نیاز دارید، با پشتیبانی تماس بگیرید .
اعمال را انتخاب کنید.
اگر درخواست شما پس از درخواست توصیه رد شود، چه باید کرد؟
اگر متوجه شدید که یک برنامه یا وبسایت پس از اعمال محدودیت رد میشود، به دنبال محدودیت برنامهای باشید که باید در پیام خطای پاسخ API اضافه کنید.
SDKها و APIهای سمت کلاینت
- برنامههای مبتنی بر مرورگر و وبویو
مرورگرهای مدرن معمولاً به دلایل حفظ حریم خصوصی، هدر
Refererرا در درخواستهای بین مبدا حذف میکنند و اغلب آن را بهOriginمحدود میکنند. با این حال، رفتار دقیق آن بهreferrer-policyاعمال شده توسط سایت میزبان بستگی دارد و ممکن است بر اساس مرورگر و نسخه کاربر نیز متفاوت باشد.برنامههای وب که از طرحهای URI مبهم یا محلی برای بارگذاری محتوا استفاده میکنند، معمولاً مرورگر رندر یا نمای وب، هدر
Refererرا از هرگونه فراخوانی خروجی کاملاً حذف میکنند، که ممکن است باعث شود درخواستها با استفاده از کلیدهای API با محدودیتهای وبسایت با شکست مواجه شوند.برای راهنمایی بیشتر، به میزبانی برنامههای مبتنی بر مرورگر خود روی یک سرور مراجعه کنید.
دستورالعملهای عیبیابی برای برنامههای مبتنی بر مرورگر و وبویو:
برای API جاوا اسکریپت Maps، برای جزئیات بیشتر در مورد نحوه تأیید برنامه خود، به کنسول اشکالزدایی مرورگر مراجعه کنید.
طرحهای URI نامتعارف تا حدی پشتیبانی میشوند. اگر بخشهایی از برنامه شما حتی پس از تأیید ارجاعدهنده مورد نیاز، با طرح URI نامتعارف کار نکند، احتمالاً باید برنامه خود را از راه دور روی یک سرور میزبانی کنید و آن را از طریق HTTPS (یا HTTP) بارگذاری کنید.
اگر در مورد طرحهای URI نامتعارف به کمک نیاز دارید، با پشتیبانی تماس بگیرید .
سایر APIهای پلتفرم نقشهها معمولاً ارجاعدهندهای را که باید در پاسخ خطای API تأیید کنید، برمیگردانند، با این فرض که کلاینت این اطلاعات را همراه با درخواست رد شده ارسال کرده است.
طرحهای URI نامتعارف پشتیبانی نمیشوند .
- برنامههای اندروید
از Android Debug Bridge (adb) یا Logcat استفاده کنید
- اپلیکیشنهای iOS
مشاهده پیامهای لاگ را ببینید
برنامههایی که مستقیماً سرویسهای وب را فراخوانی میکنند
برای برنامههایی که مستقیماً و بدون SDK پلتفرم نقشههای گوگل، HTTPS REST API یا نقاط انتهایی gRPC را فراخوانی میکنند، به زیر مراجعه کنید:
- اپلیکیشنهای اندروید و iOS
اگر برنامه اندروید یا iOS شما مستقیماً و بدون استفاده از هیچ یک از SDK های کلاینت موجود در پلتفرم نقشههای گوگل، سرویسهای پلتفرم نقشه را فراخوانی میکند، برای نکات عیبیابی بیشتر به برنامههای اندروید و برنامههای iOS مراجعه کنید و برای بهترین شیوههای امنیتی فعلی برای موارد استفاده موبایل، به Secure client-side web service مراجعه کنید .
اگر برنامه شما پاسخهای خطای API پلتفرم نقشهها را ثبت میکند، دستورالعملهای فوق برای SDKهای سمت کلاینت نیز ممکن است برای عیبیابی مشکلات احراز هویت مفید باشند.
- برنامههای سمت سرور
برنامههای سمت سرور که به کلیدهای API متکی هستند، از طریق محدودیتهای آدرس IP به بهترین شکل ایمن میشوند. اگر محدودیتهای آدرس IP را برای کلید خود اعمال کردهاید و سرویس شما پاسخهای خطای API پلتفرم نقشهها را ثبت میکند، برای اطلاعات بیشتر، گزارشهای سیستم خود را بررسی کنید. پاسخ خطا شامل آدرس IP سروری است که باید آن را مجاز کنید.
- برنامههای مبتنی بر مرورگر یا وبویو
اگرچه API استاتیک Maps، API استاتیک Street View و APIهای جدیدتر پلتفرم Google Maps نیز از محدودیتهای ارجاعدهنده پشتیبانی میکنند، توجه داشته باشید که مرورگرهای وب یا وبویوها احتمالاً هدر
Refererرا برای درخواستهای بینمنبعی بهOriginمحدود میکنند و احتمالاً از ارسال کامل آن، مثلاً برای منابع محلی یا برای منابعی که از طریق پروتکلهایی غیر از HTTP یا HTTPS ارائه میشوند، خودداری میکنند.اگر نمیتوانید از Maps JavaScript API در برنامه خود استفاده کنید و محدودیتهای وبسایت کار نمیکنند، برای نحوهی فراخوانی ایمن وب سرویس پلتفرم Maps از درون برنامهی سمت کلاینت مبتنی بر مرورگر خود، به بخش «فراخوانیهای وب سرویس سمت کلاینت امن» مراجعه کنید.
نکاتی برای بررسی محدودیتهای API
برای بررسی محدودیتهای API مورد نیاز خود، به بخش «تعیین APIهایی که از کلید API شما استفاده میکنند» مراجعه کنید.
اگر نمیتوانید تعیین کنید که کدام محدودیتها را باید اعمال کنید:
- محدودیتهای فعلی را برای مراجعات بعدی مستند کنید.
- آنها را موقتاً حذف کنید تا مشکل را بررسی کنید. میتوانید با استفاده از مراحل موجود در بخش «استفاده از کلید API خود را بررسی کنید» ، میزان استفاده خود را در طول زمان بررسی کنید.
- در صورت نیاز، با پشتیبانی تماس بگیرید .
کلیدهای API استفاده نشده را حذف کنید
قبل از حذف کلید API، مطمئن شوید که در محیط عملیاتی استفاده نمیشود. اگر هیچ ترافیک موفقیتآمیزی وجود ندارد، احتمالاً حذف کلید بیخطر است. برای اطلاعات بیشتر، به «بررسی میزان استفاده از کلید API» مراجعه کنید.
برای حذف کلید API:
صفحه اعتبارنامههای پلتفرم نقشههای گوگل (Google Maps Platform Credentials) در کنسول گوگل کلود (Google Cloud console) را باز کنید.
کلید API مورد نظر برای حذف را انتخاب کنید.
دکمه حذف را در نزدیکی بالای صفحه انتخاب کنید.
در صفحه حذف اعتبارنامه ، گزینه حذف را انتخاب کنید.
حذف یک کلید API چند دقیقه طول میکشد تا منتشر شود. پس از اتمام انتشار، هرگونه ترافیکی که از کلید API حذف شده استفاده میکند، رد میشود.
هنگام چرخاندن کلیدهای API مراقب باشید
چرخاندن یک کلید API، یک کلید جدید ایجاد میکند که تمام محدودیتهای کلید قدیمی را دارد. در طول این بازه زمانی، هر دو کلید قدیمی و جدید پذیرفته میشوند و به شما این فرصت را میدهند که برنامههای خود را برای استفاده از کلید جدید منتقل کنید.
قبل از چرخاندن کلید API :
ابتدا سعی کنید کلیدهای API خود را همانطور که در بخش «محدود کردن کلیدهای API» توضیح داده شده است، محدود کنید.
اگر محدود کردن کلید API شما به دلیل انواع محدودیتهای متناقض برنامه امکانپذیر نیست، همانطور که در بخش «مهاجرت به چندین کلید API» توضیح داده شده است، به چندین کلید جدید (محدود شده) مهاجرت کنید. مهاجرت به شما امکان میدهد مهاجرت را کنترل کنید و جدول زمانی را به کلیدهای API جدید اعمال کنید.
اگر پیشنهادات قبلی امکانپذیر نبود و برای جلوگیری از استفاده غیرمجاز باید کلید API خود را تغییر دهید، این مراحل را دنبال کنید:
صفحه اعتبارنامههای پلتفرم نقشههای گوگل (Google Maps Platform Credentials) در کنسول گوگل کلود (Google Cloud console) را باز کنید.
کلید API مورد نظر برای چرخش را باز کنید.
در بالای صفحه، کلید چرخش (Rotate key) را انتخاب کنید.
در صورت تمایل، نام کلید API را تغییر دهید.
ایجاد را انتخاب کنید.
برنامههای خود را برای استفاده از کلید جدید بهروزرسانی کنید.
پس از اینکه برنامههای خود را برای استفاده از کلید جدید بهروزرسانی کردید، با کلیک بر روی دکمهی «حذف کلید قبلی» در بخش «کلید قبلی» در صفحهی کلید API جدید، کلید قدیمی را حذف کنید.
به چندین کلید API مهاجرت کنید
برای تغییر از استفاده از یک کلید API برای چندین برنامه به یک کلید API منحصر به فرد برای هر برنامه، موارد زیر را انجام دهید:
مشخص کنید کدام برنامهها به کلیدهای جدید نیاز دارند :
- بهروزرسانی برنامههای وب آسانترین روش است، زیرا شما تمام کد را کنترل میکنید. برای بهروزرسانی کلیدهای تمام برنامههای تحت وب خود برنامهریزی کنید.
- برنامههای تلفن همراه بسیار سختتر هستند، زیرا مشتریان شما باید برنامههای خود را قبل از استفاده از کلیدهای جدید بهروزرسانی کنند.
ایجاد و محدود کردن کلیدهای جدید : هم یک محدودیت برنامه و هم حداقل یک محدودیت API اضافه کنید. برای اطلاعات بیشتر، به بهترین شیوههای توصیهشده مراجعه کنید.
کلیدهای جدید را به برنامههای خود اضافه کنید : برای برنامههای تلفن همراه، این فرآیند ممکن است ماهها طول بکشد تا همه کاربران شما به آخرین برنامه با کلید API جدید بهروزرسانی کنند.
تقسیم استفاده از سمت کلاینت و سمت سرور به پروژههای جداگانه
اگر نیاز دارید که سرویسهای پلتفرم نقشههای گوگل را هم از طریق برنامههای سمت سرور و هم مستقیماً از برنامههای سمت کلاینت که روی دستگاههای کاربر نهایی اجرا میشوند، فراخوانی کنید، گوگل توصیه میکند که استفاده خود را بین دو پروژه جداگانه تقسیم کنید.
این رویکرد به شما امکان میدهد محدودیتهای سهمیهای مناسب برای هر دقیقه و هر کاربر را در اکثر سرویسهای پلتفرم نقشههای گوگل در پروژه سمت کلاینت خود اعمال کنید و به شما کمک میکند تا مطمئن شوید که همه کاربران نهایی سهم منصفانهای از سهمیه کلی پروژه شما را بدون تأثیر بر یکدیگر دریافت میکنند.
با این حال، از آنجایی که محدودیتهای سهمیه هر کاربر، هم برنامههای سمت کلاینت و هم برنامههای سمت سرور را تحت تأثیر قرار میدهد، اگر برای کارهای سمت سرور خود به پهنای باند بالایی نیز نیاز دارید، یک پروژه جداگانه برای این مورد استفاده تنظیم کنید که با محدودیت سهمیه هر کاربر بالاتر پیکربندی شده باشد یا اصلاً هیچ محدودیتی نداشته باشد.
غیرفعال کردن سرویسهای بلااستفاده
سرویسهای بلااستفاده را در یک پروژه فعال نگذارید، زیرا این روش در برابر سوءاستفاده آسیبپذیر است، به خصوص اگر تمام کلیدهای API عمومی خود را محدود نکرده باشید. به عنوان یک روش بهتر، فقط زمانی یک سرویس را در یک پروژه فعال کنید که برنامههای شما به آن نیاز داشته باشند.
اضافه کردن محدودیتهای API روی یک کلید، از استفاده آن در سرویسهایی که برای آنها مجوز صادر نشده است، جلوگیری میکند، اما محدودیتهای API فقط برای آن کلید خاص اعمال میشوند. غیرفعال کردن یک سرویس در سطح پروژه، از استفاده غیرمجاز از سرویس روی هر کلید مرتبط با پروژه جلوگیری میکند.
استفاده از SDK های سمت کلاینت
هنگام استفاده از SDK های ارائه شده سمت کلاینت پلتفرم نقشه های گوگل، شما همیشه قادر خواهید بود محدودیت های مناسبی را برای کلید API خود اعمال کنید تا استفاده از سرویس خود را ایمن کنید.
استفاده از SDK های سمت کلاینت همچنین به شما امکان میدهد مکانیسم امنیتی پیشرفتهتری مانند Firebase App Check را روی سطوح API پلتفرم Maps که از آن پشتیبانی میکنند، اتخاذ کنید. برای جزئیات بیشتر به بخش «استفاده از App Check برای ایمنسازی کلید API» مراجعه کنید.
اگر SDK های سمت کلاینت برای پلتفرم شما در دسترس نیستند، به بخش «امنسازی فراخوانیهای سرویس وب سمت کلاینت» مراجعه کنید.
برای اطلاع از در دسترس بودن SDK های پلتفرم نقشه های گوگل سمت کلاینت برای پلتفرم های مختلف، به محدودیت های پیشنهادی برنامه و API مراجعه کنید.
محافظت از استفاده از API وب استاتیک
APIهای وب استاتیک، مانند API استاتیک نقشهها و API استاتیک نمای خیابان، مشابه فراخوانیهای API سرویس وب هستند.
شما هر دو را با استفاده از یک HTTPS REST API فراخوانی میکنید و معمولاً URL درخواست API را روی سرور ایجاد میکنید. با این حال، به جای بازگرداندن پاسخ JSON، APIهای وب استاتیک تصویری تولید میکنند که میتوانید آن را در کد HTML تولید شده جاسازی کنید. مهمتر از همه، معمولاً این کلاینت کاربر نهایی است، نه سرور، که سرویس پلتفرم نقشههای گوگل را فراخوانی میکند.
استفاده از امضای دیجیتال
به عنوان یک روش بهینه، همیشه علاوه بر کلید API از امضاهای دیجیتال نیز استفاده کنید. همچنین، بررسی کنید که میخواهید روزانه چند درخواست امضا نشده مجاز باشد و سهمیه درخواستهای امضا نشده خود را بر اساس آن تنظیم کنید .
برای جزئیات بیشتر در مورد امضاهای دیجیتال، به راهنمای امضای دیجیتال مراجعه کنید.
از راز امضای خود محافظت کنید
برای محافظت از APIهای وب استاتیک، رمزهای امضای API خود را مستقیماً در کد یا در درخت منبع جاسازی نکنید، یا آنها را در برنامههای سمت کلاینت نمایش ندهید. برای محافظت از رمزهای امضای خود، این بهترین شیوهها را دنبال کنید:
هنگام ارائه یک صفحه وب یا در پاسخ به درخواستی از برنامه تلفن همراه خود، URL های درخواست Maps Static API و Street View Static API امضا شده خود را در سمت سرور ایجاد کنید .
برای محتوای وب استاتیک، میتوانید از ویجت «اکنون یک URL را امضا کنید» در صفحه اعتبارنامههای پلتفرم نقشههای گوگل در کنسول ابری استفاده کنید.
برای محتوای وب پویا، به نمونههای کد امضای درخواست URL موجود مراجعه کنید.
اسرار امضا را خارج از کد منبع و درخت منبع برنامه خود ذخیره کنید . اگر اسرار امضا یا هرگونه اطلاعات خصوصی دیگری را در متغیرهای محیطی قرار دهید یا فایلهایی را که جداگانه ذخیره میشوند، اضافه کنید و سپس کد خود را به اشتراک بگذارید، اسرار امضا در فایلهای مشترک گنجانده نمیشوند. اگر اسرار امضا یا هرگونه اطلاعات خصوصی دیگری را در فایلها ذخیره میکنید، فایلها را خارج از درخت منبع برنامه خود نگه دارید تا اسرار امضا از سیستم کنترل کد منبع شما دور بماند. این احتیاط به ویژه در صورتی که از یک سیستم مدیریت کد منبع عمومی مانند GitHub استفاده میکنید، بسیار مهم است.
محافظت از کلیدهای API سرویس وب
For secure use of Google Maps Platform APIs and services from client-side apps, see Use client-side SDKs and Secure client-side web service calls .
Store API keys outside of your application's source code or source tree . If you put your API keys or any other information in environment variables or include files that are stored separately and then share your code, the API keys are not included in the shared files. This is particularly important if you use a public source code management system, such as GitHub.
To help shield your web service API key against accidental use, Google recommends applying API restrictions to any key used for Maps Platform. Furthermore, also applying IP address restrictions to your web service key will protect it against help protect it against unauthorized use from other source IP addresses, even if the key accidentally leaks.
Use OAuth for server-side apps
OAuth 2.0 is an open standard for access delegation.
While the OAuth 2.0 protocol supports use cases, where an end user authorizes an application to access personal data on their behalf, the intended use case for OAuth 2.0 with Maps Platform is for the developer to utilize temporary access tokens for authorizing their application to call an API on behalf of their Google Cloud project service account with the permissions of the service account.
As a service account may have extremely broad permissions, OAuth 2.0 is recommended for authorizing server-to-server calls between a developer's trusted server-side applications and Google's Maps Platform servers.
For client-side applications running on end user devices, other authentication methods, such as API keys, are recommended.
If you want to use OAuth 2.0 to authorize server-to-server traffic, look for the OAuth topic in your API documentation.
For example, here is the OAuth topic for the Address Validation API .
Secure client-side web service calls
If client-side SDKs are not available, see the recommendations below.
Use a proxy server
Using a secure proxy server provides a solid source for interacting with a Google Maps Platform web service endpoint from a client-side application without exposing your API key, signing secret or Google Cloud service account to unauthorized users.
Key points:
Construct your Google Maps Platform requests on the proxy server. Don't allow clients to relay arbitrary API calls using the proxy.
Post-process the Google Maps Platform responses on your proxy server. Filter out data that the client doesn't need.
For more information about using a proxy server, see Living Vicariously: Using Proxy Servers with the Google Data API Client Libraries .
Secure direct mobile web service calls
If you are unable to set up a secure proxy server for your client-side app, secure your application using the following steps:
Use HTTP headers:
Android : Use the
X-Android-PackageandX-Android-CertHTTP headers.iOS : Use the
X-Ios-Bundle-IdentifierHTTP header.
Add the corresponding application restrictions to your Android or iOS key.
Before you consider issuing calls directly from your mobile application to a Google Maps Platform REST API web service, verify that requests with incorrect Android or iOS application identifiers are rejected.
If Android and iOS application restrictions are not supported on the tested endpoint, Google strongly recommends that you use a secure proxy server between your mobile clients and the Google Maps Platform web service endpoint.
Tips for Android applications:
Before you integrate your Android application with Google Maps Platform services, verify that your application ID (also called package name) is formatted correctly. For details, see Configure app module . in the Android documentation.
To pass
X-Android-Packagedirectly from your application, look it up programmatically usingContext.getPackageName().To pass
X-Android-Certdirectly from your applications, calculate the required SHA-1 fingerprint of your application signing certificates, accessible throughPackageInfo.signingInfo.If you authorize your Android application using the Google Cloud console, note that the UI expects the SHA-1 fingerprint to be a colon-delimited string, eg,
00:11:22:33:44:55:66:77:88:99:AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF:00:11:22:33. However, thegcloudtool and the API keys API expect the hexadecimal string without delimiters.
Tips for iOS applications:
Before you integrate your iOS application with Google Maps Platform services, verify that your Bundle ID is formatted correctly .
You should typically always pass the Bundle ID of your main bundle in the
X-Ios-Bundle-Identifierheader, when authorizing your iOS application.
For further information, refer to articles Manage API keys and Use API keys to access APIs .
Host your browser based apps on a server
Frameworks, such as Apache Cordova, allow you to conveniently create multi-platform hybrid apps running inside a webview. However, API key website restrictions are not guaranteed to work correctly, unless your web app is loaded using HTTP or HTTPS from a website that you control and have authorized.
Bundled resources, loaded locally from within a hybrid application, or accessed using a local file URL will in many cases prevent referrer based authorization from working as the browser engine powering your webview will omit sending the Referer header. To avoid this, host your web applications server-side, not client-side.
Alternatively, for mobile applications, consider using available native Google Maps Platform Android and iOS SDKs, instead of using a web based SDK.
Use App Check to secure your API key
Certain Maps SDKs and APIs allow you to integrate with Firebase App Check . App Check provides protection for calls from your app to Google Maps Platform by blocking traffic that comes from sources other than legitimate apps. It does this by checking for a token from an attestation provider. Integrating your apps with App Check helps to protect against malicious requests, so you're not charged for unauthorized API calls.
App Check integration instructions:
Handle unauthorized use of an API key
If you detect use of your API key that is unauthorized, do the following to address the problem:
Restrict your keys : If you've used the same key in multiple apps, migrate to multiple API keys, and use separate API keys for each app. For more details, see:
If you use the Places SDK or the Maps Javascript API, you can also use App Check to secure your API Key .
Only replace or rotate keys if the following is true:
You detect unauthorized usage on keys that either cannot be restricted or are already restricted, and App Check is not applicable.
You want to move more quickly to secure your API key and stop the abuse, even if it might impact legitimate traffic from your application.
Before proceeding, read through Be careful when rotating API keys .
If you are still having issues or need help, contact support .
Recommended application and API restrictions
The following sections suggest appropriate application and API restrictions for each Google Maps Platform API, SDK or service.
Recommended API Restrictions
The following guidelines for API restrictions apply to all Google Maps Platform services:
Restrict your API key to only the APIs you are using it for, with the following exceptions:
If your app uses the Places SDK for Android or Places SDK for iOS, authorize Places API (New) or Places API, depending on the SDK versions you use. 1
If your app uses Maps JavaScript API, always authorize it on your key.
If you also use any of the following Maps JavaScript API services, you should also authorize these corresponding APIs:
خدمات API restriction Directions Service (Legacy) Directions API (Legacy) Distance Matrix Service (Legacy) Distance Matrix API (Legacy) Elevation Service Elevation API Geocoding Service API کدگذاری جغرافیایی Place class, Place Autocomplete Widget (New) & Place Autocomplete Data API Places API (New) 2 Places Library, Places Service & Place Autocomplete Widget Places API 2
1 For more details, see the Places SDK for Android and Places SDK for iOS documentation.
2 If you are unsure if you need to authorize Places API (New) or Places API, see the Maps JavaScript API documentation.
چند مثال:
You are using the Maps SDK for Android and Places SDK for Android, so you include the Maps SDK for Android and Places API (New) as API restrictions.
Your website uses the Maps JavaScript API Elevation Service and the Maps Static API, so you add API restrictions for all of the following APIs:
- Maps JavaScript API
- Elevation API
- Maps Static API
Recommended application Restriction
وبسایتها
For websites using Maps JavaScript API services, Maps Static API or Street View Static API or calling recent Google Maps Platform services directly over the HTTPS REST API or gRPC, use the Websites application restriction:
1 For mobile applications, consider using the native Maps SDK for Android and Maps SDK for iOS .
2 For mobile applications, consider using the native Places SDK for Android and Places SDK for iOS .
3 See also Protect Static Web API usage .
Websites with the Maps Embed API
While using the Maps Embed API is no charge, you should still restrict any used API key to prevent abuse on other services.
Best practice : Create a separate API key for Maps Embed API use, and restrict this key to only the Maps Embed API. This restriction sufficiently secures the key, preventing its unauthorized use on any other Google service. For full control over where your Maps Embed API key can be used from, Google recommends also applying Websites application restrictions.
If you are unable to separate your Maps Embed API usage to a separate API key, secure your existing key using the Websites application restriction.
Apps and servers using web services
For servers and client-side apps from trusted corporate internal networks using web services together with API keys, use the IP addresses application restriction.
Use for apps and servers using these APIs:
4 For mobile applications, consider using the Navigation SDK.
5 For safe mobile usage, use a secure proxy server .
6 For client-side applications, consider using the native geolocation service offered by the platform; for example, W3C Geolocation for web browsers, LocationManager or the Fused Location Provider API for Android, or the Apple Core Location framework for iOS.
7 For mobile applications, consider using the native Places SDK for Android and Places SDK for iOS .
8 For safe client-side usage, use a secure proxy server .
برنامههای اندروید
For apps on Android, use the Android apps application restriction. Use for apps using these SDKs:
In addition, prevent accidentally checking API keys into version control by using the Secrets Gradle Plugin to inject secrets from a local file rather than storing them in the Android Manifest.
iOS apps
For apps on iOS, use the iOS apps application restriction. Use for apps and servers using these SDKs:
مطالعه بیشتر
- Manage API keys
- Use API keys to access APIs
- Optimize your Google Maps Platform usage with quotas (video)
- How to generate and restrict API keys for the Google Maps Platform (video)
- Restricting API keys
- Securing API keys when using Static Maps and Street View APIs
- 15 Google Maps platform Best Practices

