این بخش SimpleExampleServlet را معرفی میکند که سادهترین نمونه اجرای یک منبع داده است که همراه با کتابخانه ارائه میشود. این بخش همچنین دستورالعمل های گام به گام در مورد نحوه اجرا و آزمایش SimpleExampleServlet را ارائه می دهد.
معرفی SimpleExampleServlet
کلاس SimpleExampleServlet در بسته examples قرار دارد. این کلاس نمونه ای از ساده ترین پیاده سازی یک منبع داده را ارائه می دهد. SimpleExampleServlet از DataSourceServlet به ارث می برد، generateDataTable() پیاده سازی می کند و باید در یک کانتینر servlet اجرا شود.
یک قطعه از SimpleExampleServlet در زیر ارائه شده است. تابع generateDataTable داده ها را در معرض کتابخانه قرار می دهد. این تابع یک توضیح جدول داده ایجاد می کند، ستون های جدول داده را تعریف می کند و جدول داده ها را با داده ها پر می کند. کتابخانه تمام اقدامات مورد نیاز برای بازگرداندن جدول داده ها به تصویرسازی پرس و جو را انجام می دهد.
// This example extends DataSourceServlet
public class SimpleExampleServlet extends DataSourceServlet {
@Override
public DataTable generateDataTable(Query query, HttpServletRequest request) {
// Create a data table,
DataTable data = new DataTable();
ArrayList cd = new ArrayList();
cd.add(new ColumnDescription("name", ValueType.TEXT, "Animal name"));
cd.add(new ColumnDescription("link", ValueType.TEXT, "Link to wikipedia"));
cd.add(new ColumnDescription("population", ValueType.NUMBER, "Population size"));
cd.add(new ColumnDescription("vegeterian", ValueType.BOOLEAN, "Vegetarian?"));
data.addColumns(cd);
// Fill the data table.
try {
data.addRowFromValues("Aye-aye", "http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aye-aye", 100, true);
data.addRowFromValues("Sloth", "http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sloth", 300, true);
data.addRowFromValues("Leopard", "http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leopard", 50, false);
data.addRowFromValues("Tiger", "http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tiger", 80, false);
} catch (TypeMismatchException e) {
System.out.println("Invalid type!");
}
return data;
}
} اجرای و آزمایش SimpleExampleServlet
این بخش دستورالعمل هایی در مورد نحوه اجرا و آزمایش SimpleExampleServlet ارائه می دهد.
اگر قبلاً این کار را نکردهاید، برای اطلاعات در مورد پیش نیازها و دستورالعملهای نحوه دانلود و ساخت کتابخانه به بخش نصب مراجعه کنید. اگر قبلاً روی سیستم خود ندارید، مطمئن شوید که یک وب سرور را نصب کرده اید که به عنوان یک کانتینر سرولت نیز عمل می کند، مانند Apache Tomcat. دستورالعمل های این بخش مختص آپاچی تامکت در سیستم ویندوز است.
برای اجرا و آزمایش SimpleExampleServlet ، یک برنامه وب ایجاد کنید که منبع داده SimpleExampleServlet را اجرا کند، سپس یک صفحه وب نمونه را با تصویرسازی که داده های درخواست شده از منبع داده را نشان می دهد اجرا کنید. این در بخش های زیر توضیح داده شده است:
ایجاد یک برنامه وب در آپاچی تامکت
دستورالعمل های زیر را برای ایجاد یک برنامه وب در Apache Tomcat دنبال کنید یا آن را تطبیق دهید. این دستورالعمل ها مختص آپاچی تامکت در سیستم ویندوز است:
- به دایرکتوری که Tomcat را در آن نصب کرده اید بروید. این در این سند به عنوان
<tomcat_home>نوشته شده است. - به زیر شاخه
webappsبروید. - یک زیر شاخه به نام
myWebAppایجاد کنید. - به زیر شاخه ای که ایجاد کرده اید تغییر دهید و زیر شاخه دیگری به نام
WEB-INFایجاد کنید. - به زیر شاخه
WEB-INFتغییر دهید و زیر شاخه دیگری به نامlibایجاد کنید.
مسیر کامل باید<tomcat_home>/webapps/myWebApp/WEB-INF/libباشد. -
web.xmlاز<data_source_library_install>/examples/src/htmlدر پوشهWEB-INFکپی کنید. جایی که<data_source_library_install>دایرکتوری است که کتابخانه منبع داده را در آن نصب کرده اید. خطوط زیر درweb.xmlSimpleExampleServletرا تعریف و ترسیم می کند:<servlet> <servlet-name>My Servlet</servlet-name> <description>My servlet description.</description> <servlet-class>SimpleExampleServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>My Servlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/simpleexample</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
- به دایرکتوری که کتابخانه منبع داده را در آن نصب کرده اید بروید. این در این سند به عنوان
<data_source_library_install>نوشته شده است. - همه بستههای وابستگی را در
<tomcat_home>/webapps/myWebApp/WEB-INF/libکپی کنید. بسته ها در<data_source_library_install>/libنصب می شوند، مگر اینکه آنها را در دایرکتوری دیگری قرار دهید. - اگر خودتان کتابخانه را ساخته اید،
visualization-datasource-1.0.2.jarوvisualization-datasource-examples.jarرا کپی کنید.
از<data_source_library_install>/build
به<tomcat_home>/webapps/myWebApp/WEB-INF/lib.
اگر فایل فشرده را از حالت فشرده خارج کرده اید،visualization-datasource-1.0.2.jarوvisualization-datasource-examples.jarرا کپی کنید.
از<data_source_library_install>
به<tomcat_home>/webapps/myWebApp/WEB-INF/lib.
توجه داشته باشید که شماره نسخه در نام فایل jar ممکن است بسته به آخرین شماره نسخه متفاوت باشد. - تامکت را راه اندازی کنید، یا اگر تامکت در حال اجرا است، مجددا راه اندازی کنید.
- روی لینک زیر کلیک کنید:
http://localhost:8080/myWebApp/simpleexample
بسته به عرض صفحه نمایش، 6 تا 7 خط متن نمایش داده می شود.
متن باgoogle.visualization.Query.setResponseشروع می شود
و به/Tiger'},{v:80.0},{v:false}]}]}});
این داده هایی است که توسط منبع داده شما به تصویرسازی پرس و جو بازگردانده می شود.
استفاده از تجسم برای مشاهده داده ها
فایل getting_started.html در دایرکتوری <data_source_library_install>/examples/src/html می تواند برای مشاهده تجسم داده ها استفاده شود. خط زیر که از getting_started.html گرفته شده است، سرور مورد استفاده را مشخص می کند. نقشه برداری سرورلت در مرحله 8 ایجاد یک برنامه وب در آپاچی تامکت تنظیم شد.
var query = new google.visualization.Query('simpleexample');برای اطلاعات بیشتر در مورد نحوه تعیین تجسم و استفاده از زبان پرس و جو، به استفاده از نمودارها و مرجع زبان پرس و جو مراجعه کنید.
برای مشاهده تصویری از داده های ارائه شده توسط منبع داده، دستورالعمل های زیر را دنبال کرده یا تطبیق دهید:
- فایل
getting_started.htmlرا از دایرکتوری<data_source_library_install>/examples/src/htmlکپی کنید.
به دایرکتوری<tomcat_home>/webapps/myWebApp/. - روی پیوند زیر کلیک کنید http://localhost:8080/myWebApp/getting_started.html ، باید موارد زیر را مشاهده کنید:
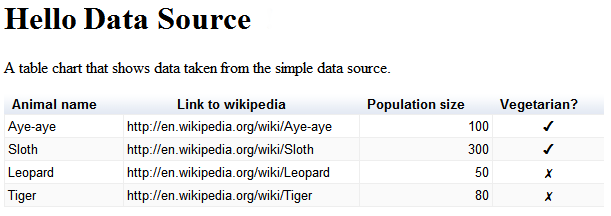
خودشه! شما اولین منبع داده خود را تنظیم کرده اید.
مراحل بعدی
مثال بعدی در بخش Using an External Data Store توضیح داده شده است. یا می توانید به مقدمه بازگردید یا پیوندهای زیر را بررسی کنید:
- برای آشنایی با پرکاربردترین کلاسهای کتابخانه، به کلاسهای کلیدی مراجعه کنید.
- برای مثالی از نحوه پیادهسازی جریان رویدادها و قابلیتهای جستجو، به تعریف قابلیتها و جریان رویدادها مراجعه کنید.
- اگر نمی خواهید از
DataSourceServletارث ببرید، می توانید یک منبع داده را همانطور که در Using Your Own Servlet توضیح داده شده است پیاده سازی کنید. به عنوان مثال، اگر یک servlet را از کلاس دیگری به ارث برده اید، ممکن است نخواهید ازDataSourceServletارث بری کنید. - اگر نمیخواهید از سرورلت استفاده کنید، به پیادهسازی منبع داده غیرسرولتی مراجعه کنید.
- برای آشنایی با نحوه انتقال پارامترها از یک برنامه کاربردی به منبع داده، به انتقال پارامترها به
DataTableGenerator.generateDataTableمراجعه کنید.
