작업별로 특정 작업으로 직접 연결되는 URL을 생성할 수 있습니다. 웹브라우저 또는 모바일 브라우저에서 어시스턴트 링크 (이전의 작업 링크)를 클릭하면 기기의 어시스턴트로 연결되고 여기에서 상응하는 작업과 직접 상호작용합니다.
유용한 어시스턴트 링크의 예는 다음과 같습니다.
- 방법 웹사이트의 음성 안내로 사용자를 연결합니다.
- '도움말 보기'에서 사용자를 고객 지원 환경으로 연결 있습니다.
- 사용자가 향후 업데이트를 선택할 수 있도록 업데이트 인텐트에 연결
작업의 URL을 생성하려면 다음 단계를 따르세요.
- Actions 콘솔에서 개발 > 작업.
- 링크를 생성할 작업을 클릭합니다.
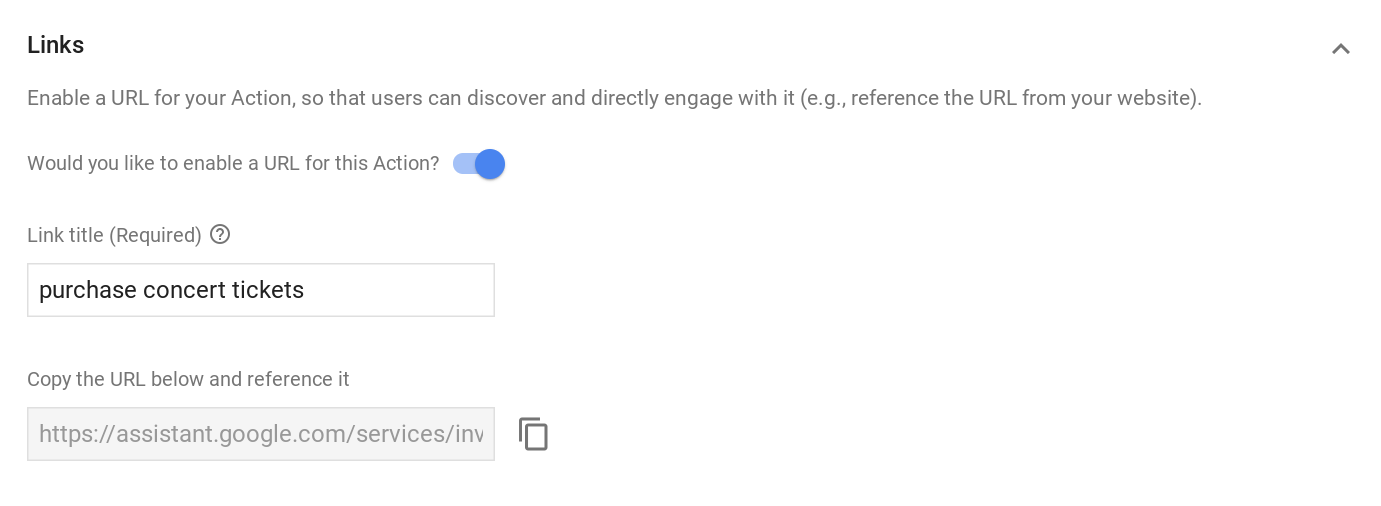
- 링크 섹션에서 이 작업에 URL을 사용 설정하시겠습니까를 사용 설정합니다.
- 링크 제목을 입력합니다. 이 제목에는 작업이 수행할 작업을 설명하는 동사가 포함되어야 합니다. 예를 들어 작업에서 사용자가 콘서트 티켓을 구매하기 위해 거래 절차로 이동하도록 하는 경우 '콘서트 티켓 구매'와 같은 링크 제목이 유용합니다.
- 저장을 클릭합니다.
제공된 URL을 복사하여 사용자를 이 특정 작업으로 안내하려는 경우 참조할 수 있습니다.
어시스턴트 링크 매개변수
어시스턴트 링크는 선택적으로 URL에 인텐트와 매개변수를 포함할 수 있습니다. Google은 URL에 지정된 인텐트 유형에 따라 매개변수를 처리합니다.
어시스턴트 링크 URL 사양
어시스턴트 링크의 URL에 관한 일반적인 문법은 다음과 같습니다.
https://assistant.google.com/services/invoke[/$action_id][?intent=$intent¶m.$param=$value][&$utm_param=$utm_value]
설정할 수 있는 URL 매개변수는 다음 표에 설명되어 있습니다.
| URL 매개변수 | 설명 |
|---|---|
$action_id |
작업의 숫자 식별자입니다. |
$intent |
내장 인텐트 또는 맞춤 인텐트의 전체 이름입니다. |
$param |
작업 패키지에 지정된 인텐트 매개변수의 전체 이름입니다. |
$value |
다음에서 $param에 대해 선언된 유형의 URL 인코딩 값입니다.
작업 패키지. |
$utm_param |
하나 이상의 UTM 매개변수 유형 목록입니다. 유효한 값은 다음과 같습니다.
utm_source, utm_medium,
utm_campaign, utm_term,
utm_content입니다. |
$utm_value |
UTM 매개변수의 문자열 값입니다. |
내장 인텐트가 포함된 어시스턴트 링크 URL
어시스턴트 링크에
내장 인텐트 (인텐트가 actions.intent.*로 시작)를 사용할 경우 Google은 URL에서 내장 인텐트 매개변수를 추출하여 작업에 전달하려고 시도합니다. Google에서 내장 인텐트 매개변수로 인식하지 못하는 매개변수는 모두 제거됩니다.
대화형 작업의 경우 Google은 AppRequest 메시지의 일부로 이러한 매개변수를 처리에 전송합니다.
다음 예는 단일 인텐트 매개변수가 있는 내장 인텐트를 포함하는 어시스턴트 링크 URL을 지정하는 방법을 보여줍니다.
https://assistant.google.com/services/invoke/uid/0000008ddd7eabec?intent=actions.intent.GET_HOROSCOPE¶m.astrologySign=%22cancer%22
맞춤 인텐트가 포함된 어시스턴트 링크 URL
맞춤 인텐트의 경우 Google은 작업에서 인텐트의 일부로 정의한 매개변수만 추출하고 다른 매개변수는 삭제합니다.
다음 예는 맞춤 인텐트가 포함된 어시스턴트 링크 URL을 지정하는 방법을 보여줍니다.
https://assistant.google.com/services/invoke/uid/0000001f575305a0?intent=NEWS_UPDATE_DEEP_LINK¶m.topic=sports
위 URL 예의 경우 AppRequest에서 Google은 JSON 객체를 다음과 같이 추가합니다.
다음과 같습니다.
argument {
name: ‘topic’,
raw_text: ‘sports’,
text_value: ‘sports’,
}
인텐트가 없는 어시스턴트 링크 URL
어시스턴트 링크에서 인텐트를 지정하지 않으면 Google은 기본적으로 다음 동작과 함께 작업의 MAIN 인텐트 (actions.intent.MAIN)에 연결합니다.
- 어시스턴트 링크에서
MAIN인텐트를 명시적으로 사용 설정하지 않았다면 Google은 'app_name에 연결' 동작과 유사하게 매개변수 없이 기본 인텐트를 트리거합니다. MAIN인텐트를 명시적으로 사용 설정한 경우 Google은 매개변수를 작업에 전달합니다.
다음 예는 인텐트 없이 어시스턴트 링크 URL을 지정하는 방법을 보여줍니다.
https://assistant.google.com/services/invoke/uid/000000d139bbc4d4
UTM 매개변수가 포함된 어시스턴트 링크 URL
UTM 매개변수는 사용자가 어시스턴트 링크를 클릭할 때 Google에서 작업에 전송하는 문자열로, 나중에 분석에 사용할 수 있습니다.
Google이 작업에 전송하는 UTM 매개변수에는 다음이 포함됩니다.
utm_sourceutm_mediumutm_campaignutm_termutm_content
다음 예는 UTM 매개변수를 포함하는 어시스턴트 링크 URL을 지정하는 방법을 보여줍니다.
https://assistant.google.com/services/invoke/uid/000000d139bbc4d4?utm_source=Google&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=holiday+sale
위 예시 URL의 경우 Google은 AppRequest 메시지에 다음 인수를 추가합니다.
argument {
name: ‘utm_source’,
raw_text: ‘Google’,
text_value: ‘Google’,
}
argument {
name: ‘utm_medium’,
raw_text: ‘email’,
text_value: ‘email’,
}
argument {
name: ‘utm_campaign’,
raw_text: ‘holiday sale’,
text_value: ‘holiday sale’,
}
어시스턴트 링크 테스트
시뮬레이터나 기기를 통해 모든 인텐트 (매개변수 유무와 관계없는 기본 또는 맞춤)의 어시스턴트 링크를 테스트할 수 있습니다.
어시스턴트 링크를 테스트하려면 다음 단계를 따르세요.
- 콘솔에서 어시스턴트 링크를 사용 설정합니다.
- Actions on Google 프로젝트를 만들 때 사용한 것과 동일한 계정으로 어시스턴트에 로그인합니다.
- 어시스턴트 링크의 클릭 가능한 버전을 만듭니다 (이메일, 채팅, 문서 등).
- 어시스턴트 지원 기기에서 이전 단계에서 만든 링크를 클릭합니다.
어시스턴트 링크가 예상대로 작동하는지 확인한 후 사용자에게 링크를 제공할 수 있도록 작업을 다시 배포해야 합니다.
제한사항 및 권장사항
이제 어시스턴트 링크 URL을 디렉터리나 다른 Google 서비스 외부로 배포하고 참조할 수 있으므로 다음과 같은 제한사항 및 권장사항이 적용됩니다.
- 모든 어시스턴트 링크를 계속 지원해야 합니다. 나중에 깨지는 어시스턴트 링크를 배포하면 작업 프로젝트가 비정상으로 신고되어 게시 중단될 수 있습니다.
링크를 게시하면 신뢰할 수 없는 소스에서의 트리거를 지원합니다. 연결된 작업의 경우 '실제 작업'을 수행하기 전에 사용자에게 명시적으로 확인해야 합니다. 예를 들어 스마트 홈 가전제품을 끄는 작업은 사용자에게 '
$applianceName을(를) 끄시겠습니까?'라고 묻는 메시지를 표시해야 합니다.이 맥락에서 '실제 행동'은 사용자의 서비스, 데이터, 기기, 네트워크, 컴퓨터 또는 API에 영향을 주는 모든 작업입니다. 예를 들어 이메일 전송, 거래 수행, 스마트 홈 어플라이언스 상태 변경, 구독 생성, 콘텐츠 업데이트 등이 있습니다.