Der Verknüpfungstyp OAuth unterstützt zwei branchenübliche OAuth 2.0-Abläufe: der implizite und Autorisierungscode-Abläufe.
Im impliziten Codeablauf öffnet Google Ihren Autorisierungsendpunkt im Browser des Nutzers. Nach erfolgreicher Anmeldung geben Sie ein langlebiges Zugriffstoken an Google zurück. Dieses Zugriffstoken ist jetzt in jeder Anfrage enthalten, die von Assistant an Ihre Aktion gesendet wird.
Für den Autorisierungscodeablauf benötigen Sie zwei Endpunkte:
- Der Endpunkt für die Autorisierung, der für die Darstellung der Anmelde-UI für Nutzer sorgt, die noch nicht angemeldet sind, und die Einwilligung zum angeforderten Zugriff in Form eines kurzlebigen Autorisierungscodes erfasst.
- Der Endpunkt Tokenaustausch, der für zwei Arten von Austauschen verantwortlich ist:
- Tauscht einen Autorisierungscode gegen ein langlebiges Aktualisierungstoken und ein kurzlebiges Zugriffstoken aus. Dieser Austausch erfolgt, wenn der Nutzer die Kontoverknüpfung durchläuft.
- Tauscht ein langlebiges Aktualisierungstoken gegen ein kurzlebiges Zugriffstoken aus. Dieser Austausch findet statt, wenn Google ein neues Zugriffstoken benötigt, weil das abgelaufene Token abgelaufen ist.
Der implizite Codeablauf ist zwar einfacher zu implementieren, aber Google empfiehlt, dass mit dem impliziten Vorgang ausgestellte Zugriffstokens nie ablaufen, da die Verwendung des Tokenablaufs mit dem impliziten Vorgang den Nutzer zwingt, sein Konto noch einmal zu verknüpfen. Wenn Sie aus Sicherheitsgründen ein Token auslaufen müssen, sollten Sie stattdessen den Autorisierungscode-Ablauf verwenden.
OAuth-Kontoverknüpfung implementieren
Projekt konfigurieren
So konfigurieren Sie Ihr Projekt für die Verwendung der OAuth-Kontoverknüpfung:
- Öffnen Sie die Actions Console und wählen Sie das Projekt aus, das Sie verwenden möchten.
- Klicken Sie auf den Tab Entwickeln und wählen Sie Kontoverknüpfung aus.
- Aktivieren Sie den Schalter neben Kontoverknüpfung.
- Wählen Sie im Abschnitt Kontoerstellung die Option Nein, ich möchte nur die Kontoerstellung auf meiner Website zulassen aus.
Wählen Sie unter Verknüpfungstyp die Option OAuth und Implizit aus.
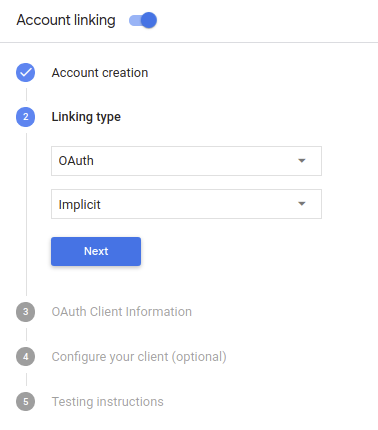
Gehen Sie unter Client Information (Kundeninformationen) folgendermaßen vor:
- Weisen Sie der Client-ID, die von Ihren Aktionen an Google ausgegeben wird einen Wert zu, um von Google stammen.
- Fügen Sie die URLs für Ihre Autorisierungs- und Tokenaustausch-Endpunkte ein.
- Klicken Sie auf Speichern.
OAuth-Server implementieren
To support the OAuth 2.0 implicit flow, your service makes an authorization endpoint available by HTTPS. This endpoint is responsible for authenticating and obtaining consent from users for data access. The authorization endpoint presents a sign-in UI to your users that aren't already signed in and records consent to the requested access.
When your Action needs to call one of your service's authorized APIs, Google uses this endpoint to get permission from your users to call these APIs on their behalf.
A typical OAuth 2.0 implicit flow session initiated by Google has the following flow:
- Google opens your authorization endpoint in the user's browser. The user signs in if not signed in already, and grants Google permission to access their data with your API if they haven't already granted permission.
- Your service creates an access token and returns it to Google by redirecting the user's browser back to Google with the access token attached to the request.
- Google calls your service's APIs, and attaches the access token with each request. Your service verifies that the access token grants Google authorization to access the API and then completes the API call.
Handle authorization requests
When your Action needs to perform account linking via an OAuth2 implicit flow, Google sends the user to your authorization endpoint with a request that includes the following parameters:
| Authorization endpoint parameters | |
|---|---|
client_id |
The client ID you assigned to Google. |
redirect_uri |
The URL to which you send the response to this request. |
state |
A bookkeeping value that is passed back to Google unchanged in the redirect URI. |
response_type |
The type of value to return in the response. For the OAuth 2.0 implicit
flow, the response type is always token. |
For example, if your authorization endpoint is available at https://myservice.example.com/auth,
a request might look like:
GET https://myservice.example.com/auth?client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&redirect_uri=REDIRECT_URI&state=STATE_STRING&response_type=token
For your authorization endpoint to handle sign-in requests, do the following steps:
Verify the
client_idandredirect_urivalues to prevent granting access to unintended or misconfigured client apps:- Confirm that the
client_idmatches the client ID you assigned to Google. - Confirm that the URL specified by the
redirect_uriparameter has the following form:https://oauth-redirect.googleusercontent.com/r/YOUR_PROJECT_ID
- Confirm that the
Check if the user is signed in to your service. If the user isn't signed in, complete your service's sign-in or sign-up flow.
Generate an access token that Google will use to access your API. The access token can be any string value, but it must uniquely represent the user and the client the token is for and must not be guessable.
Send an HTTP response that redirects the user's browser to the URL specified by the
redirect_uriparameter. Include all of the following parameters in the URL fragment:access_token: the access token you just generatedtoken_type: the stringbearerstate: the unmodified state value from the original request The following is an example of the resulting URL:https://oauth-redirect.googleusercontent.com/r/YOUR_PROJECT_ID#access_token=ACCESS_TOKEN&token_type=bearer&state=STATE_STRING
Google's OAuth 2.0 redirect handler will receive the access token and confirm
that the state value hasn't changed. After Google has obtained an
access token for your service, Google will attach the token to subsequent calls
to your Action as part of the AppRequest.
Authentifizierungsvorgang starten
Den Intent „Account Sign-in Helper“ (Kontoanmeldung) verwenden um den Authentifizierungsvorgang zu starten. Die folgenden Code-Snippets beschreiben, wie Sie Antwort in Dialogflow und im Actions SDK senden, um diesen Hilfsprogramm-Assistenten zu verwenden.
Dialogflow
<ph type="x-smartling-placeholder">const {dialogflow, SignIn} = require('actions-on-google'); const app = dialogflow({ // REPLACE THE PLACEHOLDER WITH THE CLIENT_ID OF YOUR ACTIONS PROJECT clientId: CLIENT_ID, }); // Intent that starts the account linking flow. app.intent('Start Signin', (conv) => { conv.ask(new SignIn('To get your account details')); });
@ForIntent("Start Signin") public ActionResponse text(ActionRequest request) { ResponseBuilder rb = getResponseBuilder(request); return rb.add(new SignIn().setContext("To get your account details")).build(); }
{ "payload": { "google": { "expectUserResponse": true, "richResponse": { "items": [ { "simpleResponse": { "textToSpeech": "PLACEHOLDER" } } ] }, "userStorage": "{\"data\":{}}", "systemIntent": { "intent": "actions.intent.SIGN_IN", "data": { "@type": "type.googleapis.com/google.actions.v2.SignInValueSpec", "optContext": "To get your account details" } } } }, "outputContexts": [ { "name": "/contexts/_actions_on_google", "lifespanCount": 99, "parameters": { "data": "{}" } } ] }
Actions-SDK:
<ph type="x-smartling-placeholder">const {actionssdk, SignIn} = require('actions-on-google'); const app = actionssdk({ // REPLACE THE PLACEHOLDER WITH THE CLIENT_ID OF YOUR ACTIONS PROJECT clientId: CLIENT_ID, }); // Intent that starts the account linking flow. app.intent('actions.intent.TEXT', (conv) => { conv.ask(new SignIn('To get your account details')); });
@ForIntent("actions.intent.TEXT") public ActionResponse text(ActionRequest request) { ResponseBuilder rb = getResponseBuilder(request); return rb.add(new SignIn().setContext("To get your account details")).build(); }
{ "expectUserResponse": true, "expectedInputs": [ { "inputPrompt": { "richInitialPrompt": { "items": [ { "simpleResponse": { "textToSpeech": "PLACEHOLDER" } } ] } }, "possibleIntents": [ { "intent": "actions.intent.SIGN_IN", "inputValueData": { "@type": "type.googleapis.com/google.actions.v2.SignInValueSpec", "optContext": "To get your account details" } } ] } ], "conversationToken": "{\"data\":{}}", "userStorage": "{\"data\":{}}" }
Datenzugriffsanfragen verarbeiten
Wenn die Assistant-Anfrage ein Zugriffstoken enthält, gehen Sie so vor: Überprüfen Sie zunächst, ob das Zugriffstoken gültig (und nicht abgelaufen) ist, und rufen Sie dann das zugehörige Nutzerkonto aus Ihrer Datenbank ab.