เอกสารนี้จะอธิบายวิธีใช้การอัปโหลดสื่อโดยตรงและการอัปโหลดต่อได้ด้วย ไลบรารีของไคลเอ็นต์ Google API สำหรับ Java
อัปโหลดสื่อต่อได้
เมื่อคุณอัปโหลดไฟล์สื่อขนาดใหญ่ไปยังเซิร์ฟเวอร์ ให้ใช้การอัปโหลดสื่อที่ดำเนินการต่อได้เพื่อ ให้ส่งไฟล์ทีละส่วน ไลบรารีที่ Google API สร้างขึ้นประกอบด้วย วิธีอำนวยความสะดวกในการโต้ตอบกับการอัปโหลดสื่อที่กลับมาทำงานต่อได้
โปรโตคอลการอัปโหลดสื่อที่ดำเนินการต่อได้คล้ายกับการอัปโหลดสื่อที่ดำเนินการต่อได้ ตามที่อธิบายไว้ในเอกสารประกอบของ Google Drive API
การออกแบบโปรโตคอล
แผนภาพลำดับต่อไปนี้แสดงวิธีการทำงานของโปรโตคอลการอัปโหลดสื่อที่กลับมาทำงานต่อได้
วันที่ 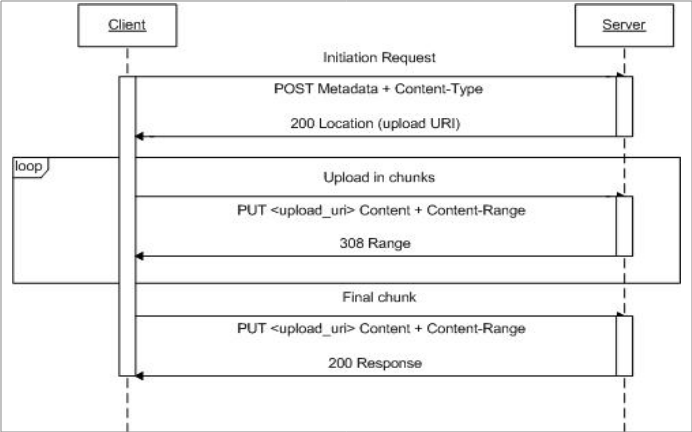
รายละเอียดการใช้งาน
ประเภทหลักๆ ที่สนใจได้แก่ MediaHttpUploader และ MediaHttpProgressListener
หากเมธอดในไลบรารีที่สร้างขึ้นเฉพาะบริการมี mediaUpload
ในเอกสาร Discovery
ระบบจะสร้างเมธอดที่สะดวกขึ้นสำหรับวิธีการเหล่านี้ ซึ่งต้องแบ่ง
InputStreamContent
เป็นพารามิเตอร์ (สำหรับข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้การอัปโหลดสื่อด้วย Google APIs
บริการ Discovery โปรดดู
การอัปโหลดสื่อ)
เช่น เมธอด insert ของ Drive API
สนับสนุน mediaUpload และคุณสามารถใช้รหัสต่อไปนี้เพื่ออัปโหลดไฟล์:
class CustomProgressListener implements MediaHttpUploaderProgressListener { public void progressChanged(MediaHttpUploader uploader) throws IOException { switch (uploader.getUploadState()) { case INITIATION_STARTED: System.out.println("Initiation has started!"); break; case INITIATION_COMPLETE: System.out.println("Initiation is complete!"); break; case MEDIA_IN_PROGRESS: System.out.println(uploader.getProgress()); break; case MEDIA_COMPLETE: System.out.println("Upload is complete!"); } } } File mediaFile = new File("/tmp/driveFile.jpg"); InputStreamContent mediaContent = new InputStreamContent("image/jpeg", new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(mediaFile))); mediaContent.setLength(mediaFile.length()); Drive.Files.Insert request = drive.files().insert(fileMetadata, mediaContent); request.getMediaHttpUploader().setProgressListener(new CustomProgressListener()); request.execute();
นอกจากนี้ คุณยังใช้ฟีเจอร์การอัปโหลดสื่อที่กลับมาทำงานอีกครั้งได้โดยไม่ต้องใช้ฟีเจอร์เฉพาะบริการ ไลบรารีที่สร้างขึ้น มีตัวอย่างดังต่อไปนี้
File mediaFile = new File("/tmp/Test.jpg"); InputStreamContent mediaContent = new InputStreamContent("image/jpeg", new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(mediaFile))); mediaContent.setLength(mediaFile.length());MediaHttpUploader uploader = new MediaHttpUploader(mediaContent, transport, httpRequestInitializer); uploader.setProgressListener(new CustomProgressListener()); HttpResponse response = uploader.upload(requestUrl); if (!response.isSuccessStatusCode()) { throw GoogleJsonResponseException(jsonFactory, response); }
การอัปโหลดสื่อโดยตรง
การอัปโหลดสื่อที่ดำเนินการต่อได้จะเปิดใช้โดยค่าเริ่มต้น แต่คุณสามารถปิดใช้และเลือกใช้ สื่อโดยตรงแทน เช่น ในกรณีที่คุณอัปโหลดไฟล์ขนาดเล็ก โดยตรง การอัปโหลดสื่อเปิดตัวใน1.9.0-beta ไลบรารีของไคลเอ็นต์ Google API เวอร์ชันสำหรับ Java
การอัปโหลดสื่อโดยตรงจะอัปโหลดทั้งไฟล์ในคำขอ HTTP รายการเดียว โปรโตคอลการอัปโหลดสื่อที่กลับมาทำงานต่อได้ ซึ่งจะอัปโหลดไฟล์ในหลายคำขอ การอัปโหลดโดยตรงจะลดจำนวนคำขอ HTTP แต่เพิ่ม โอกาสความล้มเหลว (เช่น การเชื่อมต่อล้มเหลว) ที่อาจเกิดขึ้นได้ ทั้งหมด
การใช้งานสำหรับการอัปโหลดสื่อโดยตรงนั้นเหมือนกับที่อธิบายไว้ข้างต้นสำหรับ การอัปโหลดสื่อที่ดำเนินการต่อได้ รวมถึงการเรียกใช้ต่อไปนี้ที่บอก MediaHttpUploader ทำเฉพาะการอัปโหลดโดยตรงเท่านั้น
mediaHttpUploader.setDirectUploadEnabled(true);