API Lịch sử cho phép ứng dụng của bạn thực hiện hàng loạt thao tác trên kho nội dung thể dục: đọc, chèn, cập nhật và xoá dữ liệu sức khoẻ thể chất và tinh thần trước đây. Hãy dùng API Lịch sử để thực hiện những việc sau:
- Đọc dữ liệu sức khoẻ thể chất và tinh thần được chèn hoặc ghi lại bằng của chúng tôi.
- Nhập dữ liệu hàng loạt vào Google Fit.
- Cập nhật dữ liệu trong Google Fit.
- Xoá dữ liệu trong quá khứ mà ứng dụng của bạn đã lưu trữ trước đây.
Để chèn dữ liệu chứa siêu dữ liệu về phiên hoạt động, hãy sử dụng API phiên.
Đọc dữ liệu
Các phần sau đây trình bày cách đọc các loại dữ liệu tổng hợp khác nhau.
Đọc dữ liệu chi tiết và tổng hợp
Để đọc dữ liệu trong quá khứ, hãy tạo một
DataReadRequest
thực thể.
Kotlin
// Read the data that's been collected throughout the past week. val endTime = LocalDateTime.now().atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()) val startTime = endTime.minusWeeks(1) Log.i(TAG, "Range Start: $startTime") Log.i(TAG, "Range End: $endTime") val readRequest = DataReadRequest.Builder() // The data request can specify multiple data types to return, // effectively combining multiple data queries into one call. // This example demonstrates aggregating only one data type. .aggregate(DataType.AGGREGATE_STEP_COUNT_DELTA) // Analogous to a "Group By" in SQL, defines how data should be // aggregated. // bucketByTime allows for a time span, whereas bucketBySession allows // bucketing by <a href="/fit/android/using-sessions">sessions</a>. .bucketByTime(1, TimeUnit.DAYS) .setTimeRange(startTime.toEpochSecond(), endTime.toEpochSecond(), TimeUnit.SECONDS) .build()
Java
// Read the data that's been collected throughout the past week. ZonedDateTime endTime = LocalDateTime.now().atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()); ZonedDateTime startTime = endTime.minusWeeks(1); Log.i(TAG, "Range Start: $startTime"); Log.i(TAG, "Range End: $endTime"); DataReadRequest readRequest = new DataReadRequest.Builder() // The data request can specify multiple data types to return, // effectively combining multiple data queries into one call. // This example demonstrates aggregating only one data type. .aggregate(DataType.AGGREGATE_STEP_COUNT_DELTA) // Analogous to a "Group By" in SQL, defines how data should be // aggregated. // bucketByTime allows for a time span, while bucketBySession allows // bucketing by sessions. .bucketByTime(1, TimeUnit.DAYS) .setTimeRange(startTime.toEpochSecond(), endTime.toEpochSecond(), TimeUnit.SECONDS) .build();
Ví dụ trước sử dụng các điểm dữ liệu tổng hợp, trong đó mỗi DataPoint
thể hiện số bước đã đi bộ trong một ngày. Đối với trường hợp sử dụng cụ thể này,
điểm dữ liệu tổng hợp có hai lợi thế:
- Ứng dụng của bạn và cửa hàng thể dục trao đổi lượng dữ liệu nhỏ hơn.
- Ứng dụng của bạn không phải tổng hợp dữ liệu theo cách thủ công.
Dữ liệu tổng hợp cho nhiều loại hoạt động
Ứng dụng của bạn có thể sử dụng các yêu cầu dữ liệu để truy xuất nhiều loại dữ liệu. Chiến lược phát hành đĩa đơn
ví dụ sau cho biết cách tạo một
DataReadRequest để tiêu thụ lượng calo đã đốt cháy cho mỗi hoạt động được thực hiện trong
phạm vi thời gian chỉ định. Dữ liệu thu được sẽ so khớp lượng calo trên mỗi hoạt động thành
được báo cáo trong ứng dụng Google Fit, trong đó mỗi hoạt động sẽ có nhóm riêng
dữ liệu calo.
Kotlin
val readRequest = DataReadRequest.Builder() .aggregate(DataType.AGGREGATE_CALORIES_EXPENDED) .bucketByActivityType(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS) .setTimeRange(startTime.toEpochSecond(), endTime.toEpochSecond(), TimeUnit.SECONDS) .build()
Java
DataReadRequest readRequest = new DataReadRequest.Builder() .aggregate(DataType.AGGREGATE_CALORIES_EXPENDED) .bucketByActivityType(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS) .setTimeRange(startTime.toEpochSecond(), endTime.toEpochSecond(), TimeUnit.SECONDS) .build();
Sau khi bạn tạo một thực thể DataReadRequest, hãy sử dụng
HistoryClient.readData()
để đọc không đồng bộ dữ liệu lịch sử.
Ví dụ sau minh hoạ cách lấy các thực thể DataPoint từ
DataSet:
Kotlin
Fitness.getHistoryClient(this, GoogleSignIn.getAccountForExtension(this, fitnessOptions)) .readData(readRequest) .addOnSuccessListener { response -> // The aggregate query puts datasets into buckets, so flatten into a // single list of datasets for (dataSet in response.buckets.flatMap { it.dataSets }) { dumpDataSet(dataSet) } } .addOnFailureListener { e -> Log.w(TAG,"There was an error reading data from Google Fit", e) } fun dumpDataSet(dataSet: DataSet) { Log.i(TAG, "Data returned for Data type: ${dataSet.dataType.name}") for (dp in dataSet.dataPoints) { Log.i(TAG,"Data point:") Log.i(TAG,"\tType: ${dp.dataType.name}") Log.i(TAG,"\tStart: ${dp.getStartTimeString()}") Log.i(TAG,"\tEnd: ${dp.getEndTimeString()}") for (field in dp.dataType.fields) { Log.i(TAG,"\tField: ${field.name.toString()} Value: ${dp.getValue(field)}") } } } fun DataPoint.getStartTimeString() = Instant.ofEpochSecond(this.getStartTime(TimeUnit.SECONDS)) .atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()) .toLocalDateTime().toString() fun DataPoint.getEndTimeString() = Instant.ofEpochSecond(this.getEndTime(TimeUnit.SECONDS)) .atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()) .toLocalDateTime().toString()
Java
Fitness.getHistoryClient(this, GoogleSignIn.getAccountForExtension(this, fitnessOptions)) .readData(readRequest) .addOnSuccessListener (response -> { // The aggregate query puts datasets into buckets, so convert to a // single list of datasets for (Bucket bucket : response.getBuckets()) { for (DataSet dataSet : bucket.getDataSets()) { dumpDataSet(dataSet); } } }) .addOnFailureListener(e -> Log.w(TAG, "There was an error reading data from Google Fit", e)); } private void dumpDataSet(DataSet dataSet) { Log.i(TAG, "Data returned for Data type: ${dataSet.dataType.name}"); for (DataPoint dp : dataSet.getDataPoints()) { Log.i(TAG,"Data point:"); Log.i(TAG,"\tType: ${dp.dataType.name}"); Log.i(TAG,"\tStart: ${dp.getStartTimeString()}"); Log.i(TAG,"\tEnd: ${dp.getEndTimeString()}"); for (Field field : dp.getDataType().getFields()) { Log.i(TAG,"\tField: ${field.name.toString()} Value: ${dp.getValue(field)}"); } } } private String getStartTimeString() { return Instant.ofEpochSecond(this.getStartTime(TimeUnit.SECONDS)) .atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()) .toLocalDateTime().toString(); } private String getEndTimeString() { return Instant.ofEpochSecond(this.getEndTime(TimeUnit.SECONDS)) .atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()) .toLocalDateTime().toString(); }
Đọc dữ liệu tổng hằng ngày
Google Fit cũng cung cấp quyền truy cập đơn giản vào tổng số ngày
kiểu dữ liệu được chỉ định. Sử dụng
HistoryClient.readDailyTotal()
để truy xuất loại dữ liệu mà bạn chỉ định kể từ nửa đêm của ngày hiện tại
ngày theo múi giờ hiện tại của thiết bị. Ví dụ: chuyển vào
Loại dữ liệu TYPE_STEP_COUNT_DELTA cho phương thức này để truy xuất tổng số hằng ngày
bước. Bạn có thể chuyển vào một loại dữ liệu tức thì có số liệu tổng hợp hằng ngày
tổng cộng. Để biết thêm thông tin về các loại dữ liệu được hỗ trợ, hãy xem
DataType.getAggregateType.
Google Fit không yêu cầu ủy quyền để đăng ký
TYPE_STEP_COUNT_DELTA nội dung cập nhật từ HistoryClient.readDailyTotal()
khi phương thức này được gọi bằng tài khoản mặc định và không
phạm vi được chỉ định.
Điều này có thể hữu ích nếu bạn cần dữ liệu bước để sử dụng ở những khu vực mà bạn không thể
để hiện bảng điều khiển quyền, chẳng hạn như trên mặt đồng hồ Wear OS.
Người dùng muốn thấy số bước nhất quán trên ứng dụng Google Fit,
các ứng dụng khác và mặt đồng hồ Wear OS, vì tính năng này cung cấp cho chúng
trải nghiệm nhất quán và đáng tin cậy. Để giữ số bước nhất quán, hãy đăng ký
các bước trong nền tảng Google Fit từ ứng dụng hoặc mặt đồng hồ, sau đó
cập nhật số lượng trong
onExitAmbient().
Để biết thêm thông tin về cách sử dụng dữ liệu này trên mặt đồng hồ, hãy xem
Chức năng trên mặt đồng hồ
và ứng dụng mẫu Android Watch.
Chèn dữ liệu
Để chèn dữ liệu trong quá khứ, trước tiên, hãy tạo một thực thể DataSet:
Kotlin
// Declare that the data being inserted was collected during the past hour. val endTime = LocalDateTime.now().atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()) val startTime = endTime.minusHours(1) // Create a data source val dataSource = DataSource.Builder() .setAppPackageName(this) .setDataType(DataType.TYPE_STEP_COUNT_DELTA) .setStreamName("$TAG - step count") .setType(DataSource.TYPE_RAW) .build() // For each data point, specify a start time, end time, and the // data value -- in this case, 950 new steps. val stepCountDelta = 950 val dataPoint = DataPoint.builder(dataSource) .setField(Field.FIELD_STEPS, stepCountDelta) .setTimeInterval(startTime.toEpochSecond(), endTime.toEpochSecond(), TimeUnit.SECONDS) .build() val dataSet = DataSet.builder(dataSource) .add(dataPoint) .build()
Java
// Declare that the data being inserted was collected during the past hour. ZonedDateTime endTime = LocalDateTime.now().atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()); ZonedDateTime startTime = endTime.minusHours(1); // Create a data source DataSource dataSource = new DataSource.Builder() .setAppPackageName(this) .setDataType(DataType.TYPE_STEP_COUNT_DELTA) .setStreamName("$TAG - step count") .setType(DataSource.TYPE_RAW) .build(); // For each data point, specify a start time, end time, and the // data value -- in this case, 950 new steps. int stepCountDelta = 950; DataPoint dataPoint = DataPoint.builder(dataSource) .setField(Field.FIELD_STEPS, stepCountDelta) .setTimeInterval(startTime.toEpochSecond(), endTime.toEpochSecond(), TimeUnit.SECONDS) .build(); DataSet dataSet = DataSet.builder(dataSource) .add(dataPoint) .build();
Sau khi bạn tạo một thực thể DataSet, hãy sử dụng
HistoryClient.insertData
để thêm không đồng bộ dữ liệu lịch sử này.
Kotlin
Fitness.getHistoryClient(this, GoogleSignIn.getAccountForExtension(this, fitnessOptions)) .insertData(dataSet) .addOnSuccessListener { Log.i(TAG, "DataSet added successfully!") } .addOnFailureListener { e -> Log.w(TAG, "There was an error adding the DataSet", e) }
Java
Fitness.getHistoryClient(this, GoogleSignIn.getAccountForExtension(this, fitnessOptions)) .insertData(dataSet) .addOnSuccessListener (unused -> Log.i(TAG, "DataSet added successfully!")) .addOnFailureListener(e -> Log.w(TAG, "There was an error adding the DataSet", e)); }
Quản lý các điểm dữ liệu có xung đột
Một
DataPoint
trong DataSet của ứng dụng phải có startTime và endTime xác định một
khoảng thời gian duy nhất trong DataSet đó, không có sự chồng chéo giữa DataPoint
thực thể.
Nếu ứng dụng của bạn cố chèn một DataPoint mới xung đột với một thẻ
Thực thể DataPoint, DataPoint mới sẽ bị loại bỏ. Để chèn một thẻ mới
DataPoint có thể trùng lặp với các điểm dữ liệu hiện có, hãy sử dụng
HistoryClient.updateData
theo mô tả trong phần Cập nhật dữ liệu.
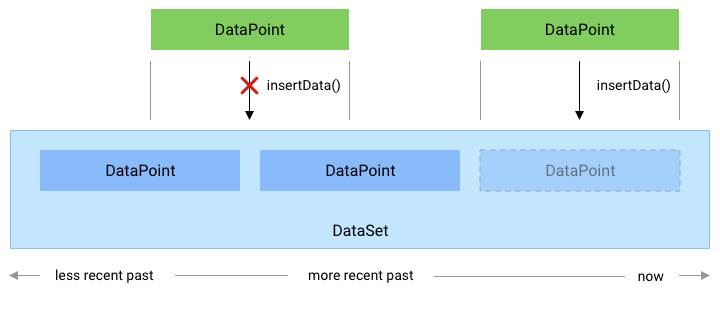
Hình 1. Cách phương thức insertData() xử lý các điểm dữ liệu mới
xung đột với một DataPoint hiện có.
Cập nhật dữ liệu
Google Fit cho phép ứng dụng của bạn cập nhật dữ liệu trước đây về sức khoẻ thể chất và tinh thần
đã chèn trước đó. Để thêm dữ liệu trong quá khứ cho một DataSet mới hoặc để thêm dữ liệu mới
Các thực thể DataPoint không xung đột với dữ liệu hiện có
điểm, hãy sử dụng phương thức HistoryApi.insertData.
Để cập nhật dữ liệu trong quá khứ, hãy sử dụng phương thức HistoryClient.updateData. Chiến dịch này
phương thức sẽ xoá mọi thực thể DataPoint hiện có chồng chéo với DataPoint
các thực thể được thêm bằng phương thức này.
Để cập nhật dữ liệu sức khoẻ thể chất và tinh thần trước đây, trước tiên, hãy tạo một DataSet
thực thể:
Kotlin
// Declare that the historical data was collected during the past 50 minutes. val endTime = LocalDateTime.now().atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()) val startTime = endTime.minusMinutes(50) // Create a data source val dataSource = DataSource.Builder() .setAppPackageName(this) .setDataType(DataType.TYPE_STEP_COUNT_DELTA) .setStreamName("$TAG - step count") .setType(DataSource.TYPE_RAW) .build() // Create a data set // For each data point, specify a start time, end time, and the // data value -- in this case, 1000 new steps. val stepCountDelta = 1000 val dataPoint = DataPoint.builder(dataSource) .setTimeInterval(startTime.toEpochSecond(), endTime.toEpochSecond(), TimeUnit.SECONDS) .setField(Field.FIELD_STEPS, stepCountDelta) .build() val dataSet = DataSet.builder(dataSource) .add(dataPoint) .build()
Java
// Declare that the historical data was collected during the past 50 minutes. ZonedDateTime endTime = LocalDateTime.now().atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()); ZonedDateTime startTime = endTime.minusMinutes(50); // Create a data source DataSource dataSource = new DataSource.Builder() .setAppPackageName(this) .setDataType(DataType.TYPE_STEP_COUNT_DELTA) .setStreamName("$TAG - step count") .setType(DataSource.TYPE_RAW) .build(); // Create a data set // For each data point, specify a start time, end time, and the // data value -- in this case, 1000 new steps. int stepCountDelta = 1000; DataPoint dataPoint = DataPoint.builder(dataSource) .setTimeInterval(startTime.toEpochSecond(), endTime.toEpochSecond(), TimeUnit.SECONDS) .setField(Field.FIELD_STEPS, stepCountDelta) .build(); DataSet dataSet = DataSet.builder(dataSource) .add(dataPoint) .build();
Sau đó, hãy sử dụng DataUpdateRequest.Builder() để tạo một yêu cầu cập nhật dữ liệu mới và
hãy sử dụng phương thức HistoryClient.updateData để tạo yêu cầu:
Kotlin
val request = DataUpdateRequest.Builder() .setDataSet(dataSet) .setTimeInterval(startTime.toEpochSecond(), endTime.toEpochSecond(), TimeUnit.SECONDS) .build() Fitness.getHistoryClient(this, GoogleSignIn.getAccountForExtension(this, fitnessOptions)) .updateData(request) .addOnSuccessListener { Log.i(TAG, "DataSet updated successfully!") } .addOnFailureListener { e -> Log.w(TAG, "There was an error updating the DataSet", e) }
Java
DataUpdateRequest request = new DataUpdateRequest.Builder() .setDataSet(dataSet) .setTimeInterval(startTime.toEpochSecond(), endTime.toEpochSecond(), TimeUnit.SECONDS) .build(); Fitness.getHistoryClient(this, GoogleSignIn.getAccountForExtension(this, fitnessOptions)) .updateData(request) .addOnSuccessListener(unused -> Log.i(TAG, "DataSet updated successfully!")) .addOnFailureListener(e -> Log.w(TAG, "There was an error updating the DataSet", e));
Xoá dữ liệu
Google Fit cho phép ứng dụng của bạn xoá dữ liệu trước đây về sức khoẻ thể chất và tinh thần đã chèn trước đó.
Để xoá dữ liệu trong quá khứ, hãy sử dụng
HistoryClient.deleteData
phương thức:
Kotlin
// Declare that this code deletes step count information that was collected // throughout the past day. val endTime = LocalDateTime.now().atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()) val startTime = endTime.minusDays(1) // Create a delete request object, providing a data type and a time interval val request = DataDeleteRequest.Builder() .setTimeInterval(startTime.toEpochSecond(), endTime.toEpochSecond(), TimeUnit.SECONDS) .addDataType(DataType.TYPE_STEP_COUNT_DELTA) .build() // Invoke the History API with the HistoryClient object and delete request, and // then specify a callback that will check the result. Fitness.getHistoryClient(this, GoogleSignIn.getAccountForExtension(this, fitnessOptions)) .deleteData(request) .addOnSuccessListener { Log.i(TAG, "Data deleted successfully!") } .addOnFailureListener { e -> Log.w(TAG, "There was an error with the deletion request", e) }
Java
// Declare that this code deletes step count information that was collected // throughout the past day. ZonedDateTime endTime = LocalDateTime.now().atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()); ZonedDateTime startTime = endTime.minusDays(1); // Create a delete request object, providing a data type and a time interval DataDeleteRequest request = new DataDeleteRequest.Builder() .setTimeInterval(startTime.toEpochSecond(), endTime.toEpochSecond(), TimeUnit.SECONDS) .addDataType(DataType.TYPE_STEP_COUNT_DELTA) .build(); // Invoke the History API with the HistoryClient object and delete request, and // then specify a callback that will check the result. Fitness.getHistoryClient(this, GoogleSignIn.getAccountForExtension(this, fitnessOptions)) .deleteData(request) .addOnSuccessListener (unused -> Log.i(TAG, "Data deleted successfully!")) .addOnFailureListener(e -> Log.w(TAG, "There was an error with the deletion request", e));
Ứng dụng có thể xoá dữ liệu khỏi một số phiên hoặc
xoá tất cả dữ liệu. Để biết thêm thông tin, hãy xem tài liệu tham khảo API cho
DataDeleteRequest.
Đăng ký nhận thông tin cập nhật về dữ liệu
Ứng dụng của bạn có thể đọc dữ liệu cảm biến thô theo thời gian thực bằng cách đăng ký với
SensorsClient.
Đối với các loại dữ liệu khác có ít thường xuyên hơn và được tính theo cách thủ công,
ứng dụng có thể đăng ký nhận thông tin cập nhật khi các số đo này được chèn vào
cơ sở dữ liệu Google Fit. Ví dụ về các loại dữ liệu này bao gồm chiều cao,
tạ và các bài tập như nâng tạ; để biết thêm chi tiết, hãy xem danh sách đầy đủ
loại dữ liệu được hỗ trợ.
Để đăng ký nhận thông tin cập nhật, hãy sử dụng
HistoryClient.registerDataUpdateListener.
Đoạn mã sau đây cho phép ứng dụng được thông báo khi người dùng nhập một giá trị cho trọng lượng của chúng:
Kotlin
val intent = Intent(this, MyDataUpdateService::class.java) val pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getService(this, 0, intent, PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT) val request = DataUpdateListenerRegistrationRequest.Builder() .setDataType(DataType.TYPE_WEIGHT) .setPendingIntent(pendingIntent) .build() Fitness.getHistoryClient(this, GoogleSignIn.getAccountForExtension(this, fitnessOptions)) .registerDataUpdateListener(request) .addOnSuccessListener { Log.i(TAG, "DataUpdateListener registered") }
Java
Intent intent = new Intent(this, MyDataUpdateService.class); PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getService(this, 0, intent, PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT) DataUpdateListenerRegistrationRequest request = new DataUpdateListenerRegistrationRequest.Builder() .setDataType(DataType.TYPE_WEIGHT) .setPendingIntent(pendingIntent) .build(); Fitness.getHistoryClient(this, GoogleSignIn.getAccountForExtension(this, fitnessOptions)) .registerDataUpdateListener(request) .addOnSuccessListener(unused -> Log.i(TAG, "DataUpdateListener registered"));
Bạn có thể dùng IntentService để nhận thông báo về nội dung cập nhật:
Kotlin
class MyDataUpdateService : IntentService("MyDataUpdateService") { override fun onHandleIntent(intent: Intent?) { val update = DataUpdateNotification.getDataUpdateNotification(intent) // Show the time interval over which the data points were collected. // To extract specific data values, in this case the user's weight, // use DataReadRequest. update?.apply { val start = getUpdateStartTime(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) val end = getUpdateEndTime(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) Log.i(TAG, "Data Update start: $start end: $end DataType: ${dataType.name}") } } }
Java
public class MyDataUpdateService extends IntentService { public MyDataUpdateService(String name) { super("MyDataUpdateService"); } @Override protected void onHandleIntent(@Nullable Intent intent) { if (intent != null) { DataUpdateNotification update = DataUpdateNotification.getDataUpdateNotification(intent); // Show the time interval over which the data points // were collected. // To extract specific data values, in this case the user's weight, // use DataReadRequest. if (update != null) { long start = update.getUpdateStartTime(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); long end = update.getUpdateEndTime(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } Log.i(TAG, "Data Update start: $start end: $end DataType: ${dataType.name}"); } } }
Bạn phải khai báo IntentService trong tệp AndroidManifest.xml.
