Page Summary
-
This document describes the OAuth 2.0 protocol designed for limited-input devices, such as TVs and printers, to access the YouTube Data API without the need for traditional browsers or extensive input capabilities.
-
Applications must first request a
device_codeanduser_codefrom the authorization server, then display these codes along with averification_urlto the user who must complete the authentication process on a separate device. -
The application must continuously poll the authorization server using the
device_codeuntil the user authorizes the application on another device, at which point the server will respond with the needed access tokens, or send an error if the user denies authorization. -
Once access is granted, the app uses the
access_tokento make authorized calls to Google APIs, with the option to refresh the token using therefresh_token, and users have the ability to revoke permissions. -
Applications will need to use the correct scopes depending on what is necessary, and there is a list of the supported scopes within the document, with a specific list of youtube scopes, and a list of other non-youtube scopes as well.
This document explains how to implement OAuth 2.0 authorization to access the YouTube Data API via applications running on devices like TVs, game consoles, and printers. More specifically, this flow is designed for devices that either do not have access to a browser or have limited input capabilities.
OAuth 2.0 allows users to share specific data with an application while keeping their usernames, passwords, and other information private. For example, a TV application could use OAuth 2.0 to obtain permission to select a file stored on Google Drive.
Since the applications that use this flow are distributed to individual devices, it is assumed that the apps cannot keep secrets. They can access Google APIs while the user is present at the app or when the app is running in the background.
Alternatives
If you are writing an app for a platform like Android, iOS, macOS, Linux, or Windows (including the Universal Windows Platform), that has access to the browser and full input capabilities, use the OAuth 2.0 flow for mobile and desktop applications. (You should use that flow even if your app is a command-line tool without a graphical interface.)
If you only want to sign in users with their Google accounts and use JWT ID token to obtain basic user profile information, see Sign-In on TVs and Limited Input Devices.
Prerequisites
Enable APIs for your project
Any application that calls Google APIs needs to enable those APIs in the API Console.
To enable an API for your project:
- Open the API Library in the Google API Console.
- If prompted, select a project, or create a new one.
- Use the Library page to find and enable the YouTube Data API. Find any other APIs that your application will use and enable those, too.
Create authorization credentials
Any application that uses OAuth 2.0 to access Google APIs must have authorization credentials that identify the application to Google's OAuth 2.0 server. The following steps explain how to create credentials for your project. Your applications can then use the credentials to access APIs that you have enabled for that project.
- Go to the Clients page.
- Click Create Client.
- Select the TVs and Limited Input devices application type.
- Name your OAuth 2.0 client and click Create.
Identify access scopes
Scopes enable your application to only request access to the resources that it needs while also enabling users to control the amount of access that they grant to your application. Thus, there may be an inverse relationship between the number of scopes requested and the likelihood of obtaining user consent.
Before you start implementing OAuth 2.0 authorization, we recommend that you identify the scopes that your app will need permission to access.
The YouTube Data API v3 uses the following scopes:
| Scope | Description |
|---|---|
https://www. |
Manage your YouTube account |
https://www. |
See a list of your current active channel members, their current level, and when they became a member |
https://www. |
See, edit, and permanently delete your YouTube videos, ratings, comments and captions |
https://www. |
View your YouTube account |
https://www. |
Manage your YouTube videos |
https://www. |
View and manage your assets and associated content on YouTube |
https://www. |
View private information of your YouTube channel relevant during the audit process with a YouTube partner |
See the Allowed scopes list for installed apps or devices.
Obtaining OAuth 2.0 access tokens
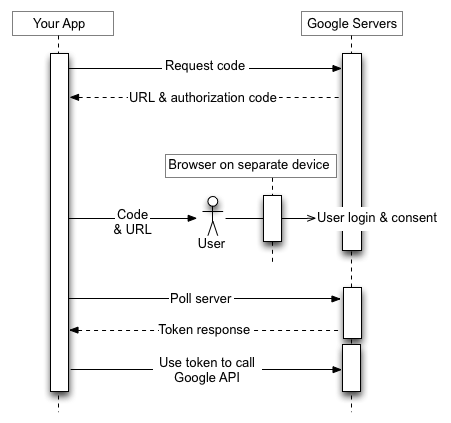
Even though your application runs on a device with limited input capabilities, users must have separate access to a device with richer input capabilities to complete this authorization flow. The flow has the following steps:
- Your application sends a request to Google's authorization server that identifies the scopes that your application will request permission to access.
- The server responds with several pieces of information used in subsequent steps, such as a device code and a user code.
- You display information that the user can enter on a separate device to authorize your app.
- Your application starts polling Google's authorization server to determine whether the user has authorized your app.
- The user switches to a device with richer input capabilities, launches a web browser, navigates to the URL displayed in step 3 and enters a code that is also displayed in step 3. The user can then grant (or deny) access to your application.
- The next response to your polling request contains the tokens your app needs to authorize requests on the user's behalf. (If the user refused access to your application, the response does not contain tokens.)
The image below illustrates this process:
The following sections explain these steps in detail. Given the range of capabilities and runtime
environments that devices may have, the examples shown in this document use the curl
command line utility. These examples should be easy to port to various languages and runtimes.
Step 1: Request device and user codes
In this step, your device sends an HTTP POST request to Google's authorization server, at
https://oauth2.googleapis.com/device/code, that identifies your application
as well as the access scopes that your application wants to access on the user's behalf.
You should retrieve this URL from the
Discovery document using the
device_authorization_endpoint metadata value. Include the following HTTP request
parameters:
| Parameters | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
client_id |
Required
The client ID for your application. You can find this value in the Cloud Console Clients page. |
||||||||||||||||
scope |
Required
A space-delimited list of scopes that identify the resources that your application could access on the user's behalf. These values inform the consent screen that Google displays to the user. See the Allowed scopes list for installed apps or devices. Scopes enable your application to only request access to the resources that it needs while also enabling users to control the amount of access that they grant to your application. Thus, there is an inverse relationship between the number of scopes requested and the likelihood of obtaining user consent. The YouTube Data API v3 uses the following scopes:
The OAuth 2.0 API Scopes document provides a full list of scopes that you might use to access Google APIs. |
||||||||||||||||
Examples
The following snippet shows a sample request:
POST /device/code HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.googleapis.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded client_id=client_id&scope=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.googleapis.com%2Fauth%2Fyoutube.force-ssl
This example shows a curl command to send the same request:
curl -d "client_id=client_id&scope=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.googleapis.com%2Fauth%2Fyoutube.force-ssl" \
https://oauth2.googleapis.com/device/code
Step 2: Handle the authorization server response
The authorization server will return one of the following responses:
Success response
If the request is valid, your response will be a JSON object containing the following properties:
| Properties | |
|---|---|
device_code |
A value that Google uniquely assigns to identify the device that runs the app requesting
authorization. The user will be authorizing that device from another device with richer
input capabilities. For example, a user might use a laptop or mobile phone to authorize an
app running on a TV. In this case, the device_code identifies the TV.
This code lets the device running the app securely determine whether the user has granted or denied access. |
expires_in |
The length of time, in seconds, that the device_code and
user_code are valid. If, in that time, the user doesn't complete the
authorization flow and your device doesn't also poll to retrieve information about the
user's decision, you might need to restart this process from step 1. |
interval |
The length of time, in seconds, that your device should wait between polling requests. For
example, if the value is 5, your device should send a polling request to
Google's authorization server every five seconds. See
step 3 for more details. |
user_code |
A case-sensitive value that identifies to Google the scopes that the application is requesting access to. Your user interface will instruct the user to enter this value on a separate device with richer input capabilities. Google then uses the value to display the correct set of scopes when prompting the user to grant access to your application. |
verification_url |
A URL that the user must navigate to, on a separate device, to enter the
user_code and grant or deny access to your application. Your user interface
will also display this value. |
The following snippet shows a sample response:
{ "device_code": "4/4-GMMhmHCXhWEzkobqIHGG_EnNYYsAkukHspeYUk9E8", "user_code": "GQVQ-JKEC", "verification_url": "https://www.google.com/device", "expires_in": 1800, "interval": 5 }
Quota exceeded response
If your device code requests have exceeded the quota associated with your client ID, you will receive a 403 response, containing the following error:
{ "error_code": "rate_limit_exceeded" }
In that case, use a backoff strategy to reduce the rate of requests.
Step 3: Display the user code
Display the verification_url and user_code obtained in step 2 to the
user. Both values can contain any printable character from the US-ASCII character set. The content
that you display to the user should instruct the user to navigate to the
verification_url on a separate device and enter the user_code.
Design your user interface (UI) with the following rules in mind:
user_code- The
user_codemust be displayed in a field that can handle 15 'W' size characters. In other words, if you can display the codeWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWcorrectly, your UI is valid, and we recommend using that string value when testing the way theuser_codedisplays in your UI. - The
user_codeis case-sensitive and should not be modified in any way, such as changing the case or inserting other formatting characters.
- The
verification_url- The space where you display the
verification_urlmust be wide enough to handle a URL string that is 40 characters long. - You should not modify the
verification_urlin any way, except to optionally remove the scheme for display. If you do plan to strip off the scheme (e.g.https://) from the URL for display reasons, be sure your app can handle bothhttpandhttpsvariants.
- The space where you display the
Step 4: Poll Google's authorization server
Since the user will be using a separate device to navigate to the verification_url
and grant (or deny) access, the requesting device is not automatically notified when the user
responds to the access request. For that reason, the requesting device needs to poll Google's
authorization server to determine when the user has responded to the request.
The requesting device should continue sending polling requests until it receives a response
indicating that the user has responded to the access request or until the device_code
and user_code obtained in
step 2 have expired. The interval returned in step 2 specifies the amount of
time, in seconds, to wait between requests.
The URL of the endpoint to poll is https://oauth2.googleapis.com/token. The polling request
contains the following parameters:
| Parameters | |
|---|---|
client_id |
The client ID for your application. You can find this value in the Cloud Console Clients page. |
client_secret |
The client secret for the provided client_id. You can find this value in the
Cloud Console
Clients page. |
device_code |
The device_code returned by the authorization server in
step 2. |
grant_type |
Set this value to urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:device_code. |
Examples
The following snippet shows a sample request:
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.googleapis.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded client_id=client_id& client_secret=client_secret& device_code=device_code& grant_type=urn%3Aietf%3Aparams%3Aoauth%3Agrant-type%3Adevice_code
This example shows a curl command to send the same request:
curl -d "client_id=client_id&client_secret=client_secret& \
device_code=device_code& \
grant_type=urn%3Aietf%3Aparams%3Aoauth%3Agrant-type%3Adevice_code" \
-H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \
https://oauth2.googleapis.com/tokenStep 5: User responds to access request
The following image shows a page similar to what users see when they navigate to the
verification_url that you displayed in step 3:
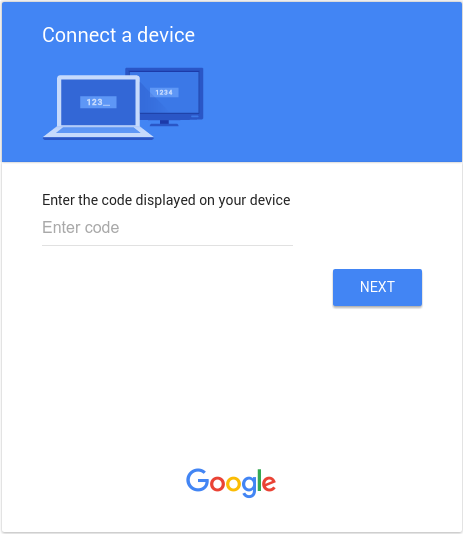
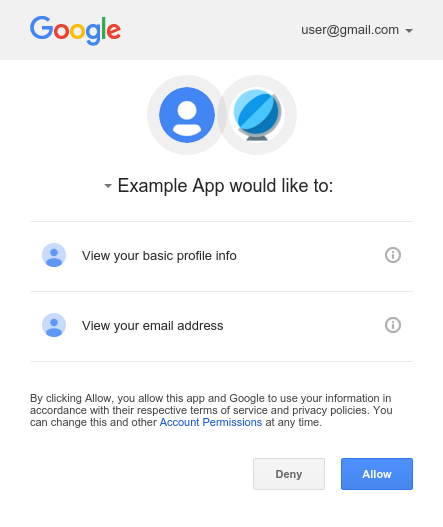
After entering the user_code and, if not already logged-in, logging in to Google,
the user sees a consent screen like the one shown below:
Step 6: Handle responses to polling requests
Google's authorization server responds to each polling request with one of the following responses:
Access granted
If the user granted access to the device (by clicking Allow on the consent screen),
then the response contains an access token and a refresh token. The tokens enable your device to
access Google APIs on the user's behalf. (The scope
property in the response determines which APIs the
device can access.)
In this case, the API response contains the following fields:
| Fields | |
|---|---|
access_token |
The token that your application sends to authorize a Google API request. |
expires_in |
The remaining lifetime of the access token in seconds. |
refresh_token |
A token that you can use to obtain a new access token. Refresh tokens are valid until the user revokes access or the refresh token expires. Note that refresh tokens are always returned for devices. |
refresh_token_expires_in |
The remaining lifetime of the refresh token in seconds. This value is only set when the user grants time-based access. |
scope |
The scopes of access granted by the access_token expressed as a list of
space-delimited, case-sensitive strings. |
token_type |
The type of token returned. At this time, this field's value is always set to
Bearer. |
The following snippet shows a sample response:
{ "access_token": "1/fFAGRNJru1FTz70BzhT3Zg", "expires_in": 3920, "scope": "openid https://www.googleapis.com/auth/userinfo.profile https://www.googleapis.com/auth/userinfo.email", "token_type": "Bearer", "refresh_token": "1/xEoDL4iW3cxlI7yDbSRFYNG01kVKM2C-259HOF2aQbI" }
Access tokens have a limited lifetime. If your application needs access to an API over a long period of time, it can use the refresh token to obtain a new access token. If your application needs this type of access, then it should store the refresh token for later use.
Access denied
If the user refuses to grant access to the device, then the server response has a
403 HTTP response status code (Forbidden). The response contains the
following error:
{ "error": "access_denied", "error_description": "Forbidden" }
Authorization pending
If the user has not yet completed the authorization flow, then the server returns a
428 HTTP response status code (Precondition Required). The response
contains the following error:
{ "error": "authorization_pending", "error_description": "Precondition Required" }
Polling too frequently
If the device sends polling requests too frequently, then the server returns a 403
HTTP response status code (Forbidden). The response contains the following
error:
{ "error": "slow_down", "error_description": "Forbidden" }
Other errors
The authorization server also returns errors if the polling request is missing any required
parameters or has an incorrect parameter value. These requests usually have a 400
(Bad Request) or 401 (Unauthorized) HTTP response status
code. Those errors include:
| Error | HTTP Status Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
admin_policy_enforced |
400 |
The Google Account is unable to authorize one or more scopes requested due to the policies of their Google Workspace administrator. See the Google Workspace Admin help article Control which third-party & internal apps access Google Workspace data for more information about how an administrator may restrict access to scopes until access is explicitly granted to your OAuth client ID. |
invalid_client |
401 |
The OAuth client was not found. For example, this error occurs if the
The OAuth client type is incorrect. Ensure that the application type for the client id is set to TVs and Limited Input devices. |
invalid_grant |
400 |
The code parameter value is invalid, has already been claimed or cannot be
parsed. |
unsupported_grant_type |
400 |
The grant_type parameter value is invalid. |
org_internal |
403 |
The OAuth client ID in the request is part of a project limiting access to Google Accounts in a specific Google Cloud Organization. Confirm the user type configuration for your OAuth application. |
Calling Google APIs
After your application obtains an access token, you can use the token to make calls to a Google
API on behalf of a given
user account if the scope(s) of access required by the API have been granted. To do this, include
the access token in a request to the API by including either an access_token query
parameter or an Authorization HTTP header Bearer value. When possible,
the HTTP header is preferable, because query strings tend to be visible in server logs. In most
cases you can use a client library to set up your calls to Google APIs (for example, when
calling the YouTube Live Streaming API).
Note that the YouTube Live Streaming API does not support the service account flow. Since there
is no way to link a Service Account to a YouTube account, attempts to authorize requests with this
flow will generate a NoLinkedYouTubeAccount error.
You can try out all the Google APIs and view their scopes at the OAuth 2.0 Playground.
HTTP GET examples
A call to the
liveBroadcasts.list
endpoint (the YouTube Live Streaming API) using the Authorization: Bearer HTTP
header might look like the following. Note that you need to specify your own access token:
GET /youtube/v3/liveBroadcasts?part=id%2Csnippet&mine=true HTTP/1.1 Host: www.googleapis.com Authorization: Bearer access_token
Here is a call to the same API for the authenticated user using the access_token
query string parameter:
GET https://www.googleapis.com/youtube/v3/liveBroadcasts?access_token=access_token&part=id%2Csnippet&mine=true
curl examples
You can test these commands with the curl command-line application. Here's an
example that uses the HTTP header option (preferred):
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer access_token" https://www.googleapis.com/youtube/v3/liveBroadcasts?part=id%2Csnippet&mine=true
Or, alternatively, the query string parameter option:
curl https://www.googleapis.com/youtube/v3/liveBroadcasts?access_token=access_token&part=id%2Csnippet&mine=true
Refreshing an access token
Access tokens periodically expire and become invalid credentials for a related API request. You can refresh an access token without prompting the user for permission (including when the user is not present) if you requested offline access to the scopes associated with the token.
To refresh an access token, your application sends an HTTPS POST
request to Google's authorization server (https://oauth2.googleapis.com/token) that
includes the following parameters:
| Fields | |
|---|---|
client_id |
The client ID obtained from the API Console. |
client_secret |
Optional
The client secret obtained from the API Console. |
grant_type |
As
defined in the
OAuth 2.0 specification,
this field's value must be set to refresh_token. |
refresh_token |
The refresh token returned from the authorization code exchange. |
The following snippet shows a sample request:
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.googleapis.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded client_id=your_client_id& refresh_token=refresh_token& grant_type=refresh_token
As long as the user has not revoked the access granted to the application, the token server returns a JSON object that contains a new access token. The following snippet shows a sample response:
{ "access_token": "1/fFAGRNJru1FTz70BzhT3Zg", "expires_in": 3920, "scope": "https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.metadata.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.readonly", "token_type": "Bearer" }
Note that there are limits on the number of refresh tokens that will be issued; one limit per client/user combination, and another per user across all clients. You should save refresh tokens in long-term storage and continue to use them as long as they remain valid. If your application requests too many refresh tokens, it may run into these limits, in which case older refresh tokens will stop working.
Token revocation
In some cases a user may wish to revoke access given to an application. A user can revoke access by visiting Account Settings. See the Remove site or app access section of the Third-party sites & apps with access to your account support document for more information.
It is also possible for an application to programmatically revoke the access given to it. Programmatic revocation is important in instances where a user unsubscribes, removes an application, or the API resources required by an app have significantly changed. In other words, part of the removal process can include an API request to ensure the permissions previously granted to the application are removed.
To programmatically revoke a token, your application makes a request to
https://oauth2.googleapis.com/revoke and includes the token as a parameter:
curl -d -X -POST --header "Content-type:application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \
https://oauth2.googleapis.com/revoke?token={token}The token can be an access token or a refresh token. If the token is an access token and it has a corresponding refresh token, the refresh token will also be revoked.
If the revocation is successfully processed, then the HTTP status code of the response is
200. For error conditions, an HTTP status code 400 is returned along
with an error code.
Allowed scopes
The OAuth 2.0 flow for devices is supported only for the following scopes:
OpenID Connect, Google Sign-In
emailopenidprofile
Drive API
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.appdatahttps://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.file
YouTube API
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/youtubehttps://www.googleapis.com/auth/youtube.readonly
Time-based access
Time-based access allows a user to grant your app access to their data for a limited duration to complete an action. Time-based access is available in select Google products during the consent flow, giving users the option to grant access for a limited period of time. An example is the Data Portability API which enables a one-time transfer of data.
When a user grants your application time-based access, the refresh token will expire after the
specified duration. Note that refresh tokens may be invalidated earlier under specific
circumstances; see these cases for
details. The refresh_token_expires_in field returned in the
authorization code
exchange response represents the time remaining until the refresh token expires in such cases.
Implementing Cross-Account Protection
An additional step you should take to protect your users' accounts is implementing Cross-Account Protection by utilizing Google's Cross-Account Protection Service. This service lets you subscribe to security event notifications which provide information to your application about major changes to the user account. You can then use the information to take action depending on how you decide to respond to events.
Some examples of the event types sent to your app by Google's Cross-Account Protection Service are:
-
https://schemas.openid.net/secevent/risc/event-type/sessions-revoked -
https://schemas.openid.net/secevent/oauth/event-type/token-revoked -
https://schemas.openid.net/secevent/risc/event-type/account-disabled
See the Protect user accounts with Cross-Account Protection page for more information on how to implement Cross Account Protection and for the full list of available events.