概要
OAuth ベースの Google ログイン スムーズ リンクは、OAuth リンクの上層に Google ログインを追加します。これにより、Google ユーザーはシームレスにリンクできます。また、アカウント作成も有効になり、ユーザーは Google アカウントを使用してサービスに新しいアカウントを作成できます。
OAuth と Google ログインを使用してアカウント リンクを行うには、次の一般的な手順に従います。
- まず、ユーザーの Google プロフィールにアクセスすることについてユーザーに同意を求めます。
- プロフィールの情報を使用して、ユーザー アカウントが存在するかどうかを確認します。
- 既存のユーザーの場合は、アカウントをリンクします。
- 認証システムで Google ユーザーに一致するユーザーが見つからない場合は、Google から受け取った ID トークンを検証します。その後、ID トークンに含まれているプロフィール情報に基づいてユーザー アカウントを作成できます。
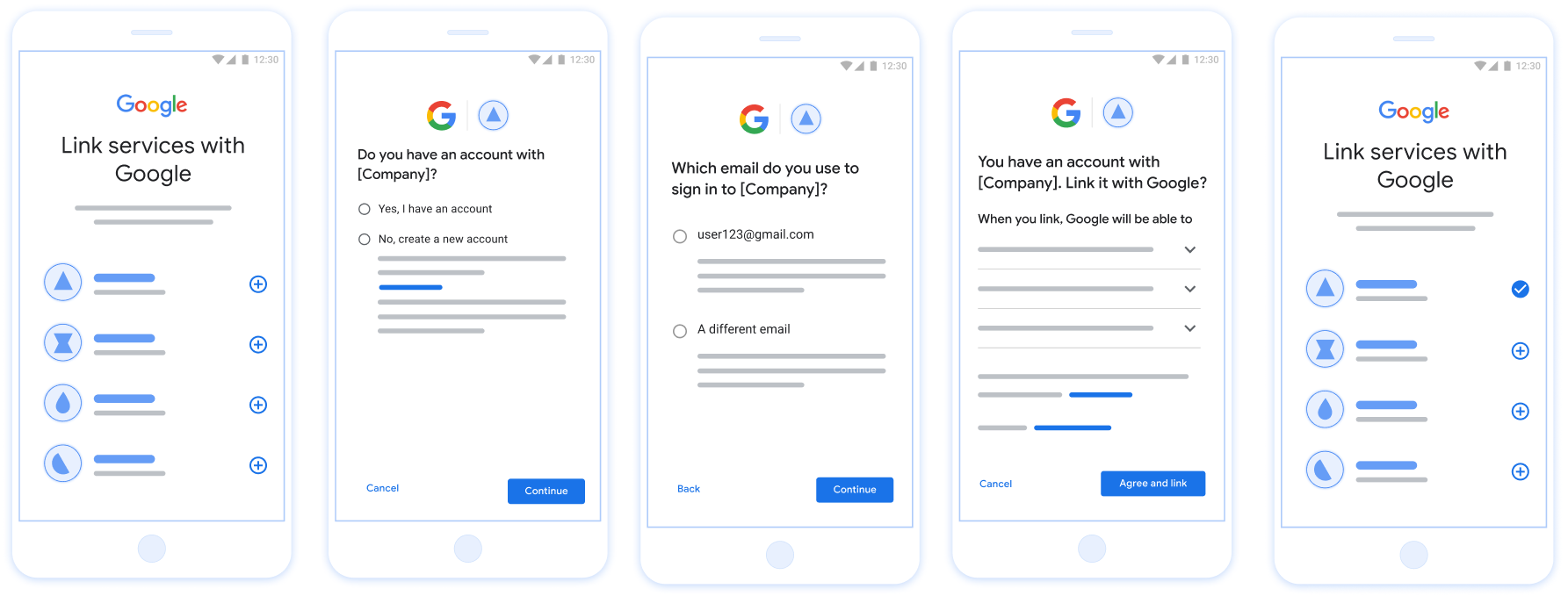
図 1. 簡素化されたリンクを使用したユーザーのスマートフォンでのアカウント リンク
簡素化されたリンクの要件
- 基本的なウェブ OAuth リンクフローを実装します。サービスは、OAuth 2.0 準拠の認可エンドポイントとトークン交換エンドポイントをサポートする必要があります。
- トークン交換エンドポイントは、JSON Web Token(JWT)アサーションをサポートし、
check、create、getインテントを実装する必要があります。
OAuth サーバーを実装する
トークン交換エンドポイントは、check、create、get インテントをサポートする必要があります。以下の図は、アカウントのリンクフローで完了する手順と、さまざまなインテントの呼び出しタイミングを示しています。
- ユーザーは認証システムにアカウントを持っていますか?(ユーザーが [はい] または [いいえ] を選択して決定)
- はい : ユーザーは Google アカウントに関連付けられているメールアドレスを使用してプラットフォームにログインしていますか?(ユーザーが [はい] または [いいえ] を選択して決定)
- はい : ユーザーの認証システムに一致するアカウントがありますか?(確認のために
check intentが呼び出されます)- YES :
get intentが呼び出され、get intent が正常に返された場合はアカウントがリンクされます。 - 「いいえ」の場合 : 新しいアカウントを作成しますか?(ユーザーが [はい] または [いいえ] を選択して決定)
- YES :
create intentが呼び出され、作成インテントの戻り値が成功した場合はアカウントがリンクされます。 - いいえ : ウェブ OAuth フローがトリガーされ、ユーザーはブラウザにリダイレクトされ、別のメールアドレスでリンクするオプションが表示されます。
- YES :
- YES :
- いいえ : ウェブ OAuth フローがトリガーされ、ユーザーはブラウザにリダイレクトされ、別のメールアドレスにリンクするオプションが表示されます。
- はい : ユーザーの認証システムに一致するアカウントがありますか?(確認のために
- 「いいえ」の場合 : ユーザーの認証システムに一致するアカウントがありますか?(確認のために
check intentが呼び出されます)- YES :
get intentが呼び出され、get intent が正常に返された場合はアカウントがリンクされます。 - いいえ :
create intentが呼び出され、作成インテントの戻り値が正常であればアカウントがリンクされます。
- YES :
- はい : ユーザーは Google アカウントに関連付けられているメールアドレスを使用してプラットフォームにログインしていますか?(ユーザーが [はい] または [いいえ] を選択して決定)
既存のユーザー アカウントを確認する(インテントを確認する)
ユーザーが Google プロフィールへのアクセスに同意すると、 Google ユーザーの ID に関する署名付きアサーションを含むリクエスト。「 アサーションには、ユーザーの Google アカウント ID、 表示されます。アプリケーション用に構成されたトークン交換エンドポイント プロジェクトがリクエストを処理できます
対応する Google アカウントが認証にすでに存在する場合
トークン交換エンドポイントは account_found=true を返します。もし
Google アカウントが既存のユーザーと一致しません。トークン交換エンドポイントがあります
account_found=false で HTTP 404 Not Found エラーを返す。
リクエストは次のようになります。
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded grant_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer&intent=check&assertion=JWT&scope=SCOPES&client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET
トークン交換エンドポイントでは、以下のパラメータを処理する必要があります。
| トークン交換エンドポイントのパラメータ | |
|---|---|
intent |
これらのリクエストでは、このパラメータの値は
check。 |
grant_type |
交換されるトークンの種類。これらのリクエストでは、
パラメータの値は urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer です。 |
assertion |
Google ユーザー ID の署名付きアサーションを提供する JSON Web Token(JWT)。この JWT には、ユーザーの認証情報、 Google アカウント ID、名前、メールアドレス。 |
client_id |
Google に割り当てたクライアント ID。 |
client_secret |
Google に割り当てたクライアント シークレット。 |
check インテント リクエストに応答するには、トークン交換エンドポイントで次の手順を行う必要があります。
- JWT アサーションを検証してデコードします。
- Google アカウントが認証システムにすでに存在するかどうかを確認します。
JWT アサーションを検証してデコードする
JWT アサーションの検証とデコードは、 ご使用の言語に対応した JWT デコード ライブラリ。使用 Google の公開鍵は、Google Cloud で提供されている JWK または PEM 形式を使用しており、 トークンの署名。
デコードされた場合、JWT アサーションは次の例のようになります。
{ "sub": "1234567890", // The unique ID of the user's Google Account "iss": "https://accounts.google.com", // The assertion's issuer "aud": "123-abc.apps.googleusercontent.com", // Your server's client ID "iat": 233366400, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's creation time "exp": 233370000, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's expiration time "name": "Jan Jansen", "given_name": "Jan", "family_name": "Jansen", "email": "jan@gmail.com", // If present, the user's email address "email_verified": true, // true, if Google has verified the email address "hd": "example.com", // If present, the host domain of the user's GSuite email address // If present, a URL to user's profile picture "picture": "https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/a-/AOh14GjlTnZKHAeb94A-FmEbwZv7uJD986VOF1mJGb2YYQ", "locale": "en_US" // User's locale, from browser or phone settings }
トークンの署名を検証するだけでなく、アサーションの
発行者(iss フィールド)が https://accounts.google.com の場合、
(aud フィールド)は、割り当てられたクライアント ID で、トークンの有効期限が切れていないことを確認します。
(exp フィールド)。
email、email_verified、hd フィールドを使用すると、
Google はメールアドレスをホストし、その権威があります。Google が
そのユーザーが現在正当なアカウント所有者であることが判明している場合
パスワードやその他の本人確認の方法をスキップすることもできます。それ以外の場合、これらのメソッドは
を使用して、リンクする前にアカウントを確認できます。
Google が信頼できるケース:
emailには@gmail.comという接尾辞が付いています。これは Gmail アカウントです。email_verifiedは true で、hdが設定されています。これは G Suite アカウントです。
ユーザーは Gmail や G Suite を使用せずに Google アカウントを登録できます。日時
email に @gmail.com という接尾辞がなく、hd が存在しない場合、Google には含まれません。
認証には、信頼できる認証方法、パスワード、その他の本人確認方法を使用することが推奨されます。
できます。email_verified も、Google が最初に検証した
ユーザーに付与できますが、サードパーティの所有権が付与されます。
アカウントが変更された可能性があります。
Google アカウントが認証システムに存在するかどうかの確認
次のいずれかの条件を満たしていることを確認します。
- アサーションの
subフィールドにある Google アカウント ID がユーザーのものである データベースです - アサーションに含まれているメールアドレスが、ユーザーのデータベースに登録されているユーザーと一致している。
いずれかの条件が true の場合、ユーザーは登録済みです。その場合、 次のようなレスポンスが返されます。
HTTP/1.1 200 Success
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
{
"account_found":"true",
}
Google アカウント ID もメールアドレスも
アサーションがデータベース内のユーザーと一致した場合、ユーザーはまだ登録されていません。イン
この場合、トークン交換エンドポイントは HTTP 404 エラーを返す必要があります。
"account_found": "false" を指定します。次に例を示します。
HTTP/1.1 404 Not found
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
{
"account_found":"false",
}
自動リンクを処理する(インテントの取得)
ユーザーが Google プロフィールへのアクセスに同意すると、 Google ユーザーの ID に関する署名付きアサーションを含むリクエスト。「 アサーションには、ユーザーの Google アカウント ID、 表示されます。アプリケーション用に構成されたトークン交換エンドポイント プロジェクトがリクエストを処理できます
対応する Google アカウントが認証にすでに存在する場合
トークン交換エンドポイントはユーザーにトークンを返します。もし
Google アカウントが既存のユーザーと一致しない(トークン交換エンドポイント)
linking_error エラーとオプションの login_hint を返します。
リクエストは次のようになります。
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded grant_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer&intent=get&assertion=JWT&scope=SCOPES&client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET
トークン交換エンドポイントでは、以下のパラメータを処理する必要があります。
| トークン交換エンドポイントのパラメータ | |
|---|---|
intent |
これらのリクエストでは、このパラメータの値は get になります。 |
grant_type |
交換されるトークンの種類。これらのリクエストでは、
パラメータの値は urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer です。 |
assertion |
Google ユーザー ID の署名付きアサーションを提供する JSON Web Token(JWT)。この JWT には、ユーザーの認証情報、 Google アカウント ID、名前、メールアドレス。 |
scope |
省略可: Google がリクエストするように構成したスコープ できます。 |
client_id |
Google に割り当てたクライアント ID。 |
client_secret |
Google に割り当てたクライアント シークレット。 |
get インテント リクエストに応答するには、トークン交換エンドポイントで次の手順を行う必要があります。
- JWT アサーションを検証してデコードします。
- Google アカウントが認証システムにすでに存在するかどうかを確認します。
JWT アサーションを検証してデコードする
JWT アサーションの検証とデコードは、 ご使用の言語に対応した JWT デコード ライブラリ。使用 Google の公開鍵は、Google Cloud で提供されている JWK または PEM 形式を使用しており、 トークンの署名。
デコードされた場合、JWT アサーションは次の例のようになります。
{ "sub": "1234567890", // The unique ID of the user's Google Account "iss": "https://accounts.google.com", // The assertion's issuer "aud": "123-abc.apps.googleusercontent.com", // Your server's client ID "iat": 233366400, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's creation time "exp": 233370000, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's expiration time "name": "Jan Jansen", "given_name": "Jan", "family_name": "Jansen", "email": "jan@gmail.com", // If present, the user's email address "email_verified": true, // true, if Google has verified the email address "hd": "example.com", // If present, the host domain of the user's GSuite email address // If present, a URL to user's profile picture "picture": "https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/a-/AOh14GjlTnZKHAeb94A-FmEbwZv7uJD986VOF1mJGb2YYQ", "locale": "en_US" // User's locale, from browser or phone settings }
トークンの署名を検証するだけでなく、アサーションの
発行者(iss フィールド)が https://accounts.google.com の場合、
(aud フィールド)は、割り当てられたクライアント ID で、トークンの有効期限が切れていないことを確認します。
(exp フィールド)。
email、email_verified、hd フィールドを使用すると、
Google はメールアドレスをホストし、その権威があります。Google が
そのユーザーが現在正当なアカウント所有者であることが判明している場合
パスワードやその他の本人確認の方法をスキップすることもできます。それ以外の場合、これらのメソッドは
を使用して、リンクする前にアカウントを確認できます。
Google が信頼できるケース:
emailには@gmail.comという接尾辞が付いています。これは Gmail アカウントです。email_verifiedは true で、hdが設定されています。これは G Suite アカウントです。
ユーザーは Gmail や G Suite を使用せずに Google アカウントを登録できます。日時
email に @gmail.com という接尾辞がなく、hd が存在しない場合、Google には含まれません。
認証には、信頼できる認証方法、パスワード、その他の本人確認方法を使用することが推奨されます。
できます。email_verified も、Google が最初に検証した
ユーザーに付与できますが、サードパーティの所有権が付与されます。
アカウントが変更された可能性があります。
Google アカウントが認証システムに存在するかどうかの確認
次のいずれかの条件を満たしていることを確認します。
- アサーションの
subフィールドにある Google アカウント ID がユーザーのものである データベースです - アサーションに含まれているメールアドレスが、ユーザーのデータベースに登録されているユーザーと一致している。
ユーザーのアカウントが見つかった場合、アクセス トークンを発行し、次の例のように HTTPS レスポンスの本文で JSON オブジェクトの値を返します。
{ "token_type": "Bearer", "access_token": "ACCESS_TOKEN", "refresh_token": "REFRESH_TOKEN", "expires_in": SECONDS_TO_EXPIRATION }
場合によっては、ユーザーが ID トークンに基づくアカウントのリンクが失敗することがあります。もし
トークン交換エンドポイントは、HTTP HTTPS レスポンスで応答する必要があります。
error=linking_error を指定する 401 エラーが返されます。
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
{
"error":"linking_error",
"login_hint":"foo@bar.com"
}
Google は、linking_error を含む 401 エラー レスポンスを受信すると、
login_hint をパラメータとして使用して、ユーザーを認可エンドポイントに送信します。「
ユーザーがブラウザで OAuth リンクフローを使用してアカウントのリンクを完了します。
Google ログインを介したアカウント作成の処理(インテントの作成)
ユーザーがニュース メディアのサービスでアカウントを作成する必要がある場合、Google は
intent=create を指定するトークン交換エンドポイントに追加します。
リクエストは次のようになります。
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded response_type=token&grant_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer&scope=SCOPES&intent=create&assertion=JWT&client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET
トークン交換エンドポイントは、次のパラメータを処理できる必要があります。
| トークン交換エンドポイントのパラメータ | |
|---|---|
intent |
これらのリクエストの場合、このパラメータの値は create です。 |
grant_type |
交換されるトークンの種類。これらのリクエストでは、
パラメータの値は urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer です。 |
assertion |
Google ユーザー ID の署名付きアサーションを提供する JSON Web Token(JWT)。この JWT には、ユーザーの認証情報、 Google アカウント ID、名前、メールアドレス。 |
client_id |
Google に割り当てたクライアント ID。 |
client_secret |
Google に割り当てたクライアント シークレット。 |
assertion パラメータ内の JWT には、ユーザーの Google アカウント ID が含まれます。
名前とメールアドレスです。これらの情報を使用して、
あります。
create インテント リクエストに応答するには、トークン交換エンドポイントで次の手順を行う必要があります。
- JWT アサーションを検証してデコードします。
- ユーザー情報を確認し、新しいアカウントを作成する。
JWT アサーションを検証してデコードする
JWT アサーションの検証とデコードは、 ご使用の言語に対応した JWT デコード ライブラリ。使用 Google の公開鍵は、Google Cloud で提供されている JWK または PEM 形式を使用しており、 トークンの署名。
デコードされた場合、JWT アサーションは次の例のようになります。
{ "sub": "1234567890", // The unique ID of the user's Google Account "iss": "https://accounts.google.com", // The assertion's issuer "aud": "123-abc.apps.googleusercontent.com", // Your server's client ID "iat": 233366400, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's creation time "exp": 233370000, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's expiration time "name": "Jan Jansen", "given_name": "Jan", "family_name": "Jansen", "email": "jan@gmail.com", // If present, the user's email address "email_verified": true, // true, if Google has verified the email address "hd": "example.com", // If present, the host domain of the user's GSuite email address // If present, a URL to user's profile picture "picture": "https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/a-/AOh14GjlTnZKHAeb94A-FmEbwZv7uJD986VOF1mJGb2YYQ", "locale": "en_US" // User's locale, from browser or phone settings }
トークンの署名を検証するだけでなく、アサーションの
発行者(iss フィールド)が https://accounts.google.com の場合、
(aud フィールド)は、割り当てられたクライアント ID で、トークンの有効期限が切れていないことを確認します。
(exp フィールド)。
email、email_verified、hd フィールドを使用すると、
Google はメールアドレスをホストし、その権威があります。Google が
そのユーザーが現在正当なアカウント所有者であることが判明している場合
パスワードやその他の本人確認の方法をスキップすることもできます。それ以外の場合、これらのメソッドは
を使用して、リンクする前にアカウントを確認できます。
Google が信頼できるケース:
emailには@gmail.comという接尾辞が付いています。これは Gmail アカウントです。email_verifiedは true で、hdが設定されています。これは G Suite アカウントです。
ユーザーは Gmail や G Suite を使用せずに Google アカウントを登録できます。日時
email に @gmail.com という接尾辞がなく、hd が存在しない場合、Google には含まれません。
認証には、信頼できる認証方法、パスワード、その他の本人確認方法を使用することが推奨されます。
できます。email_verified も、Google が最初に検証した
ユーザーに付与できますが、サードパーティの所有権が付与されます。
アカウントが変更された可能性があります。
ユーザー情報を検証して新しいアカウントを作成する
次のいずれかの条件を満たしていることを確認します。
- アサーションの
subフィールドにある Google アカウント ID がユーザーのものである データベースです - アサーションに含まれているメールアドレスが、ユーザーのデータベースに登録されているユーザーと一致している。
いずれかの条件が true の場合、既存のアカウントをリンクするようユーザーに促す
ログインする必要がありますそのためには、リクエストに対して HTTP 401 エラーを返します。
error=linking_error を指定し、ユーザーのメールアドレスを
login_hint。レスポンスの例を次に示します。
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
{
"error":"linking_error",
"login_hint":"foo@bar.com"
}
Google は、linking_error で 401 エラー レスポンスを受信すると、
login_hint をパラメータとして使用して、ユーザーを認可エンドポイントに送信します。「
ユーザーがブラウザで OAuth リンクフローを使用してアカウントのリンクを完了します。
どちらの条件も当てはまらない場合は、その情報で新しいユーザー アカウントを作成します。 JWT で提供します。通常、新しいアカウントにはパスワードが設定されていません。です。 他のプラットフォームにも Google ログインを追加して、ユーザーが Google でログインできるようになります。または パスワードの再設定フローを開始するリンクをメールで送信できます。 ユーザーが他のプラットフォームにログインするためのパスワードを設定できるようにする必要があります。
作成が完了したら、アクセス トークンを発行します。 JSON オブジェクトで値を HTTPS レスポンスの本文に URL を付加します。
{ "token_type": "Bearer", "access_token": "ACCESS_TOKEN", "refresh_token": "REFRESH_TOKEN", "expires_in": SECONDS_TO_EXPIRATION }
Google API クライアント ID を取得する
アカウント リンクの登録プロセスで、Google API クライアント ID を指定する必要があります。
OAuth のリンクの手順で作成したプロジェクトを使用して API クライアント ID を取得します。そのための手順は次のとおりです。
Google API プロジェクトを作成または選択します。
プロジェクトにウェブ アプリケーション タイプのクライアント ID がない場合は、[クライアントを作成] をクリックして作成します。[承認済みの JavaScript 生成元] ボックスに、サイトのドメインを含めてください。ローカルテストまたは開発を行う場合は、[Authorized JavaScript origins] フィールドに
http://localhostとhttp://localhost:<port_number>の両方を追加する必要があります。
実装の検証
実装を検証するには、OAuth 2.0 Playground ツールを使用します。
ツールで、次の操作を行います。
- [Configuration] をクリックして [OAuth 2.0 Configuration] ウィンドウを開きます。
- [OAuth flow] フィールドで、[Client-side] を選択します。
- [OAuth Endpoints](OAuth エンドポイント)で、[Custom](カスタム)を選択します。
- 対応するフィールドに、OAuth 2.0 エンドポイントと Google に割り当てたクライアント ID を指定します。
- [ステップ 1] セクションで、Google スコープは選択しないでください。代わりに、このフィールドを空白のままにするか、サーバーで有効なスコープを入力します(OAuth スコープを使用しない場合は任意の文字列を入力します)。完了したら、[API を承認] をクリックします。
- ステップ 2 とステップ 3 のセクションで OAuth 2.0 フローを実行し、各ステップが意図したとおりに機能することを確認します。
実装を検証するには、Google アカウント リンクのデモツールを使用します。
ツールで次の操作を行います。
- [Google でログイン] ボタンをクリックします。
- リンクするアカウントを選択します。
- サービス ID を入力します。
- 必要に応じて、アクセスをリクエストするスコープを 1 つ以上入力します。
- [デモを開始] をクリックします。
- リンク リクエストに同意できることを確認して、リクエストを拒否します。
- プラットフォームにリダイレクトされることを確認します。