يوضح هذا المستند كيفية استخدام تحميلات الوسائط المباشرة والقابلة للاستئناف مع مكتبة برامج Google API للغة Java.
تحميل وسائط قابل للاستئناف
عند تحميل ملف وسائط كبير إلى خادم، استخدِم تحميل الوسائط القابل للاستئناف من أجل إرسال مقطع الملف مقطع. تحتوي المكتبات التي تم إنشاؤها بواسطة Google API على طريقة سهلة للتفاعل مع تحميل وسائط قابل للاستئناف.
يشبه بروتوكول تحميل الوسائط القابل للاستئناف عملية تحميل الوسائط القابلة للاستئناف. كما هو موضَّح في مستندات واجهة برمجة تطبيقات Google Drive.
تصميم البروتوكول
يوضح الرسم البياني للتسلسل التالي كيفية عمل بروتوكول تحميل الوسائط القابل للاستئناف:
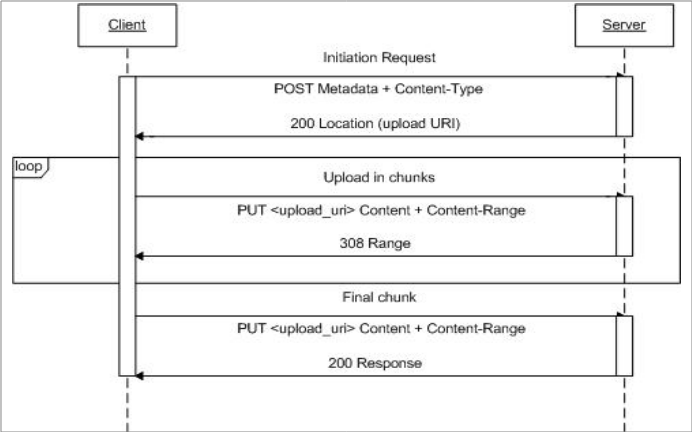
تفاصيل التنفيذ
إن فئات الاهتمام الرئيسية هي MediaHttpUploader وMediaHttpProgressListener.
إذا كانت الطرق في المكتبات التي تم إنشاؤها خاصة بالخدمة تحتوي على mediaUpload
في مستند Discovery،
ثم يتم إنشاء طريقة ملائمة لهذه الطرق التي تتطلب
InputStreamContent
كمعلمة. (لمزيد من المعلومات عن استخدام تحميل الوسائط مع Google APIs
خدمة Discovery، راجع
تحميل الوسائط).
على سبيل المثال، الطريقة insert لـ Drive API
يدعم mediaUpload، ويمكنك استخدام الرمز التالي لتحميل ملف:
class CustomProgressListener implements MediaHttpUploaderProgressListener { public void progressChanged(MediaHttpUploader uploader) throws IOException { switch (uploader.getUploadState()) { case INITIATION_STARTED: System.out.println("Initiation has started!"); break; case INITIATION_COMPLETE: System.out.println("Initiation is complete!"); break; case MEDIA_IN_PROGRESS: System.out.println(uploader.getProgress()); break; case MEDIA_COMPLETE: System.out.println("Upload is complete!"); } } } File mediaFile = new File("/tmp/driveFile.jpg"); InputStreamContent mediaContent = new InputStreamContent("image/jpeg", new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(mediaFile))); mediaContent.setLength(mediaFile.length()); Drive.Files.Insert request = drive.files().insert(fileMetadata, mediaContent); request.getMediaHttpUploader().setProgressListener(new CustomProgressListener()); request.execute();
يمكنك أيضًا استخدام ميزة تحميل الوسائط القابلة للاستئناف بدون المكتبات التي تم إنشاؤها. يُرجى الاطّلاع على المثال أدناه:
File mediaFile = new File("/tmp/Test.jpg"); InputStreamContent mediaContent = new InputStreamContent("image/jpeg", new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(mediaFile))); mediaContent.setLength(mediaFile.length());MediaHttpUploader uploader = new MediaHttpUploader(mediaContent, transport, httpRequestInitializer); uploader.setProgressListener(new CustomProgressListener()); HttpResponse response = uploader.upload(requestUrl); if (!response.isSuccessStatusCode()) { throw GoogleJsonResponseException(jsonFactory, response); }
تحميل الوسائط مباشرةً
يتم تمكين تحميل الوسائط القابلة للاستئناف بشكل افتراضي، ولكن يمكنك تعطيله واستخدام تحميل وسائط مباشرة بدلاً من ذلك، إذا كنت تحمّل ملفًا صغيرًا مثلاً. بشكل مباشر تم تقديم تحميل الوسائط في الإصدار 1.9.0-beta من مكتبة برامج Google API للغة Java.
أما التحميل المباشر للوسائط، فهو يحمّل الملف بأكمله في طلب HTTP واحد، بدلاً من بروتوكول تحميل الوسائط القابل للاستئناف، والذي يحمّل الملف في طلبات متعددة. يؤدي إجراء تحميل مباشر إلى تقليل عدد طلبات HTTP ولكنه يزيد فرصة إخفاقات (مثل إخفاقات الاتصال) يمكن أن تحدث عندما تكون عمليات التحميل.
يتطابق استخدام تحميل الوسائط المباشر مع ما هو موضح أعلاه تحميل وسائط قابل للاستئناف، بالإضافة إلى المكالمة التالية لإعلام MediaHttpUploader لإجراء عمليات تحميل مباشرة فقط:
mediaHttpUploader.setDirectUploadEnabled(true);